Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02228180 1998-01-29
W o 97/06906 PCT/SE96/01020
A - ~ ~and a ~ forcasting a metalstrip
This invention relates to a strip casting m~r~ine comprising a cooled and power driven
endless belt with side dams~ and a device for supplying molten metal to the upper side of
a flat and ~ul,~ lly horizontal part of the endless belt. It relates also to a method of
casting a metal strip.
A single belt strip casting m~hine ofthis kind is described in WO 93/01015.
When casting strips, there will usually be edge drops, that is the edges will be thinner, so
that the edges must be cut away.
It is an object of the invention to counteract edge drop and this is accomplished
principally by having inwardly inclined side dams. Another object is to permit the casting
of thinner strips than has been possible before. To these ends, the invention has been
given the characteristics stated in the claims.
The invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
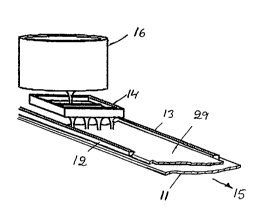
Figure I is a fr~gment~ry perspective view of a strip casting machine in accordance with
the invention,
Figure 2 is a fragmentary longitudinal section through a m~l~hine that is somewhat
modified from the machine in Figure 1,
Figure 3 is a transverse section taken along line 2-2 in Figure 3, and Figure 4 is a
schematic transverse section through a strip cast by a machine described, the width and
thickness of the strip being not in scale.
The m~rl~ine shown in Figure 1 has a substantially horizontal. water cooled, and power
driven belt 11 of a heat conductive material for example copper. The belt 11 has side
darns 12, 13 which can be movable with the belt, but which can also be fixed. They can
advantageously be movable laterally and fixed in various lateral positions so that strips of
various width can be cast. Above the belt, there is a tundish 14 that functions as a
distributor of molten metal. It has a number of ceramic nozzles distributed over the entire
SUB~ ~ ~ ~ ~TE SHEEr
CA 02228180 1998-01-29
W O 97/06906 PCT/SE96/01020
width of the belt so that they produce several separate jets that meet the belt 11 which
moves as in-lic~t~d by the arrow 15. The orifices should be so located that the molten
metal flows out and solidifies as a cast thin continuous strip 29 on the substrate, that is,
on the movable belt 1 1. A container 16, for example a furnace or a ladle, supplies a
controlled flow of molten metal to the tundish/distributor 14. The flow out of the
cont~iner 16 can be regulated in various conventional ways, for example by means of a
stopper rod or a sliding gate nozzle.
The Figures 3 and 4 show a design which is somewhat modified from the design shown
in Figure 1. The container is replaced by a rotatable tube 17 of the kind disclosed in WO
9301015. The level of the molten metal in the tube 17 is kept constant by means of a
non-illustrated regulator that regulates the supply of molten metal to the tube 17. The
tube 17 has an outlet 18 in the form of a slot and the flow out of the tube can be regulated
by turning of the tube 17 since such turning changes the ferrostatic pressure that drives
the flow out through the slot 18. The tundish 14 has two fixed walls 20, 21 that slows
down the flow in the tundish and make the flow laminar before it reaches orifices 22. The
endless belt I 1 is cooled by a large number of cooling noz7.1es 23 that eject water jets
against the underside of the belt 11 so that the molten metal solidifies on the copper belt
into a cast continuous strip.
Since the endless belt 11 moves fast when the vertical and parallel jets 30 from the
orifices 22 of the tundish meet the belt 11 and the molten metal does not wet the belt. the
molten metal will not flow backwardly on the belt and a rear da~n is therefore not
~-~ce~!~n.y. The molten metal should flow out on the belt 11 into an even layer and the
distance between the jets 30 must therefore not be too big. There is no contact between
the tundish/distributor 14 and the belt 1 1 and the side dams 12, 13 of the belt, which is
advantageous particularly when a casting is ended or if a casting goes wrong, since the
molten metal cannot freeze on the mzl~hine and prevent it from being started again. The
jets are shown vertical but they can also be inclined. Another tundish/distributor can
quickly and easily be exchanged for the one on the machine when one wants to cast strips b
of another width or one wants to change to a casting process that needs other orifices or
another number of orifices since the tundish is neither coupled to the endless belt 11 nor
SUB~ JTE SHE~ET
CA 02228180 1998-01-29
W O 97/06906 PCT~E96/01020
to the container 16 or 17. The number of orifices and their size need to be varied in
relation to the combination of strip width, belt velocity, viscosity of the molten metal, and
desired thickness of the strip.
The side dams 13,14 are shown having inwardly inclined walls. A steel strip 29 is shown
in Figure 1, which has been cast with the machine described. Because of the inward
inclination of the side dams, the metal surface is hol;GonL~I along the lines in which solid
matter (the dams), the molten metal, and gas (argon) meet. If the surfaces of the dams
should instead be vertical, the surface would bend downwards at the edges since the
molten metal does not wet the side dams. The inclined dams in combination with the
supply of molten metal in the form of separate jets make the upper surface of the strip
very even. It will also be possible to cast thinner strips when the influence of the surface
tension is counteracted in this way. The inclination of the side walls of the dams 12,13
should be chosen so that it matches the angle of wetting in order to get a flat surface of
the molten metal.
It should be understood that the figures are schematic and frz-gm~nt~ry. A cover is for
example not shown. Such a cover holding a protective atmosphere, e.g. argon, protects
the free jets of molten metal and the free surface of the molten metal on the belt from
being oxidised.
The strip casting machine according to the invention can be made in different sizes and
for various kinds of metals and alloys. It can for example be suited for fast casting of
carbon steel in strip thi~kn~sses down to 6 mm or less and for strip widths of up to 2
metres or more.
SUBSlllUTE SHE~Er