Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
DESCRIPTION
Title of Invention
DECODER AND DECODING METHOD
Field of the Art
The present invention relates to a decoder and a decoding
method and more particularly, is preferably applicable to a
decoder and a decoding method for an image receiver for displaying
a plurality of screens on the same screen.
Background Art
For example, in the case of a television receiver 1 shown in
Fig. 1, a first video signal Si and a first audio signal S10,
which are selected by a tuner 3, of a television signal recei=ved
b-y an antenna 2, and a second video signal S2 and a second audio
signal S20 of a video signal transmitted through a terminal EX
from the second input source of a VTR, or the like are
respectively transmitted to a switch SW1.
The switch SW1 selects an input signal in the side of either
the first video signal Si and the first audio signal S10, or the
second video signal S2 and the second audio signal S20 as a main
video signal SA under the control of a microprocessor 5 and sends
it to a video processor 6 and the microprocessor 5.
The video processor 6 separates a horizontal synchronizing
1
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
signal SH and a vertical synchronizing signal SV from the main
video signal SA, then, transmits the main video signal SA to a
CRT7 and transmits the horizontal synchronizing signal SH and the
vertical synchronizing signal SV to the microprocessor 5 and a
deflecting circuit 8 for driving the CRT7.
Herein, the microprocessor 5 decodes a closed caption ciata
being a caption signal added to the main video signal SA by means
of a caption vision decoder 9. In addition, an XDS (extended data
service: EDS) signal added to the main video signal SA is decoded
by means of the caption vision decoder 9.
The XDS signal is a packet signal transferred so as to be
interleaved in the space of a closed caption data by which various
data such as a start time, contents or the like concerning a
program can be transferred.
Thus, there has been investigated the control of screeri
display of a TV broadcasting program which is undesirable to ]be
watched by nonage using this XDS signal.
A broadcasting station previously evaluates recommendable
viewer age about the contents of each program and transmits a code
a:bout the viewer age (rating) as an XDS signal. On the other side,
a receiver side, a level of viewer age is set and compared with
t:he code transmitted. And only when satisfying a prescribed
condition, the broadcasting program can be displayed on the screen.
T:he microprocessor 5 compares the rating set by the user with the
rating stage set and transmitted by the broadcasting station, and
2
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
controlling the display of a program based on this comparison
result.
The "rating" herein essentially means a step evaluation for
deciding whether the contents of expression such as extremely
violent scenes in a movie should be regulated so as not to be
watched by nonage. A regulation such as the age limit has been
established when a film is put on the screen based on the rating.
In the case where the user sets the rating to his desired
level, the caption vision decoder 9 in the microprocessor 5 first
decodes the XDS signal and compares the stage set by the user. As
a result of this comparison, if the prescribed condition is not
satisfied, a control signal YS for controlling the display of
screen is generated and supplied to the video processor 6. The
caption vision decoder 9 also transmits a closed caption signal
SA2 obtained by converting the closed caption data of the main
video signal SA into a video signal.
At this time, the video processor 6 converts the main video
signal SA into the three primary color signals of R, G and B and
conducts the on/off control of the display of a main picture on
the screen based on the control signal YS.
On the other hand, the above television receiver 1 is
provided with only one caption vision decoder 9. Thus, for
example, in a television receiver having a picture-in-picture
function for displaying video signals obtained from more than two
input sources on the same screen as the so-called picture-in-
3
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
picture screen (main screen, sub-screen) and a multi-picture
function for linearly displaying pictures of a plurality of
channels, the closed caption data or the XDS data only for the
main video signal SA can be decoded, but the closed caption data
or the XDS data for a sub-picture cannot be decoded.
Therefore, for example, even when the user sets a rating to,
a broadcasting program, the display regulation on the screen has
been effective only for the main picture and the regulation has
not been undesirably imposed on the sub-picture whose XDS data is
not decoded, and thus, the sub-picture has been disadvantageously
displayed.
To solve such problem, for example, a method has been
considered in which two caption vision decoders are provided to
respectively decode closed caption data and XDS data for the main
video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB. However, in thi:s
case, too much cost has been undesirably required.
Disclosure of Invention
The present invention has been made considering the above
points, and proposes a decoder having a simple structure and a
decoding method in which a plurality of input signals are
displayed on the same screen and the display of the input signals
on the screen can be individually controlled depending on the
additional information of each input signal.
To solve the above problems, the present invention
4
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
concerning a decoder provides picture display means for forming a
plurality of pictures corresponding to each input signal from a
plurality of input signals having additional information, and
displaying them on the same screen; switch means for switching and
sequentially inputting the plurality of input signals at
prescribed switch timing; additional information decoding means
for detecting and decoding additional information included in each
input signal from each of the plurality of input signals which are
sequentially input by the switch means; and display control means
for individually controlling the display of the plurality of
pictures in accordance with the plurality of additional
information corresponding to the plurality of input signals.
When a plurality of pictures are formed from a plurality of
input signals supplied at once and displayed on the same screen,
the plurality of input signals are sequentially transmitted to
additional information decoding means by switching switch means at
a prescribed timing, and additional information included in each
input signal is detected and decoded from the plurality of input
signals. Thus, the display of each picture corresponding to the
additional information can be individually controlled based on the
plurality of additional information.
Brief description of Drawings
Fig. 1 is a block diagram showing the entire structure of a
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
conventional television receiver.
Fig. 2 is a block diagram showing the entire structure of a
television receiver according to the present invention.
Figs. 3A to 3D are schematic diagrams showing an example of
image display.
Fig. 4 is a schematic view showing the structure of a YW
switch.
Fig. 5 is a block diagram showing the entire structure of a
television receiver according to other embodiment.
Figs. 6A to 6D are schematic views showing examples of image
display according to other embodiment.
Best Mode for carrying Out the Invention
Referring to the drawings, an embodiment of the present
invention will be described in detail below.
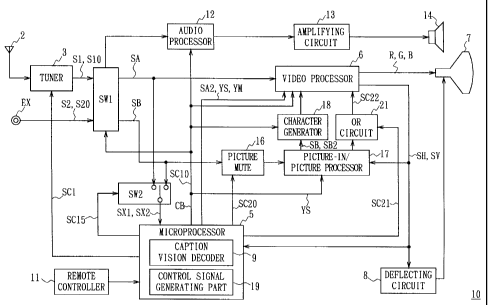
With reference to Fig. 2 in which the same reference
numerals are added to parts corresponding to those in Fig. 1, 10
generally designates a television receiver. When a television
signal received by an antenna 2 is transmitted to a tuner 3, a
desired broadcasting station is selected in accordance with a
control signal SC1 transmitted from a microprocessor 5 based on
the control of a remote controller 11 by a user and a first video
signal S1 and a first audio signal S10 are transmitted to a switch
SW1.
In a similar manner, a second video signal S2 and a second
6
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
audio signal S20 input through an external terminal EX from a
second input source such as a VTR are transmitted to the switch
SW1.
The switch SW1 selects either the input signal by the tuner
3 or the input signal by the VTR under the control of the
microprocessor 5 through an internal control bus CB. The audio
signal selected by the switch SW1 whose low-pitched tone, high-
pitched tone, right and left balance, surrounding effect and sound
volume or the like are adjusted under the control of the control
signal SC10 output via the internal control bus CB from the
microprocessor 5 through an audio processor 12, is sound-amplified
by an amplifying circuit 13 and the sound amplified audio signal
is output from a speaker 14.
In the meantime, the microprocessor 5 controls the switch
SW1 through the internal control bus CB based on an operation
through the remote controller 11 of the user, selects an input
signal of either the first video signal S1 or the second video
signal S2 as a main video signal SA and transmits it to a video
processor 6 and transmits an input signal of either the first
video signal S1 or the second video signal S2 as a sub-video
signal SB to a picture-in-picture processor 17 through a picture
mute 16.
The main video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB output
from the switch SW1 are simultaneously branched and also output to
a switch SW2.
7
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
While the main video signal SA is input to the video
processor 6 through the switch SW1, the sub-video signal SB is
input to the video processor 6 through a character generator 18
from the picture-in-picture processor 17.
The video processor 6 separates a synchronizing signal
comprising a horizontal synchronizing signal SH and a vertical
synchronizing signal SV from the main video signal SA, and then,
transmits respectively the main video signal SA and the
synchronizing signals to a CRT7 and a deflecting circuit 8. Then,
the R, G and B signals which are output signals of the video
processor 6 are synchronized with the horizontal synchronizing
signal SH and the vertical synchronizing signal SV, the
synchronized signals are scanned by the deflecting circuit 8 and
displayed on the screen of the CRT7. At this time, the quality of
an image displayed on the CRT7 is adjusted by controlling the
video processor 6 through the internal control bus CB from the
nicroprocessor 5.
The video processor 6 furthermore respectively transmits the
horizontal synchronizing signal SH and the vertical synchronizing
signal SV to the microprocessor 5 and the picture-in-picture
processor 17.
The picture-in-picture processor 17 outputs a sub-picture
comprising Y, U and V signals of the sub-video signal SB to the
video processor 6 via the character generator 18 in accordance
with a control signal SC10 output through the internal control bus
8
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
CB from the microprocessor 5. The sub-picture is inserted into a
part of the main picture by the video processor 6. The R, G and B
signals which are the output signals of the video processor 6 are
synchronized with the horizontal synchronizing signal SH and the
vertical synchronizing signal SV and scanned by the deflecting
circuit 8 so that an obtained image is displayed on the screen of
the CRT7.
As a result, as shown in Fig. 3A, a sub-picture P2 smaller
than a main picture P1 is inserted into a part of the main picture
P1 on the display screen of the CRT7.
Moreover, the video processor 6 synchronizes the caption
vision of a main screen with the horizontal synchronizing signal
SH and the vertical synchronizing signal SV based on a control
signal YS from the microprocessor 5, so that an obtained image is
displayed on a desired position of the screen of the CRT7.
Similarly, the character generator 18 is designed to iiisert
the caption vision of a sub-picture into the desired position of
the sub-picture depending on the control signal SC10 output
through the internal control bus CB from the microprocessor 5.
The output signal of the character generator 18 into which the
caption vision or the character of the sub-picture such as a
channel number or the like is inserted is sent to the video
processor 6. Thereby, as shown in Fig. 3A, a channel number being
selected as the sub-picture P2 is displayed on the sub-picture P2
as a channel number character PC2.
9
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
Furthermore, the character generator 18 displays a channel
number of the main picture P1 being selected at this time as a
channel number character PC1 in a part of the main picture P1 by
the control signal SC10 from the microprocessor 5.
The microprocessor 5 switches the switch SW2 by a control
signal SC15 for switching control which is generated by a control
signal generating part 19 and alternately transmits the main video
signal SA and the sub-video signal SB to a caption vision decoder
9.
That is, the microprocessor 5 generates the control signal
SC15 to switch the switch SW2 when the horizontal synchronizing
signal SH of the main video signal SA which is selected through
the switch SW2 reaches the 21st line of scanning lines (21 lines)
after the detection of the vertical synchronizing signal SV, and
switches the SW2 to the sub-video signal SB side.
The microprocessor 5 controls to generate again the control
signal SC15 from the control signal generating part 19 when the
horizontal synchronizing signal SH of the sub-video signal SB
switched from the main video signal SA reaches the 21st line
counting from a position in which the vertical synchronizing
signal SV is detected and switch the switch SW2 to the main video
signal SA side. The microprocessor 5 repeats the above-mentioned
switching control relative to the switch SW2.
During this time, the microprocessor 5 respectively detects
and decodes data for controlling the display on the screen which
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
is set as to XDS signals SX1 and SX2 respectively transmitted at
the 21st line of the fields 2 of the main video signal SA and the
sub-video signal SB, from the main video signal SA and sub-video
signal SB which are switched and alternately input by the control
signal generating part 19 in the caption vision decoder 9.
The XDS data is a data formed into a packet on the line 21
in the field 2 of a television signal and provides a data service
as the additional information of the video signal.
The caption vision decoder 9 respectively decodes the XDS
signals SX1 and SX2 added to the main video signal SA and the sub-
video signal SB to detect a picture display control data added to
the XDS signals SX1 and SX2. Thereby, a rating which has
previously set to a main picture and a sub-picture at the
transmitting side is discriminated.
Herein, the microprocessor 5 respectively compares the
result of discrimination of the rating as to the main picture and
the sub-picture by the caption vision decoder 9 with the rating
data previously set in the microprocessor 5 of the receiving side
by the user.
Then, the microprocessor 5 generates control signals SC20
and SC21 for controlling the display of the main picture and the
sub-picture on the screen based on the compared result and
respectively transmits them to a picture mute 16 and an OR circuit
21.
The picture mute 16 has a function for setting the sub-video
11
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
signal SB transmitted from the switch SW1 to the picture-in-
picture processor 6 to a black level and is on/off controlled by
the control signal SC20 output from the microprocessor 5.
The OR circuit 21 transmits the logical OR of a timing for
displaying the main picture on the screen controlled by the
control signal SC21 transmitted from the microprocessor 5 and a
timing for displaying the sub-picture on the screen transmitted
from the picture-in-picture processor 6 as a control signal SC22,
to the YW switch SW10 of the video processor 6 which is shown in
Fig. 2.
The YUV switch SW10 switches the main video signal SA and
the sub-video signal SB depending on the control signal SC22 and
outputs them to the CRT7.
In this case, first, in order to block only the display of
the main picture, such a control signal SC21 to set an output to
off by setting the video signal of the main picture to the black
level by means of the microprocessor 5, is transmitted to the OR
circuit 21. As a result, as shown in Fig. 3B, the YW switch SW10
is set to be kept switched to the sub-picture side during a
display control period of the main picture on the screen, and the
display of a part of displaying the main picture P1 is controlled
in black and only an image of a part of the sub-picture P2 is
projected onto the CRT7.
At this time, the microprocessor 5 outputs the control
signal SC10 to the audio processor 12 to control a sound output
12
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
from a speaker 14 corresponding to the main picture P1 in a normal
state where the display is not controlled into a state of stopping
the output in accordance with the display control of the main
picture P1. At this time, a sound of the sub-picture P2 may be
output in place of the sound of the main picture P1 (however, only
when the display of the sub-picture is not controlled).
Furthermore, when the display of the main picture P1 is
controlled in black, the character generator 18 displays a rating
display character PC3 in a part of the main picture P1 displayed on
the CRT7 by the control signal SC10 supplied from the
microprocessor 5, so that what the display of the main picture P1
is controlled can be perceived by a viewer.
In this connection, also when the display of the main
picture P1 is controlled, the character generator 18 displays the
channel display character PC1 in the main picture P1 by the control
signal SC10 supplied from the microprocessor 5. Thereby, even in
the state where the main picture P1 is not appeared by controlled
into a black level, the channel number of the main picture P1
being selected at this time can be informed the viewer.
Furthermore, when only the display of the sub-picture is
blocked, the picture mute is turned on by the control signal SC20
output to the picture mute 16 from the microprocessor 5, and the
sub-video signal SB transmitted to the picture-in-picture
processor 6 is set to the black level. At this time, the main
video signal SA or the sub-video signal SB is transmitted to the
13
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
CRT7 with switched by the control signal SC22. As a result, as
shown in Fig. 3C, the main picture P1 by the main video signal SA
is displayed on the display screen of the CRT7 with the sub-
picture P2 controlled in the black level by the picture mute 16
displayed in a part of the main picture P1.
At this time, the character generator 18 displays a rating
dlisplay character PC4 into a part of the sub-picture P2 controlled
in the black level by the control signal SC10 supplied from the
microprocessor 5, thus that the display of the sub-picture P2 is
controlled can be perceived by the viewer.
In this connection, also when the display of the sub-picture
P2 is controlled, the character generator 18 displays the channel
clisplay character PC2 into the sub-picture P2 by the control signal
SC10 supplied from the microprocessor 5, so that even in the state
where the sub-picture P2 is not appeared because of controlled
into the black level, a channel number of the sub-picture being
selected can be informed the viewer.
Furthermore, when the display of both the main picture and
the sub-picture on the screen is blocked, the control signal SC21
for setting the output of the main picture to off is output from
the microprocessor 5 to the OR circuit 21 and the control signal
SC20 for setting the picture mute to on is output from the
rnicroprocessor 5 to the picture mute 16.
As a result, the YW switch SW10 is set to be kept switched
to the sub-picture side during the display control period of the
14
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
main picture and the sub-picture on the screen, and the sub-video
signal SB is set into the black level, so that, as shown in F'ig.
3D, both the main picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 are blocked
and are not output to the CRT7. At this time, the microprocessor
sends the control signal SC10 to the audio processor 12 to
control the sound which is output from the speaker 14
corresponding to the main picture P1 in the normal state where the
olisplay is not controlled, into an output stopping state according
t.o the display control of the main picture P1.
Furthermore, when both displays of the main picture P1 and
the sub-picture P2 are controlled in black, the character
g-enerator 18 respectively displays the rating display character Pc3,
PC9 into a part of the main picture P1 and a part of the sub-
picture P2 controlled into the black level, so that what both
displays of the main picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 are
controlled can be perceived to the audience.
In this connection, also when both displays of the main
picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 are controlled, the character
generator 18 displays the channel display character PC1 in the main
picture P1 by the control signal SC10 supplied from the
microprocessor 5 while displays the channel display character PC2
in the sub-picture P2. Thereby, even in the state where the main
picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 cannot be seen because of
controlled into the black level, each channel number of the main
picture and the sub-picture being selected at this time can be
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
informed the viewer.
Furthermore, when both of the main picture and the sub--
picture are displayed, the control signal SC21 for setting the
output of the main picture to on is output to the OR circuit 21
from the microprocessor 5. At this time, the picture mute 16 is
simultaneously set to off by the control signal SC20 output from
the microprocessor 5. In this case, the YUV switch SW10 is
switched synchronizing with the respective timing for turning on
the output of the main picture and the sub-picture, based on the
horizontal synchronizing signal SH and the vertical synchronizing
signal SV of the main picture, during a period for displaying the
main picture and the sub-picture on the screen. Consequently, as
shown in Fig. 3A, the main picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 are
both output onto the same screen of the CRT7.
By the way, as methods of canceling the display control at
the receiving side, that the user inputs a code number to the
microprocessor 5 or resets a viewer age of the rating with opening
a menu screen or the like can be considered.
Furthermore, the microprocessor 5 transmits the caption
vision signal SA2 of the main picture decoded by a closed caption
signal from the caption vision decoder 9 to the video processor 6.
At this time, the microprocessor 5 simultaneously transmits a
control signal YS for controlling whether the caption vision is
displayed or not to the video processor 6.
Moreover, the microprocessor 5 controls whether the caption
16
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
vision of the sub-picture is displayed or not according to a
caption vision signal SB2 decoded from the closed caption data of
the sub-image by the control signal SC10 output through the
internal control bus CB to the character generator 18.
Furthermore, the microprocessor 5 controls a position for
displaying the caption vision of the sub-picture by the control
signal SC10 output to the character generator 18 through the
internal control bus CB.
The character generator 18 controls the position for
displaying the caption vision by synchronizing the horizontal
synchronizing signal SH and the vertical synchronizing signal SV
transmitted from the video processor 6 with the caption vision
signal SB2, based on the control signal SC10, and forms the
caption vision of the sub-picture screen based on the caption
vision signal SB2.
When the television signal and the video signal are
respectively input through the tuner 3 and the terminal EX, in the
above described structure, they are respectively selected as the
main video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB at the switch SW1.
The main video signal SA is transmitted to the video processor 6.
The sub-video signal SB is transmitted to the picture-in-picture
processor 17. At this time, the main video signal SA and the sub-
video signal SB are also simultaneously branched and transmitted
to the switch SW2.
In the switch SW2, the main video signal SA and the sub-
17
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
video signal SB are alternately switched under the control of the
microprocessor 5 and transmitted to the caption vision decoder 9.
At this time, the microprocessor 5 counts respective horizontal
synchronizing signals SH of the main video signal SA and the sub-
video signal SB and switches and controls the switch SW2 at a
timing for every 21 lines counting from the vertical synchronizing
signal SV in each field 2.
Accordingly, when the switch SW2 selects the main video
signal SA, the microprocessor 5, after detecting the vertical
synchronizing signal SV of the main video signal SA, counts the
horizontal synchronizing signal SH for 21 lines counting from the
vertical synchronizing signal SV to fetch the main video signals
SA up to the 21st line to the caption vision decoder 9. Thus the
XDS signal SX1 added to the 21st line of the field 2 in the main
video signal SA is fetched to the caption vision decoder 9.
After counting 21 lines of the main video signal SA, the
microprocessor 5 switches the switch SW2 to fetch the sub-video
signal SB to the caption vision decoder 9. Then the
microprocessor 5, after detecting the vertical synchronizing
signal SV of the sub-video signal SB, counts the horizontal
synchronizing signals SH for 21 lines from the vertical
synchronizing signal SV to fetch the sub-video signal SB up to the
21st line to the caption vision decoder 9. Thus the XDS signal
SX2 added to the 21st line of the field 2 in the sub-video signal
SB to the caption vision decoder 9.
18
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
The caption vision decoder 9 respectively alternately
decodes the XDS signals SX1 and SX2 respectively added to the main
video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB of the 21st line, so
that a display control of each screen of the main video signal SA
and the sub-video signal SB is discriminated.
Thus each screen display control data respectively set in
two video signals selected via the switch SW1 (the main video
signal SA and the sub-video signal SB) is repeatedly alternately
discriminated in one caption vision decoder 9.
In this connection, the screen display control data added to
each XDS signal SX1, SX2 of the main video signal SA, the sub-
video signal SB is set its level in accordance with the contents
of image. Therefore, if the level of each screen display control
data discriminated in the caption vision decoder 9 is higher than
the level previously set by the user and corresponding to the
viewer age, this represents that the image corresponding to the
screen display control data is undesirable for the viewer younger
than the age set by the user. In this case, the microprocessor 5
controls the display of the picture with the screen display
control data is added thereto.
In the case where the picture to be controlled of the
display regulation is a main picture, the microprocessor 5
switches the YUV switch SW10 in the video processor 6 into a sub-
video side to forcedly control the display of the part where the
main picture is displayed into black. This display control of the
19
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
main picture is continued until the level of the display control
data added to the main video signal SA becomes the same as or
lower than the level corresponding to the viewer age previously
set by the user in the microprocessor 5.
Besides, in the case where the picture to be controlled of
the display is a sub-picture, the microprocessor 5 forcedly
controls the display of the sub-video into black by the picture
mute 16. This display control of the sub-picture is continued
until the level of the display control data added to the sub-video
signal SB becomes the same as or lower than the level
corresponding to the viewer age previously set by the user in the
microprocessor 5.
According to the above mentioned structure, since the main
video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB input from the two
input sources are respectively switched by the switch SW2 and
alternately transmitted to the caption vision decoder 9, the XDS
signal SX1 recorded on the main video signal SA as additional
information and the XDS signal SX2 recorded on the sub-video
signal SB as additional information are detected and decoded.
Thus, the ratings concerning the display control on the screen
which are respectively set to the XDS signals SX1 and SX2 can be
individually decoded by the caption vision decoder 9 with one
input. Besides, the screen display control corresponding to each
video signal SA and SB can be individually performed on both of
the main picture and the sub-picture to be displayed on the same
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
screen of the CRT7 by the microprocessor 5.
Furthermore, since the closed caption data respectively
added to the main video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB
which are input from the two input sources are switched through
the switch SW2, alternately supplied to the caption vision decoder
9 with one input, and decoded, in the main picture and the sub-
picture to be displayed on the same screen, the caption vision
data can be individually displayed.
Although, the above described embodiment has dealt with the
case of displaying a plurality of pictures using the video signals
input from the tuner 3 and the external terminal. However, the
present invention is not only limited to this but also, as shown
in Fig. 5 in which the same reference numerals are added to parts
corresponding to those in Fig. 2, by providing a second tuner 4 in
addition to the first tuner 3, two video signals may be selected
among from these two tuners 3, 4 and the external terminal EX by
the switch SW1 to respectively transmit these signals to the video
processor 6 and the picture mute 16 as the main video signal SA
and the sub-video signal SB.
In this case, a TV broadcasting selected by the second tuner
4 is transmitted from a different broadcasting station from the TV
broadcasting selected by the first tuner 3. Thus, if a third
video signal S3 and a third audio signal S30 selected by the
second tuner 4 are transmitted to the switch SW1 and the desired
video signal is selected in the switch SW1, a channel of the other
21
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
TV station which cannot be selected by the first tuner 3 can be
selected.
In this arrangement, since the main video signal SA and the
sub-video signal SB can be selected among from video signals
supplied from two channels on the air and the external terminal EX,
the screen display control and the display of caption vision can
be individually conducted based on the main video signal SA and
the sub-video signal SB being selected.
Furthermore, the above described embodiment has dealt with
the case of displaying the sub-picture P2 smaller than the main
picture P1 in a part of the main picture P1 on the display screen
of the CRT7. However, the present invention is not only limited
to this but also, as shown in Fig. 6A, the present invention can
be applied to the case of linearly displaying the main picture P1
and the sub-picture P2 in the display regions having the almost
same size.
Furthermore, the above described embodiment has dealt with
the case of displaying the two pictures (the main picture P1 and
the sub-picture P2) on the display screen of the CRT7. However,
the present invention is not only limited to this but also, as
shown in Fig. 6B, the present invention can be applied to the case
of displaying more than 3 pictures P1 - P7 on one display screen
of the CRT7. In this case, by providing a switch for switching a
plurality of, more than 3, inputs in place of the switch SW2 for
switching two inputs mentioned above in Fig. 2, the screen display
22
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
control can be conducted individually to each plurality of, more
than 3, pictures.
Furthermore, the above described embodiment has dealt with
the case of displaying the channel number characters PC1 and PC2 in
the main picture P1 and/or the sub-picture P2 by the character
generator 18. However, the present invention is not only limited
to this but also, as shown in Fig. 6C, a logotype of broadcasting
station transmitted in the form of respective XDS signals to the
m.ain picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 may be displayed as
broadcasting station logotype character(s) Pc5 and/or PC6. Thereby,
the viewer can perceive the broadcasting station being the
provider of each picture. In this connection, Fig. 6D shows the
state where the display of each picture is controlled when the
main picture P1 and the sub-picture P2 are linearly displayed.
Also in this case, since the rating display characters PC3 or PC4
and the broadcasting station logotype characters Pc5 or PC6 are
displayed, the viewer can perceive that the displays of pictures
P1, P2 are controlled respectively, and further can confirm the
broadcasting stations of the pictures P1 and P2 of which the
contents cannot be confirmed because it is in the process of
display control.
The data service using the XDS signal may be applied to
information including, 1) various information concerning a program
such as the start time, lapse of time, contents of a currently
transmitted program, 2) various information concerning a program
23
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
such as the start time, lapse of time, contents of a program to be
sent in future, 3) information concerning a broadcast station
which is broadcasting, 4) time information, 5) information of
weather or accident or the like, and may be applied to a case in
which these information are all decoded.
Furthermore, the additional information may be broadly
applied to a case in which general signal information added to a
video signal such as a signal superimposed on a part other than a
text or a 21st line as well as the closed caption data and the XDS
signal are decoded.
Moreover, the above described embodiment has dealt with the
case where a timing when 21 horizontal synchronizing signals are
counted after the vertical synchronizing signal is detected is
used as a switching timing for switching the switch SW2. However,
the present invention is not only limited to this but also the
switch SW2 may be switched every one field by the vertical
synchronizing signal. Additionally, the count number of the
horizontal synchronizing signals may be set to a count other than
21 according to the additional position of the XDS signal
transmitted along with the count number in the horizontal
synchronizing signal.
Furthermore, the switch SW2 may be switched and controlled
at high speed by a clock of, for example, ten and several
megahertz, the main video signal SA and the sub-video signal SB
may be respectively alternately read, transmitted to the
24
CA 02232154 1998-03-13
microprocessor 5 and respectively stored in a RAM (random access
memory) for the main video signal SA and a RAM for the sub-video
signal SB, and then, the XDS signals added thereto may be
respectively sampled and decoded by the caption vision decoder 9.
Moreover, by respectively storing 21 lines of the horizontal
synchronizing signals of the main picture and the sub-picture in a
main picture buffer and a sub-picture buffer, they may be read
from each buffer at a higher speed than its writing speed,
supplied to the microprocessor 5, and input to the caption vision
decoder 9 in the microprocessor 5.
Industrial Applicability
In a television receiver, the present invention can be
applied to the case of linearly displaying pictures of a plurality
of channels on the same display screen.