Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCT~US96/07863
SEIZING INSTRUMENT
The present invention relates to medical in-
struments generally, and particularly to seizing instru-
ments inserted into body cavities.
In certain medical procedures it is necessary
to insert an instrument into a body cavity and seize the
inner walls of the cavity. For example, in some gyneco-
logical procedures, it is necessary to seize the endocer-
vix while introducing instruments and/or substances
through the vagina and the cervix into the uterus. In
addition, for some procedures, such as embryo implanta-
tions, it is necessary to hold the uterus fixed.
In the prior art, for example, the endocervix
is typically seized with a type of sharp pincers called
tenaculum.
The present invention seeks to provide a simple
seizing instrument for inserting into a body cavity and
seizing the inner walls of the cavity.
The present invention is described hereinbelow
in detail with reference to preferred embodiments useful
in seizing the inner wall of the lower uterine cavity
(endocervix). Using the preferred embodiments to seize
the endocervix does not require anesthesia and does not
endanger the patient or cause pain, discomfort or bleed-
ing thereto. However, it should be emphasized that this
is only one example of a possible use for the present
invention and is not limiting. The invention is manufac-
turable in a variety of sizes and shapes, and is readily
adaptable for use in the rectum, urethra, esophagus,
stomach or other bodily openings, as well as blood ves-
sels.
The present invention comprises a pair of
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96107863
slender tubes, one disposed inside the other. The outside
diameter of the pair of tubes is chosen for easy inser-
tion into the particular body cavity, without causing
pain thereto or to tissue or sphincters surrounding the
opening of the cavity. The insertion end of the tubes is
also smoothly tapered and shaped to facilitate insertion.
Once safely inserted, the insertion end of one
of the tubes is caused to be deformed generally radially
outwards inside the cavity. In one embodiment of the
present invention, this is accomplished by making the
inner tube from a spring-like material and forming at its
insertion end a plurality of axial strips. As long as the
inner tube is disposed inside the outer tube, the strips
remain constrained together inside the outer tube. After
insertion into the body cavity, the outer tube is slid
along the inner tube in a direction opposite the inser-
tion direction, thereby exposing the strips of the inner
tube and allowing them to spring radially outwards. The
instrument can then be used to seize the inner walls of
the cavity with the outwardly protruding strips.
In another embodiment o~ the present invention,
the outer tube is formed at one end thereof with stiff
axial strips, each formed with a rearwardly facing shoul-
der. The strips initially touch each other at the tip of
the insertion end and do not protrude radially outwards
beyond the chosen diameter. This ensures safe insertion
into the particular body cavity. The strips may even be
weakly joined at their tips to prevent premature opening
which could interfere with safe insertion.
The inner tube is slid axially along the outer
tube in the insertion direction, thereby butting and
pushing against the shoulders. This causes the strips to
bend radially outwards. If the tips are weakly joined,
the pushing force is sufficient to rupture the joint to
allow the strips to bend outwards. The instrument is then
used to seize the inner walls of the cavity with the
CA 02222672 l997-ll-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
outwardly protruding strips.
In accordance with another preferred embodiment
of the present invention, the tubes may be bent or curved
towards the insertion end to facilitate insertion into
certain cavities. Apertures may be provided at the bent
or curved portion of the tubes to allow another path of
insertion of devices and/or substances therethrough, in
addition to the normal path through the insertion ends of
the tubes.
In accordance with yet another preferred embod-
iment of the present invention, the tubes may be tapered
towards the insertion end. The tapering provides the
necessary relatively small diameter for insertion into
the cavity, while providing a relatively larger diameter
opposite to the insertion end which facilitates introduc-
tion of instruments and/or materials through the inner
tube.
The insertion end of the tapered tubes may be
additionally formed with aligned axial slits which allow
the tubes to expand radially outwards during insertion of
instruments and/or materials, thereby further aiding in
the introduction of such instruments and/or materials
through the inner tube.
The preferred embodiments of the invention are
each provided with handles reversibly attachable to each
other. In addition, a safety catch is provided to prevent
premature opening of the strips which could hinder safe
insertion of the instrument into the body cavity.
The invention may also be adapted to be used in
conjunction with fiber optic and/or other devices. Axial
apertures may be formed in the tubes for passing there-
through the optic filaments or other devices. Alterna-
tively, or additionally, radial apertures may be formed
in the tubes for passing therethrough substances and/or
instruments.
In addition, the invention is provided with a
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O96/38197 PCT~US96107863
slitted funnel guide to further aid safe insertion of the
seizing instrument into the body cavity. In a preferred
embodiment, the guide is shaped somewhat like a sheet
rolled into a cone-shaped funnel and is adapted to re-
ceive the insertion end of the seizing instrument. After
insertion of the funnel and seizing instrument into the
body cavity, the funnel may be pulled transversely
against the instrument, thereby unrolling and opening the
funnel and allowing it to be slipped off the instrument.
The seizing instrument is left inside the cavity where it
can be used to seize the inner walls of the cavity as
described above.
There is thus provided in accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention an instru-
ment for seizing walls of a body cavity including a first
portion and a second portion, the second portion being
insertable into the cavity and to be reversibly deform-
able from a first to a second configuration while inside
the cavity, the first portion being operative to reversi-
bly deform the second portion from the first to the
second configuration, the second portion when in the
second configuration being operative to seize the walls
of the cavity.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the first portion of the instru-
ment includes a first end of a pair of inner and outer
tubes, the inner tube being disposed inside the outer
tube and the outer tube being adapted to slide along the
inner tube, and the second portion of the instrument
includes a second end of the pair of the inner and the
outer tubes, the second end of the inner tube having a
plurality of axial slits which define a pluraLity of
axial deformable strips, the strips being deformed radi-
ally outwards when the outer tube is slid along the inner
tube towards the first end of the inner tube.
Preferably, the material of the strips is
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCT~US96/07863
resilient and spring-like.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, each of the plurali-
ty of deformable strips is provided with a lip at an end
thereof, wherein in the first configuration, the lips do
not protrude radially outwards of the outer tube.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodi-
ment of the present invention, the lip is shaped to
facilitate insertion into the body cavity.
Preferably the first end of the inner tube is
fitted with a first handle and the first end of the outer
tube is fitted with a second handle, the first handle
being reversibly attachable to the second handle.
Preferably there is provided a safety catch to
prevent unintentional axial movement of the inner tube
and the outer tube with respect to each other.
In accordance with another preferred embodiment
of the present invention, the inner and the outer tubes
each have an axial slit extending from their second ends
towards their first ends, the axial slits being substan-
tially aligned with each other.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, the inner and the
outer tubes are tapered. In such an embodiment, the inner
and the outer tubes may also have aligned axial slits
extending from their second ends towards their first
ends.
In accordance with another preferred embodiment
of the present invention, the first portion of the seiz-
ing instrument includes a first end of a pair of inner
and outer tubes, the inner tube being disposed inside the
outer tube and the outer tube being adapted to slide
along the inner tube, and the second portion of the
instrument includes a second end of the pair of the inner
and the outer tubes, the second end of the outer tube
having a plurality of axial slits which define a plurali-
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
ty of axial deformable strips, the strips being deformed
radially outwards when the inner tube is slid along the
outer tube towards the second end of the outer tube.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, each deformable
strip includes an inner shoulder, such that sliding the
inner tube towards the second end of the outer tube
causes the second end of the inner tube to butt and push
against the shoulder, thereby causing the plurality of
strips to deform radially outwards.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodi-
ment of the present invention, the plurality of strips
are shaped to facilitate insertion into the body cavity.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the instrument further includes a
safety sleeve which covers at least a portion of the
strips in the first configuration and which is retract-
able to expose the strips in the second configuration.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, the instrument
includes a guiding device which is attached to a distal
end of the strips in the first configuration, the guiding
device substantially preventing deformation of the plu-
rality of strips radially outwards when in the first
configuration, and wherein sliding of the inner tube
towards the second end of the outer tube causes detach-
ment of the guiding device from the strips, thereby
permitting deformation of the plurality of strips radial-
ly outwards, and wherein further sliding of the inner
tube towards the second end of the outer tube causes the
plurality of strips to deform radially outwards.
The guiding device preferably has a soft tip
for guiding the seizing instrument through sharp bends
and tight corners.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the plurality of strips are sub-
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
stantially in contact with one another in the first
configuration. In accordance with another preferred
embodiment of the present invention, tips of the strips
are joined together in the first configuration.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the seizing instrument includes a
device for substantially preventing linear and rotational
misalignment of the axial slits.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the seizing instrument includes a
device for substantially preventing linear and rotational
misalignment of the first and second tubes with respect
to each other.
There is also provided in accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention, a slitted
funnel guide for guiding insertion of an instrument,
comprising a resiliently openable, conical coiled funnel,
being adapted to receive an insertable end of the instru-
ment and being retractable transversely from the instru-
ment.
There is also provided in accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention, a method
for seizing walls of a body cavity comprising the steps
of providing an instrument comprising a first portion and
a second portion, the second portion being insertable
into the cavity and to be reversibly deformable from a
first to a second configuration while inside the cavity,
the first portion being operative to reversibly deform
the second portion from the first to the second configu-
ration, and the second portion when in the second config-
uration being operative to seize the walls of the cavity,
inserting the second portion of the instrument into the
cavity, and deforming the second portion into the second
configuration and seizing the walls of the cavity.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, the step of inserting further
CA 02222672 1997-ll-28
W O9~/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
comprises~ the steps of providing a slitted funnel guide
comprising a resiliently openable, conical coiled funnel,
inserting the funnel into the cavity, inserting the
second portion of the instrument into the funnel, re-
tracting the funnel outwards from the cavity, transverse-
ly pulling the funnel against the instrument, thereby
causing the coiled funnel to split open and permitting
removing the funnel from the instrument, leaving the
instrument inside the cavity.
Alternatively, in accordance with another
preferred embodiment of the present invention, the step
of inserting further comprises the steps of providing a
slitted funnel guide comprising a resiliently openable,
conical coiled funnel, inserting the funnel and the
second portion of the instrument into the cavity, re-
tracting the funnel outwards from the cavity, transverse-
ly pulling the funnel against the instrument, thereby
causing the coiled funnel to split open and permitting
removing the funnel from the instrument, leaving the
instrument inside the cavity.
Additionally in accordance with yet another
preferred embodiment of the present invention, the step
of providing further comprises the step of providing a
guiding device for guiding the instrument through non-
straight body cavities, the guiding device substantially
preventing deformation of the second portion when in the
first configuration and being removable so as to permit
deformation of the second portion when in the second
configuration, and wherein prior to the step of deform-
ing, the guiding device is removed from the second por-
tion to permit deformation of the second portion.
The present invention will be understood and
appreciated from the following detailed description,
taken in conjunction with the drawings in which:
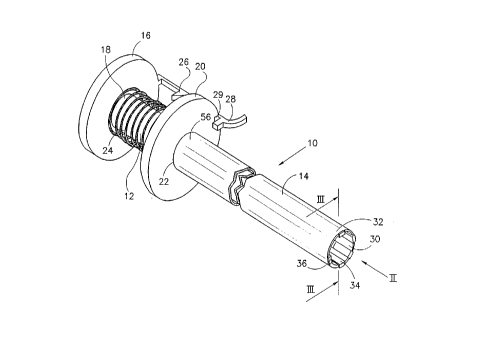
Fig. 1 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument constructed and operative in
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O 96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the seizing instrument being in a first con-
figuration;
Fig. 2 is a frontal illustration of the seizing
instrument of Fig. 1 as viewed along the arrow II in Fig.
l;
Fig. 3 is a sectional illustration of a portion
of the seizing instrument of Fig. 1, taken along lines
III - III in Fig. 1;
Fig. 4 is simplified pictorial illustration of
the seizing instrument of Fig. 1 in a second configura-
tion;
Fig. 5A is a simplified sectional side view of
the seizing instrument of Fig. 1 inserted in a cervix and
in the first configuration;
Fig. 5B is a simplified sectional side view of
the seizing instrument of Fig. 1 inserted in the cervix
and in the second configuration;
Fig. 5C is a simplified sectional side view of
the seizing instrument of Fig. 1 in the second configura-
tion and positioned for seizing the cervix;
Fig. 6A is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument constructed and operative in
accordance with another preferred embodiment of the
present invention, and wherein the inner and the outer
tubes are bent;
Fig. 6B is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a the seizing instrument of Fig. 6A and including
radial apertures in the bent portion of the inner and
outer tubes;
Fig. 7 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument constructed and operative in
accordance with another preferred embodiment of the
present invention, and wherein the inner and the outer
tubes are tapered;
Fig. 8 is a simplified pictorial illustration
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O 96/38197 PCT~US96/07863
of the seizing instrument of Fig. 7, and wherein the
inner and the outer tubes have aligned axial slits;
Fig. 9 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument constructed and operative in
accordance with another preferred embodiment of the
present invention, the seizing instrument being in a
first configuration;
Fig. 10 is a frontal illustration of the seiz-
ing instrument of Fig. 9 as viewed along the arrow X in
Fig. 9;
Fig. 11 is a sectional illustration of a por-
tion of the seizing instrument of Fig. 9, taken along
lines XI - XI in Fig. 9;
Fig. 12 is simplified pictorial illustration of
the seizing instrument of Fig. 9 in a second configura-
tion;
Fig. 13 is a frontal illustration of the seiz-
ing instrument of Fig. 12 as viewed along the arrow XIII
in Fig. 12;
Fig. 14 is a sectional illustration of a por-
tion of the seizing instrument of Fig. 12 taken along
lines XIV - XIV in Fig. 12;
Fig. 15 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument provided with radial apertures
constructed and operative in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 16 is a simplified sectional illustration
of a seizing instrument provided with axial apertures
constructed and operative in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 17 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a seizing instrument provided with roughened strips
constructed and operative in accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention;
Figs. 18 and 19 are simplified sectional illus-
trations of a seizing instrument in a first configuration
-
CA 02222672 1997-ll-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
11
and provided with a retractable safety sleeve, construct-
ed and operative in accordance with a preferred embodi-
ment of the present invention, before and after retrac-
tion of the safety sleeve, respectively;
Fig. 20 is a simplified sectional illustration
of the seizing instrument of Figs. 18 and 19 in a second
configuration for seizing a cervix;
Figs. 21 and 22 are enlarged illustrations of a
portion of the seizing instrument shown in Figs. 18 and
20, respectively;
Figs. 23 and 24 are simplified sectional illus-
trations of a seizing instrument in a first configuration
and provided with a guiding device, constructed and
operative in accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, before and after removal of the
guiding device, respectively;
Fig. 25 is a simplified sectional illustration
of the seizing instrument of Figs. 23 and 24 in a second
configuration for seizing a cervix;
Fig. 26 is a simplified pictorial illustration
of a slitted funnel guide constructed and operative in
accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention; and
Figs. 27A - 27D are illustrations of the opera-
tion of the funnel guide of Fig. 26.
Reference is now made to Figs. 1 - 3 which
illustrate a seizing instrument 10 constructed and opera-
tive in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present invention. The seizing instrument 10 comprises an
inner tube 12 and an outer tube 14, the inner tube 12
being disposed inside the outer tube 14 and the outer
tube 14 being adapted to slide along the inner tube 12.
The inner tube 12 preferably has a first handle
16 disposed at a first end 18 thereof. The outer tube 14
preferably has a second handle 20 disposed at a first end
22 thereof. As seen in Fig. 1, the first handle 16 is
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O 96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
preferable biased against the second handle 20 with a
biasing device, such as a spring 24.
As seen in Fig. 1, the first handle 16 is
provided with one or more attachment devices 26, such as
hooks, clips or snaps, which may be used to reversibly
attach the first handle 16 to the second handle 20. The
first handle 16 is also preferably provided with a safety
catch 28. The safety catch 28 prevents unintentional
axial movement of the first handle 16 and the second
handle 20 with respect to each other, and thus also axial
movement of the inner tube 12 and the outer tube 14 with
respect to each other. The importance of the safety catch
28 is described further hereinbelow.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, seizing instrument 10 has a
provision for substantially preventing radial motion of
inner tube 12 with respect to outer tube 14. In the
embodiment illustrated in Fig. 1, second handle 20 has a
groove 29 which is engageable with attachment device 26
and safety catch 28. As long as either attachment device
26 or safety catch 28 is engaged with groove 29, radial
motion of second handle 20 and outer tube 14 with respect
to first handle 16 and inner tube 12, is substantially
prevented. It is appreciated that other devices may be
employed to substantially prevent radial motion of the
tubes 12 and 14 with respect to each other.
The inner tube 12 has a plurality of axial
slits 30 at a second end 32 thereof which define a plu-
rality of axial deformable strips 34. Each strip 34 is
preferably provided with a lip 36 which is shaped, such
as being rounded, to facilitate insertion of the seizing
instrument 10 into a cervix.
The inner tube 12 and the outer tube 14 are
preferably made of any durable, medically safe material.
The material of the strips 34, or optionally of the
entire inner tube 12, further has the property of being
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
13
resilient and spring-like. The spring-like strips 34 are
manufactured such that they protrude radially outwards
when not stored inside the outer tube 14.
Figs. 1 - 3 illustrate a first configuration of
the inner tube 12 and the outer tube 14, in which the
strips 34 are held within the outer tube 14. As seen best
in Fig. 3, a second end 38 of the outer tube 14 is sub--
stantially butted against the lips 36 of the strips 34 in
the first configuration. The lips 34 do not protrude
radially outwards of the outer tube 14.
Reference is now made to Fig. 4 which illus-
trates the seizing instrument 10 in a second configura-
tion in which the seizing instrument 10 is operative to
seize the cervix. The outer tube 14 is slid along the
inner tube 12 in the direction of arrow 40, thereby
exposing the strips 34. The spring-like property of the
strips 34 causes them return to their manufactured state
and deform radially outwards.
It is noted that the safety catch 28 is re-
leased from the second handle 20 to allow axial movement
of the outer tube 14. As long as the safety catch 28 is
attached to the second handle 20, axial movement of the
outer tube 14 is prevented and the strips 34 can not
prematurely open which could hinder safe insertion into
the cervix. The at least one attachment device 26 fas-
tens the first handle 16 to the second handle 20.
Reference is now made to Figs. 5A - 5C which
illustrate the operation of the seizing instrument 10. In
Fig. 5A, the seizing instrument 10 is inserted into the
cervix in the first configuration described hereinabove
with reference to Figs. 1 - 3.
In Fig. 5B, the outer tube 14 is slid in the
direction of arrow 40 along the inner tube 12, thereby
exposing the strips 34 which deform radially outwards,
and putting the seizing instrument 10 into the second
configuration described hereinabove with reference to
CA 02222672 l997-ll-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
14
Fig. 4.
In Fig. 5C, the seizing instrument 10 is pulled
against and seizes the cervix.
The inner tube 12 and the outer tube 14 of the
embodiment described hereinabove with reference to Figs.
1 -- 5C are generally straight along their entire length.
Reference is now made to Fig. 6A which illustrates a
seizing instrument 42 constructed and operative in ac--
cordance with another preferred embodiment of the present
invention, and comprising bent inner 44 and outer 46
tubes. Throughout the specification and claims, the term
bent includes having a sharp bend or a bend with a radius
of curvature. The bending of the tubes may be useful for
insertion in certain body cavities.
Referring now to Fig. 6B, it is seen that
apertures 47 may be formed in the bent portion of tubes
44 and 46. In this embodiment, devices and/or substances
may be introduced into the cervix via apertures 47 in the
direction of arrow 48 as well as through the end of tubes
44 and 46 in the direction of arrow 49.
Reference is now made to Fig. 7 which illus--
trates a seizing instrument 50 constructed and operative
in accordance with yet another preferred embodiment of
the present invention, and which comprises an inner tube
52 and an outer tube 54 which have a relatively larger
diameter at a first end 56 and taper to a relatively
smaller diameter at a second end 58. The tapering pro-
vides the necessary relatively small diameter for inser-
tion into the cervix, while providing a relatively larger
diameter at the first end 56 which facilitates introduc-
tion of instruments and/or materials through the inner
tube 52.
Reference is now made to Fig. 8 which shows
that the inner 52 and the outer 54 tubes of seizing
instrument 50, described hereinabove with reference to
Fig. 7, may additionally be provided with axial slits 60
CA 02222672 1997-ll-28
WO 96/38197 PCT~US96/07863
and 61 respectively which are substantially aligned with
each other. The slits 60 and 61 allow the second ends 58
of the inner 52 and the outer 54 tubes to expand radially
outwards during insertion of instruments and/or materi-
als, thereby further aiding in the introduction of such
instruments and/or materials through the inner tube 52.
Preferably, seizing instrument 50 is also
provided with at least one attachment device 62, a safety
catch 64 and a groove 66, which are respectively identi-
cal with attachment device 26, safety catch 28 and groove
29 of seizing instrument 10 described hereinabove with
reference to Figs. 1 -- 5C. AS long as either attachment
device 62 or safety catch 64 is engaged with groove 66,
radial motion of outer tube 54 and slit 61 with respect
to inner tube 52 and slit 60, is substantially prevented.
It is appreciated that other devices may be employed to
substantially prevent radial motion of the tubes 52 and
54, as well as slits 60 and 61, with respect to each
other.
Reference is now made to Figs. 9 - 11 which
illustrate a seizing instrument 110 constructed and
operative in accordance with another preferred embodiment
of the present invention. The seizing instrument 110
comprises an inner tube 112 and an outer tube 114, the
inner tube 112 being disposed inside the outer tube 114
and the outer tube 114 being adapted to slide along the
inner tube 112.
The inner tube 112 preferably has a first
handle 116 disposed at a first end 118 thereof. The outer
tube 114 preferably has a second handle 120 disposed at a
first end 122 thereof. As seen in Fig. 9, the first
handle 116 is preferable biased against the second handle
120 with a biasing device, such as a spring 124.
As seen in Fig. 9, the first handle 116 is
provided with one or more attachment devices 126, such as
hooks, clips or snaps, which are operative to reversibly
CA 02222672 l997-ll-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
16
attach the first handle 116 to the second handle 120. The
first handle 116 is also preferably provided with a
safety catch 128. The safety catch 128 prevents uninten-
tional axial movement of the first handle 116 and the
second handle 120 with respect to each other, and thus
also axial movement of the inner tube 112 and the outer
tube 114 with respect to each other.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention, seizing instrument 110 has a
provision for substantially preventing radial motion of
inner tube 112 with respect to outer tube 114. In the
embodiment illustrated in Fig. 9, second handle 120 has a
groove 129 which is engageable with attachment device 126
and safety catch 128. As long as either attachment device
126 or safety catch 128 is engaged with groove 129,
radial motion of second handle 120 and outer tube 114
with respect to first handle 116 and inner tube 112, is
substantially prevented. It is appreciated that other
devices may be employed to substantially prevent radial
motion of the tubes 112 and 114 with respect to each
other.
The outer tube 114 has a plurality of axial
slits 130 at a second end 132 thereof which define a
plurality of axial deformable strips 134. As seen in Fig.
11, each deformable strip 134 preferably includes an
inner shoulder 136. Preferably slits 130 are formed in
outer tube 114 with no sharp corners, but rather with
rounded corners to prevent stress concentrations, as is
known in the art.
Figs. 9 - 11 illustrate a first configuration
of the inner tube 112 and the outer tube 114. It is noted
that the strips 134 are substantially in contact with one
another in the first configuration, which is important
for safe insertion into the cervix. Optionally, the tips
of strips 134 may be weakly joined together, such as by
bonding, to ensure that the strips 134 contact one anoth-
CA 02222672 1997-ll-28
W O96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
er in the first configuration. This is important to
prevent the strips 134 from opening outwards prematurely
which could interfere with safe insertion of the seizing
instrument 110 into the cervix.
Reference is now made to Figs. 12 - 14 which
illustrate the operation of the seizing instrument 110.
As shown in Fig. 12, the inner tube 112 is slid along the
inside of the outer tube 114 in the direction of arrow
140, such that an end 142 of the inner tube 112 butts
against the inner shoulders 136 of the strips 134 of the
outer tube 114. Further sliding of the inner tube 112 in
the direction of the arrow 140 causes the end 142 to push
against the shoulders 136, thereby causing the plurality
of strips 134 to deform radially outwards as shown picto-
rially in Fig. 13 and in section in Fig. 14. If the tips
of the strips 134 are weakly joined, the pushing force is
sufficient to rupture the joint to allow the strips 134
to bend outwards. The seizing instrument 110 is then used
to seize the cervical walls with the outwardly protruding
strips 134.
It is appreciated that seizing instrument 110
may be provided with a bend with apertures, may be ta-
pered and/or may be provided with axial slits as de-
scribed hereinabove for seizing instrument 10 with refer-
ence to Figs. 6B, 7 and 8.
Reference is now made to Fig. 15 which illus-
trates seizing instrument 110 provided with substantially
aligned radial apertures 150 and 152 formed in the inner
112 and the outer 114 tubes respectively. Apertures 150
and 152 may be used to pass therethrough instruments
and/or substances into the cervix.
Reference is now made to Fig. 16 which shows
that alternatively, or additionally, axial apertures 154
may be formed in the outer tube 114 for passing there-
through devices, such as fiber optic and/or other de-
vices. Apertures 154 are shown in section in Fig. 16. It
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
W O96138197 PCTrUS96107863
18
is appreciated that radial and axial apertures may be
formed in seizing instrument 10 as well.
Reference is now made to Fig. 17 which illus-
trates seizing instrument 110 with an outer surface of
strips 134 roughened such as by forming grooves 156
thereon. Roughening may help in seizing certain tissues.
Reference is now made to Figs. 18 - 22 which
illustrate a seizing instrument 200, constructed and
operative in accordance with still another preferred
embodiment of the present invention.
Seizing instrument 200 is preferably construct-
ed substantially similarly to seizing instrument 110
described hereinabove, with like numerals designating
like elements. Seizing instrument 200 is preferably
provided with a retractable safety sleeve 202 which
initially substantially covers and envelops deformable
strips 134, as seen in Figs. 18 and 21. Safety sleeve 202
is preferably constructed of a thin pliable material,
such as a thin plastic sheet fashioned to closely fit
over outer tube 114 and deformable strips 134. A third
handle 204 (Fig. 18) is preferably attached to a proximal
end 206 of safety sleeve 202.
As seen in Fig. 18, first handle 116 may be
provided with one or more attachment devices 208, such as
hooks, clips or snaps, which may be used to reversibly
attach first handle 116 to third handle 204. It is noted
that second handle 120 is shown to be of smaller size
than first handle 116 and third handle 204, however,
second handle 120 may be any other convenient size. A
safety catch 210 may also be provided which prevents
unintentional axial movement of first handle 116 and
third handle 204 with respect to each other.
As seen in Fig. 19, by retracting third handle
204 generally in the direction of an arrow 212, retract-
able safety sleeve 202 is pulled towards its proximal end
206, thereby exposing deformable strips 134.
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCTrUS96/07863
19
As seen in Figs. 20 and 22, by pushing first
handle 116 generally in the direction of an arrow 214,
the plurality of strips 134 are deformed radially out-
wards and are in a position to seize the inner walls of a
body cavity (not shown).
Reference is now made to Figs. 23 - 25 which
illustrate a seizing instrument 250 with a guiding device
252, constructed and operative in accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention. Seizing
instrument 250 is preferably constructed substantially
similarly to seizing instrument 110 described hereina-
bove, with like numerals designating like elements.
Guiding device 252 is preferably constructed of
a soft, resilient and flexible material, such as a soft
rubber, so as to facilitate the insertion of seizing
instrument 250 into a body cavity (not shown), such as
through sharp bends and tight corners. Guiding device 252
may have any suitable shape for facilitating entrance
into a body cavity. Guiding device 252 is preferably
fixedly attached to a rod 254 which passes through the
first and second handles (not shown) of seizing instru-
ment 250. In Fig. 23, guiding device 252 initially butts
against a distal end of deformable strips 134, thereby
substantially preventing deformation of strips 134 radi-
ally outwards.
Reference is now made to Fig. 24. By pushing
rod 254 generally in the direction of an arrow 256,
guiding device 252 is pushed away from strips 134, there-
by permitting subsequent deformation of the strips 134.
Reference is now made to Fig. 25. Sliding inner
tube 112 generally in the direction of arrow 256 causes
strips 134 to deform radially outwards, thereby bringing
seizing instrument 250 into a configuration for seizing a
cervix or other body cavity. Once strips 134 have been
deformed, rod 254 may be used to retract guiding device
252 through seizing instrument 250. Guiding device 252
CA 02222672 l997-ll-28
WO96/38197 PCTAUS96/07863
may then be disposed of, or may be sterilized for further
use.
Reference is now made to Fig. 26 which illus-
trates a slitted funnel guide 160 constructed and opera-
tive in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present invention. Guide 160 is constructed of resilient
material and comprises an insertion portion 162 which is
shaped somewhat like a sheet rolled into a cone-shaped
funnel 164 with a generally axial slit 166. Funnel 164 is
adapted to receive the insertion end of any seizing
instrument, such as instrument 10 or 110, constructed and
operative in accordance with a preferred embodiment of
the present invention.
Guide 160 preferably further comprises a handle
168.
Reference is now made to Figs. 27A - 27D which
illustrate the operation of the funnel guide 160. As seen
in Fig. 27A, a user inserts the funnel guide 160 into the
cervix. Since the funnel 164 tapers outwards from the
cervix, a seizing instrument 170 is easily inserted
through the funnel guide 160 into the cervix, as seen in
Fig. 27B. Alternatively, seizing instrument 170 may be
inserted together with funnel guide 160 into the cervix.
Once the instrument 170 is inserted in the
cervix, the funnel guide 160 may be pulled outwards from
the cervix. The slit 166 of the funnel 164 widens as the
funnel 164 is pulled back somewhat transversely to the
instrument 170, as seen in Fig. 27C. This allows the
funnel guide 160 to slip off the instrument 170 and
leaves the instrument 170 inside the cervix, as seen in
Fig. 27D. Instrument 170 can then be used to seize the
endocervix as described ahove for seizing instrument 10
or 110.
It will be appreciated by persons skilled in
the art that the present invention is not limited to what
has been particularly shown and described hereinabove.
CA 02222672 1997-11-28
WO 96/38197 PCT~US96/07863
Rather, the scope of the present invention is defined
only by the claims that follow: