Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 1 -
System and Method for Storing and Processing Date Information
Which Spans More than One Century
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to systems and methods for
storing and processing date information which spans more than
one century.
Background of the Invention
The "year 2000 problem" is now a well known
phenomenon which has resulted from the fact that most existing
application software particularly in the business data
processing area stores and processes date information in a
six-digit format which does not include any century
information. The date might for example be stored using the
day/month/year format in which case the date January 21, 1999
would be stored as 210199.
Until recently, it was an acceptable assumption to
make that any and all years stored belonged to the 20th
century and as such there was no ambiguity in such dates.
However, now it is necessary to be capable of processing dates
for years belonging to the 21st century. This presents a
problem both for storing and processing the date information.
It would be desirable to be able to include century
information without changing storage requirements as this
would require substantive changes to software accessing the
date information. For processing, conventional applications
can sort date information within a given century but cannot
sort dates from different centuries. Consider for example
that a date having the year 2005 would have a year field equal
to 05, and a date having the year 1995 would have a year field
equal to 95 which would be incorrectly interpreted as being
after the stored version of the date 2005. Furthermore, files
containing date information are often indexed by that date
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 2 -
information. It should be possible to use the date
information to uniquely index stored information and clearly
this is not possible when the century is ambiguous.
Various solutions have been proposed. U.S. patent
Number 5,600,836 to Alter entitled "System and Method for
Processing Date-Dependent Information which Spans One or Two
Centuries" which issued on February 4, 1997 involves using
"zone data files" which contain dates which have been
converted to "zone times" and "local data files" which contain
the dates in the conventional format. This requires
significant calculation and logic to encode and decode the
date information.
U.S. Patent Number 5,644,762 to Soeder entitled
"System and method for Processing Date-Dependent Information
which Spans One or Two Centuries" which issued on July l, 1997
discloses a solution for storing the century in a six digit
date by adding the century and converting the century and year
combination to a binary value. While this will work for some
applications, it has the disadvantages of requiring a mixed
mode storage strategy.
U.S. Patent Number 5,668,989 to Mao entitled "Two-
Digit Hybrid Radix Year Numbers for Year 2000 and Beyond"
which issued September 16, 1997 treats the higher digit of a
two digit year number as hexadecimal but displayed in a
decimal-like format with font patterns such as 0 - 9 and '0 -
'5 so that the year 1900 is represented and processed as 00
while the year 2000 is represented and processed as '00. This
will only handle dates up to 2059.
Finally, other methods include full expansion which
requires 33% more storage space, windowing, the "Roman
Format", packed format, and extended Julian.
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 3 -
Summary of the Invention
It is an object of the invention to obviate or
mitigate one or more of the above identified disadvantages.
According to a first broad aspect, the invention
provides a series of operational steps to be performed on or
with the aid of a computer, said steps comprising:
a) whenever necessary, determining a six digit
overloaded date from day, month and year information by
performing the steps of:
al) determining a three digit prefix from the year
information which maintains sort order and includes century
information;
a2) determining a three digit suffix from the day
and month information which maintains sort order; and
a3) determining a six digit overloaded date by
combining the three digit prefix and the three digit suffix.
According to a second broad aspect, the invention
provides a series of operational steps to be performed on or
with the aid of a computer, said steps comprising:
b) whenever necessary determining day, month, year and
century information from a six digit overloaded date by
performing the steps of:
bl) determining a three digit prefix and a three
digit suffix from the six digit overloaded date;
b2) determining the year and century information
from the three digit prefix; and
b3) determining the day and month information from
the three digit suffix.
According to a third broad aspect, a method is
provided including the steps of the first and second broad
aspects described above. Preferably in such an aspect, step
al) comprises the steps of:
i) determining if the year information includes
century information;
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 4 -
ii) if the result of step i) is false, determining
if the year information is less than a predetermined pivot
year and if so determining the three digit prefix to be one
hundred plus the year information and if not determining the
prefix to be the year information;
iii) if the result of step i) is true, determining
the prefix to be the year information and preferably the year
information minus a predetermined base year;
step a2) comprises the steps of subtracting one from
the month information, multiplying by 31 and adding the day
information;
step bl) comprises the steps of:
i) dividing the six digit overloaded date by 1000
to get the three digit prefix;
ii) subtracting 1000 times the prefix from the six
digit overloaded date to get the three digit suffix;
step b2) comprises the steps of:
i) dividing the three digit prefix by 100000 to
get a century index;
ii) subtracting 100 times the century index from
the prefix to get the year information;
and step b3) comprises the steps of subtracting one
from the suffix and then dividing by 31 to get a number of
prior months, and adding one to the number of prior months to
get the month information, and determining the day information
to be the suffix minus the number of prior months times 31.
Advantageously, the method allows the overloaded
date to be stored in six numeric decimal digits. The
overloaded date maintains sort sequence. The processing
overhead introduces is not unreasonable.
Preferably, the six numeric digits computed for a
given overloaded date can be stored in three bytes.
Preferably, the date is mathematically calculated.
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 5 -
Preferably, the century is determined using
windowing, windowing being a process of inferring the century
based on the year portion of a date such that a year less than
a given number is deemed to be in the latter century.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Preferred embodiments of the invention will now be
described with reference to the attached drawings in which:
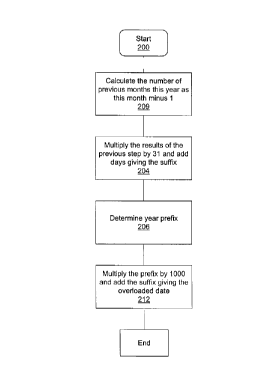
Figure 1 is a flowchart for a method of determining
an overloaded date according to an embodiment of the
invention;
Figures 2A - 2C are flowcharts for the step of
determining the year prefix appearing in Figure 1;
Figures 3A and 3B are flowcharts for methods of
determining a six or eight digit date representation
respectively from an overloaded date determined with the
method of Figure 1; and
Figure 4 is a block diagram of a computing device
according to an embodiment of the invention.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiments
Referring now to Figure 1 a method of determining an
overloaded date according to an embodiment of the invention
has as its input a date which includes day, month and year
information and may or may not include century information.
The method will be described in detail with respect to the
example date of 25 November 2012 for the case where century
information is included, or 25 November '12 for the case where
century information is not included.
In the first step 202 the number of complete
previous months that year is determined by subtracting one
from the numeric representation of the month. In this
example, the number is 11 (numeric representation of November)
minus 1 equals 10. In the second step 204, the results of the
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 6 -
previous step 202 are multiplied by 31 and added to the day
field of the date to give a suffix quantity. In this example,
this yields 10 x 31 + 25 = 335 as the suffix. In step 206 a
three digit year prefix is determined according to one of the
methods described in detail below. For the purposes of this
example, assume that the year prefix is 112. In step 208 the
overloaded date is determined by multiplying the year prefix
(output of step 206A) by 1000 and adding the suffix (output of
step 204). In our example, this yields 1000 x 112 + 335 -
112335 as the overloaded date.
Various methods may be used to determine the year
prefix, the important factor being that it may be stored in
three digits (i.e. prefix less than or equal to 999) and
maintains sorting and indexing of years.
The methods used may depend upon the format of the
year information being input to the method and more
particularly whether it includes century information. First
of all, a "base year" must be selected, this preferably being
a century year. The method will be incapable of representing
dates prior to the base year. For most applications currently
contemplated the base year would be 1900.
For input data which does not include century
information an assumption about the century must be made. For
the 1900 base year example, the year 2012 would have a two
digit year field of 12 in input data which does not include
century information. For this case, an assumption may be made
that all two digit years equal to or greater than a certain
year which will be referred to herein as the "pivot year"
belong to the century beginning with the base year and that
all years less than the pivot year belong to the century
following the base year. The flowchart of Figure 2A will be
used to describe the processing of such input information and
this will be referred to as "method A". In step 232 the year
field is compared with the pivot year. If the year input is
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
less than the pivot year then step 234 is executed, this
consisting of determining the prefix to be the year input +
100. If the year input is not less than the pivot year then
step 236 is executed, this consisting of determining the
prefix to be the year input.
For data for which no assumption regarding century
needs to be made, the year prefix may be determined simply by
subtracting the base year from the year information. For
example, if the year is 2012, then the year prefix is
determined from 2012 - 1900 = 112. This is depicted in
flowchart form in Figure 2B and will be referred to as "method
B.. .
For data which is mixed in the sense that it may or
may not include century information, either method A or method
B may be executed. This is depicted in Figure 2C wherein a
test (step 240) is used to determine which method to use,
method A or method B. If the year is greater than 99 then
century information must be present and method B can be used.
Otherwise method A is used. In either case, the first digit
of the prefix is an indicator of the century of the year with
respect to the base year and will be referred to as the
century index. For years within 100 years of the base year,
the century index is "0", for years within between 100 and 200
years of the base year, the century index is "1" and so on.
The date information may then be stored in any
conventional fashion, and more particularly can be stored in
as little as three bytes using conventional storage
techniques.
In order to present either a six digit or an eight
digit date in conventional format from the overloaded date
requires the above process to be reversed. A method for
obtaining the date in six digit format (two digit year) will
be described with reference to the flowchart in Figure 3A in
the context of the above developed overloaded date of 112335.
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
_ g _
The first step 302 is to divide the overloaded date by 100000
and to take the integer part thereby yielding the century
index. For the example this yields a century indicator of
"1". The next 304 step is to divide the overloaded date by
1000 and to take the integer part to produce the prefix. For
the example this yields a prefix of 112. In the next step
306A to get the two digit year, 100 times the century index is
subtracted from the prefix determined in step 304. In the
example this yields 112 - 100 x 1 = 12. In step 308, to get
the suffix, 1000 times the prefix is subtracted from the
overloaded date. In our example, this yields a suffix of 335.
In step 310, the month is retrieved by carrying out steps 312,
314 and 316. Step 312 consists of subtracting one from the
suffix computed in step 308 to prevent incorrectly determining
the subsequent month when dividing by 31 if the day is the
31st. Step 314 comprises dividing the result by 31 to get the
number of prior months. In our example, this yields 10 as the
number of prior months. Finally step 316 comprises adding one
to the result of step 314 to get the actual month. In our
example, the month is determined to be 11. In step 318, the
day information is determined by subtracting the number of
previous months times 31 from the suffix. In our example, the
day is determined to be 25.
When an eight digit date is to be produced (four
digit year) the prefix is determined by dividing the
overloaded date by 1000. The year is determined by adding the
base year to the prefix. The remaining steps are the same as
for the six digit format. This is shown in Figure 3B which is
the same as Figure 3A with the exception that step 306B is
executed in place of step 306A.
Figure 4 shows a computing device for implementing
the invention. Computing device 348 includes storage 360 for
storing dates, these normally forming part of some larger
records. Read/write device 358 reads from and writes to the
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 9 -
storage under control of a processor such as microprocessor
350. The microprocessor 350 has logic circuitry for executing
the methods of Figures 1-3 described above, or may be a
computing device appropriately programmed to execute the
methods. The device may include any or all of input 352,
printer 354, or display 356 as needed, for example. The
storage 360 may be a permanent storage medium such as a disk
or tape in which case the read/write device 358 provides
access to this permanent storage medium. Alternatively,
storage 360 may be any type of volatile storage such as RAM or
microprocessor registers for example in which case the
functionality of the read/write device 358 may be part of the
functionality of the microprocessor.
In the above described examples, the suffix is
determined by subtracting one from the current month,
multiplying by 31, and adding the day. More generally, any
technique of sortably representing the day and month in three
digits may be used. For example, the month may be multiplied
by any "month multiplier" between 31 and 80 inclusive may be
used to create a number which when added to the day will yield
a number less than 1000, the requirement for three digit
storage. Furthermore, if a number greater than 31 is used,
then steps 204,312, and 316 described previously are not
required. For example, if 32 is used, then for our November
25, 2012 date the suffix would simply be 11*32+15=377. The
month would be recoverable from the suffix by dividing the
suffix by the month multiplier (in our example 377/32 - 11)
and the day would be recoverable by subtracting the month
times the month multiplier from the suffix (in our example 377
- 11*32 - 25).
In the above examples, the prefix and suffix are
determined using numerical methods, and require no string
manipulations. This is desirable because string manipulations
are slow to perform. However, in the case that string
CA 02234991 1998-04-16
- 10 -
manipulations are permissible, even though there is no
apparent advantage to doing so, the three digits of the suffix
and the three digits of the prefix may be arranged in any
predetermined order since the suffix and prefix would still be
recoverable. In addition, different methods of generating the
prefix and suffix may be used which are self-evident from the
above described numerical methods.
Should input dates be available in the format yy/ddd
where ddd is from 1-366, the suffix may simply be selected to
equal the ddd field if it is understood that all dates will be
in that format since this satisfies the requirement that the
suffix be sortable and contain values less than 999.
Otherwise, the input date must be converted to a day/month
format and the methods described previously are then executed.
Any of the above described methods may be used to
convert an entire array of dates to overloaded dates.
Alternatively, the methods may be used one at a time each time
a date is accessed.
It is to be understood that any processing means
capable of executing the above described methods could be used
to implement the invention including computers,
microprocessors, ASICs (application specific integrated
circuits), FPGAs (field programmable gate arrays) etc.
Numerous modifications and variations of the present
invention are possible in light of the above teachings. It is
therefore to be understood that within the scope of the
appended claims, the invention may be practised otherwise than
as specifically described herein.