Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 0222086~ l997-ll-l2
W ~96~5928 PC~r/U~ 'C~
TT-T-~'TN~T~n FLUID ~EVEL INDICATOR
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to illumination
devices and more particularly to a waterproof and explosion-proof
illuminator which is used to backlight a visual fluid indicator or to
directly illuminate a magnetic fluid indicator.
sac~y v~.d of the Invention
A variety of liquid or fluid level indicators are known
for monitoring and displaying the lèvel of a liquid or fluid in a
c~nt~;n~ in applications where the fluid is not directly visible. One
such device is a visual fluid indicator which comprises a flat glass
fluid level gauge which provides an indication of the vertical level of
fluid in a contA;n~r. Typically, the flat glass fluid level gauge is
mounted vertically alongside the cnnt~;n~ and is connected at both its
top and bottom ends with the interior o~ the container. The level of
fluid in the container, when occupying levels between the top and
bottom o~ the fluid level gauge, may be viewed through the glass in the
gauge.
Another type of fluid level indicator is a magnetic fluid
indicator which employs a plurality of magnetically responsive
indicator elements which move in response to IIIOV . - - t of a magnetic
float cont~;ne~ within a fluid c~nt~;n~r (see, e.g. U.S. Patent Nos.
3,964,312 and 4,483,193). The magnet is typically disposed in a
vessel, such as a pipe, which is vertically mounted to the outside of
the c~nt~;n~r and which is connected to the interior of the container
at its top and bottom ends. The vertical position of the floating
magnet changes as the level of fluid in the container, and thus the
pipe, changes. The magnetically responsive indicator elements
positioned at the level of the magnet are actuated in response to this
.,.ov~,..ellt. The indicator elements are typically painted or coated on
the side which is visible when actuated to provide a visual indication
of the fluid level.
Illuminators for enhancing the visibility of such fluid
level indicator devices are known, typically including an ;nc~n~scent
bulb for applying light to the device. For example, in the visual
fluid indicator described above, illuminators are known which comprise
an illumination source and a reflector which reflects light provided by
.. CA 0222086~ 1997-11-12
W 096/35928 PCT/U~'~,'OCq~1
--2--
the illumination source onto the back of the fluid level gauge. For
example, Series GA illuminators manufactured by Jerguson0, which are
designed to improve the readability of flat glass fluid level gauges in
poorly lighted areas, include an ;nCAn~ ccent light bulb and a large
wedge-shaped reflector mounted h~h;nrl the fluid level gauge. The
output of the light source is spread by the wedge-shaped reflector and
applied to the back of the gauge.
The above-described illuminator, however, suffers from
several drawbacks. Installation typically requires the illuminator to
be bolted to the gauge, and the bolts tighten~ to a specific torque
value. If the illuminator is attached to the gauge using the same
bolts that hold the gauge together, the torque applied to the gauge may
be affected by the illuminator. Installation is also made difficult
due to the size and weight of the ;nc~n~lescent bulb and the large
wedge-shaped reflector.
In addition, the wedge-shaped reflector of the known
illuminator does not evenly distribute light from the light source
across the length of the wedge. This ph~n~ - r n iS particularly
noticeable if a string of wedge-shaped illuminators are connected end-
to-end in a particular application to illuminate a longer gauge. In
any particular reflector of the string, the brightest point of the
illumination occurs at the point opposite the light source and the
dimmest point occurs at the points furthest away from the light source.
The human eye ad~usts to these bright spots which greatly affects
readability in the dimmer regions. Moreover, the wedge-shaped
reflector tends to catch the wind in external environments which may
apply unacceptable levels of stress to the vertical gauge to which it
is attached. Still further, the bulky size of the wedge-shaped
reflector poses a risk of being inadvertently dislodged from its
mounting by service personnel.
In addition, the use of an inC~n~CCent bulbs in known
illuminators requires recurrent ~;nt~nAnce. Because the fluid level
gauges are used in environments where processing e~ t. such as
pumps are operating, vibration may cause filament damage and eventual
bulb failure. Vibration other than that caused by the processes being
monitored, such as that caused by wind as described above, can also
lead to bulb failure. Even absent such vibration, the ;nc~ndeccent
bulbs are typically rated for only about a 2500 hour lifetime, in part
because they operate at relatively high voltages. The environments in
which these illuminators are installed are typically operated around
the clock, and thus the bulbs must be replaced every 100 days or so.
Because the illuminators are often installed in areas which are not
easily accessed, recurrent maintenance of the illuminators is a
problem.
CA 0222086~ l997-ll-l2
WO 96/359~ 5~
Moreover, because level indicator illuminators are often
used in wet envi-~ ts where combustible gases are present, the
potential for explosion must also be accommodated by the illuminator
design. Wet envi~ ts increase the risk of illuminator failure. If
the illuminator has become heated as a result of cont;nuous operation,
~ and the outer enclosure of the illuminator begins to get wet, the
enclosure begins to cool, causing air cont~ ~ n~ therein to cool and
contract. The resulting vacuum draws moisture which AC_ l~tes on the
outer enclosure into the interior cavity of the enclosure. If any of
this moisture comes into contact with the hot illumination source, the
illumination source is likely to explode. Although an explosion-proof
enclosure will likely cont~in the explosion, the exploding bulbs
present a I ;nt~nAnre problem in that they must repeatedly be replaced,
especially in wet illuminator envi~ ts.
15It is therefore also desirable that illuminators for fluid
level indicator devices be waterproof and explosion-proof. Standards,
such as those est~hl~h~ by the National Electrical ~nllf~urel~
Association (NEMA), have been promulgated by which devices such as
illuminators may be rated in terms of being waterproof and explosion-
proof.
Accordingly, it is an objective of the present invention
to provide a waterproof and explosion-proof illuminator for a fluid
level gauge which provides even illumination across the entire fluid
level gauge, requires little maintenance, is lightweight and of
manageable size to facilitate easy attachment and det~r' t from a
fluid level gauge, and is suitable for both interior and exterior
applications.
~ ~ of the Invention
An illuminator for a fluid level indicator is provided.
The illuminator enhances the visibility of the indicator when attached
thereto. The illuminator may be attached to a variety of fluid level
indicators, including both visual fluid level indicators and magnetic
fluid level indicators.
When adapted for use with a visual fluid level indicator,
the illuminator comprises a backlighting assembly which is attached to
the back of the indicator. The backlighting assembly comprises (i) an
enclosure cont~;n;ng an illumination source such as a halogen or other
gas filled bulb, (ii) an illumination panel housing which c~nt~;n~ an
illumination panel such as a fiber optic panel, and (iii) spring clips
which attach the illumination panel housing, and hence the entire
backlighting assembly, to the visual fluid indicator. The enclosure
includes a transformer for converting standard line power to a
subst~nti~lly lower voltage at which the illumination source operates.
CA 0222086~ 1997-11-12
W 096~5928 ~ PCT/u~3GJ
_4_
The enclosure is designed to meet NEMA 7 explosion-proof standards and
NEMA 4 waterproof standards.
The illumination source is optically coupled to the
illumination panel by means of a bundled fiber optic light cable. The
illumination source shines downwardly toward the fiber optic light
cable which transmits light to the illumination panel. The
illumination panel provides an evenly illuminated surface which is used
to backlight the visual fluid level indicator.
When adapted for use with a magnetic fluid level
indicator, the illuminator comprises an illuminator/ magnetic indicator
assembly adapted to be used with a vertically extending vessel such as
a pipe contA;n;ng a floating magnet. The assembly includes an
illumination panel housing which (like the first embodiment) contains
the illumination panel. In addition to using the same illumination
panel as the first '~_~; t, the same transformer, illumination
source, and light cable are also used.
The illumination panel housing also includes an array of
magnetic indicating elements which respond to l,,~v - t of the magnet in
the pipe to provide a visual indication of the level of fluid in the
pipe. The illumination panel is positioned within the illumination
panel housing generally perpendicular to the array of magnetic
indicating elements to shine sufficient light onto the array of
indicating elements to enhance their visibility. A hose clamp is used
to attach the illumination panel housing, and thus the illuminator/
magnetic indicator assembly, to the pipe.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure 1 shows a side view of a first embodiment of an
illuminated fluid level indicator constructed according to the
principles of the present invention;
Figure 2 shows a top view of the illuminated fluid level
indicator of Figure 1;
Figure 3 shows a more detailed side view of the
backlighting assembly of the illuminated fluid level indicator of
Figure 1;
Figure 4 shows a perspective view of the retainer used in
the backlighting assembly of Figure 3;
Figure 5 shows a top view of a second embodiment of an
illuminated fluid level indicator constructed according to the
principles of the present invention; and
Figure 6 shows a front view of the of the
illuminator/magnetic indicator assembly of the illuminated fluid level
indicator of Figure 5.
CA 0222086~ l997-ll-l2
WO 9613592~ PCT/U~
Detailed Description of the Preferred '-'; t
The inventive illuminator has ;nt~n~ applications for a
variety of fluid level indicators. When attached to a fluid level
indicator, the illuminator enhances the visibility of the indicator,
5 especially in envi~ fi where visibility would otherwise be poor.
Two of the intended fluid level indicator applications for the
illuminator are more fully described below.
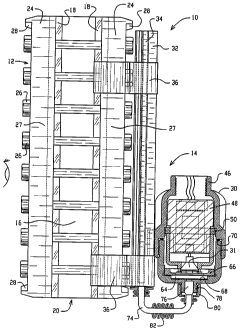
Referring first to Figures 1 and 2, a first ~mho~ nt of
an illuminated fluid level indicator 10, constructed according to the
10 principles of the present invention, is shown. Figure 1 shows a side
view of the illuminated indicator 10 while Figure 2 shows a top view of
the illuminated indicator. The illuminated indicator 10 comprises a
standard visual fluid indicator 12 to which is attached a backlighting
assembly 14.
The standard visual fluid indicator 12 may be connected
directly to the wall of a vessel or tank, or connected in-line with a
pipe or conduit, as is generally known in the art. The indicator 12
comprises a steel chamber 16 having viewing windows 18 in front and
back. As used herein with respect to the first embodiment of the
20 invention, "front" shall mean the surface of the indicator which is
viewed when looking left to right in Figure 1 or bottom to top in
Figure 2, and "back" shall mean the surface of the indicator to which
is attached the backlighting assembly 14.
The chamber 16 and the windows 18 enclose a rhFlnn~l 20
25 which is milled into a metal bar. Holes 21 are drilled into each end
of the bar stock through to the chamber 16. Each of the holes 21 is
threaded so that a threaded pipe from a container may be fitted
therein. The glass panels (transparent viewing windows) 18 (see Figure
2) serve to close the chamber so that the only co~ n; cation with the
30 chamber is made through the threaded holes 21. Sealing gaskets 22 seal
the glass/steel interface between the steel chamber 16 and the front
and back viewing windows 18.
The structural integrity of the indicator 12 is insured by
front and back covers 24, which are forged or formed from bar stock and
35 connected to each other by a series of nuts and bolts 26. The nuts are
drawn down on threaded ends of the bolts to couple the chamber 16 to
the cover 24, and to compress sealing gaskets 22 at the glass/steel
interface between the chamber and the front and back viewing windows
18. Cushioning gaskets 25 are provided at the interface of the glass
40 panels 18 and the forged steel covers 24.
Each of the forged steel covers includes spaced
longitudinal portions 27 which allow viewing of the windows
therebetween. The spaced longitudinal portions 27 are connected at
. CA 02220865 l997-ll-l2
W 096~5928 iCTrUS96l06434
their top and bottom ends by reinforcing ribs 28 which are integrally
forged with the spaced longitudinal portions.
The visual fluid indicator 12 as described above is a
known item. The backlighting assem.bly 14 which is attached to the back
of the indicator and the resulting illuminated indicator 10, however,
form the basis of the first em.bo~; t of the present invention. The
backlighting assembly 14 comprises an enclosure 30 contA;n;ng an
illumination source 31, an illumination panel housing 32 which cs~tA;n~
an illumination panel 34 and with which the enclosure 30 is slidably
engageable, and upper and lower spring clips 36 which attach the
illumination panel housing 32, and hence the entire backlighting
assem.bly 14, to the visual fluid indicator 12.
Figure 3 shows a more detailed view of the enclosure 30 of
the backlighting assembly 14. The enclosure 30 includes upper and
lower portions 30A and 30B respectively, which together enclose the
illumination source 31 for the illumination panel 34 (see Fig. 2) and
a transformer assembly 40 for providing power to the illumination
source 31. The transformer assembly 40 converts 120 VAC or 240 VAC
power provided on input lines 42 to a low voltage AC power of less than
25 VAC on output lines 44. The input lines 42 are routed to the
transformer assem.bly 40 through a threaded conduit coupling 46 in the
upper portion 3OA of the enclosure.
In the preferred emho~; t, the transformer assembly
converts either type of input (120 or 240 VAC) into a low power output
on the order of 5 VAC. The preferred illumination source is a non-
;nCAn~cent light source, such as a gas filled (e.g. halogen) light
source. One such light source is a gas filled bulb which operates on
approximately 5 VAC, provided by Lumitex, Inc. of North Royalton, Ohio.
Such a bulb has an expected lifetime of about 15,000 to 17,000 hours,
depending on operating voltage.
~ The transformer assem.~bly 40 is potted in a non-conductivematerial to form a potted transformer assem.bly 48 molded into a shape
which corresponds generally to the interior surface of the upper
portion 30A of the enclosure. Potting the transformer also ~l;m;nAtes
dead air space in the enclosure which reduces the risk of explosion by
reducing the volume in which combustible gases may form. Once seated
within the top portion 30A, the potted transformer assem.bly 48 is
secured within the upper portion 3OA of the enclosure by means of a
transformer retainer 50 (see Figure 4). The retainer 50 is provided
with a threaded portion 52 which screws into corresponding threads 54
in the upper portion 3OA.
The output wires from the potted transformer assembly 48
connect to the illumination source 31 which resides in a recess 56 in
an extension 58 of the retainer 50. A clip 60 snaps over a groove 62
CA 0222086~ 1997-11-12
WO 96J35928 PCr~U.,, .-'~S~
.
_7_
in the extension 58 to secure the illumination source 31 to the
retainer 50.
The lower portion 3OB of the enclosure 30 includes a
transparent (glass) protecti~e panel 64 for the illumination source 31.
The panel 64 seats within a recess in the inner surface of the lower
portion 30B and is secured in place by a threaded panel retainer 66
which screws into an internal surface of lower portion 30B of the
enclosure. An O-ring seal 68 seals the interface between the
transparent panel 64 and the lower portion 30B of the enclosure.
After the transparent panel 64 is secured to the internal
surface of lower portion 30B of the enclosure, the lower portion 30B
may be screwed into the upper portion 30A of the enclosure to complete
the assembly of the enclosure 30. An O-ring seal 70 is provided at the
upper portion - lower portion interface to seal the enclosure 30. The
upper and lower portions of the enclosure 30 are constructed from cast
aluminum. ~eat generated by the transformer assembly 40 and the
illumination source 31 is ~;ssipAted from the cast all 'nn~ enclosure
to the outside envi,~ t by means of heat-radiating fins 72 on the
upper portion 3OA of the enclosure (see Figure 2).
The assembled enclosure 30 is designed to meet NEMA 7
explosion-proof standards and NEMA 4 waterproof standards. To meet the
NEMA 7 explosion-proof standard to c~n~A; n any explosion which may
occur within the enclosure, all joints ("flame paths") connecting the
interior of the enclosure the outside must safely extinguish all flames
and hot gases which might otherwise be expelled in an explosion. In
the enclosure 30 of Figure 3, the two critical flame paths are the
interface between the lower portion 30B of the enclosure and the
transparent panel 64, and the interface between the upper and lower
portions 30A, 30B of the enclosure. O-rings 68 and 70 are positioned
to provide watertight seals at these interfaces, respectively.
As shown in Figures 1 and 3, the illumination source 31 is
optically coupled to the illumination panel 34 by means of a bundled
fiber optic light cable 74. The light cable is connected at one end to
the illumination panel 34 and at the other end to a ferrule 76. The
ferrule serves as the interface between the illumination source 31 and
the optical fiber ends of the light cable 74. The individual fiber
ends are aligned and polished to form a smooth planar surface which is
perpendicular to the optical axis of the illumination source 31.
The ferrule is positioned in front of the illumination
source 31 by being inserted into an extension 78 in the lower portion
30B of the enclosure. A threaded cap 80 is screwed onto threads on the
extension 78 to secure the ferrule in this position. Such an
arrangement permits the illumination source 31 to shine downwardly
toward the fiber optic light cable. A flexible protective sheath 82
.. CA 0222086~ l997-ll-l2
W 096~5928 PCT/U~
covers the fiber optic light cable and is secured at one end to the cap
80 and at the other end to the illumination panel 34.
The illumination panel 34 is substAnti Al 1y flat and
located proximate the rear transparent viewing window of the visual
fluid indicator 12, within a rhAnn~l 84 which extends the length of the
illumination panel housing 32 (see Figure 2). "Flat", as used herein,
is meant to describe a relatively broad surface in relation to its
thickness or depth. A protective transparent plate 86 is provided
within the illumination panel housing to protect the flat illumination
panel 34 from the outside envi-~ t. A gasket 87 seals the edges of
the plate 86.
In one em.bodiment of the invention, the substantially flat
illumination panel 34 is comprised of a plurality of fiber optic
fibers. The illumination device in the preferred embodiment of the
present invention is a fiber optic light emitting panel such as that
disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,885,663 to Parker and assigned to
Lumitex, Inc. from which assignee the light emitting panel is
commercially available. The panel includes an emitter surface having
one or more layers of woven fiber optic fibers. Bends along the length
of fibers permit light to be emitted from the emitter surface. Light
is transmitted to the emitter surface from the illumination source 31
through light cable 74.
The enclosure 30 is attached to the illllm;nAti~n panel
housing 32 cont~A;n~ng the illumination panel 34 by means of a T-bar
extension 88 which slidably engages a corresponding slot in the
illumination panel housing (see Figure 2). The resulting illumination
panel housing and enclosure com.bination may then be attached to the
visual fluid indicator 12 by means of the spring clips 36, which are
fixedly attached to the illumination panel housing by a~y~ iate
means.
The spring clips permit the backlighting assembly 14 to be
easily and removably attachable to the visual fluid indicator 12. Each
of the spring clips 36 includes a pair of extending arms 90 which
extend from the illumination panel housing and are designed to
resiliently deflect during coupling of the backlighting assem.bly to the
visual fluid indicator, (ii) engage an outer surface of the rear cover
24 of the visual fluid indicator with a predetermined amount of
resistance when the backlighting assembly is attached to the visual
fluid indicator, and (iii) resiliently deflect during uncoupling of the
backlighting assembly the visual fluid indicator.
A second em.bodiment of the invention is shown in Figures
5-6 as illuminated indicator 92. Unlike the first em.bodiment of the
invention described above which provides a backlighting assem.bly 14 for
a visual fluid indicator 12, this second embodiment of the invention
CA 0222086~ l997-ll-l2
WO 96135928 P<,'li'U~ '., 6
_9_
provides a side-lighting --hAn;! for a magnetic fluid indicator.
This second ~mho~i - utilizes the same enclosure 30, including the
transformer assembly 40 and the illumination source 31 described above,
as well as the same illumination panel 34 and light cable 74.
This second ~ ;m~nt of the invention comprises an
~ illuminator/magnetic indicator assembly 94 adapted to be used with a
vertically extending vessel such as a pipe 96 contA;ning a floating
magnet (not shown). The assembly 94 includes a illumination panel
housing 98 which (like the first e~o~; t) contains the illumination
panel 34. Also like the first ; '-c~; t, the enclosure 30 is slidably
engageable with the illumination panel housing 98 by means of the T-bar
extension 88 which extends from the enclosure. A hose clamp 100 is
used to attach the illumination panel housing 98, and thus the
illuminator/ magnetic indicator assembly 94, to the pipe 96. Other
attA~' t devices, such as the spring clips 36 described above with
respect to the first embodiment, may also be used.
The assembly 94 also includes an array of magnetic
indicating elements 102. The magnetic indicating elements 102 respond
to ~ v t of the magnet in the pipe, in a manner known in the art, to
provide a visual indication of the level of fluid in the pipe. The
indicating elements 102 may be coated with a phosphorescent or other
type of highly visible paint or coating to ~nhAn~e visibility.
A front view of the illuminator/magnetic indicator
assembly 94 is shown in Figure 6. As used herein with respect to the
second '~o~ t of the invention, "front" shall mean the surface of
the array of magnetic indicating elements 100 which is viewed when
looking right to left in Figure 5 or when viewing Figure 6 directly.
The array of magnetic indicating elements 102, and the illumination
panel 34 positioned alongside, are protected from the outside
environment, as in the first embodiment, by protective transparent
plate 86 and gasket 87. In addition, an internal transparent (acrylic)
plate 104 is provided for directing light from the illumination panel
34 to the magnetic indicating elements 102.
As shown in Figure 5, the illumination panel 34 is
positioned generally perpendicular to the array of magnetic indicating
elements 102. It is contemplated, however, that the panel and the
array may be positioned in other orientations with respect to each
other, as long as the position of the panel is such as to shine
sufficient light onto the array of indicating elements.
Accordingly, the preferred embodiments of an illuminator
for a fluid level indicator have been described. With the foregoing
description in mind, however, it is understood that this description is
made only by way of example, and that the invention is not limited to
the particular embo~ described herein. For example, it is
CA 0222086~ 1997-11-12
W 096/35928 PCTrUS96/06434
--10--
contemplated that the invention may be used on sight flow indicators,
sight gauges, or sight glasses as well as on the disclosed liquid level
devices. Moreover, various reaLl~..y~...ents, modifications, and
substitutions may be implemented without departing from the true scope
of the invention as defined by the following claims and their
equivalents.