Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
A-21324/A
-1-
Liguid polyfunctional additives
The present invention relates to novel liquid polyfunctional additives with
low volatility,
to compositions comprising an organic material, preferably a fuel, a polymer
or lubricant,
and the additives mentioned, and to their use for stabilising organic
materials against
oxidative, thermal or light-induced degradation.
The stabilisation, in particular of lubricants or of plastics, with
antioxidants from the series
of the sterically hindered phenols or reaction products thereof with other
compounds is
known, for example, from US-A-3 839 278, US-A-4 032 562, US-A-4 058 502,
US-A-4 093 587, US-A-4 132 702, US-A-5 478 875 and EP-A-O 644 195.
WO 91/13134 describes a method for improving the solubility of antioxidants in
a second
medium.
The present invention relates to a product which can be obtained by reacting
components
a), b), c) and d), where component a) is a compound of the formula I or a
mixture of
compounds of the formula I, component b) is a compound of the formula II or a
mixture of
compounds of the formula II, component c) is a compound of the formula III or
a mixture
of compounds of the formula III and component d) is a compound of the formula
IV or a
mixture of compounds of the formula IV,
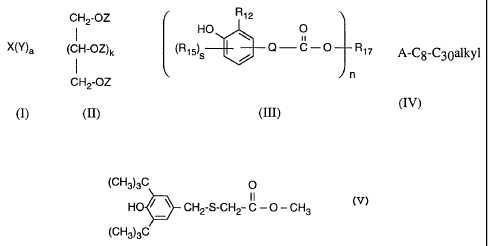
CH2-OZ R 12
I HO 0 11
X(Y)a (CH-OZ)k (Rt5)S / Q-C-O R17 A-Cg-C30alkyl
n
CH2-OZ
(I) (II) (III) (IV)
in which, in the compound of the formula I,
Y independently of one another is OH, (HOCH2CH2)2N- or -HNR1 and
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-2-
CH3 CH3
R1 is hydrogen, C1-Clgalkyl, C5-C12cycloalkyl, R2- N , C3-C6alkenyl,
CH3 CH3
C7-C9Phenylalkyl, phenyl, or phenyl which is substituted by 1 to 3 radicals
Ai, the
radicals A1 independently of one another being C1-C12alkyl, halogen, hydroxyl,
methoxy
or ethoxy, in which
R2 is hydrogen, C1-C8alkyl, O, OH, NO, -CH2CN, Cl-Clgalkoxy, CS-
C12cycloalkoxy,
C3-C6alkenyl, C7-C9phenylalkyl or C7-C9phenylalkyl which is mono-, di- or
trisubstituted
on the phenyl ring by C1-C4alkyl, or R2 is furthermore Cl-Cgacyl or HOCH2CH2-,
and
a is the number 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6, where,
if Y is OH and a is 1,
CH3
CH3
X is Cl-C45alkyl, C3-C18alkenyl, -CH2CH2T1(CH2CH2O)bR4 or R2- N , in
CH3 CH3
which R2 is as defined above, and
\
Ti is oxygen, sulfur or N - R5,
R4 is Cl-C20alkyl,
b is an integer ranging from 0 to 10 and
R5 is hydrogen, C1-Clgalkyl or phenyl, or,
if Y is OH and a is 2,
X is -CH2CH2T2(CH2CH2O)bCH2CH2-, in which b is as defined above,
R CH3 CH3
~ 6
-CH2CH2- N\ , -CCH2c , -CH2CH2 - N CH3 CHg
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-3-
CH3 CH3
C;H3 CH3
N (CH2)~ N , -CH2-CH=CH-CH2 - ,
CH3 3 CH3
CH3
O O
-CH2CH2-NH - C - C - NH-CH2CH2- or
CH3
I
-CH2CH20 C OCH2CH2- , in which
CH3
R7
T2 is oxygen, sulfur, N - R5 or - S C - S - and R5 is as defined above,
R8
R6 is hydrogen, Cl-C18alkyl or phenyl,
c is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
d is an integer ranging from 2 to 6 and
R7 and R8 independently of one another are hydrogen, Cl-Clgalkyl or phenyl, or
R7 and R8
together with the C atom to which they are bonded form a C5-C12cycloalkylidene
ring, or,
if a is 3,
X is C3-Cloalkanetriyl or N(CH2CH2-)3, or,
if Y is OH and a is 4,
X is C4-Cloalkanetetrayl, (-CH2-CH-CH2)20,
-CH2 0 0 CH2- - CH2 _CH2
-CH2-CH-CH2-0-CH CH2- ,R9--NH-C-C-NH--R9 , -CH O or O
~\CH2 -CH2 JH2-
in which
Rq is Ci-C4alkyl, or,
if Y is OH and a is 6,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-4-
-CH2 CH2- -CH2 0 0 CH2-
I I 1 1111 1
X is -CH2-i-CH2-O-CH2-i-CH2- , -CH2-i-NH-C-C-NH-C-CH2- or C6-Cloalkanehexayl,
or,
-CH2 CH2- -CH2 CH2-
if Y is HNRI and a is 1,
X is Cl-Clgalkyl, C3-C18alkenyl, CS-C12cycloalkyl, C7-Cqphenylalkyl, phenyl,
CH3
CH3 Rlo
R2- N , in which R2 is as defined above or X is furthermore CN-(CH2)e_
CH3 CH3
or X together with Rl is a group of the formula -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- or
-CH2CH2OCH2CH2-, in which
Rlo is hydrogen or methyl and
e is 2 or 3, or,
if Y is -HNR1 and a is 2,
~ H
I
X is -CfH2f-, / ,-(CH2CHZN 9 CH2CH2- or -(CH2)6-NH-(CH2)6-, in which
f is an integer ranging from 2 to 10 and
g is an integer ranging from 1 to 6, and,
in the compound of the formula II,
O
Z is hydrogen or a group of the formula -(ChH2h0); C-Rjj and
k is an integer ranging from 0 to 6, in which
his2or3,
i is an integer ranging from 0 to 12 and
R11 is C8-C30alkyl, C8-C30alkenyl which may be straight-chain or branched and
whose
chain(s) may have not more than three double bonds at any desired point on
said chain(s),
C8-C30hydroxyalkyl or C8-C30hydroxyalkenyl, whose alk(en)yl chain may be
straight-chain or branched and whose chain(s) may have at least one hydroxyl
function at
any desired point on said chain(s), with the proviso that the compound of the
formula II
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-5-
O
has a ou 11
gT P -(ChH2h0)j-C-R11 ;
in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is C1-Clgalkyl, CS-C12cycloalkyl, phenyl or C7-C9Phenylalkyl,
R15 is hydrogen, C1-C18alkyl, C5-C12cycloalkyl, phenyl or C7-C9Phenylalkyl,
s is 0, 1 or 2,
R15
-CH CH- H ~_~ C - CH2-
Q is -CmH2m , 2- ~ ,-CH2-S-(CH2)t or H3C CH , in which R15 is
3
R16 C~CH
H3C 3
as defined above,
m is an integer ranging from 0 to 3,
R16 is C1-Cgalkyl,
t is 1 or 2, and
n is an integer ranging from 1 to 6, where,
if n is 1,
R17 is hydrogen, C1-C45alkyl, C5-C12cycloalkyl, C2-C18alkenyl, a monovalent
radical of a
CH2OH CH3 CH3
hexose, a monovalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-C-CH2OH , R2 - N , in which
CH2OH CH3 CH3
R2 is as defined above, or furthermore R17 is -CH2CH2-T3-Rlq or
(CH2)PO CH2)POR19, in which
q
T3 is oxygen, sulfur or N - R22
R12
R23R240 ~
Rlq is -CH-CH-C-O-R25 or - CH2 _ OH in which R12 and R15 are as defined
R15
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-6-
above, or R19 is furthermore hydrogen, Cl-C24alkyl, phenyl, C5-C12cycloalkyl
or
0
-CH2-C-O-R25 , in which
p is an integer ranging from 2 to 4,
q is an integer ranging from 2 to 20,
R22 is C1-Clgalkyl, phenyl or phenyl which is substituted by 1 to 3 radicals
A1, in which
the radicals A1 independently of one another are Cl-C12alkyl, halogen,
hydroxyl, methoxy
or ethoxy, or R22 is furthermore C5-C8cycloalkyl,
R23 and R24 independently of one another are hydrogen or methyl, with the
proviso that
R23 and R24 are not simultaneously methyl;
R25 is hydrogen or Cl-C24alkyl, or,
if n is 2,
-CH2
I
R17 is a divalent radical of a hexose, a divalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-i-
CH2OH ,
CH2OH
R18
C ~~-, -CrH2r ,~(CH2)PO CH2)P- , in which p and q are as
R~ q
defined above,
CH3 CH3
-CH2CH2-T4-CH2CH2-, -CH2-CH=CH-CH2-, -CH2-C=C-CH2- , - CH2CH2- N ~
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3 CHs CH3
N - CH2 CH= CH- CH2- N , N-(CH2)4 N D C CH3 CH3 CH3 C 3H3 CH3 CH3
00 O
Il 11
-CH2-CH2-NH-C-C-NH-CH2-CH2- or , in which
O
R18 and R20 independently of one another are hydrogen or Cl-C12alkyl or
together are the
radical -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2-,
r is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-7-
R7
T4 is sulfur, N - R26 or - S C - S - , in which R7 and R8 are as defined
above, and
R8
R26 is hydrogen, C1-Clgalkyl, phenyl or phenyl which is substituted by 1 to 3
radicals A1,
in which the radicals A1 are as defined above in formula I, or R26 is
furthermore
CH3
CH3
C5-Cgcycloalkyl or R2' N , in which R2 is as defined above, or,
CH3 CH3
if n is 3,
CH2CH2-
R17 is a trivalent radical of a hexose, a trivalent radical of a hexitol,
_CH2CH2 N CH2CH2-
~ -CH2
CH2-CH-CH3 I
I or -CH2-C-R27 , in which
CH3-CH-CH2-N-CH2-CH-CH3 (
I I -CH2
R27 is hydrogen, -CH2OH, Cl-C4alkyl, Cl-Clgalkylamido or
O R12
1)
-HN - C- Q OH , in which Q, R12 and R15 are as defined above, or,
R15
if n is 4,
R17 is a tetravalent radical of a hexose, a tetravalent radical of a hexitol,
I I - CH2
CH3-CH-CH2 CH2-CH-CH3 -CH O
C4-Cloalkanetetrayl, ~N-CH2CH2-N or
CH3-CH-CH2 ~CH2-CH-CH3
_CH2
or,
r 0
CH2
if n is 5,
R17 is a pentavalent radical of a hexose or a pentavalent radical of a
hexitol, or,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-g-
ifnis6,
-CH2 CH2-
I I
R17 is a hexavalent radical of a hexitol or -CH2-i-CH2-0-CH2-i-CH2- , and
-CH2 CH2-
in the compound of the formula IV,
A is hydrogen, C1-C4alkyl or phenyl.
The liquid products of the present invention, which have low volatility, are
distinguished
by a very good stabilisation of organic materials, for example fuels, polymers
or oils, and
against oxidative, thermal and light-induced degradation.
Alkyl having not more than 45 C atoms is a branched or unbranched radical such
as, for
example, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, isobutyl, tert-
butyl,
2-ethylbutyl, n-pentyl, isopentyl, 1-methylpentyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl, n-hexyl,
1-methylhexyl, n-heptyl, isoheptyl, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl, 1-methylheptyl,
3-methylheptyl, n-octyl, 2-ethylhexyl, 1,1,3-trimethylhexyl, 1,1,3,3-
tetramethylpentyl,
nonyl, decyl, undecyl, 1-methylundecyl, dodecyl, 1,1,3,3,5,5-hexamethylhexyl,
tridecyl,
tetradecyl, pentadecyl, hexadecyl, heptadecyl, octadecyl, eicosyl, docosyl or
pentacosyl.
One of the preferred meanings of Rl, R4 and R16 is, for example, Cl-C4alkyl,
of R2
methyl, of Rll Cl-C20alkyl, of R12 and R15 C1-C4alkyl, in particular tert-
butyl, and of R17
Cl-Clgalkyl.
Cycloalkyl having not more than 12 C atoms is, for example, cyclopentyl,
cyclohexyl,
cycloheptyl, cyclooctyl, cyclodecyl or cyclododecyl. One of the preferred
meanings of Rl,
R11, R12 and R15 is CS-C7cycloalkyl. Cyclohexyl is particularly preferred.
C5-C12Cycloalkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted by C1-C4alkyl is, for
example,
cyclopentyl, methylcyclopentyl, dimethylcyclopentyl, cyclohexyl,
methylcyclohexyl,
dimethylcyclohexyl, trimethylcyclohexyl, tert-butylcyclohexyl, cycloheptyl or
cyclooctyl.
C5-CgCycloalkyl is preferred, in particular cyclohexyl and tert-
butylcyclohexyl.
Alkenyl having not more than 30 C atoms is, for example, vinyl, propenyl,
isopropenyl,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-9-
2-butenyl, 3-butenyl, isobutenyl, n-penta-2,4-dienyl, 3-methylbut-2-enyl, n-
oct-2-enyl,
n-dodec-2-enyl, iso-dodecenyl, oleyl, n-octadec-2-enyl or n-octadec-4-enyl. If
R1, R2 and
X are C3-C6alkenyl, then the C atom which is bonded to the nitrogen is
advantageously
saturated.
Hydroxyl-substituted C8-C30alkyl is a branched or unbranched radical
containing
preferably 1 to 3, especially 1 or 2 OH groups, for example 8-hydroxyoctyl,
7-hydroxyoctyl, 6-hydroxyoctyl, 5-hydroxyoctyl, 4-hydroxyoctyl, 3-
hydroxyoctyl,
2-hydroxyoctyl, 9-hydroxynonyl, 10-hydroxydecyl, 11-hydroxyundecyl,
12-hydroxydodecyl, 13-hydroxytridecyl, 14-hydroxytetradecyl, 15-
hydroxypentadecyl,
16-hydroxyhexadecyl, 17-hydroxyheptadecyl, 18-hydroxyoctadecyl, 20-
hydroxyeicosyl or
22-hydroxydocosyl. A preferred definition of R11 is hydroxyl-substituted C8-
C20alkyl,
especially hydroxyl-substituted C8-C12alkyl.
Hydroxyl-substituted C8-C30alkenyl is a branched or unbranched radical
containing
preferably 1 to 3, especially 1 or 2 OH groups, for example 8-hydroxyocten-2-
yl,
7-hydroxyocten-2-yl, 6-hydroxyocten-2-yl, 5-hydroxyocten-2-yl, 4-hydroxyocten-
2-yl,
3-hydroxyocten-4-yl, 2-hydroxyocten-4-yl, 9-hydroxynonen-2-yl, 10-hydroxydecen-
2-yl,
11-hydroxyundecen-2-yl, 12-hydroxydodecen-2-yl, 13-hydroxytridecen-2-yl,
14-hydroxytetradecen-2-yl, 15-hydroxypentadecen-2-yl, 16-hydroxyhexadecen-2-
yl,
17-hydroxyheptadecen-2-yl, 18-hydroxyoctadecen-2-yl, 20-hydroxyeicosen-2-yl or
22-hydroxydocosen-2-yl. A preferred definition of R11 is hydroxyl-substituted
C8-C20alkenyl, especially hydroxyl-substituted Cg-C12alkenyl.
Phenylalkyl having 7 to 9 C atoms is, for example, benzyl, a-methylbenzyl,
a,a-dimethylbenzyl or 2-phenylethyl. Benzyl is preferred.
Examples of phenyl which is substituted by 1 to 3 radicals A1 are o-, m- or
p-methylphenyl, 2,3-dimethylphenyl, 2,4-dimethylphenyl, 2,5-dimethylphenyl,
2,6-di-
methylphenyl, 3,4-dimethylphenyl, 3,5-dimethylphenyl, 2-methyl-6-ethylphenyl,
2-methyl-4-tert-butylphenyl, 2-ethylphenyl, 2,6-diethylphenyl, 2,6-diethyl-4-
methyl-
phenyl, 2,6-diisopropylphenyl, 4-tert-butylphenyl, p-nonylphenyl, o-, m- or p-
chloro-
phenyl, 2,3-dichlorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-dichlorophenyl, 2,6-
dichlorophenyl,
3,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,4,5-trichlorophenyl, 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl, o-, m- or p-
hydroxy-
phenyl, o-, m- or p-methoxyphenyl, o- or p-ethoxyphenyl, 2,4-dimethoxyphenyl,
2,5-di-
methoxyphenyl, 2,5-diethoxyphenyl, o-, m- or p-methoxycarbonyl, 2-chloro-6-
methyl-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-10-
phenyl, 3-chloro-2-methylphenyl, 3-chloro-4-methylphenyl, 4-chloro-2-
methylphenyl,
5-chloro-2-methylphenyl, 2,6-dichloro-3-methylphenyl, 2-hydroxy-4-
methylphenyl,
3-hydroxy-4-methylphenyl, 2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl, 4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl,
3-chloro-4- methoxyphenyl, 3-chloro-6-methoxyphenyl, 3-chloro-4,6-
dimethoxyphenyl
and 4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl. Preferred is phenyl which is substituted by
1 or 2, in
particular 1, radical(s) A1, A1 being, in particular, alkyl.
Phenyl which preferably has 1 to 3, in particular 1 or 2, alkyl groups and
which is
substituted by Cl-Clgalkyl is, for example, o-, m- or p-methylphenyl, 2,3-
dimethylphenyl,
2,4-dimethylphenyl, 2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-dimethylphenyl, 3,4-
dimethylphenyl,
3,5-dimethylphenyl, 2-methyl-6-ethylphenyl, 4-tert-butylphenyl, 2-ethylphenyl,
2,6-diethylphenyl, butylphenyl, pentylphenyl, hexylphenyl, heptylphenyl,
octylphenyl,
nonphenyl, decylphenyl, undecylphenyl or dodecylphenyl. Phenyl which is
substituted by
C1-C12alkyl is preferred, in particular phenyl which is substituted by C4-
C8alkyl.
A C5-C12cycloalkylidene ring is, for example, cyclopentylidene,
cyclohexylidene,
cycloheptylidene, cyclooctylidene or cyclononylidene. Cyclohexylidene is
preferred.
Alkoxy having 1 to 18 C atoms is, for example, methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy,
isopropoxy,
n-butoxy, isobutoxy, pentoxy, isopentoxy, hexoxy, heptoxy, octoxy, decyloxy,
tetradecyloxy, hexadecyloxy or octadecyloxy. One of the preferred meanings of
R2 is
C6-C12alkoxy. Heptoxy and octoxy are particularly preferred.
Cycloalkoxy having 5 to 12 C atoms is, for example, cyclopentoxy, cyclohexoxy,
cyclo-
heptoxy, cyclooctoxy, cyclodecyloxy or cyclododecyloxy. One of the preferred
meanings
of R2 is C5-Cgcycloalkoxy. Cyclopentoxy and cyclohexoxy are particularly
preferred.
Examples of C7-Cqphenylalkyl which is mono-, di- or trisubstituted on the
phenyl ring by
C1-C4alkyl are methylbenzyl, dimethylbenzyl, trimethylbenzyl or tert-
butylbenzyl.
Acyl having 1 to 8 C atoms is, for example, formyl, acetyl, propionyl,
butyryl, pentanoyl,
hexanoyl, heptanoyl, octanoyl, benzoyl, acryloyl or crotonyl.
C1-CgAlkanoyl, C3-Cgalkenoyl or benzoyl, in particular acetyl, are preferred.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-11-
Alkanetriyl having 3 to 10 C atoms is, for example, -CH2-CH-CH2- ,-CH2-CH2-CH-
CH2-,
-CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2- , -CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2 -
or -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2- , Glyceryl is preferred.
CH2-
I
Alkanetetrayl having 4 to 10 C atoms is, for example, -CH2- i-CH2-
CH2-
~ C I
--CH2-CH-CH-CH2- ~ -CH2-CH2- H-CH-CH2- , -CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH2-CH2- ,
-CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2- or -CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2
Pentaerythrityl is preferred.
Alkanehexayl having 6 to 10 C atoms is, for example, -CH2-CH-CH-CH-&CH2-
-CH2-CH-CH-CH2-CH-CH-CH2- or -CH2-CH-CH-CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH2-
If R17 with n = 1 to 6 is an n-valent radical of a hexose, then this radical
is derived, for
example, from allose, altrose, glucose, mannose, gulose, idose, galactose or
talose, i.e. to
obtain the corresponding compounds of the formula III, one, two, three, four,
five or six
-OH groups must be replaced by the ester group E- 1,
R12
HO O
(Rt5) O-C -O (E-1)
in which R12, R15, s and Q are as defined above. For example, R17 with n = 5
can be a
group
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-12-
CH2O-
H H O H
-O O_ H
O-
H 0-
If R17 is the n-valent radical of a hexitol, then the corresponding compounds
of the
formula III are obtained by replacing n -OH groups by the abovementioned ester
group
E-1. R17 as a hexavalent radical of a hexitol can be, for example,
I
O
I
-O-CH2-CH-CH-CH-CH-CH2-O- ='This group is derived from D-sorbitol.
0 O O
I I I
Alkylamido having I to 18 C atoms is, for example, CH3-CO-NH-, CH3CH2-CO-NH-,
C6H13-CO-NH- or C18H37-CO-NH-.
means that the phenyl ring can be ortho-, meta- or para-substituted.
The four components a), b), c) and d) can be reacted with each other to give
the products
of the present invention in any desired sequence.
Preferably, the four components a), b), c) and d) are initially introduced and
reacted
simultaneously.
Component d) can, however, also be added to reaction mixtures a) and b), b)
and c) or a)
and c) and the missing fourth component can then be reacted.
A particularly preferred embodiment is the addition of component d) after the
reaction of
the three components a), b) and c).
The reaction is advantageously carried out in the presence of a catalyst.
Suitable catalysts
are Lewis acids or bases.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
- 13-
Examples of suitable basic catalysts are metal hydrides, metal alkylides,
metal arylides,
metal hydroxides, metal alcoholates, metal phenolates, metal amides or metal
carboxylates.
Examples of preferred metal hydrides are lithium hydride, sodium hydride or
potassium
hydride.
Examples of preferred metal alkylides are butyllithium or methyllithium.
An example of a preferred metal arylide is phenyllithium.
Examples of preferred metal hydroxides are lithium hydroxide, sodium
hydroxide,
potassium hydroxide, caesium hydroxide, rubidium hydroxide, magnesium
hydroxide,
calcium hydroxide, barium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide.
An example of a particularly preferred metal hydroxide is potassium hydroxide.
Examples of preferred metal alcoholates are lithium methanolate, sodium
methanolate,
sodium ethanolate, potassium methanolate, potassium ethanolate, sodium
isopropylate or
potassium tert-butylate. These can be employed in the pure state or as a
solution.
An example of a particularly preferred metal alcoholate is lithium
methanolate.
Examples of preferred metal phenolates are sodium phenolate or potassium
phenolate.
Examples of preferred metal amides are sodium amide or lithium amide.
Examples of preferred metal carboxylates are calcium acetate and calcium
salicylate.
An example of a particularly preferred metal carboxylate is superbasic calcium
salicylate.
0
R30 R32 0-8-R34
Examples of suitable Lewis acid catalysts are 0-n-o or
Ra1 R33 O-C-R35
0
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-14-
OR37
(
R360- i i-OR38 , the radicals R30, R31, R32, R33, R34, R35, R36, R37, R38 and
R39 being,
OR39
independently of one another, for example C1-Ctgalkyl or phenyl. C1-CgAlkyl is
preferred.
A particularly preferred Lewis acid catalyst is dibutyltin oxide.
In a two-stage reaction regime it is also possible to employ different
catalysts.
The catalyst is added to components a), b), c) and, if used, d) in an amount,
for example,
of from 0.03 to 20 parts per thousand by weight, preferably in an amount of
from 0.1 to 10
parts per thousand by weight, based on the sum of the weight of components a),
b) and c).
Particular preference is given to the addition of from 1 to 10 parts per
thousand by weight
of SAP -001.
The reaction can also be performed in the presence of a catalyst which is
adsorbed on a
carrier and which comprises as the active material an alkali metal compound of
the
formula VII
MvAn (VII)
where
M is Li, Na, K, Rb or Cs,
v is the valency of An, and
An is a fluoride, hydroxide, phosphate, formate, acetate (generally,
carboxylate)
or -OR40 radical, and R40 is alkyl having 1 to 4 C atoms or a phenolate
radical,
and comprising as carrier an alkaline material which measured in 10% by weight
aqueous
suspension has a pH of greater than 10 and is selected from one or more
substances from
the series of the alkaline earth metal oxides, hydroxides, aluminates or
silicates.
The carrier substances from the series of the alkaline earth metal compounds
mentioned
can be present in hydrated or anhydrous form; the hydrated forms are
preferred.
Judicious supported catalysts are those comprising the oxides, hydroxides,
aluminates or
silicates of the alkaline earth metals Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba or mixtures thereof
as carriers.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
- 15-
Particularly judicious carriers are the compounds MgO, Mg(OH)2, CaO, Ca(OH)2,
BaO,
Ba(OH)2, Ba(OH)2=8H20, calcined dolomite MgO.CaO, calcined and hydrated
dolomite
MgCa(OH)4, calcined barytocalcite BaO=CaO, calcined and hydrated barytocalcite
BaCa(OH)4, spinel MgA12O4, MgAl2O4=nH2O, CaA12O4, CaA12O4=nH2O, hydrocalumite
2Ca(OH)2=Al(OH)3=nH2O, Ca2SiO4, hillebrandite Ca2SiO4=H2O, foskagite and
mixtures
thereof.
Preference is given to CaO, MgO or a mixture of these, produced for example by
burning
dolomite CaCO3=MgCO3, as carrier.
Preferably, the carrier substances are essentially free from iron; in other
words, the content
of iron, including iron in the form of its compounds, should judiciously not
exceed
ppm. Overall, the carrier materials should be of high purity, also with
respect to further
metals, such as copper, lead and other heavy metals, for example. The copper
content
should judiciously be below 10 ppm, as should the content of heavy metals; for
example,
the lead content should be below 10 ppm, and overall (all heavy metals) the
content should
be, for example, below 40 ppm.
Likewise preferably, the carriers are substantially free from carbonate
groups. A carbonate
content of less than 0.1% by weight should judiciously be observed. Oxygen-
transferring
anions, such as Mn04 , Cr04 , AsO43-, N03-, for example, should judiciously be
present at
not more than 100 ppm, judiciously overall at not more than 200 ppm. Active
oxygen
should judiciously not exceed 100 ppm. Strongly acidic anions, examples being
SO42' or
Cl-, should judiciously be present at not more than 500 ppm each and
judiciously overall
at not more than 1000 ppm.
Judicious supported catalysts are those comprising as the active material the
hydroxides or
fluorides of the alkali metals Na, K, Rb or Cs.
Preferred active material is KOH, KF, NaOH, NaF or CsF; KOH or KF is
particularly
preferred.
The proportion of the active material is, for example, from 0.15 to 30% by
weight,
mathematically based on the anhydrous carrier. The percentage relates
mathematically to
the corresponding alkali metal ion alone, i.e. without taking into account the
respective
anion, whereas the figure for the carrier relates to the carrier as a whole.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-16-
Judiciously, from 0.15 to 10% by weight of active material is provided, and,
in a preferred
embodiment, there is from 1 to 10% by weight of active material, based in each
case on
the alkali metal ion and on the anhydrous carrier.
The reaction of components a), b) and c) can be carried out in component d) as
solvent,
examples being Norpar Ex 15 or Exxsol D-110 (from EXXON) or Marlican
(linear
alkylbenzene from HULS AG). The reaction of components a) and b) and c) is
preferably
carried out without solvent. The solvent and component d), for example Norpar
Ex 15 or
Exxsol D-110, is added subsequently.
The reaction temperature lies, for example, between 120 and 250 C. The
reaction is
preferably carried out in a temperature range from 150 to 200 C, particular
preference
being given to the range from 160 C to 190 C.
If components a), b) and c) are not commercially available, they can be
prepared by
known processes or analogously. Possible preparation processes for the
compounds of the
formula III can be found, for example, in the following publications: GB-A-0
996 502,
US-A-3 330 859, US-A-3 944 594, US-A-4 593 057, EP-A-0 154 518 or US-A-3 960
928.
In formula III, s is preferably the number 1 or 2.
The invention also preferably relates to products
in which, in the compound of the formula I,
Y independently of one another is OH, (HOCH2CH2)2N- or -HNRI and
CH3 CH3
R1 is hydrogen, C1-Cloalkyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl, R2' N , C3-C6alkenyl, benzyl
CH3 CH3
or phenyl, in which
R2 is hydrogen, C1-C4alkyl, OH, -CH2CN, C6-C12alkoxy, C5-Cgcycloalkoxy, allyl,
benzyl,
acetyl or HOCH2CH2- and
a is the number 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6, where,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
- 17-
if Y is OH and a is 1,
CH3 CH3
X is Cl-C30alkyl, C3-C18alkenyl, -CH2CH2T1(CH2CH2O)bR4 or R2- N , in
CHg CH3
which R2 is as defined above, and
\
Tl is oxygen, sulfur or N - R5,
R4 is Cl-Cloalkyl,
b is an integer ranging from 0 to 10 and
R5 is hydrogen, C1-Cloalkyl or phenyl, or,
if Y is OH and a is 2,
X is -CH2CH2T2(CH2CH2O)bCH2CH2-, in which b is as defined above,
R CH3 CH3
~s
-CH2CH2- \ , -CCH2c , CH2CH2 - N
CH3 H3
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3
N (CH2) N ~-CH2-CH=CH-CH2- ~
d
CH3 3 CH3 CH3
O O
-CH2CH2-NH - C - C - NH-CH2CH2- or
CH3
I
CH2CH2 C OCH2CH2 ' in which
I
CH3
\ R7
T2 is oxygen, sulfur, N - R5 or - S - C- S- and R5 is as defined above,
R8
R6 is hydrogen, Cl-Cloalkyl or phenyl,
c is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-18-
d is an integer ranging from 2 to 6 and
R7 and R8 independently of one another are hydrogen, Cl-Cloalkyl or phenyl, or
R7 and R8
together with the C atom to which they are bonded form a C5-C7cycloalkyl ring,
or,
if Y is -HNRI and a is 1,
CH3 CH3
X is Cl-Cloalkyl, C3-Clgalkenyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl, benzyl, phenyl, R2 - N , in
CH3 CH3
Rto
which R2 is as defined above, or X is furthermore CN-(CH2)e_ , or X together
with Rl
is a group of the formula -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- or -CH2CH2OCH2CH2-, in which
R10 is hydrogen or methyl and
e is 2 or 3, and,
in the compound of the formula II,
O
Z is hydrogen or a group of the formula -(ChH2h0); C-R1 I and
k is an integer ranging from 0 to 4, in which
his2or3,
i is an integer ranging from 0 to 6 and
R11 is Cg-C20alkyl, C8-C20alkenyl which may be straight-chain or branched and
whose
chain(s) may have not more than three double bonds at any desired point on
said chain(s),
C8-C20hydroxyalkyl or C8-C20hydroxyalkenyl, whose alk(en)yl chain may be
straight-chain or branched and whose chain(s) may have at least one hydroxyl
function at
any desired point on said chain(s), with the proviso that the compound of the
formula II
0
comprises a group -(ChH2hO)r C-R1 1;
in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is C1-C6alkyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl, phenyl or benzyl
R15 is hydrogen, C1-C6alkyl, CS-C7cycloalkyl, phenyl or benzyl,
s is 1 or 2,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-19-
R15
H C - CH2-
Q is -CmH2m ,'CH2- i H' ,-CH2-S-(CH2)~ or H C CH , in which R15
3 , C 3
R1s ~ ~
H3C CH3
is as defined above,
m is an integer ranging from 0 to 3,
R16 is C1-C4alkyl,
t is 1 or 2, and
n is an integer ranging from 1 to 6, where,
if n is 1,
R17 is hydrogen, C1-C30alkyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl, C2-Clgalkenyl, a monovalent
radical of a
CH2OH CH3 CH3
hexose, a monovalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-C-CH2OH , R2- N , in which
I
CH2OH CH3 CH3
R2 is as defined above, or furthermore R17 is -CH2CH2-T3-Rlq or
(CH2)PO CH2)pOR19, in which
q
T3 is oxygen, sulfur or / N- R22
R12
R23R240
~
R19 is ( 1 11 or CH2 OH ~ in which R12 and R15 are as defined
-CH-CH-C-O-R25
R15
above, or R19 is furthermore hydrogen, Cl-C18alkyl, phenyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl or
0
-CH2-C-O-R25 , in which
p is an integer ranging from 2 to 4,
q is an integer ranging from 2 to 20,
R22 is C1-Cloalkyl, phenyl or C5-Cgcycloalkyl,
R23 and R24 independently of one another are hydrogen or methyl with the
proviso that
R23 and R24 are not simultaneously methyl;
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-20-
R25 is hydrogen or Cl-Clgalkyl, or,
if n is 2,
-CH2
I
R17 is a divalent radical of a hexose, a divalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-i-
CH2OH ,
CH2OH
R1$
i
C -CrH2r , f (CH2)POCH2)p , in which p and q are as
RZp 4
defined above, -CH2CH2-T4-CH2CH2-, -CH2-CH=CH-CH2-,
CH3 CH3
-CH2-C=C-CH2- , - CH2CH2- N ~
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
N - CH2 CH= CH- CH2- N N-(CH2)4 N ~
C CH3 CH3 CH3 C 3H3 CH3 CH3
00 O
-CH2-CH2-NH-C -C-NH-CH2-CH2- or , in which
O
R18 and R20 independently of one another are hydrogen or Cl-C6alkyl or
together are the
radical -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2-,
r is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
~ R7
T4 is sulfur, N- R26 or - S- C- S-, in which R7 and R8 areas defined above and
R8
CH3 CH3
R26 is hydrogen, C1-Cloalkyl, phenyl, C5-Cgcycloalkyl or R2 - N in which R2
CH3 CH3
is as defined above.
The invention particularly preferably relates to products
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-21-
in which, in the compound of the formula I,
Y independently of one another is OH, (HOCH2CH2)2N- or -HNR1 and
CH3 CH3
Rl is hydrogen, C1-C4alkyl or R2 - N , in which
CH3 CH3
R2 is hydrogen, C1-C4alkyl, OH, allyl, benzyl, acetyl or HOCH2CH2- and
a is the number 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6, where,
if Y is OH and a is 1,
CH3 CH3
X is Cl-Clgalkyl, C3-C18alkenyl, -CH2CH2T1(CH2CH2O)bR4 or R2- N , in
CH3 CH3
which R2 is as defined above, and
Tl is oxygen,
R4 is Cl-C4alkyl and
b is an integer ranging from 0 to 10, or,
if Y is OH and a is 2,
X is -CH2CH2T2(CH2CH2O)bCH2CH2-, in which b is as defined above, or
furthermore X
CH3 CH3
is -CCH2c , -CH2CH2 - N or -CH2-CH=CH-CH2- , in which
CH3 CH3
~
T2 is oxygen, sulfur or / N - R5,
R5 is hydrogen,
b is the number 0 or 1 and
c is an integer ranging from 2 to 8, or,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-2.2-
ifais3,
X is -CH2-CH-CH2- or N(CH2CH2-)3, or,
if Y is OH and a is 4,
CH2-
I I I CH2-
X is -CH2- i-CH2- , (-CH2-CH-CH2)20 or -CH2-CH-CH2-O-CH-CH2- , or,
CH2-
ifYisOHandais6,
-CH2 CH2-
I I I I I
X is -CH2-i-CH2-O-CH2-i-CH2- or -CH2-CH CH-CH- H-CH2- , or,
-CH2 CH2-
if Y is -HNRi and a is 1,
CH3 CH3
X is Cl-Cloalkyl, C3-C18alkenyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl or R2- N , where R2 is as
CH3 CH3
defined above, or,
if Y is -HNRI and a is 2,
X is -CfH2f- in which
f is an integer ranging from 2 to 10 and,
in the compound of the formula II,
0
II
Z is hydrogen or a group of the formula -(CnH2h0); C-RIj and
kis 1,2or3,
his2or3,
i is an integer ranging from 0 to 4 and
R11 is Cg-C20alkyl, C8-C20alkenyl which may be straight-chain or branched and
whose
chain(s) may have not more than three double bonds at any desired point on
said chain(s),
C8-C20hydroxyalkyl or C8-C20hydroxyalkenyl, whose alk(en)yl chain may be
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-23-
straight-chain or branched and whose chain(s) may have at least one hydroxyl
function at
any desired point on said chain(s), with the proviso that the compound of the
formula II
0
II
comprises a group -(ChH2h0);-C-Rj 1 ;
in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is C1-C6alkyl or CS-C7cycloalkyl,
R15 is hydrogen, C1-C6alkyl or C5-C7cycloalkyl,
s is 1 or 2,
Q is -CmH2m or -CH2- i H-
R1s
m is an integer ranging from 0 to 3,
R16 is C1-C4alkyl and
n is an integer ranging from 1 to 6, where,
if n is 1,
R17 is hydrogen, C1-C18alkyl, C5-C7cycloalkyl, C2-Clgalkenyl, a monovalent
radical of a
CH2OH CH3 CH3
hexose, a monovalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-G-CH20H or R2' N in which
I
CH2OH CH3 CH3
R2 is as defined above,
or furthermore R17 is (CH2)p0 CH2)POR19 in which
q
Rlq is hydrogen, C1-Clgalkyl or C5-C7cycloalkyl, in which
p is an integer ranging from 2 to 4,
q is an integer ranging from 2 to 10, or,
if n is 2,
-CH2
I
R17 is a divalent radical of a hexose, a divalent radical of a hexitol, -CH2-i-
CH2OH ,
CH2OH
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-24-
-GH2r , f(CH2)POCH2)P- , in which p and q are as defined above,
CH3 CH3 CH3
-CH2CH2-T4-CH2CH2-, or - CH2CH2- N , in which
CH3 CH3
r is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
\
T4 is sulfur or / N - R26 and
R26 is hydrogen, C1-Cloalkyl or CS-Cgcycloalkyl, or,
ifnis3,
CH2CH2-
R17 is a trivalent radical of a hexose, a trivalent radical of a hexitol,
_CH2CH2-N-CH2CH2-
CH2-CH-CH3
or I , or,
CH3- i H-CH2-N-CH2- C H-CH3
if n is 4,
-'H2
R17 is a tetravalent radical of a hexose, a tetravalent radical of a hexitol, -
CH2- C-CH2- or
-CH2
I I
CH3-CH-CH2 CH2 CH-CH3
N-CH2CH2-N \ .
CH3- i H-CH2 CH2-CH-CH3
The invention furthermore preferably relates to products
in which, in the compound of the formula I,
Y independently of one another is hydroxyl or -NH2 and
a is an integer ranging from 1 to 4, where,
if a is 1,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-25-
CH3 CH3
X is R2- N and
CH3 CH3
R2 is hydrogen, methyl or HOCH2CH2-, or,
if Y is OH and a is 2,
CH3 CH3
X is -CH2CH2T2(CH2CH2O)bCH2CH2-, -CcH2c or CH2CH2 - N
CH3 H3
in which
\
T2 is oxygen, sulfur or / N- R5 ,
R5 is hydrogen,
b is the number 0 or 1 and
c is the number 2, 3 or 4, or,
if Y is OH and a is 3,
X is -CH2-CH-CH2- , or,
if Y is OH and a is 4,
CH2
I
X is -CH2- i -CH2- and,
CH2-
in the compound of the formula II,
O
Z is hydrogen or a group of the formula -C-R,
k is the number 1 and
R11 is C8-C20alkyl, C8-C20alkenyl which may be straight-chain or branched and
whose
chain(s) may have not more than three double bonds at any desired point on
said chain(s),
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-26-
Cg-C20hydroxyalkyl or C8-C20hydroxyalkenyl, whose alk(en)yl chain may be
straight-chain or branched and whose chain(s) may have at least one hydroxyl
function at
any desired point on said chain(s), with the proviso that the compound of the
formula II
O
comprises a group -~-Rand,
in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is tert-butyl,
R15 is C1-C4alkyl and is bonded in the ortho-position relative to the OH
group,
s is the number 1,
Q is -CmH2m and is bonded in the para-position relative to the OH group, where
m is the number 2,
n is 1 and
R17 is Cl-C4alkyl.
The invention furthermore preferably relates to products
in which, in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is C1-C4alkyl or cyclohexyl,
R15 is C1-C4alkyl or cyclohexyl and is bonded in the ortho-position relative
to the OH
group,
s is the number 1,
Q is -CmH2m- and is bonded in the para-position relative to the OH group,
where
m is an integer ranging from 0 to 3 and
n is an integer ranging from 1 to 4, where,
if n is 1,
CH2OH
R17 is hydrogen, Cl-Cloalkyl, cyclohexyl, C2-Clgalkenyl or -CH2-C-CH2OH , or,
CH2OH
ifnis2,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-27-
-CH2
R17 is -CH2-C-CH2OH , -CrH 2r , fCH2)PoCH2)P or -CH2CH2-T4-CH2CH2- in
I CH2OH q
which
p is an integer ranging from 2 to 4,
q is an integer ranging from 2 to 10,
r is an integer ranging from 2 to 6,
\
T4 is sulfur or / N - R26 and
R26 is hydrogen or Cl-C4alkyl, or,
if n is 3,
CH2CH2-
CH2-CH-CH3
R17 is I -CH2CH2-N-CH2CH2- or CH3-CH-CH2-N-CH2- i H-CH3 or,
if n is 4,
~ H2 CH3-CH-CH2 CH2-CH-CH3
R17 is -CH2-C-CH2- or \ N-CH2CH2-N /
-CH2 CH3-CH-CH2 H-CH2 \ CH2-CH-CH3
The invention furthermore particularly preferably relates to products
in which, in the compound of the formula III,
R12 is tert-butyl,
R15 is C1-C4alkyl and is bonded in the ortho-position relative to the OH
group,
s is the number 1,
Q is -CmH2m and is bonded in the para-position relative to the OH group, where
n is the number 2 and
n is an integer 1, 2 or 4, where,
if n is 1,
R17 is C1-C4alkyl, or,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-28-
ifnis2,
R17 is f(cH2)0]cH2)or -CH2CH2-T4-CH2CH2- , in which
q
p is the number 2,
q is the number 2 and
T4 is sulfur, or,
if n is 4,
-CH2
I
R17 is -CH2-C-CH2-
-CH2
Examples of preferred compounds of the formula I are pentaerythritol,
thiodiethylene
glycol, 1,4-butanediol, 1,2-propanediol, diethylene glycol, triethylene
glycol,
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
diethanolamine, glycerol, HOCH2CH2 - N OH ~ HN OH or
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3
HN NH2
CH3 CH3
Glycerol is particularly preferred.
Preferred compounds of the formula II are naturally occurring vegetable oils,
fats and
waxes, animal oils and fats as well as artificial polyol derivatives.
Preferred vegetable oils, fats and waxes are, for example, coconut fat,
rapeseed oil,
sunflower oil, soya oil, castor oil, maize germ oil, safflower oil, olive oil,
groundnut oil,
cottonseed oil, sesame seed oil, tallow oil, pumpkin seed oil or linseed oil.
Preferred animal oils and fats are, for example, butter fat, lard, fish oil,
sperm oil, neat's
foot oil or train oils.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-29-
Examples of preferred artificial polyol derivatives are Radiamuls (glycerol
tri C8/C10) or
sorbitan derivatives. The sorbitan derivatives are commercially available, for
example,
under the names Span 20, Span 40, Span 60, Span 65, Span 80, Span 85,
Tween 20, Tween 40, Tween 60, Tween 65, Tween 80 or Tween 85.
Coconut fat, rapeseed oil, sunflower oil or castor oil are particularly
preferred, coconut fat
is very particularly preferred.
Preferred compounds of the formula III are
(CH3)3C 0 (CH3)3C
O
H CH2-CH2- C- O- CH3 , H CH2CH2-C-O-CH2 C
(CH3)3C (CH3)3C 4
(CH3)3C O
H CH2-CH2 ~C-O-CH2-CH2-O-CH
(CH3)3C 2
(CH3)3C 0 (CH3)3C 0
11 11
H CH2-CH2-C-O-C18H37, H CH2-S-CH2-C-O-CH3 ,
(CH3)3C (CH3)3C
(CH3)3C
O
11
H CH2-CH2-C-O-CH2-CH2 S,
(CH3)3C 2
(CH3)3C 0
H~3 CH2-CH2- d - O- isoCt8H37 ,
(CH3j3C
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-30-
OH
C(CH3)3
(CH3)3C
H H2-CH2-C-O-CH2 CH2 or H3C CH2 O CH2
O
(CHAC 2
C(CHA
OH
2
Particularly preferred compounds of the formula III are methyl 3-(3',5'-di-
tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate and methyl 3-(3'-tert-butyl-4'-hydroxy-5'-
methylphenyl)-
propionate.
Particularly preferred compounds of the formula IV are alkanes having 12 to 18
carbon
atoms and/or C9-C13alkylbenzene.
In a specifically preferred manner, the invention relates to products which
can be obtained
by reacting components a), b), c) and d), the component a) being a compound of
the
formula I, in particular pentaerythritol, thiodiethylene glycol, 1,4-
butanediol,
1,2-propanediol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, diethanolamine or
glycerol, or a
mixture of these, component b) is a compound of the formula II, in particular
coconut fat,
rapeseed oil, sunflower oil, soya oil or castor oil or a mixture of these,
component c) is a
compound of the formula III, in particular methyl
3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-hydroxyphenyl)propionate, methyl
3-(3'-tert-butyl-4'-hydroxy-5'-methylphenyl)propionate or
(CH3)3C O
11
HCH2-S-CH2- C - O- CH3 or a mixture of these, and component d) is a
(CH3)3C
compound of the formula IV, in particular C9-C13alkylbenzene or an alkane
having 12 to
20 carbon atoms or a mixture of these.
Components a), b), c) and d) are expediently present in a molar quantitative
ratio of
0.1:1:0.1:0.1 to 15:1:30:10. A molar quantitative ratio of 1:1:1:0.5 to
10:1:20:10 is
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-31-
preferred. A molar quantitative ratio of 1:1:2:2 to 10:1:10:10 is particularly
preferred.
The products according to the invention can comprise, for example, 5 to 95 %
by weight,
preferably 30 to 80 % by weight, in particular 50 to 80 % by weight, of the
active group
E-2
R12
HO O
(R15) Q-C- (E-2).
s
Particularly judicious products are those obtainable by reacting components a)
and b) with
methyl 3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-hydroxy-phenyl)propionate and with a C12-
Clgalkane.
This invention additionally relates to a product obtainable by reacting
components a), b),
e) and f), where components a) and b) are defined as described above and e)
corresponds
to one or more compounds of the formula V
R12
HO
Nz:~ (V)
(R15)
and f) corresponds to one or more compounds of the formula VI
0
II
H2C-C-C-O-R28 (VI)
(
RX
in which R28 is hydrogen or Cl-Clgalkyl and RX is hydrogen or methyl and R12,
R15 and s
are defined as described above.
Particular preference is given to products in which R28 is C1-C4alkyl,
especially methyl.
Preference is also given to products where in addition the above-described
component d)
of the formula N is added.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-32-
Very particular preference is given to products where component e) of the
formula V is
2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and component f) of the formula VI is methyl acrylate.
This reaction takes place with particular advantage with the aid of potassium
hydroxide
(30% strength solution) at from 80 to 150 C, in particular from 100 to 120 C.
Within this
temperature range the sterically hindered phenol is reacted with a small molar
excess of
unsaturated alkyl ester in, for example, a one-hour reaction and, following
the removal of
the excess ester by distillation the product is reacted with, for example,
coconut fat and
glycerol in the course, for example, of five hours at, for example, 190 C. If
desired, the
reaction is performed under vacuum or under an inert gas atmosphere. Lithium
methanolate, for example, is preferably employed as catalyst. However, it is
also possible
for the originally employed potassium hydroxide solution to catalyse the
reaction.
Preferably, components e) and f) are first of all reacted with one another and
then with
components a) and b) and, if used, d) are reacted in any desired sequence, the
process
conditions corresponding accordingly to those mentioned above.
The present invention also relates to products obtainable by reacting
components a), b)
and c), all three components being initially introduced and reacted
simultaneously.
Catalysts, proportions and reaction conditions correspond, accordingly, to
those indicated
above for the first subject of the invention.
As already mentioned, the products according to the invention are suitable
above all for
stabilising organic materials against oxidative, thermal or light-induced
degradation.
Particular mention is made of their outstanding action as antioxidants in the
stabilisation
of organic materials.
Examples of such materials are:
1. Polymers of monoolefins and diolefins, for example polypropylene,
polyisobutylene,
polybut-l-ene, poly-4-methylpent-l-ene, polyisoprene or polybutadiene, and
polymers of
cycloolefins, for example of cyclopentene or norbomene; furthermore
polyethylene
(which optionally can be crosslinked), for example high density polyethylene
(HDPE),
high density polyethylene of high molecular weight (HDPE-HMW), high density
polyethylene of ultrahigh molecular weight (HDPE-UHMW), medium density
polyethylene (MDPE), low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density
polyethylene
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-33-
(LLDPE), (BLDPE) and (ULDPE).
Polyolefins, i.e. polymers of monoolefins exemplified in the preceding
paragraph, in
particular polyethylene and polypropylene, can be prepared by different, and
especially by
the following, methods:
a) by means of free radicals (norrnally under high pressure and at elevated
temperature).
b) by means of a catalyst, the catalyst normally containing one or more metals
of
group IVb, Vb, VIb or VIII of the Periodic Table. These metals usually have
one or more ligands, such as oxides, halides, alcoholates, esters, ethers,
amines,
alkyls, alkenyls and/or aryls that may be either n- or a-coordinated. These
metal
complexes may be in the free form or fixed on substrates, for example on
activated magnesium chloride, titanium(III) chloride, alumina or silicon
oxide.
These catalysts may be soluble or insoluble in the polymerisation medium. The
catalysts can be active as such in the polymerisation or further activators
may
be used, for example metal alkyls, metal hydrides, metal alkyl halides, metal
alkyl oxides or metal alkyloxanes, the metals being elements of groups Ia, IIa
and/or IIIa of the Periodic Table. The activators may be modified, for
example,
with further ester, ether, amine or silyl ether groups. These catalyst systems
are
usually termed Phillips, Standard Oil Indiana, Ziegler (-Natta), TNZ (DuPont),
metallocene or single site catalysts (SSC).
2. Mixtures of the polymers mentioned under 1), for example mixtures of
polypropylene
with polyisobutylene, polypropylene with polyethylene (for example PP/HDPE,
PP/LDPE) and mixtures of different types of polyethylene (for example
LDPE/HIDPE).
3. Copolymers of monoolefins and diolefins with each other or with other vinyl
mono-
mers, for example ethylene/propylene copolymers, linear low density
polyethylene
(LLDPE) and mixtures thereof with low density polyethylene (LDPE), propylene-
but-
1-ene copolymers, propylene-isobutylene copolymers, ethylene-but-l-ene
copolymers,
ethylene-hexene copolymers, ethylene-methylpentene copolymers, ethylene-
heptene
copolymers, ethylene-octene copolymers, propylene-butadiene copolymers,
isobutylene-
isoprene copolymers, ethylene-alkyl acrylate copolymers, ethylene-alkyl
methacrylate
copolymers, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers and their copolymers with carbon
mon-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-34-
oxide, or ethylene-acrylic acid copolymers and their salts (ionomers), and
terpolymers of
ethylene with propylene and a diene, such as hexadiene, dicyclopentadiene or
ethylidene-
norbornene; furthermore mixtures of such copolymers with one another and with
polymers
mentioned under 1), for example polypropylene/ethylene-propylene copolymers,
LDPE/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, LDPE/ethylene-acrylic acid copolymers,
LLDPE/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, LLDPE/ethylene-acrylic acid
copolymers and
alternating or random polyalkylene-carbon monoxide copolymers and mixtures
thereof
with other polymers, for example polyamides.
4. Hydrocarbon resins (for example C5-Cq) including hydrogenated modifications
thereof
(e.g. tackifiers) and mixtures of polyalkylenes and starch.
5. Polystyrene, poly(p-methylstyrene), poly((x-methylstyrene).
6. Copolymers of styrene or a-methylstyrene with dienes or acrylic
derivatives, for
example styrene-butadiene, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-alkyl methacrylate,
styrene-buta-
diene-alkyl acrylate, styrene-butadiene-alkyl methacrylate, styrene-maleic
anhydride,
styrene-acrylonitrile-methyl acrylate; mixtures of high impact strength of
styrene copoly-
mers and another polymer, for example a polyacrylate, a diene polymer or an
ethylene-
propylene-diene terpolymer; and block copolymers of styrene, such as styrene-
butadiene-
styrene, styrene-isoprene-styrene, styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene or
styrene-ethy-
lene-propylene-styrene.
7. Graft copolymers of styrene or a-methylstyrene, for example styrene on
polybutadiene,
styrene on polybutadiene-styrene or polybutadiene-acrylonitrile copolymers,
styrene and
acrylonitrile (or methacrylonitrile) on polybutadiene; styrene, acrylonitrile
and methyl
methacrylate on polybutadiene; styrene and maleic anhydride on polybutadiene;
styrene,
acrylonitrile and maleic anhydride or maleimide on polybutadiene; styrene and
maleimide
on polybutadiene, styrene and alkyl acrylates or alkyl methacrylates on
polybutadiene,
styrene and acrylonitrile on ethylene/propylene/diene terpolymers, styrene and
acrylonitrile on polyalkyl acrylates or polyalkyl methacrylates, styrene and
acrylonitrile
on acrylate/butadiene copolymers, and mixtures thereof with the copolymers
mentioned
under 6), for example the copolymer mixtures known as ABS, MBS, ASA or AES
polymers.
8. Halogen-containing polymers, such as polychloroprene, chlorinated rubber,
chlorinated
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-35-
and brominated copolymer of isobutylene/isoprene (halobutyl rubber),
chlorinated or
sulfochlorinated polyethylene, copolymers of ethylene and chlorinated
ethylene, epi-
chlorohydrin homo- and copolymers, especially polymers of halogen-containing
vinyl
compounds, for example polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride, polyvinyl
fluoride,
polyvinylidene fluoride; as well as copolymers thereof, such as vinyl
chloride/vinylidene
chloride, vinyl chloride/vinyl acetate or vinylidene chloride/vinyl acetate.
9. Polymers derived from (x,(3-unsaturated acids and derivatives thereof, such
as polyacry-
lates and polymethacrylates; polymethyl methacrylates, polyacrylamides and
polyacrylo-
nitriles, impact-modified with butyl acrylate.
10. Copolymers of the monomers mentioned under 9) with each other or with
other
unsaturated monomers, for example acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymers, acrylo-
nitrile-alkyl acrylate copolymers, acrylonitrile-alkoxyalkyl acrylate
copolymers,
acrylonitrile-vinyl halide copolymers or acrylonitrile-alkyl methacrylate-
butadiene
terpolymers.
11. Polymers derived from unsaturated alcohols and amines or the acyl
derivatives or
acetals thereof, such as polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate, polyvinyl
stearate, polyvinyl
benzoate, polyvinyl maleate, polyvinylbutyral, polyallyl phthalate or
polyallyl melamine;
and their copolymers with olefins mentioned in item 1.
12. Homopolymers and copolymers of cyclic ethers such as polyalkylene glycols,
poly-
ethylene oxide, polypropylene oxide or copolymers thereof with bisglycidyl
ethers.
13. Polyacetals, such as polyoxymethylene and those polyoxymethylenes which
contain
ethylene oxide as a comonomer, polyacetals modified with thermoplastic
polyurethanes,
acrylates or MBS.
14. Polyphenylene oxides and sulfides, and mixtures thereof with styrene
polymers or
polyamides.
15. Polyurethanes derived from hydroxyl-terminated polyethers, polyesters and
polybuta-
dienes on the one hand and aliphatic or aromatic polyisocyanates on the other,
and pre-
cursors thereof.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-36-
16, Polyamides and copolyamides derived from diamines and dicarboxylic acids
and/or
from aminocarboxylic acids or the coiresponding lactams, such as polyamide 4,
poly-
amide 6, polyamide 6/6, 6/10, 6/9, 6/12, 4/6, 12/12, polyamide 11, polyamide
12, aromatic
polyamides made from m-xylene, diamine and adipic acid; polyamides prepared
from
hexamethylenediamine and isophthalic and/or terephthalic acid with or without
an
elastomer as modifier, for example poly-2,4,4-
trimethylhexamethyleneterephthalamide or
poly-m-phenyleneisophthalamide. Block copolymers of the aforementioned
polyamides
with polyolefins, olefin copolymers, ionomers or chemically bonded or grafted
elastomers;
or with polyethers, e.g. with polyethylene glycol, polypropylene glycol or
poly-
tetramethylene glycol. Furthermore polyamides or copolyamides modified with
EPDM or
ABS; and polyamides condensed during processing (RIM polyamide systems).
17. Polyureas, polyimides, polyamide-imides, polyether-imides, polyester-
imides,
polyhydantoins and polybenzimidazoles.
18. Polyesters derived from dicarboxylic acids and diols and/or from
hydroxycarboxylic
acids or the corresponding lactones, such as polyethylene terephthalate,
polybutylene
terephthalate, poly-l,4-dimethylolcyclohexane terephthalate and
polyhydroxybenzoates,
and block polyether esters derived from hydroxyl-terminated polyethers;
furthermore
polyesters modified with polycarbonates or MBS.
19. Polycarbonates and polyester carbonates.
20. Polysulfones, polyether sulfones and polyether ketones.
21. Crosslinked polymers derived from aldehydes on the one hand and phenols,
urea or
melamine on the other hand, such as phenol/formaldehyde resins,
urea/formaldehyde
resins and melamine/formaldehyde resins.
22. Drying and non-drying alkyd resins.
23. Unsaturated polyester resins derived from copolyesters of saturated and
unsaturated
dicarboxylic acids with polyhydric alcohols, vinyl compounds as crosslinking
agents, and
also halogen-containing modifications thereof of low flammability.
24. Crosslinkable acrylic resins derived from substituted acrylates, for
example from
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-37-
epoxy acrylates, urethane acrylates or polyester acrylates.
25. Alkyd resins, polyester resins and acrylate resins crosslinked with
melamine resins,
urea resins, isocyanates, isocyanurates, polyisocyanates or epoxy resins.
26. Crosslinked epoxy resins derived from aliphatic, cycloaliphatic,
heterocyclic or
aromatic glycidyl compounds, for example products of bisphenol A diglycidyl
ethers,
bisphenol F diglycidyl ethers, which have been crosslinked by means of
conventional
curing agents, such as anhydrides or amines, with or without accelerators.
27. Natural polymers such as cellulose, natural rubber, gelatin and chemically
modified
polymer-homologous derivatives thereof, such as cellulose acetates, cellulose
propionates
and cellulose butyrates, or the cellulose ethers such as methylcellulose; and
rosins and
derivatives.
28. Blends (polyblends) of the aforementioned polymers, for example PP/EPDM,
poly-
amide/EPDM or ABS, PVC/EVA, PVC/ABS, PVC/MBS, PC/ABS, PBTP/ABS,
PC/ASA, PC/PBT, PVC/CPE, PVC/acrylates, POWthermoplastic PUR,
PC/therrnoplastic
PUR, POM/acrylate, POM/MBS, PPO/HIPS, PPO/PA 6.6 and copolymers, PA/HDPE,
PA/PP, PA/PPO, PBT/PC/ABS or PBT/PET/PC.
29. Naturally occurring and synthetic organic materials which are pure
monomeric com-
pounds or mixtures of such compounds, for example mineral oils, animal or
vegetable fats,
oil and waxes, or oils, waxes and fats based on synthetic esters (e.g.
phthalates, adipates,
phosphates or trimellitates), as well as mixtures of synthetic esters with
mineral oils in any
weight ratios, typically those used as spinning compositions, and aqueous
emulsions of
such materials.
30. Aqueous emulsions of natural or synthetic rubbers, e.g. natural rubber
latex or latices
of carboxylated styrene-butadiene copolymers.
The invention therefore furthermore relates to compositions comprising an
organic
material which is sensitive to oxidative, thermal or light-induced degradation
and at least
one product obtainable by reacting components a), b), c) and optionally d),
and to the use
of these products for stabilising organic material against oxidative, thermal
or
light-induced degradation.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-38-
The invention therefore also relates to a process for stabilising organic
material against
thermal, oxidative or light-induced degradation, which comprises adding, to
this material,
at least one product obtainable by reacting components a), b), c) and
optionally d).
The use of these products as antioxidants in organic materials is of
particular interest.
Preferred organic materials are polymers, for example synthetic polymers, in
particular
thermoplastic polymers. Particularly preferred organic materials are
polyolefins and
styrene copolymers, for example those mentioned above under items 1 to 3 and
items 6
and 7, in particular polyethylene and polypropylene as well as ABS and
styrene/butadiene
copolymers. The invention therefore preferably relates to compositions in
which the
organic material is a synthetic organic polymer or a mixture of such polymers,
in
particular a polyolefin or a styrene copolymer.
As a rule, the products are added to the material to be stabilised in amounts
from 0.01 to
%, preferably 0.01 to 5 %, in particular 0.01 to 2 %, relative to the total
weight of the
material to be stabilised. It is particularly preferred to employ the products
according to
the invention in amounts of 0.01 to 0.5 %, in particular 0.05 to 0.3 %.
The invention additionally relates to compositions comprising (x) an organic
material
which is subjected to oxidative, thermal or light-induced degradation, and (3)
at least one
product according to the invention.
Component (x) can be an optionally oxygen-containing hydrocarbon fuel, a
lubricant, a
hydraulic fluid, a metalworking fluid or a synthetic polymer. Mixtures of the
respective
components a) are also possible.
As already mentioned, the products according to the invention [component ((3)]
also
possess wear- and corrosion-inhibiting properties in fuels. Particularly
noteworthy is their
outstanding increase of the lubricity (antiwear properties) in fuels having a
low sulfur
content and/or aromatics content.
The present invention therefore also relates to the use of the products of
component (0) as
antiwear additives in an engine fuel system.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-39-
In general, the products of component (p) are added to the fuel in an amount
of from
0.0001 to 10%, preferably from 0.001 to 5% and, in particular, from 0.005 to
1%, based on
the weight of component ((x).
The products of component (0) can also be mixed with liquid carriers
compatible with the
end-product fuels in order to produce concentrates which are added
subsequently to base
fuels or formulated fuels. Such concentrates may facilitate the mixing,
intermixing,
pouring or transfer (on mass or in units/portions) of the products of
component (0).
The carriers are customarily organic solvents for the products of component
(0), examples
being hydrocarbons such as xylol or toluene, ethers, alcohols or mixtures
thereof, or they
may be constituents of the base fuels or of the formulated fuels which are
desired as end
products. The addition of the concentrates to the base materials of formulated
fuels in
order to obtain end-product fuels can be carried out discontinuously, for
example from
unit containers with concentrates which are obtainable in retail or at other
points of sale,
or by means of additions within refineries or fuel distribution sites. Further
methods of
addition are likewise possible.
The products of component (0) may be present in different amounts in the
concentrate,
depending on the desired properties of the concentrate, such as its viscosity.
A suitable
amount in the carrier medium, in general, is from approximately 10 to 90% by
weight,
more usually from approximately 20 to 50% by weight, of the products of
component ((3).
The end-product fuels can be hydrocarbons, oxygen-containing compounds or
mixtures
thereof. The hydrocarbon fractions which can be used for the fuel compositions
include
distillate fuels whose boiling points are in the kerosene and gas-oil range
(165 to 565 C).
Customary middle-distillate fuels of this kind include road diesel and other
diesel oils
having boiling points in the range from 200 to 370 C, and also jet fuels,
kerosenes, gas-oil
and cycle oils. Middle-distillate fuels of this kind can be straight-run
distillate oils,
catalytically or thermally cracked distillate fuel oils or mixtures of
straight-run
combustion oils/heavy oils/heating oils/oils, naphthas and similar materials
with cracked
distillate materials. These fuels are normally derived from petroleum, but may
also derive
at least partly from other sources, for example slate, tar sands, coal,
lignite, biomass and
the like. The fuels may include a proportion of oxygen-containing co-
components, for
example alcohols or ethers, including methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). The
fuels may also
comprise in their entirety oxygen-containing compounds such as methanol and/or
ethanol.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-40-
Also suitable are those fuels which have been subjected to conventional
treatment
processes, for example a treatment with an acid or base, hydrogenation,
solvent refining or
an earthing treating.
Of particular interest are compositions in which component (a) is a diesel
fuel.
The fuels can be employed, for example, in the operation of jet, motor-
vehicle, gas turbine
or diesel engines. In a preferred embodiment of this invention a fuel is used
which is
suitable for use in a diesel engine.
The composition of these diesel fuels is highly variable, in accordance with
the nature of
the crude oil, the refining process, the components with which the crude oil
is mixed and
the climate in which the fuel is to be sold. As noted earlier above, this
invention is
employed primarily in the diesel fuels with a reduced sulfur content and/or
aromatics
content, which are produced nowadays to comply with local statutory
requirements/regulations. These fuels normally have a sulfur content of less
than 500 ppm
(0.05%) and/or an aromatics content of less than 35% by weight.
Consequently, compositions of particular interest include those in which
component (a) is
a fuel which contains less than 0.10% by weight, preferably less than 0.05% by
weight
and, in particular, less than 0.01% by weight of sulfur.
The composition of the fuel, and hence also its inherent lubricity, can vary
in accordance
with the level of the requirements of the local statutory regulations.
The invention is also employed in aviation fuels, for example in those which
generally are
used in jet turbine engines. Fuels of this kind have a composition close to
that of the diesel
oils with a low content of aromatics and of sulfur. The addition of the
products of
component (p) according to the invention to these fuels may reduce wear in the
engine.
The invention could also be employed in lead-free or reformed automotive fuels
which are
now generally used in aircraft piston engines and in motor vehicles. The
addition of the
products of component (p) to these fuels may improve engine performance and
makes it
possible to employ the fuel in place of leaded fuels, in use for example in
aircraft piston
engines where leaded fuel is currently used.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-41-
Therefore, the present invention also relates to a method of reducing wear in
an engine
fuel system, which comprises adding a product of component (p) to the fuel.
In addition to the products of component (0) the compositions according to the
invention
may also include conventional additives which are added in order to improve
still further
the basic properties of the fuel, as is described in the handbook "Lubricant
and Fuel
Additives", Kline & Company Inc., International Business Consultants,
Fairfield, NJ,
USA, pages 309-320 (1990). These additives include: antioxidants, metal
passivators, rust
protection agents, viscosity improvers, pour-point depressants, dispersants,
detergents,
high-pressure additives, friction-reducing additives, antiwear additives,
demulsifiers,
cloud-point depressants, waxlike antisettling additives, antistatic additives,
defoamers,
evaporation additives, biocides, odour masks, colorants, ignition
accelerators, antifreezes,
antiknock additives, conductivity improvers, PFI/IVD purity additives and
other lubricity
additives.
In addition to the product, the compositions according to the invention can
also contain
conventional additives, for example those mentioned below.
1. Antioxidants
1.1. Alkylated monophenols, for example 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2-
butyl-4,6-
dimethylphenol, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-n-
butylphenol, 2,6-di-
tert-butyl-4-isobutylphenol, 2,6-dicyclopentyl-4-methylphenol, 2-(a-
methylcyclohexyl)-
4,6-dimethylphenol, 2,6-dioctadecyl-4-methylphenol, 2,4,6-tricyclohexylphenol,
2,6-di-
tert-butyl-4-methoxymethylphenol, nonylphenols which are linear or branched in
the side
chain, such as 2,6-di-nonyl-4-methylphenol, 2,4-dimethyl-6-(1'-methylundec-1'-
yl)phenol,
2,4-dimethyl-6-(1'-methylheptadec-1'-yl)phenol, 2,4-dimethyl-
6-(1'-methyltridec-1'-yl)phenol and mixtures thereof.
1.2. Alkylthiomethylphenols, for example 2,4-dioctylthiomethyl-6-tert-
butylphenol,
2,4-dioctylthiomethyl-6-methylphenol, 2,4-dioctylthiomethyl-6-ethylphenol, 2,6-
di-do-
decylthiomethyl-4-nonylphenol.
1.3. Hydroquinones and alkylated hydMuinones, for example 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-
methoxyphenol, 2,5-di-tert-butylhydroquinone, 2,5-di-tert-amylhydroquinone,
2,6-di-
phenyl-4-octadecyloxyphenol, 2,6-di-tert-butylhydroquinone, 2,5-di-tert-butyl-
4-hydroxy-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-42-
anisole, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl
stearate,
bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) adipate.
1.4. Tocopherols, for example a-tocopherol, P-tocopherol, y-tocopherol, S-
tocopherol and
mixtures thereof (vitamin E).
1.5. Hydroxylated thiodiphenyl ethers, for example 2,2'-thiobis(6-tert-butyl-4-
methyl-
phenol), 2,2'-thiobis(4-octylphenol), 4,4'-thiobis(6-tert-butyl-3-
methylphenol), 4,4'-thio-
bis(6-tert-butyl-2-methylphenol), 4,4'-thiobis(3,6-di-sec-amylphenol), 4,4'-
bis(2,6-dim-
ethyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) disulfide.
1.6. Alkylidenebisphenols, for example 2,2'-methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-
methylphenol),
2,2'-methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol), 2,2'-methylenebis [4-methyl-6-
((x-methyl-
cyclohexyl)phenol], 2,2'-methylenebis(4-methyl-6-cyclohexylphenol), 2,2'-
methylene-
bis(6-nonyl-4-methylphenol), 2,2'-methylenebis(4,6-di-tert-butylphenol), 2,2'-
ethylidene-
bis(4,6-di-tert-butylphenol), 2,2'-ethylidenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-
isobutylphenol), 2,2'-methy-
lenebis[6-(a-methylbenzyl)-4-nonylphenol], 2,2'-methylenebis[6-(a,(x-
dimethylbenzyl)-
4-nonylphenol], 4,4'-methylenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol), 4,4'-
methylenebis(6-tert-
butyl-2-methylphenol), 1,1-bis(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)butane,
2,6-bis(3-
tert-butyl-5-methyl-2-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methylphenol, 1,1,3-tris(5-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxy-
2-methylphenyl)butane, 1,1-bis(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-3-n-
dodecylmer-
captobutane, ethylene glycol bis[3,3-bis(3'-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)butyrate], bis(3-
tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)dicyclopentadiene, bis[2-(3'-tert-butyl-2'-
hydroxy-
5'-methylbenzyl)6-tert-butyl-4-methylphenyl]terephthalate, 1,1-bis(3,5-
dimethyl-2-
hydroxyphenyl)butane, 2,2-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propane, 2,2-
bis(5-tert-
butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-4-n-dodecylmercaptobutane, 1,1,5,5-tetra-(5-
tert-butyl-
4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)pentane.
1.7. 0-, N- and S-benzyl compounds, for example 3,5,3',5'-tetra-tert-butyl-
4,4'-dihydroxy-
dibenzyl ether, octadecyl-4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylbenzylmercaptoacetate,
tridecyl
4-hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butylbenzylmercaptoacetate, tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-
4-hydroxybenzyl)amine, bis(4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzyl)
dithiotereph-
thalate, bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) sulfide, isoocty13,5-di-tert-
butyl-4-
hydroxybenzylmercaptoacetate.
1.8. Hydroxybenzylated malonates, for example dioctadecyl 2,2-bis(3,5-di-tert-
butyl-2-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-43-
hydroxybenzyl)malonate, dioctadecyl 2-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-
methylbenzyl)malo-
nate, didodecylmercaptoethyl 2,2-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzyl)malonate, bis [4-
(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenyl] 2,2-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzyl)malonate.
1.9. Aromatic hydroxybenzyl compounds, for example 1,3,5-tris(3,5-di-tert-
butyl-4-hy-
droxybenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene, 1,4-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzyl)-2,3,5,6-
tetramethylbenzene, 2,4,6-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)phenol.
1.10. Triazine compounds, for example 2,4-bis(octylmercapto)-6-(3,5-di-tert-
butyl-4-
hydroxyanilino)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-octylmercapto-4,6-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxy-
anilino)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-octylmercapto-4,6-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxyphenoxy)-
1,3,5-triazine, 2,4,6-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenoxy)-1,2,3-triazine,
1,3,5-tris-
(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)isocyanurate, 1,3,5-tris(4-tert-butyl-3-
hydroxy-2,6-di-
methylbenzyl)isocyanurate, 2,4,6-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenylethyl)-
1,3,5-tri-
azine, 1,3,5-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenylpropionyl)-hexahydro-1,3,5-
triazine,
1,3,5-tris(3,5-dicyclohexyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)isocyanurate.
1.11. Benzylphosphonates, for example dimethyl 2,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzylphos-
phonate, diethy13,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylphosphonate, dioctadecy13,5-
di-tert-
butyl-4-hydroxybenzylphosphonate, dioctadecyl 5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-3-
methylbenzyl-
phosphonate, the calcium salt of the monoethyl ester of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzyl-
phosphonic acid.
1.12. Acylaminophenols, for example 4-hydroxylauranilide, 4-
hydroxystearanilide, octyl
N-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)carbamate.
1.13. Esters of R-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid with mono-
or poly-
hydric alcohols, e.g. with methanol, ethanol, n-octanol, i-octanol,
octadecanol,
1,6-hexanediol, 1,9-nonanediol, ethylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol, neopentyl
glycol,
thiodiethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, pentaerythritol,
tris-
(hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate, N,N'-bis(hydroxyethyl)oxamide, 3-thiaundecanol,
3-thiapentadecanol, trimethylhexanediol, trimethylolpropane,
4-hydroxymethyl-l-phospha-2,6,7-trioxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane.
1.14. Esters of (3-(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-3-meth l~phenyl)propionic acid with
mono- or
polyhydric alcohols, e.g. with methanol, ethanol, n-octanol, i-octanol,
octadecanol,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-44-
1,6-hexanediol, 1,9-nonanediol, ethylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol, neopentyl
glycol,
thiodiethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, pentaerythritol,
tris-
(hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate, N,N'-bis(hydroxyethyl)oxamide, 3-thiaundecanol,
3-thiapentadecanol, trimethylhexanediol, trimethylolpropane,
4-hydroxymethyl-l-phospha-2,6,7-trioxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane.
1.15. Esters of 0-(3,5-dicyclohexyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid with mono-
or poly-
hydric alcohols, e.g. with methanol, ethanol, octanol, octadecanol, 1,6-
hexanediol, 1,9-
nonanediol, ethylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol, neopentyl glycol, thiodiethylene
glycol, di-
ethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, pentaerythritol, tris(hydroxyethyl)
isocyanurate, N,N'-
bis(hydroxyethyl)oxalamide, 3-thiaundecanol, 3-thiapentadecanol,
trimethylhexanediol,
trimethylolpropane, 4-hydroxymethyl- 1 -phospha-2,6,7- trioxabicyclo[2.2.2]
octane.
1.16. Esters of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid with mono- or
polyhydric
alcohols, e.g. with methanol, ethanol, octanol, octadecanol, 1,6-hexanediol,
1,9-nonane-
diol, ethylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol, neopentyl glycol, thiodiethylene
glycol, diethylene
glycol, triethylene glycol, pentaerythritol, tris(hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate,
N,N'-bis-
(hydroxyethyl)oxalamide, 3-thiaundecanol, 3-thiapentadecanol,
trimethylhexanediol, tri-
methylolpropane, 4-hydroxymethyl-l-phospha-2,6,7-trioxabicyclo[2.2.2] octane.
1.17. Amides of 0-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, e.g. N,N'-
bis(3,5-
di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenylpropionyl)hexamethylenediamide, N,N'-bis(3,5-di-
tert-
butyl-4-hydroxyphenylpropionyl)trimethylenediamide, N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-
butyl-4-hydroxyphenylpropionyl)hydrazide,
N,N'-bis [2-(3-[3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl]propionyloxy)ethyl]
oxalamide
(Naugard XL-1 from Uniroyal).
1.18. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
1.19. Amine antioxidants, for example
N,N'-diisopropyl-p-phenylenediamine, N,N'-di-sec-butyl-p-phenylenediamine,
N,N'-bis(1,4-dimethylpentyl)-p-phenylenediamine,
N,N'-bis(1-ethyl-3-methylpentyl)-p-phenylenediamine,
N,N'-bis(1-methylheptyl)-p-phenylenediamine, N,N'-dicyclohexyl-p-
phenylenediamine,
N,N'-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine, N,N'-di-(naphthyl-2-)-p-phenylenediamine,
N-isopropyl-N'-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
- 45 -
N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N'-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine,
N-(1-methylheptyl)-N'-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine,
N-cyclohexyl-N'-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, 4-(p-
toluenesulfonamido)diphenylamine,
N,N'-dimethyl-N,N'-di-sec-butyl-p-phenylenediamine, diphenylamine,
N-allyldiphenylamine, 4-isopropoxydiphenylamine, N-phenyl-l-naphthylamine,
N-(4-tert-octylphenyl)-1-naphthylamine, N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine, octylated
diphenylamine, e.g. p,p'-di-tert-octyldiphenylamine, 4-n-butylaminophenol,
4-butyrylaminophenol, 4-nonanoylaminophenol, 4-dodecanoylaminophenol,
4-octadecanoylaminophenol, di-(4-methoxyphenyl)amine,
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-dimethylaminomethylphenol, 2,4'-di-aminodiphenylmethane,
4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane, N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-4,4'-
diaminodiphenylmethane,
1,2-di[(2-methylphenyl)amino]ethane, 1,2-di(phenylamino)propane, (o-
tolyl)biguanide,
di-[4-(1',3'-dimethylbutyl)phenyl]amine, tert-octylated N-phenyl-l-
naphthylamine, a
mixture of mono- and dialkylated tert-butyl/tert-octyldiphenylamines, a
mixture of mono-
and dialkylated nonyldiphenylamines, a mixture of mono- and dialkylated
dodecyldiphenylamines, a mixture of mono- and dialkylated
isopropyl/isohexyl-diphenylamines, mixtures of mono- and dialkylated
tert-butyldiphenylamines, 2,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl-4H-1,4-benzothiazine,
phenothiazine,
a mixture of mono- and dialkylated tert-butyl/tert-octylphenothiazines, a
mixture of mono-
and dialkylated tert-octylphenothiazines, N-allylphenothiazine,
N,N,N',N'-tetraphenyl-1,4-diaminobut-2-ene,
N,N-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl)hexamethylenediamine,
bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl) sebacate, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-
4-one,
2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-ol.
2. UV absorbers and light stabilisers
2.1. 2-(2'-Hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazoles, for example 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-
methylphenyl)-
benzotriazole, 2-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(5'-
tert-butyl-2'-
hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-(1,1,3,3-
tetramethylbutyl)phenyl)benzo-
triazole, 2-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxyphenyl)-5-chloro-benzotriazole, 2-
(3'-tert-butyl-
2'-hydroxy-5'-methylphenyl)-5-chloro-benzotriazole, 2-(3'-sec-butyl-5'-tert-
butyl-2'-
hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(2'-hydroxy-4'-octoxyphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-
(3',5'-di-
tert-amyl-2'-hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(3',5'-bis(a,(x-dimethylbenzyl)-2'-
hydroxy-
phenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxy-5'-(2-
octyloxycarbonylethyl)phenyl)-5-
chloro-benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-5'-[2-(2-ethylhexyloxy)-carbonylethyl]-
2'-hydroxy-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-46-
phenyl)-5-chloro-benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxy-5'-(2-
methoxycarbonylethyl)-
phenyl)-5-chloro-benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxy-5'-(2-
methoxycarbonylethyl)-
phenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-2'-hydroxy-5'-(2-
octyloxycarbonylethyl)phenyl)-
benzotriazole, 2-(3'-tert-butyl-5'-[2-(2-ethylhexyloxy)carbonylethyl]-2'-
hydroxyphenyl)-
benzotriazole, 2-(3'-dodecyl-2'-hydroxy-5'-methylphenyl)benzotriazole, 2-(3'-
tert-butyl-
2'-hydroxy-5'-(2-isooctyloxycarbonylethyl)phenylbenzotriazole, 2,2'-
methylenebis[4-
(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)-6-benzotriazol-2-ylphenol]; the transesterification
product of
2-[3'-tert-butyl-5'-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)-2'-hydroxyphenyl]-benzotriazole
with
polyethylene glycol 300; [R-CH2CH2-COO-CH2CH& , where R = 3'-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxy-5'-2H-benzotriazol-2-ylphenyl;
2- [2' -hydroxy-3' -(a,a-dim ethylbenzyl)-5'- (1,1, 3,3-tetramethyl
butyl)phenyl] benzotriazole;
2-[2'-hydroxy-3'-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)-5'-(a,a-dimethylbenzyl)phenyl]-
benzotriazole.
2.2. 2-Hydroxybenzophenones, for example the 4-hydroxy, 4-methoxy, 4-octoxy, 4-
decyl-
oxy, 4-dodecyloxy, 4-benzyloxy, 4,2',4'-trihydroxy and 2'-hydroxy-4,4'-
dimethoxy deri-
vatives.
2.3. Esters of substituted and unsubstituted benzoic acids, for example 4-tert-
butyl-phenyl
salicylate, phenyl salicylate, octylphenyl salicylate, dibenzoyl resorcinol,
bis(4-tert-butyl-
benzoyl) resorcinol, benzoyl resorcinol, 2,4-di-tertbutylpheny13,5-di-tert-
butyl-4-
hydroxybenzoate, hexadecy13,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate, octadecyl 3,5-
di-tert-
butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate, 2-methyl-4,6-di-tert-butylpheny13,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxy-
benzoate.
2.4. Acrylates, for example ethyl a-cyano-[3,(3-diphenylacrylate, isooctyl a-
cyano-(3,(3-di-
phenylacrylate, methyl a-carbomethoxycinnamate, methyl a-cyano-p-methyl-p-
methoxy-
cinnamate, butyl a-cyano-(3-methyl-p-methoxycinnamate, methyl a-carbomethoxy-p-
methoxycinnamate and N-((3-carbomethoxy-p-cyanovinyl)-2-methylindoline.
2.5. Nickel compounds, for example nickel complexes of 2,2'-thiobis[4-(1,1,3,3-
tetra-
methylbutyl)phenol], such as the 1:1 or 1:2 complex, with or without
additional ligands
such as n-butylamine, triethanolamine or N-cyclohexyldiethanolamine, nickel
dibutyldi-
thiocarbamate, nickel salts of the monoalkyl esters, e.g. the methyl or ethyl
ester, of 4-
hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butylbenzylphosphonic acid, nickel complexes of ketoximes,
e.g. of
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-47-
2-hydroxy-4-methylphenyl undecyl ketoxime, nickel complexes of 1-phenyl-4-
lauroyl-5-
hydroxypyrazole, with or without additional ligands.
2.6. Sterically hindered amines, for example bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-
4-yl)
sebacate, bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-4-yl) succinate, bis(1,2,2,6,6-
penta-
methylpiperidin-4-yl) sebacate, bis(1-octyloxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-
yl)
sebacate, bis(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidyl) n-butyl 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxybenzyl-
malonate, the condensate of 1-hydroxyethyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-
hydroxypiperidine and
succinic acid, linear or cyclic condensates of N,N'-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-
piperidyl)-
hexamethylenediamine and 4-tert-octylamino-2,6-dichloro-1,3,5-s-triazine,
tris(2,2,6,6-te-
tramethyl-4-piperidyl) nitrilotriacetate, tetrakis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-
piperidyl)-1,2,3,4-
butanetetraoate, 1,1'-(1,2-ethanediyl)bis(3,3,5,5-tetramethylpiperazinone),
4-benzoyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine, 4-stearyloxy-2,2,6,6-
tetramethylpiperidine,
bis(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidyl) 2-n-butyl-2-(2-hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butyl-
benzyl)malonate, 3-n-octyl-7,7,9,9-tetramethyl-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-
2,4-dione,
bis(1-octyloxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidyl) sebacate, bis(1-octyloxy-2,2,6,6-
tetramethyl-
piperidyl) succinate, linear or cyclic condensates of N,N'-bis-(2,2,6,6-
tetramethyl-
4-piperidyl)hexamethylenediamine and 4-morpholino-2,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine,
the
condensate of 2-chloro-4,6-bis(4-n-butylamino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidyl )-
1,3,5-
triazine and 1,2-bis(3-aminopropylamino)ethane, the condensate of 2-chloro-4,6-
di-
(4-n-butylamino-1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidyl)-1,3,5-triazine and 1,2-bis(3-
amino-
propylamino)ethane, 8-acetyl-3-dodecyl-7,7,9,9-tetramethyl-1,3, 8-triazaspiro-
[4.5]decane-2,4-dione, 3-dodecyl-l-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-
piperidyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione,
3-dodecyl-l-(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethyl-4-piperidyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, a
mixture of
4-hexadecyloxy- and 4-stearyloxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine, the condensate
of
N,N'-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)hexamethylenediamine and
4-cyclohexylamino-2,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine, the condensate of
1,2-bis(3-aminopropylamino)ethane and 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine and also
4-butylamino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (CAS Reg. No. [136504-96-6]);
N-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)-n-docecylsuccinimide,
N-(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethyl-4-piperidyl)-n-dodecylsuccinimide,
2-undecyl-7,7,9,9-tetramethyl-l-oxa-3,8-diaza-4-oxospiro[4.5]decane, the
reaction
product of 7,7,9,9-tetramethyl-2-cycloundecyl- 1 -oxa-3,8-diaza-4-oxospiro
[4.5]decane
and epichlorohydrin, 1,1-bis(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethyl-4-piperidyloxycarbonyl)-2-
(4-methoxyphenyl)ethene, N,N'-bisformyl-N,N'-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-
piperidyl)hexam ethylenediamine, the diester of 4-methoxymethylenemalonic acid
with
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-48-
1,2,2, 6,6-pentamethyl-4-hydroxypiperidine,
poly[methylpropyl-3-oxy-4-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)]siloxane, the
reaction
product of maleic anhydride-a-olefin copolymer and
2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-aminopiperidine or 1,2,2,6,6-pentamethyl-4-
aminopiperidine.
2.7. Oxamides, for example 4,4'-dioctyloxyoxanilide, 2,2'-diethoxyoxanilide,
2,2'-dioc-
tyloxy-5,5'-di-tert-butoxanilide, 2,2'-didodecyloxy-5,5'-di-tert-butoxanilide,
2-ethoxy-2'-
ethoxanilide, N,N'-bis(3-dimethylaminopropyl)oxalamide, 2-ethoxy-5-tert-butyl-
2'-ethox-
anilide and its mixture with 2-ethoxy-2'-ethyl-5,4'-di-tert-butoxanilide and
mixtures of o-
and p-methoxy-disubstituted oxanilides and mixtures of o- and p-ethoxy-
disubstituted
oxanilides.
2.8. 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-1,3,5-triazines, for example 2,4,6-tris(2-hydroxy-4-
octyloxy-
phenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-(2-hydroxy-4-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-
dimethylphenyl)-
1,3,5-triazine, 2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-
triazine,
2,4-bis(2-hydroxy-4-propyloxyphenyl)-6-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-
(2-hy-
droxy-4-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(4-methylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-(2-hydroxy-4-
dodecyl-
oxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)- 1,3,5-triazine,
2-(2-hydroxy-4-tridecyloxylphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)- 1,3,5-
triazine,
2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-3-butyloxypropyloxy)phenyl]-4,6-bis(2,4-
dimethylphenyl)-
1,3,5-triazine, 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-3-octyloxypropyloxy)phenyl]-4,6-
bis(2,4-
dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-[4-dodecyloxy/tridecyloxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)-
2-
hydroxyphenyl]-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylp henyl)-1,3,5-triazine, 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
hydroxy-
3-dodecyloxypropoxy)phenyl]-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine,
2-(2-hydroxy-4-hexyloxy)phenyl-4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazine,
2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazine,
2,4,6-tris[2-hydroxy-4-(3-butoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine,
2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine,
2- ( 2-hydroxy-4-[3-(2-ethylhexyl-1-oxy)-2-hydroxypropyloxy]phenyl } -4,6-
bis(2,4-di-
methylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine.
3. Metal deactivators, for example N,N'-diphenyloxamide, N-salicylal-N'-
salicyloyl
hydrazine, N,N'-bis(salicyloyl) hydrazine, N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-
hydroxyphenyl-
propionyl) hydrazine, 3-salicyloylamino-1,2,4-triazole, bis(benzylidene)oxalyl
di-
hydrazide, oxanilide, isophthaloyl dihydrazide, sebacoyl bisphenylhydrazide,
N,N'-di-
acetyladipoyl dihydrazide, N,N'-bis(salicyloyl)oxalyl dihydrazide, N,N'-
bis(salicyloyl)-
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-49-
thiopropionyl dihydrazide.
4. Phosphites and phosphonites, for example triphenyl phosphite, diphenyl
alkyl phos-
phites, phenyl dialkyl phosphites, tris(nonylphenyl) phosphite, trilauryl
phosphite, triocta-
decyl phosphite, distearyl pentaerythritol diphosphite, tris(2,4-di-tert-
butylphenyl) phos-
phite, diisodecyl pentaerythritol diphosphite, bis(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)
pentaerythritol
diphosphite, bis(2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenyl)-pentaerythritol
diphosphite, diisodecyl-
oxypentaerythritol diphosphite, bis(2,4-di-tert-butyl-6-
methylphenyl)pentaerythritol di-
phosphite, bis(2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl)pentaerythritol diphosphite,
tristearyl sorbitol tri-
phosphite, tetrakis(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) 4,4'-biphenylene diphosphonite, 6-
isooctyl-
oxy-2,4,8,10-tetra-tert-butyl-12H-dibenz[d,g]-1,3,2-dioxaphosphocin, 6-fluoro-
2,4,8,10-
tetra-tert-butyl-12-methyl-dibenz[d,g]-1,3,2-dioxaphosphocin, bis(2,4-di-tert-
butyl-6-
methylphenyl) methyl phosphite, bis(2,4-di-tert-butyl-6-methylphenyl) ethyl
phosphite,
2,2',2"-nitrilo[triethyl tris(3,3'5,5'-tetra-tert-butyl-1,1'-biphenyl-
2,2'diyl) phosphitel,
2-ethylhexy13,3',5,5'-tetra-tert-butyl-1,1'-biphenyl-2,2'-diyl) phosphite.
Particular preference is given to using the following phosphites:
Tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphite (Irgafos 168, Ciba-Geigy),
tris(nonylphenyl)
phosphite,
(CH3)3C C(CH3)3
O
(A) H3C- CH P - F
O
(CH3)3C C(CH3)3
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-50-
(CH3)3C C(CH3)3
o
'p p CH2CH2 N (B)
O
(CH3)3C C(CH3)3 3
(CH3)3C C(CH3)3
~. ~ o (C)
p O CH2CH(C4H9)CH2CH3
O
(CH3)3C
C(CH3)3
0 xci O C(CH3)3
(CH3)3C O p ~P - O
~O (D)
C(CH3)3 (CH3)3C
C(CH3)3 (CH3)3C
O ~ O
H3C / \ O p" ~ 'p - O CH3
- 'p Cj
(CH3)3C (E)
C(CH3)3
O ., 0
(F) H37Cis O-p. O P - O CisH37
O
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-51-
CH3
H3C- C - CH3
0 P - OCH2CH3 (G)
H3C ~C CH3
H3C % CH3
2
5. Hydroxylamines, for example N,N-dibenzylhydroxylamine, N,N-
diethylhydroxylamine,
N,N-dioctylhydroxylamine, N,N-dilaurylhydroxylamine, N,N-
ditetradecylhydroxylamine,
N,N-dihexadecylhydroxylamine, N,N-dioctadecylhydroxylamine, N-hexadecyl-N-octa-
decylhydroxylamine, N-heptadecyl-N-octadecylhydroxylamine, N,N-dialkylhydroxyl-
amine from hydrogenated tallow fatty amines.
6. Nitrones, for example N-benzyl alpha-phenyl nitrone, N-ethyl alpha-methyl
nitrone,
N-octyl alpha-heptyl nitrone, N-lauryl alpha-undecyl nitrone, N-tetradecyl
alpha-tridecyl
nitrone, N-hexadecyl alpha-pentadecyl nitrone, N-octadecyl alpha-heptadecyl
nitrone,
N-hexadecyl alpha heptadecyl nitrone, N-octadecyl alpha-pentadecyl nitrone,
N-heptadecyl alpha-heptadecyl nitrone, N-octadecyl alpha-hexadecyl nitrone,
nitrones
derived from N,N-dialkylhydroxylamines prepared from hydrogenated tallow fatty
amines.
7. Thiosynergists, for example dilauryl thiodipropionate or distearyl
thiodipropionate.
8. Peroxide scavengers, for example esters of R-thiodipropionic acid, for
example the
lauryl, stearyl, myristyl or tridecyl ester, mercaptobenzimidazole, the zinc
salt of 2-mer-
captobenzimidazole, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, dioctadecyl disulfide,
pentaerythritol
tetrakis(P-dodecylmercapto)propionate.
9. Polyamide stabilisers, for example copper salts in combination with iodides
and/or
phosphorus compounds and salts of divalent manganese.
10. Basic co-stabilisers, for example melamine, polyvinylpyrrolidone,
dicyandiamide, tri-
allyl cyanurate, urea derivatives, hydrazine derivatives, amines, polyamides,
polyure-
thanes, alkali metal salts and alkaline earth metal salts of higher fatty
acids, for example
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-52-
calcium stearate, zinc stearate, magnesium behenate, magnesium stearate,
sodium rici-
noleate and potassium palmitate, antimony pyrocatecholate or tin
pyrocatecholate.
11. Nucleating a ents, for example inorganic substances, such as talc, metal
oxides, such
as titanium dioxide or magnesium oxide, phosphates, carbonates or sulfates of
preferably
alkaline earth metals; organic compounds, such as mono- or polycarboxylic
acids, and
their salts, such as 4-tert-butylbenzoic acid, adipic acid, diphenylacetic
acid, sodium
succinate or sodium benzoate; polymeric compounds, such as ionic copolymers
(ionomers).
12. Fillers and reinforcing agents, for example calcium carbonate, silicates,
glass fibres,
glass beads, talc, kaolin, mica, barium sulfate, metal oxides and hydroxides,
carbon black,
graphite, wood meal and meals or fibres of other natural products, synthetic
fibres.
13. Other additives, for example plasticisers, lubricants, emulsifiers,
pigments, rheological
additives, catalysts, flow-control auxiliaries, optical brighteners,
flameproofing agents,
antistatic agents and blowing agents.
14. Benzofuranones and indolinones, for example those described in US 4 325
863;
US 4 338 244; US 5 175 312; US 5 216 052; US 5 252 643; DE-A-4 316 611;
DE-A-4 316 622; DE-A-4 316 876; EP-A-0 589 839 or EP-A-0 591 102, or 3-[4-(2-
acet-
oxyethoxy)phenyl]-5,7-di-tert-butyl-benzofuran-2-one, 5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-[4-
(2-stearoyl-
oxyethoxy)phenyl]benzofuran-2-one, 3,3'-bis[5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-(4-[2-
hydroxyethoxy]-
phenyl)benzofuran-2-one], 5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-(4-ethoxyphenyl)benzofuran-2-
one, 3-(4-
acetoxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-5,7-di-tert-butyl-benzofuran-2-one, 3-(3,5-
dimethyl-4-piva-
loyloxyphenyl)-5,7-di-tert-butyl-benzofuran-2-one, 3-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-
5,7-di-tert-butyl-benzofuran-2-one, 3-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)-5,7-di-tert-butyl-
benzofuran-
2-one.
The conventional additives are added for example at concentrations of 0.01 to
10 % based
on the total weight of the material to be stabilised.
The products and, if desired, other additives, can be incorporated into the
organic material
by known methods. They can be incorporated in the materials for example by
admixing or
applying the products and, if desired, other additives by the methods
conventionally used
in the art. If the materials are polymers, in particular synthetic polymers,
the products can
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-53-
be incorporated before or during shaping or by applying the dissolved or
dispersed
products to the polymer, with or without subsequent evaporation of the
solvent. In the case
of elastomers, the latter can also be stabilised in the form of the latices. A
further
possibility of incorporating the products according to the invention into
polymers is the
addition of the former before, during or immediately after polymerization of
the
monomers in question, or before crosslinking. The products according to the
invention can
be added as they are, but also in encapsulated fonn (for example in waxes,
oils or
polymers). If they are added before or during polymerization, the products
according to
the invention can also act as chain length regulators for the polymers (chain
terminators).
The products according to the invention can also be added to the materials to
be stabilised
in the form of a masterbatch comprising, for example, a concentration of 2.5
to 25 % by
weight of the product according to the invention.
The materials which have been stabilised in this manner can be used in a
multitude of
ways, for example in the form of films, fibres, tapes, moulding materials,
sections or as
binders for varnishes, adhesives or cements.
Preference is given to compositions according to the invention comprising a) a
lubricant, a
hydraulic fluid, a metal-working fluid or a fuel, for example for driving
engines of the
4-stroke Otto, 2-stroke, diesel, Wankel and also the orbital type, and (3) at
least one
product according to the invention.
Particularly preferred as lubricants are the mineral oils, the synthetic oils
or mixtures of
these.
The products known per se are used from the series of the lubricants, the
hydraulic fluids
and the metal-working fluids.
The lubricants and hydraulic fluids which are suitable are known to those
skilled in the art
and described, for example, in Dieter Klamann "Schmierstoffe und verwandte
Produkte"
[Lubricants and Related Products], Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 1982, in Schewe-
Kobek,
"Das Schmiermittel-Taschenbuch" [Lubricants Guide], Dr. Alfred Huthig-Verlag,
Heidelberg, 1974, or in "Ullmanns Encyklopadie der technischen Chemie"
[Ullmann's
Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry], Volume 13, pages 85-94 (Verlag Chemie,
Weinheim, 1977).
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-54-
Ex;imples are lubricants and hydraulic fluids based on mineral oil or
synthetic lubricants
or hydraulic fluids, in particular those which are derivatives of carboxylic
esters and
which are used at temperatures of 200 C and above.
Examples of synthetic lubricants embrace lubricants based on a diester of a
dibasic acid
with a monovalent alcohol, for example dioctyl sebacate or dinonyl adipate, a
triester of
trimethylolpropane with a monobasic acid or a mixture of such acids, for
example
trimethylolpropane tripelargonate, trimethylolpropane tricaprylate or mixtures
of these, a
tetraester of pentaerythritol with a monobasic acid or with a mixture of such
acids, for
example pentaerythritol tetracaprylate, or a complex ester of monobasic and
dibasic acids
with polyhydric alcohols, for example a complex ester of trimethylolpropane
with caprylic
and sebacic acid or a mixture of these.
Particularly suitable are, besides mineral oils, for example poly-a-olefins,
lubricants based
on esters, or phosphates, glycols, polyglycols and polyalkylene glycols, and
mixtures of
these with water.
The products according to the invention are oils and readily soluble
lubricants and
therefore particularly suitable as additives to lubricants, and mention must
be made of
their surprisingly good antioxidative and anticorrosive action.
The products according to the invention can display their surprising
properties for example
in lubricants for combustion engines, for example in combustion engines
operating by the
Otto principle. The products according to the invention prevent the formation
of deposits
(sludge), or reduce these deposits to a surprising extent.
So-called masterbatches can also be prepared.
The products according to the invention are active as additives in lubricants
even when
used in very small amounts. They are admixed to the lubricants advantageously
in an
amount of 0.01 to 5 % by weight, preferably in an amount of 0.05 to 3 % by
weight and
particularly preferably in an amount of 0.1 to 2 % by weight, in each case
based on the
lubricant.
The lubricants can additionally comprise other additives which are added to
improve the
basic properties of lubricants even further; these include: antioxidants,
metal passivators,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-55-
rust inhibitors, viscosity index improvers, pour-point depressers,
dispersants, detergents,
high-pressure additives, antifriction additives and antiwear additives.
A series of such compounds can be found, for example, in the above list " 1.
Antioxidants",
in particular items 1.1 to 1.16. The following additives must be mentioned
additionally by
way of example:
Examples of further antioxidants:
Aliphatic or aromatic phosphites, esters of thiodipropionic acid or of
thiodiacetic acid, or
salts of dithiocarbamic or dithiophosphoric acid,
2,2,12,12-tetramethyl-5,9-dihydroxy-3,7,11-trithiatridecane and
2,2,15,15-tetramethyl-5,12-dihydroxy-3,7,10,14-tetrathiahexadecane.
Examples of metal passivators, e.g. for copper, are:
a) Benzotriazoles and their derivatives, e.g. 4- or 5-alkylbenzotriazoles
(e.g.
tolutriazole) and derivatives thereof, 4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzotriazole,
5,5'-methylenebisbenzotriazole; Mannich bases of benzotriazole or
tolutriazole,
such as 1-[di(2-ethylhexyl)aminomethyl)tolutriazole and
1-[di(2-ethylhexyl)aminomethyl)benzotriazole; alkoxyalkylbenzotriazoles, such
as
1-(nonyloxymethyl)benzotriazole, 1-(1-butoxyethyl)benzotriazole and
1-(1-cyclohexyloxybutyl)tolutriazole.
b) 1,2,4-Triazoles and their derivatives, e.g. 3-alkyl (or aryl)-1,2,4-
triazoles, Mannich
bases of 1,2,4-triazoles, such as 1-[di(2-ethylhexyl)aminomethyl-12,4-
triazole;
alkoxyalkyl- 1,2,4-triazoles, such as 1 -(1 -butoxyethyl)- 1,2,4-triazole;
acylated
3-amino-1,2,4-triazoles.
c) Imidazole derivatives, e.g. 4,4'-methylenebis(2-undecyl-5-methylimidazole),
bis[(N-methyl)imidazol-2-yl]carbinol octyl ether.
d) Sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds, e.g. 2-mercaptobenzothiazole,
2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole and derivatives thereof;
3,5-bis[di(2-ethylhexyl)aminomethyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-2-one.
e) Amino compounds, e.g. salicylidenespropylenediamine, salicylaminoguanidine
and
salts thereof.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-56-
Examples of rust inhibitors are:
a) Organic acids, their esters, metal salts, amine salts and ahydrides, e.g.
alkyl- and
alkenylsuccinic acids and partial esters thereof with alcohols, diols or
hydroxycarboxylic acids, partial amides of alkyl- and alkenylsuccinic acids,
4-nonylphenoxyacetic acid, alkoxy- and alkoxyethoxycarboxylic acids, such as
dodecyloxyacetic acid, dodecyloxy(ethoxy)acetic acid and amine salts thereof,
and
also N-oleoylsarcosine, sorbitan monooleate, lead naphthenate, alkenylsuccinic
anhydrides, e.g. dodecenylsuccinic anhydride,
2-carboxymethyl-l-dodecyl-3-methylglycerol and its amine salts.
b) Nitrogen-containing compounds, e.g.:
1. Primary, secondary or tertiary aliphatic or cycloaliphatic amines and amine
salts
of organic and inorganic acids, e.g. oil-soluble alkylammonium carboxylates,
and
also 1-[N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-3-(4-nonylphenoxy)propan-2-ol.
II. Heterocyclic compounds, e.g.:
Substituted imidazolines and oxazolines,
2-heptadecenyl-l-(2-hydroxyethyl)imidazoline.
c) Phosphorus-containing compounds, e.g.:
Amine salts of phosphoric acid partial esters or phosphonic acid partial
esters, zinc
dialkyldithiophosphates.
d) Sulfur-containing compounds, e.g.:
Barium dinonylnaphthalenesulfonates, calcium petroleumsulfonates,
alkylthio-substituted aliphatic carboxylic acids, esters of aliphatic 2-
sulfocarboxylic
acids and salts thereof.
e) Gycerol derivatives, e.g.:
Glyceryl monooleate, 1-(alkylphenoxy)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)glycerols,
1-(alkylphenoxy)-3-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)glycerols,
2-carboxyalkyl- 1,3-dialkylglycerols.
Examples of viscosity index improvers are:
Polyacrylates, polymethacrylates, vinylpyrrolidone-methacrylate copolymers,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-57-
polyvinylpyrrolidones, polybutenes, olefin copolymers, styrene/acrylate
copolymers,
polyethers.
Examples of pour-point depressants are:
Polymethacrylate, alkylated naphthalene derivatives.
Examples of dispersants/surfactants are:
Polybutenylsuccinamides or -imides, polybutenylphosphonic acid derivatives,
basic
magnesium, calcium and barium sulfonates and phenolates.
Examples of antiwear additives are:
Sulfur- and/or phosphorus- and/or halogen-containing compounds, such as
sulfurized
olefins and vegetable oils, zinc dialkyldithiophosphates, alkylated triphenyl
phosphates,
tritolyl phosphate, tricresyl phosphate, chlorinated paraffins, alkyl and aryl
di- and
trisulfides, amine salts of mono- and dialkyl phosphates, amine salts of
methylphosphonic
acid, diethanolaminomethyltolyltriazole, di(2-
ethylhexyl)aminomethyltolyltriazole,
derivatives of 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole, ethyl
3-[(bisisopropyloxyphosphinothioyl)thio]propionate, triphenyl thiophosphate
(triphenyl
phosphorothioate), tris(alkylphenyl)phosphorothioates and mixtures thereof,
(e.g.
tris(isononylphenyl)phosphorothioate), diphenyl monononylphenyl
phosphorothioate,
isobutylphenyl diphenyl phosphorothioate, dodecylamine salt of
3-hydroxy-1,3-thiaphosphetan 3-oxide, trithiophosphoric acid 5,5,5-
tris[isooctyl
2-acetate], derivatives of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole, such as
1-[N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)aminomethyl-2-mercapto-1 H-1,3-benzothiazole,
ethoxycarbonyl-5-octyldithiocarbamate.
Specifically preferred additional additives in lubricants are amine
antioxidants, in
particular mixtures of mono- and dialkylated tert-butyl/tert-octyl
diphenylamines.
The examples which follow illustrate the invention in greater detail. Parts
and percentages
are by weight therein and in the rest of the description, unless otherwise
indicated.
Norpar Ex 15 n-paraffinic hydrocarbon mixture from EXXON
[boiling range: 245-285 C]
Exxsol D-110 dearomaticized aliphatic hydrocarbon mixture,
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-58-
partially hydrogenated, from EXXON
[boiling range: 240-275 C; Mn = 206 g mol- l]
SAP -001 superbasic calcium salicylate from Shell
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-59-
Preparation Examples
Example 1:
A mixture of 500 g(- 0.737 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol), 403 g (4.376
mol) of
glycerol, 1875 g (6.412 mol) of inethyl3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate
and 8.7 g (0.3% by weight) of SAP -001 is heated at 220 C for 2 hours under
nitrogen in
a sulfonation flask provided with reflux condenser and mechanical stirrer. The
reaction
mixture is stirred at a temperature of 220-230 C for a further 6 hours, in the
course of
which methanol (and any water) is distilled off. After the mixture has cooled,
613 g of
Norpar Ex 15 are added. Filtration gives 3100 g (98% of theory) of the
product as a
yellow oil with a refractive index nD20 of 1.4910.
Example 2:
A mixture of 109.53 g(- 0.162 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol) and 109.53
g
(- 0.119 mol) of castor oil (MW = 922 g/mol) in a sulfonation flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer is admixed with 53.32 g (0.579 mol) of
glycerol,
247.40 g (0.846 mol) of methyl 3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate and
3.96 g (0.8% by weight) of SAP -001, and the mixture is held under nitrogen at
180-190 C for 18 to 19 hours. Cooling and filtration give 469 g (96% of
theory) of the
product as a yellow oil with a refractive index nD20 of 1.4999.
Example 3:
A mixture of 80.0 g(_ 0.118 mol) of coconut fat (MW - 678 g/mol) and 20.0 g
(- 0.022 mol) of castor oil (MW = 922 g/mol) in a sulfonation flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer is admixed with 75.77 g (0.823 mol) of
glycerol,
355.21 g (1.215 mol) of inethyl3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate and
3.71 g (0.76% by weight) of SAP -001, and the mixture is held under nitrogen
at
180-190 C for 18 to 19 hours. Cooling and filtration give 478 g (98% of
theory) of the
product as a yellow syrup with a refractive index nD20 of 1.5114.
Example 4:
A mixture of 80.0 g(= 0.118 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol) and 20.0 g
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-60-
(- 0.022 mol) of castor oil (MW = 922 g/mol) in a sulfonation flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer is admixed with 75.77 g (0.823 mol) of
glycerol,
355.21 g (1.215 mol) of methyl 3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate and
3.71 g (0.76% by weight) of SAP -001, and the mixture is held under nitrogen
at
180-190 C for 18 to 19 hours. After the mixture is cooled, 121.4 g of Norpar
Ex 15 are
added. Filtration gives 594.9 g (98% of theory) of the product as a yellow oil
with a
refractive index nD20 of 1.4913.
Example 5:
A mixture of 100 g(- 0.147 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol), 80.6 g (0.875
mol) of
glycerol, 324 g (1.294 mol) of methyl
3-(3'-tert-butyl-5'-methyl-4'-hydroxyphenyl)propionate and 7.62 g(0.16% by
weight) of
lithium methanolate (10% strength solution in methanol) is heated at 180 C for
1 hour
under nitrogen in a sulfonation flask provided with reflux condenser and
mechanical
stirrer. The reaction niixture is stirred at this temperature for a further 12
hours, in the
course of which water and methanol are distilled off. Extraction with citric
acid and
subsequent washing with warm water give 448 g (99% of theory) of the product
as a
yellow syrup with a refractive index nD20 of 1.5147.
Example 6:
100 g(_ 0.147 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol), 80 g (0.869 mol) of
glycerol and
347.5 g(1.281 mol) of inethyl3-(3',5'-di-tert-butyl-4'-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate are
melted at 100 C under a nitrogen atmosphere in a sulfonation flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer. 122.5 g of Norpar Ex 15 and 1.74 g (0.3% by
weight)
of SAP -001 are added to the reaction mixture, which is stirred at a
temperature of
180-190 C for a further 15 hours, in the course of which water and methanol
are distilled
off. Cooling and filtration give 614.5 g (98% of theory) of the product as a
yellow oil with
a refractive index nD20 of 1.4913.
Example 7:
456.78 g (5.306 mol) of methyl acrylate are added over 1 hour to a mixture of
1001.3 g
(4.835 mol) of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 27.31 g(0.146 mol) of 30% strength
potassium
hydroxide solution, this addition taking place in a sulfonation flask provided
with reflux
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-61-
condenser and mechanical stirrer, under vacuum and at 110 C. After a reaction
time of
one hour and following the removal of excess methyl acrylate by distillation,
372.5 g
(- 0.549 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol) and 302.3 g (3.282 mol) of
glycerol are
added. Over the course of 2 hours under vacuum the mixture is heated to a
temperature of
190 C. The reaction mixture is stirred at this temperature for 3 hours more,
in the course
of which water and methanol are distilled off. After the mixture has been
cooled to room
temperature, 456 g of Norpar Ex 15 are added. Extraction with citric acid and
subsequent washing with warm water give 2263 g (97% of theory) of the product
as a
reddish oil with a refractive index nD20 of 1.4905.
Example 8:
79.36 g (0.922 mol) of methyl acrylate are added over 1 hour to a mixture of
173.9 g
(0.843 mol) of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 4.75 g (0.025 mol) of 30% strength
potassium
hydroxide solution, this addition taking place in a sulfonating flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer, under vacuum and at 110 C. After a reaction
time of
one hour and following the removal of excess methyl acrylate by distillation,
109.53 g
(_ 0.162 mol) of coconut fat (MW - 678 g/mol), 109.53 g(= 0.119 mol) of castor
oil
(MW - 922 g/mol) and 53.32 g (0.579 mol) of glycerol are added. Over the
course of 18
to 19 hours, the reaction mixture is held at a temperature of 180 to 190 C
under a nitrogen
atmosphere. Cooling and filtration give 469 g (97% of theory) of the product
as a
orange-coloured oil with a refractive index nD20 of 1.4999.
Example 9:
116.25 g (1.350 mol) of methyl acrylate are added over 1 hour to a mixture of
254.83 g
(1.235 mol) of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 6.95 g (0.037 mol) of 30% strength
potassium
hydroxide solution, this addition taking place in a sulfonating flask provided
with reflux
condenser and mechanical stirrer, under vacuum and at 110 C. After a reaction
time of
one hour and following the removal of excess methyl acrylate by distillation,
80.0 g
(= 0.118 mol) of coconut fat (MW - 678 g/mol), 20.0 g(- 0.022 mol) of castor
oil
(MW = 922 g/mol) and 75.77 g (0.823 mol) of glycerol are added. Over the
course of 18
to 19 hours, the reaction mixture is held at a temperature of 180 to 190 C
under a nitrogen
atmosphere. After the mixture has been cooled to room temperature, 121.4 g of
Norpar
Ex 15 are added. Filtration gives 594.9 g (98% of theory) of the product as a
reddish oil
with a refractive index nD20 of 1.4913.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-62-
Example 10:
106.05 g (1.232 mol) of methyl acrylate are added over 1 hour to a mixture of
185.06 g
(1.127 mol) of 2-tert-butyl-6-methylphenol and 6.34 g (0.034 mol) of 30%
strength
potassium hydroxide solution, this addition taking place in a sulfonating
flask provided
with reflux condenser and mechanical stirrer, under vacuum and at 110 C. After
a reaction
time of one hour and following the removal of excess methyl acrylate by
distillation,
100.0 g(- 0.147 mol) of coconut fat (MW = 678 g/mol) and 81.0 g (0.880 mol) of
glycerol are added. Over the course of 1 hour under a nitrogen atmosphere the
mixture is
heated to a temperature of 180 C. The reaction mixture is stirred at this
temperature for 9
hours more, in the course of which water and methanol are distilled off. The
cooled, crude
product is taken up in toluene and water and the phases are neutralized with
citric acid.
After multiple washing with water the organic phase is dried and is
subsequently
concentrated by evaporation, giving 387.5 g (96% of theory) of the product as
a
orange-coloured syrup with a refractive index nD20 of 1.5148.
Example A: "Deposit and Oxidation Panel Test" (DOPT)
The deposit and oxidation panel test (DOPT) is a variant of a test method for
engine oils,
in particular for diesel engine oils, which has been described by G.
Abellaneda et al., IIIrd
Symposium CEC, 1989, 61, New Cavendish Street, London WIM 8AR, England. The
suitability of the oils with stabiliser for preventing deposits on the pistons
is tested.
The test time is 20 hours, the panel temperature 260 C and the oil flex 1
ml/minutes. The
humid atmospheric environment is enriched with 260 ppm of NO2 and 26 ppm of
SO2.
After the test, the metal panel onto which the oil drops is weighed and
assessed visually.
The lower the weight, the better. The lubricating oil used is a commercial CD
oil which is
diluted with the basic oil STANCO 150 . The stabilisers according to the
invention are
admixed to this prepared oil in amounts of 0.6 % by weight based on the oil,
and this is
subjected to a DOPT test.
The products according to the invention exhibit a good stabilising effect.
CA 02237279 1998-05-11
-63-
Example B: Test for antiwear protection.
To test the stabilisers according to the invention for their suitability as
antiwear protection
agents, the ASTM standard method D 2783-81 using the Shell four ball apparatus
is used.
The basic oil used is BB oil [Mobil Stock, carbon (aromatic) 6.5 %; carbon
(aliphatic)
72 %; carbon (naphthylic) 21.5 %]. The parameter measured during one hour is
the mean
wear scar diameter in mm at a load of 40 kg. The stabilisers according to the
invention are
added to this oil in an amount of 1.0 % by weight. The lower the values, the
better the
stabilising effect.
The products according to the invention exhibit a good stabilising effect.