Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
Chiral Methylphenyloxazolidinones
The invention relates to (R)-(-)-methylphenyloxazolidinone
derivatives, the process for their production and their use as
pharmaceutical agents.
It is known from US Patent 4,186,129 that
phenyloxazolidinone derivatives have phosphodiesterase-inhibiting
properties and, moreover, have a central-depressive,
antidopaminergic, antinociceptive and anticonvulsive effect. EP-
0198919 further describes that phenyloxyazolidinones in the case
of topical application have antiinflammatory properties, and EP-
0270482 discloses the good neuropsychotropic action of
phenyloxazolidinones.
These publications only mention that the separation of the
racemate into the antipodes can be carried out with the methods
that are commonly used, without the enantiomers having been
indicated and their pharmacological activity studied or the
purity of the obtained compounds noted. To reduce the side
effects of the pharmaceutical agents, it is desirable to
administer a uniformly active substance, which can be used in
small dosages.
It has now been found that (R)-configured
methylphenyloxazolidinone derivatives are especially effective
and are better suited for use as pharmaceutical agents than the
racemate.
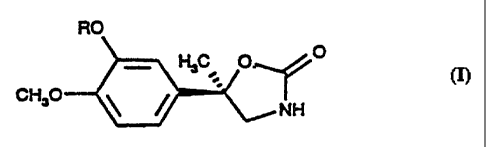
The invention relates to (R)-(-)-methylphenyloxazolidinones
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
of formula I,
RO
- HsC O O
cH o ~ (I)
~NH
in which
R means a hydrocarbon radical with up to 5 C atoms.
As hydrocarbon radicals, for example, ethyl, propyl,
isobutyl, isobutenyl, butyl, cyclobutyl and cyclopentyl can be
mentioned.
The compounds of formula I also inhibit the TNF production
and are therefore suitable for treating diseases that are
mediated by the activation of TNF.
Diseases that are mediated by TNF are defined both as
diseases that are triggered by the production of TNF and diseases
in which other cytokines, such as, for example, I1-1 or I1-6, are
altered by TNF.
TNF is defined both as TNF-a and TNF-!3, which are both
antagonized by the compounds of formula I. Preferably, TNF-a is
inhibited.
The compounds of formula I are therefore suitable for the
production of a pharmaceutical preparation that is used for the
treatment and prophylaxis of diseases in living creatures, which
are triggered by stimulation of TNF. Diseases that are altered
by excessive or unregulated TNF stimulation include, for example,
allergic and inflammatory diseases, auto-immune diseases,
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
3
pulmonary diseases, infectious diseases and bone resorption
diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis,
osteo-arthritis, gout, sepsis, septic shock, endotoxin shock,
gram-negative sepsis, toxic shock syndrome, ARDS (acute
respiratory distress syndrome), pulmonary sarcoidosis, asthma,
silicosis, cachexia, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease,
osteoporosis, organic lesions after reperfusion, inflammatory
diseases of the central nervous system such as cerebral malaria,
multiple sclerosis, panencephalitis, infectious diseases such as
AIDS, bovine insanity, inflammatory diseases of the skin such as
urticaria, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis,
lupus erythematosus as well as diabetes insipidus,
neuroprotection, e.g., in the case of Parkinson's disease,
dementia, for example, after multiple infarctions and stroke.
The effectiveness of the compounds of formula I in the
above-mentioned indications can be shown by appropriate, commonly
used pharmacological tests.
The new (R)-(-)-methylphenyloxazolidinones can be obtained
from the racemate by chromatography on chiral columns or with
diastereomers with optically active adjuvants. As an optically
active adjuvant, for example, (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)-ethyl isocyanate
is suitable, which makes possible the production of the optically
active compound in a simple way in good yields and high purity.
The reaction is performed in inert solvents, such as toluene,
benzene, i.a., or their mixtures in the presence of an organic
base, for example, a tertiary amine such as triethylamine at
elevated temperature or boiling temperature of the reaction
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
4
mixture. The obtained mixture of the diastereomeric allophanates
is quantitatively separated into the components by chromatography
on silica gel. The separated diastereomeric allophanates are
then split into the optically active methylphenyloxazolidinones
by treatment with bases, for example, with alkali alcoholates in
polar solvents. As polar solvents, for example, cyclic and
acyclic ethers, such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane and diethyl
ether, are suitable. The reaction is suitably carried out under
inert gas.
The invention also comprises the process for the production
of the compounds of formula I, in that their racemate is
transferred with an optically active adjuvant into the
diastereomeric mixture and then the optically active adjuvant is
separated or their racemate is chromatographed on chiral columns.
The production of the compounds of formula I can also be carried
out by separation of (R,S)-5-(3-benzyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-2-oxazolidinone, for example, by chromatography and
subsequent cleavage of the benzyl group and etherification. The
cleavage of the benzyl group is carried out, for example, by
hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst, such as, for
example, palladium on a suitable vehicle in inert solvents such
as ethyl acetate. The subsequent etherification of the hydroxy
derivative is carried out in the presence of bases with a
reactive derivative such as halide, tosylate or mesylate in polar
solvents such as dimethylformamide or alcohols at temperatures of
up to the boiling point of the solvent. As bases, e.g., alkali
compounds such as sodium or potassium hydroxides, -carbonates,
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
-alcoholates or -hydrides are suitable.
If substituent R contains a double bond, the latter can be
reduced in the usual way to the corresponding alkyl derivative.
For example, the reduction can be carried out catalytically with
palladium/carbon in an inert solvent at room temperature or
elevated temperature.
The processes according to the invention make possible the
production of the compounds of formula I in 99~ purity.
In the example of 5-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-2-oxazolidinone (compound 1), it can be shown that the
optically active (R)-(-)- compound, surprisingly enough,
represents the active compound.
The improved effectiveness of the new chiral
methylphenyloxazolidinone derivatives in comparison with the
racemate can be shown based on the head twitch and grooming
reactions in rats that are characteristic of phosphodiesterase
type IV (PDE IV) inhibitors. The racemate and the appropriate
enantiomers were administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) to male
Wistar rats, and the occurrence of head twitches and grooming for
15-75 minutes after injection was detected by observation. As
can be seen from Table 1, the (S)-(+)-enantiomer proved to be 4-
fold (head twitches) less effective or 60-fold (grooming) less
effective than the racemate, while the (R)-(-)-enantiomer was 4-
fold stronger (head twitches) or equally active (grooming) in
comparison with the racemate.
CA 02235264 2005-09-02
Tabl~ t
Compound Hoad-Twitch Test Grooming
MED i.p. [mg/kg] MED i.p. [mg/kg]
(R)-(-)-1 0.39 0.1
(R,8)-1 1.56 0.1
(8)-(+)-1 6. Z5 6.25
MED: Minimum effective dose, i.e., the lowest dose that ensures a
statistically significant effect.
The action of the enantiomers on the central nervous system
was studied in vitro by examining the displacement capacity of
the radiolabeled Rolipram of brain homogenates (Eur. J.
Pharmacol., Vol. 127, 105-115 (1986)). The ICSO values (the
concentration at which 50% inhibition action occurs) were
converted to inhibition constant Kt, which is calculated
according to the following formula:
K~ = ICSp / C 1 + (L/~) ] ~
in which L means the concentration of the radioactive tracer and
Kp means the dissociation constant of the 3Ii-Rolipram bond, which
is determined separately.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
7
Table 2
RO RO
_ H,C O~O _ H,C O~O
i~~ '"
CH,O ~ ~ NH CH'O ~ ~ ~ NH
(R)-(-)-(sourer (S)-(+)-Isomer
R Racemate (R)-(-)-Isomer (8)-(+)-Isomer
Ri [nM] Ri [nM] Ri [nM]
Ethyl- 0.68 0.33 20
Propyl- 0.61 0.24 16
Cyclopentyl- 0.57 0.34 3.0
Macrophages and microglia cells, which perform macrophage
functions in the brain, mediate the release of TNF-a during
experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). If macrophages
are stimulated, for example, by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a
secretion of TNF-a is carried out in vitro and in vivo within
hours.
A murine macrophage cell line (RAW 264) was preincubated for
30 minutes in the presence and in the absence of various
concentrations of PDE-IV inhibitors and then stimulated with LPS
(10 ng/ml). 18 hours after stimulation, the culture medium was
removed, and the TNF-a release was measured with a specific Elisa
test.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
8
The test can be obtained from various companies, i.a., from
the British Biotechnology company Genzyme, and it is carried out
as the manufacturer describes.
Table 3 shows the improved TNF-inhibition of the new chiral
methylphenyloxazolidinone derivatives in comparison with the
racemate in the example of 5-(3-propoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-2-oxazolidinone (compound 2):
Table 3
Compound IC [ACM,
(RS)-2 0.50
(R) - (-) -2 0 . 25
(S) - (+) -2 2 . 50
The table shows that the (-)-enantiomer doubled is as
effective as the racemate and 10-fold more effective than the
(+) -enantiomer.
Since the new compounds of formula I are distinguished not
only by increased effectiveness but also by few side effects and
reduced toxicity, the use of optically active (R)-(-)-
methylphenyloxazolidinones for the production of pharmaceutical
agents is especially advantageous.
The agents are produced according to the usual processes, by
the active ingredient being put into the form of a pharmaceutical
preparation that is suitable for enteral or parenteral
administration, with suitable vehicles, adjuvants and/or
additives. The preparations that are thus obtained can be
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
9
used as pharmaceutical agents in human or veterinary medicine.
Administration can be done orally or sublingually as a solid in
the form of capsules or tablets or as a liquid in the form of
solutions, suspensions, elixirs, aerosols or emulsions, or
rectally in the form of suppositories, or in the form of
injection solutions that can optionally also be administered
subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously, or topically or
intrathecally. As adjuvants for the desired pharmaceutical agent
formulation, inert organic and inorganic media that are known to
one skilled in the art, such as, e.g., water, gelatin, gum
arabic, lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, talc, vegetable
oils, polyalkyleneglycols, etc., are suitable. Moreover,
preservatives, stabilizers, wetting agents, emulsifiers or salts
can optionally be contained to alter the osmotic pressure or
buffer.
'fhe pharmaceutical preparations can be present in solid
form, e.g., as tablets, coated tablets, suppositories, capsules
or in liquid form, e.g., as solutions, suspensions or emulsions.
As vehicle systems, near-interface adjuvants such as salts,
bile acids or animal or plant phospholipids and mixtures thereof
as well as liposomes or their components can also be used.
For oral administration, especially tablets, coated tablets
or capsules with talc and/or hydrocarbon vehicles or binders,
such as, e.g., lactose, corn or potato starch, are especially
suitable. Administration can also be done in liquid form, such
as, e.g., in the form of juice, to which sweetener is optionally
added.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
The compounds of formula I are used in dosages that are
sufficient to reduce the TNF production to normal levels or
below.
The dosage of the active ingredients can vary depending on
the method of administration, the age and weight of the patient,
the type and severity of the disease to be treated and similar
factors. The daily dose is 0.1-25 mg, preferably 0.5-5 mg,
whereby the dose can be given as a single dose to be administered
one time or divided into two or more daily doses.
In so far as the production of the starting compounds is not
described, the latter are known from the above-mentioned
publications or can be produced analogously to the known
compounds or processes that are described here.
The following examples are to explain the process according
to the invention.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
11
starting compounds:
(R,8)-2-(3-Cyclopentyloxy-4-Bnethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-
propylam3.ne
16.9 g of 3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxy-acetophenone is
dissolved in 12.5 ml of trimethylsilyl cyanide while being
heated. After 700 mg of zinc iodide is added, a strong heat
tonality occurs; then it is cooled to 20°C and stirred for 30
minutes under nitrogen. The reaction mixture is mixed with 100
ml of tetrahydrofuran and added in drops within 20 minutes to a
solution of 4.4 g of lithium alanate in 100 ml of
tetrahydrofuran. After another 30 minutes, 100 ml of a saturated
potassium sodium tartrate solution is carefully added. A pulpy
material is formed, from which the tetrahydrofuran phase can be
decanted. The pulpy residue is extracted seven times with 100 ml
of diethyl ether each, the extracts are concentrated by
evaporation in a vacuum together with the tetrahydrofuran phase.
The residue is dissolved in 300 ml of ethyl acetate and extracted
three times with 50 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid each. The
combined acid extracts are set at pH 13 with 4N sodium hydroxide
solution and extracted six times with 100 ml of diethyl ether
each. The ether extracts are dried on sodium sulfate and
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. 16.4 g of (R,S)-2-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine with a
melting point of 82°C is obtained as a residue.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
12
(R,s)-5-(3-Cyalopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone
A solution of 16.4 g of (R,S)-2-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine in 150 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 10.2 g of N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole
and stirred for 3 hours at room temperature. The reaction
mixture is concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum, the residue
is dissolved in 500 ml of ethyl acetate, and the solution is
washed twice with 50 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid each and then
with water, dried and concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum.
17.7 g of (R,S)-5-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone is obtained as a residue. Melting point 83.5°C.
(R,s)-2-(4-Methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine
A mixture of 30 g of 4-methoxy-3-propoxy-acetophenone and 25
ml of trimethylsilyl cyanide is mixed with 1.4 g of zinc iodide
and heated for 4 hours to 110°C. After cooling, the reaction
mixture is diluted with 200 ml of tetrahydrofuran, mixed drop by
drop with a suspension of 8.0 g of lithium alanate in 200 ml of
tetrahydrofuran and heated to boiling for one hour. After
cooling to 4°C, it is diluted with 750 ml of diethyl ether, and
the mixture is then carefully mixed with saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution over a period of 45 minutes until solid
aluminum hydroxide separates. The organic phase is separated,
and the remaining inorganic material is washed with 1000 ml of
diethyl ether. The combined organic phases are concentrated by
evaporation in a vacuum, the residue is taken up in
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
13
dichloromethane and extracted four times with 80 ml of aqueous 2N
hydrochloric acid each. The combined acid aqueous phases are
brought to pH 10 with aqueous 5N sodium hydroxide solution, and,
after saturation with sodium chloride, repeatedly extracted with
ethyl acetate. The combined extracts are dried on sodium sulfate
and concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. 25.0 g of (R,S)-2-
(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine with a
melting point of 90°C is obtained as a residue.
(R,8)-5-(4-Methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 24.0 g of (R,S)-
2-(4-Methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine in 260 ml
of tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 19.4 g of N,N'-
carbonyldiimidazole, and then it is stirred for 16 hours at room
temperature. The solvent is evaporated in a vacuum, the residue
is dissolved in 300 ml of ethyl acetate, and the solution is
washed three times with 50 ml of aqueous 1N hydrochloric acid
each. Then, the organic phase is washed with sodium bicarbonate
solution as well as with sodium chloride solution, dried on
sodium sulfate and concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. The
oily residue of 28 g is purified by chromatography on a silica
gel column, with a hexane-ethyl acetate mixture as eluant.
24.5 g of (R,S)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone results. Melting point 71°C.
' CA 02235264 1998-04-17
14
(R,8)-2-(3-Ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine
A mixture of 28 g of 3-ethoxy-4-methoxy-acetophenone and 25
ml of trimethylsilyl cyanide is mixed with 1.4 g of zinc iodide
and heated for 4 hours to 100°C. After cooling, the reaction
mixture is diluted with 200 ml of tetrahydrofuran, mixed drop by
drop with a suspension of 8.0 g of lithium alanate in 200 ml of
tetrahydrofuran and heated to boiling for one hour. After
cooling to 4°C, it is diluted with 750 ml of diethyl ether, and
the mixture is then carefully mixed with saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution over a period of 45 minutes until aluminum
hydroxide separates. The organic phase is.separated and the
remaining inorganic material is washed with 1000 ml of diethyl
ether. The combined organic phases are concentrated by
evaporation in a vacuum, the residue is taken up in
dichloromethane and extracted four times with 80 ml of aqueous 2N
hydrochloric acid each. The combined acid aqueous phases are
brought to pH 10 with aqueous 5N sodium hydroxide solution and,
after saturation with sodium chloride, extracted repeatedly with
ethyl acetate. The combined extracts are dried on sodium sulfate
and concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. 26.1 g of (R,S)-2-
(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine with a melting
point of 88°C is obtained as a residue.
(R,s)-5-(3-Ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-osazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 11.2 g of (R,S)-
2-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-propylamine in 130 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 9.7 g of N,N~-carbonyldiimidazole
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
and then stirred for 16 hours at room temperature. The solvent
is evaporated in a vacuum, the residue is dissolved in 200 ml of
ethyl acetate, and the solution is washed twice with 50 ml of
aqueous 1N hydrochloric acid each. Then, the organic phase is
washed with sodium bicarbonate solution and sodium chloride
solution, dried on sodium sulfate and concentrated by evaporation
in a vacuum. The oily residue of 12 g is purified by
chromatography on a silica gel column, with a hexane-ethyl
acetate mixture as eluant. 9.6 g of (R,S)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-
m~thoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone results. Melting point
102°C.
Example 1
Preparation and Separation of Diastereomeric Allophanates
17.7 g of (R,S)-5-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-2-oxazolidinone is dissolved in 240 ml of toluene. After
9 ml of triethylamine and 12.8 g of (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)-ethyl
isocyanate are added, the reaction solution is heated to boiling
for 17 hours under nitrogen and then concentrated by evaporation
in a vacuum. The residue of 31.1 g is chromatographed on a
silica gel column (Kromasil, 10 Vim) with a hexane-diethyl ether
mixture (6:4). 11.5 g of N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone-3-
carboxylic acid amide, melting point 124°C, [a]p = -8° (CHC13),
as
well as 13.5 g of N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(S)-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone-3-
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
16
carboxylic acid amide, in oily form, [a]p = -41° (CHC13), are
eluted.
(R)-(-)-5-(3-Cyclopentylosy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxasolidinone
While being cooled with ice and in a nitrogen atmosphere, a
solution of 11.0 g of N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone-3-
carboxylic acid amide in 230 ml of tetrahydrofuran is mixed with
2.3 g of potassium ethylate, and it is stirred for 30 minutes at
room temperature. After 700 ml of ethyl acetate is added, it is
washed twice with 50 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid each and then
with water, dried and concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum.
The crude product of 12.3 g is chromatographed on a silica gel
column (Kromasil, 10 ~Cm) with an ethyl acetate-hexane mixture
(3:7). 6.68 g is eluted and recrystallized from hexane-
dichloromethane.
Yield: 6.23 g of (R)-(-)-5-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone. Melting point 84°C.
[a]D = -41° (CHC13) .
(8)-t+)-5-(3-Cyclopentyloxy-4-methoayphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone
A solution of 490 mg of N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(S)-5-
(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone-3-
carboxylic acid amide in 10 ml of tetrahydrofuran is mixed in a
nitrogen atmosphere with 90 mg of potassium ethylate and stirred
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
17
for one hour at room temperature. After 50 ml of ethyl acetate
is added, it is washed twice with 10 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid
each and then with water, dried and concentrated by evaporation
in a vacuum. The crude product of 470 mg is chromatographed on a
silica gel column (Kromasil, 10 ~Cm) with an ethyl acetate-hexane
mixture (3:7). 260 mg of crystalline (S)-(+)-5-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone is
eluted. Melting point 80°C. [a]p = +38° (CHC13) .
EBtimple 2
Preparation and Separation of Diastereomeric Allophanates
14.6 g of (R,S)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone is dissolved in 200 ml of toluene. After 7.7 ml of
triethylamine and 10.0 g of (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)-ethyl isocyanate
are added, the reaction solution is heated to boiling for 16
hours under nitrogen. After cooling to room temperature, it is
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum, the residue is dissolved
in ethyl acetate, solid components are filtered out, and the
solution is concentrated in a vacuum. The residue is
chromatographed on a silica gel column (Kromasil, 10 ~Cm) with an
ethyl acetate-hexane mixture (3:7). 10.9 g is eluted. After
recrystallization from ethyl acetate-hexane, 7.0 g of N-[(R)-1-
(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide is obtained. Melting point
106°C. [a]p = -9° (CHC13) . Further, 12.4 g of N-[ (R)-1-(1-
naphthyl)ethyl]-(S)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide is eluted as an oil.
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
18
[a]p = -43° (CHC13) .
(R)-(-)-5-(4-Methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 10.0 g of N-[(R)-
1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-
2-oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide in 200 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 2.3 g of potassium ethylate and
then stirred at room temperature for 1.5 hours. After 400 ml of
ethyl acetate is added, it is washed twice with 50 ml of 2N
hydrochloric acid each and then with water, dried and
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. The crude product of
8.3 g is chromatographed on a silica gel column with a mixture of
ethyl acetate and hexane as eluant. 5.3 g of (R)-(-)-5-(4-
methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, which is
recrystallized from an ethyl acetate-hexane mixture, is obtained.
Yield: 4.5 g. Melting point 93°C. [a]p = -48° (CHC13) .
(8)-(+)-5-(4-Methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 13.8 g of N-[(R)-
1-(1-naphthyl)ethylJ-(S)-5-(4-methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-
2-oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide in 200 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 4.8 g of potassium ethylate and
then stirred at room temperature for 16 hours. After 400 ml of
ethyl acetate is added, it is washed twice with 50 ml of 2N
hydrochloric acid each and then with water, dried and
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. The crude product of
16.5 g is chromatographed on a silica gel column with a mixture
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
19
of ethyl acetate and hexane as eluant. 8.3 g of (S)-(+)-5-(4-
methoxy-3-propoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone is obtained.
After crystallization from hexane-ethyl acetate, 6.4 g remains.
Melting point 94°C. [a]p = +45° (CHC13) .
Example 3
Preparation and Separation of Diastereomeria Allophanates
5.9 g of (R,S)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone is dissolved in 90 ml of toluene. After 3.3 ml of
triethylamine and 4.8 g of (R)-1-(1-raphthyl)-ethyl isocyanate
are added, the reaction solution is heated to boiling for 25
hours under nitrogen. After cooling to room temperature, it is
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum, the residue is dissolved
in ethyl acetate, solid components are filtered out, and the
solution is concentrated in a vacuum. The residue is
chromatographed on a silica gel column (Kromasil, 10 ~,m) with an
ethyl acetate-hexane mixture (3:7). 4.55 g of N-[(R)-1-(1-
naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide is eluted. Melting point
112°C. [a]p = -12° (CHC13) . Further, 4.4 g of N-[ (R)-1-(1-
naphthyl)ethyl]-(S)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide is eluted as an oil.
[cx]p = -39° (CHC13) .
(R)-(-)-5-(3-Ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 7.3 g of N-[(R)-
1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(R)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
CA 02235264 1998-04-17
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide in 100 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 1.8 g of potassium ethylate and
then stirred for 30 minutes at room temperature. After 300 ml of
ethyl acetate is added, it is washed twice with 50 ml of 2N
hydrochloric acid each and then with water, dried and
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. The crude product is
chromatographed on a silica gel column with a mixture of ethyl
acetate and hexane as eluant. 3.8 g of (R)-(-)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone is obtained. After
recrystallization from hexane-ethyl acetate, 3.1 g remains.
Melting point 87°C. [a]p = -51° (CHC13) .
(8)-(+)-5-(3-Ethoxy-~-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone
While being cooled with ice, a solution of 10.1 g of N-[(R)-
1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-(S)-5-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone-3-carboxylic acid amide in 200 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is mixed with 3.6 g of potassium ethylate and
then stirred for 16 hours at room temperature. After 400 ml of
ethyl acetate is added, it is washed twice with 50 ml of 2N
hydrochloric acid each and then with water, dried and
concentrated by evaporation in a vacuum. The crude product of
11.5 g is chromatographed on a silica gel column with a mixture
of ethyl acetate and hexane as eluant. 5.5 g of (S)-(+)-5-(3-
ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone is obtained.
After recrystallization from hexane-ethyl acetate, 4.1 g remains.
Melting point 85°C. [a]p = +49° (CHC13) .
CA 02235264 2005-09-02
Example
Separation o! the diastereomers of (R,8)-5-(3-benzylozy-~-
methozyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oza$olidinone
3 g of (R,S)-5-(3-benzyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone -- produced analogously to (R,S)-5-(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone -- is
chromatographed on a ChirapherTcolumn (25 Vim) in a ProcroniMunit
with a hexane-dioxane mixture. 1.2 g of (S)-(+)-5-(3-benzyloxy-
4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, melting point 116.8°C,
[a]p = +38.9° (CHC13), as well as 1.1 g of (R)-(-)-5-(3-benzyloxy-
4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, melting point 116.7°C,
[a]p = +38 .4° (CHC13) , are eluted.
(R)-(-)-5-(3-Hydrozy-~-mathozyphsnyl)-5-methyl-2-oza$olidinone
1.1 g of (R)-(-)-5-(3-benzyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone is dissolved in 40 ml of ethyl acetate and mixed
with 100 mg of palladium/10% carbon. It is hydrogenated until
hydrogen absorption is completed. After filtration on silica gel
and concentration by evaporation in a vacuum, 750 mg of (R)-(-)-
5-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, melting
point 141.6°C, is obtained. [a]p = -28.2° (CHC13) .
(R)-(-)-5-(3-Cyclobutylozy-~-sethosyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
ozasolidinone
A solution of 80 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-hydroxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone is mixed in 1 ml of
dimethylformamide with 25 mg of sodium hydride (55-65%), and it
' CA 02235264 1998-04-17
22
is stirred for 15 minutes at 60°C. After cooling, 0.04 ml of
bromocyclobutane is added in drops, and it is stirred for 2 hours
at 110°C. The reaction mixture is evaporated to the dry state in
an oil vacuum on a bulb tube. The residue is purified by
chromatography on a silica gel column, with a hexane-ethyl
acetate mixture as eluant. 52 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-cyclobutyloxy-
4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, melting point 132.5°C,
results. [a]o = -38.6° (CHC13) .
Example 5
(R)-(-,-5-(3-Isobutenyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone
A solution of 710 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-hydroxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone in 30 ml of ethanol is
mixed in succession with 658 mg of potassium carbonate and
0.48 ml of methallyl chloride. After 15 hours of stirring, it is
filtered at 70°C, and the solution is concentrated by evaporation
in a vacuum. The oily residue is purified by chromatography on a
silica gel column with a hexane-ethyl acetate mixture as eluant.
620 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-isobutenyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone, in oily form, results. [a]o = -24.3°.
Example 6
(R)-(-)-5-(3-Isobutyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-
oxazolidinone
360 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-isobutenyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-2-oxazolidinone is dissolved in 10 ml of ethyl acetate and
_ ' CA 02235264 1998-04-17
23
mixed with 50 mg of palladium/carbon (10%). It is hydrogenated
until hydrogen absorption is completed. After filtration on
diatomaceous earth and concentration by evaporation in a vacuum,
an oily residue is obtained. The crude product is purified by
chromatography on a silica gel column, with a hexane=acetone
mixture as eluant. 186 mg of (R)-(-)-5-(3-isobutyloxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-2-oxazolidinone, melting point 93.7°C,
results. [aJp = -24.7°.