Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
. ..
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries / Du/KrlS-P FIL~ r iN 3~3 ~ E5~ EI)
IIb ~TP~AN~ATL~N
Use of 1,2,3-thiadiazoleca*)oxvlic (thio)este~ for cont~lling pests
The present invention relates to the use of known and novel 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic
(thio)esters for controlling unwanted micro-org~ni~mc and animal pests.
s
Certain 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic acid derivatives are already known (cf. DE-A-
2 728 523). However, only herbicidal and plant-growth-regulating properties of these
compounds have hitherto been described.
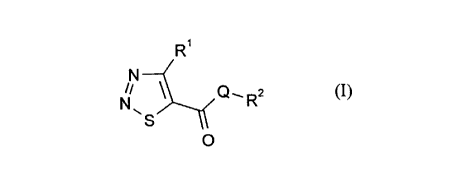
It has now been found that 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula
in which
Rl represents hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl or optionally substituted aryl,
R2 represents optionally substituted alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl,
optionally substituted cycloalkenyl or represents optionally substituted aryl and
Q represents oxygen or sulphur,
and acid addition salts and metal salt complexes thereof are highly suitable for
protecting plants against attack by unwanted micro-organisms and for controlling animal
pests.
Surprisingly, the compounds usable according to the invention are appreciably better
suited to protecting plants against attack by unwanted micro-organisms and to
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 2 -
controlling animal pests than the constitutionally most similar prior-art compounds of
the sarne direction of action.
The formula (I) provides a general definition of the 1,2,3-thi~ 7O1ecarboxylic
S (thio)esters usable according to the invention.
R~ preferably represents hydrogen, straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 4
carbon atoms, straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl having 1 to 4 carbon
atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different halogen atoms, or
R' preferably represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two radicals may in each
case be mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or different substituents from the
group consisting of halogen, cyano, nitro, straight-chain or branched alkyl
having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, straight-chain or branched alkoxy having 1 to 6
carbon atoms, straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl having 1 to 6 carbon
atoms and I to S identical or different halogen atoms and halogenoalkoxy
having I to 6 carbon atoms and I to S identical or different halogen atoms.
R2 preferably represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having I to 6 carbon
atoms, where these radicals may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of dialkylamino having I to 4
carbon atoms in each alkyl moiety, dialkylaminopropargyl having 1 to 4 carbon
atoms in each alkyl moiety, halogenoalkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and 1
to 5 identical or different halogen atoms, alkoxycarbonyl having 1 to 4 carbon
atoms in the alkoxy moiety, cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkenyl
having 3 to 6 carbon atoms and the radical of the formula
CH3 O
~N-R - , in which
"~
o
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 3 -
R represents alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or represents optionally
halogen-substituted phenyl,
or
s
R2 preferably represents cycloalkyl having 3 to 8 carbon atoms or cycloalkenyl
having 3 to 8 carbon atoms, where these radicals may contain an oxo group and
may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the
group consisting of straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 8 carbon atoms,halogenoalkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different
halogen atoms and cycloalkylalkyl having 3 to 8 carbon atoms in the cycloalkyl
moiety and 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkyl moiety,
or
R2 preferably represents phenyl, benzyl, 1-phenethyl, 2-phenethyl or
diphenylmethyl, where these radicals may be mono- to pentasubstituted in the
phenyl moiety by identical or different substituents from the group consisting of
halogen, cyano, nitro, formyl, carbamoyl, thiocarbamoyl;
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, alkylsulphinylor alkylsulphonyl having in each case I to 6 carbon atoms;
respectively straight-chain or branched alkenyl or alkenyloxy having in each
case 2 to 6 carbon atoms;
respectively straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy,
halogenoalkylthio, halogenoalkylsulphinyl or halogenoalkylsulphonyl having in
each case I to 3 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different halogen atoms;
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 4 -
respectively straight-chain or branched halogenoalkenyl or halogenoalkenyloxy
having in each case 2 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different halogen
atoms;
respectively straight-chain or branched alkylamino, dialkylamino, alkylcarbonyl,alkylcarbonyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkylsulphonyloxy, hydroximinoalkyl or
alkoximinoalkyl having in each case 1 to 6 carbon atoms in the individual alkyl
moieties;
respectively doubly attached alkylene or dioxyalkylene having in each case 1 to
6 carbon atoms and in each case optionally 1 to 4 identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of halogen, straight-chain or branched
alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl
having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different halogen atoms;
cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
phenyl, phenoxy, benzyl, heteroaryl having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two
nitrogen atoms, heteroarylmethyl having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two
nitrogen atoms and heteroaryloxy having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two
nitrogen atoms, where the six last-mentioned substituents may themselves be
mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of halogen, cyano, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and
halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different
halogen atoms,
or
R2 preferably represents the grouping -A-Ar, where
A represents straight-chain or branched alkanediyl having 3 or 4 carbon
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-~orei~n Countries
atoms, alkenediyl having 2 to 4 carbon atoms or alkinediyl having 2 to
4 carbon atoms; or represents -CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-O-,
represents -CH2-CH2-S-, represents -CH-CH2-O-or represents
CH3
- I H-CH2-O-, where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the
C2H5
radical Ar,
or
represents -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- or-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar,
orrepresents -CH2 C--N; or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2-CH2--N--~where
the nitrogen atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 preferably represents alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of
halogen, cyano, nitro, carbarnoyl,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulphinyl or alkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 to 6 carbon
atoms,
respectively straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy,
halogenoalkylthio, halogenoalkylsulphinyl or halogenoalkylsulphonyl
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 6 -
having in each case 1 to 3 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different
halogen atoms;
straight-chain or branched alkoxycarbonyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms in
S the alkoxy moiety;
phenoxy, heterocyclyl having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two
nitrogen atoms, heterocyclylmethyl having S or 6 ring members and one
or two nitrogen atoms and heterocyclyloxy or heterocyclylmethyloxy
having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two nitrogen atoms, where the
four last-mentioned substituents may themselves be mono- to
trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of halogen, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and
halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or
different halogen atoms.
Q also preferably represents oxygen or sulphur.
R' particularly preferably represents hydrogen, straight-chain or branched alkylhaving 1 to 4 carbon atoms, halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to
S fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms,
or
R' particularly preferably represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two radicals
may in each case be mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine,
cyano, nitro, straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
straight-chain or branched alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, halogenoalkyl
having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to S fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms
and halogenoalkoxy having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to S fluorine, chlorine
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 7 -
and/or bromine atoms.
R~ particularly preferably represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 4
carbon atoms, where these radicals may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical
or different substituents from the group consisting of dialkylamino having 1 to
3 carbon atoms in each alkyl moiety, dialkylaminopropargyl having 1 to 3
carbon atoms in each alkyl moiety, halogenoalkoxy having 1 to 3 carbon atoms
and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms, alkoxycarbonyl having I or
2 carbon atoms in the alkoxy moiety, cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms,
cycloalkenyl having 5 or 6 carbon atoms and the radical of the formula
CH3 O
~N-R , in which
o
R represents alkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms or represents phenyl which
is optionally mono- or disubstituted by chlorine,
or
R2 particularly preferably represents cycloalkyl having 3 to 7 carbon atoms or
cycloalkenyl having 3 to 7 carbon atoms, where these radicals may contain an
oxo group and may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of straight-chain or branched alkyl having
1 to 8 carbon atoms, halogenoalkyi having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5
fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms and cycloalkylalkyl having 3 to 7
carbon atoms in the cycloalkyl moiety and 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkyl
moiety,
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Foreign Countries
- 8 -
or
R2 particularly preferably represents phenyl, benzyl, l-phenethyl, 2-phenethyl or
diphenylmethyl, where these radicals may be mono- to pentasubstituted in the
phenyl moiety by identical or different substituents from the group consisting of
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, formyl, carbamoyl,
thiocarbamoyl,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, alkylsulphinylor alkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkenyl or alkenyloxy having in each
case 2 to 4 carbon atoms,
halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy, halogenoalkylthio, halogenoalkylsulphinyl or
halogenoalkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5
fluorine, chlorine andlor bromine atoms,
respectively straight-chain or branched halogenoalkenyl or halogenoalkenyloxy
having in each case 2 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or
bromine atoms,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkylamino, dialkylarnino, alkylcarbonyl,
alkylcarbonyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkylsulphonyloxy, hydroximinoalkyl or
alkoximinoalkyl having in each case I to 4 carbon atoms in the individual alkyl
moieties,
respectively doubly attached alkylene having 3 or 4 carbon atoms or
dioxyalkylene having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and in each case optionally 1 to 4
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine,
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
,
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
g
bromine, methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl,
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl,
S phenyl, phenoxy, benzyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl, pyrimidylmethyl,
pyridyloxy, pyrimidyloxy, pyrazinyloxy or pyridazinyloxy, where each of these
substituents may itself be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group con~i~ting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano,
methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl,
or
R2 particularly preferably represents the grouping -A-Ar, in which
ICH3
A represents -CH2-CH-CH2- ~ -CH- IC- or -CH2-C-C-, or represents
CH3 CH3
-CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-S-, represents
-CH-CH2-O- or represents -CH-CH2-O-,
CH3 C2H5
where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH7-CH2-O-CH2- or-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2 C--N- or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2-CH2 where the nitrogen
~ R3 ll R3
atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 represents alkyl having 1 to 3 carbon atoms,
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 10 -
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, nitro, carbamoyl,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulphinyl or alkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 to 4 carbon
1 0 atoms,
halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy, halogenoalkylthio,
halogenoalkylsulphinyl or halogenoalkylsulphonyl having in each case
1 or 2 carbon atoms and l to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms,
alkoxycarbonyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkoxy moiety,
phenoxy, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl, pyridyloxy,
pyridylmethyloxy, pyrimidyloxy, pyrazinyloxy or pyridazinyloxy, where
each of these substituents may itself be mono- to trisubstituted by
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of fluorine,
chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl.
Q particularly preferably represents oxygen or sulphur.
R' very particularly preferably represents hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl,
isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl or tert-butyl, or
very particularly preferably represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two
radicals may in each case be mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or differentsubstituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine,
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 11 -
cyano, nitro, methyl, ethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, trichloromethyl, trifluoromethyl,
trichloromethoxy and trifluoromethoxy.
R2 very particularly preferably represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl,where these radicals may be mono- or disubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of dimethylamino, diethylamino,
3 -dimethylamino- 1 -propargyl, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy,
difluorochloromethoxy, trifluoroethoxy, 1,3-difluoro-2-propoxy,
methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, cyclohexyl, cyclohexenyl and the radical of
the formula
CH3 O
~N-R , in which
~0
R represents methyl, ethyl, phenyl or chlorophenyl,
lS or
R2 very particularly preferably represents cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl,cyclopentenyl, cyclohexenyl, cycloheptenyl or cycloheptatrienyl, where these
radicals may contain an oxo group and may be mono- to trisubstituted by
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
trifluoromethyl, n- or i-propyl, n-, i-, s- or t-butyl, 1-, 2-, 3- or neopentyl, 1-, 2-,
3- or 4-(2-methylbutyl), 1-, 2- or 3-hexyl, 1-, 2-, 3-, 4- or 5-(2-methylpentyl),
1-, 2- or 3-(3-methylpentyl), 2-ethylbutyl, 1-, 3- or 4-(2,2-dimethylbutyl), 1- or
2-(2,3-dimethylbutyl), 2,4,4-pent-2-yl, cyclohexylmethyl or 2-cyclohexyl-
2-propyl,
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 12 -
or
R2 very particularly preferably represents phenyl, benzyl, l-phenethyl, 2-phenethyl
or diphenylethyl, where these radicals may be mono- to pentasubstituted in the
phenyl moiety by identical or different constituents from the group consisting
of
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, formyl, methyl, ethyl, n- or
i-propyl, n-, i-, s- or t-butyl, vinyl, allyl, trifluoromethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n- or
i-propoxy, n-, i-, s- or t-butoxy, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy,
difluorochloromethoxy and trifluoroethoxy,
respectively doubly attached alkylene having 3 or 4 carbon atoms or
dioxyalkylene having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and respectively optionally 1 to 4
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl,
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl,
phenyl, phenoxy, benzyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl, pyrimidylmethyl,
pyridyloxy, pyrimidyloxy, pyrazinyloxy or pyridazinyloxy, where each of these
substituents itself may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, methyl, ethyl and
trifluoromethyl,
or
R2 very particularly preferably represents the grouping -A-Ar, in which
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
Le A 31 406-Foreign Countries
- 13 -
ICH3
A represents -CH2- ICH-CH2- . -CH-C- or -CH2-C_C, or
CH3 CH3
represents -CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-S-,
represents -CH-CH2-O- or represents -CH-CH2-O-,
CH3 C2H5
where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- or-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2--C--N- or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- I H2 where the nitrogen
atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl,
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, cyano, nitro, carbamoyl, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl,
n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, methoxy, methylthio,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl,
phenoxy, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl, pyridyloxy, pyrimidyloxy
pyridylmethyloxy, pyrazinyloxy or pyridazinyloxy, where each of these
substituents may itself be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 14 -
Q very particularly preferably represents oxygen or sulphur.
Compounds according to the invention which are preferably usable also include the
adducts of acids and those 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula (I) in
which R', R2 and Q each have those meanings which have been mentioned as being
preferred for these radicals.
The acids which can be subjected to an additional reaction preferably include hydrohalic
acids, such as, for example, hydrochloric acid and hydrobromic acid, in particular
hydrochloric acid, furthermore phosphoric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, mono- and
bifunctional carboxylic acids and hydroxycarboxylic acids, such as, for example, acetic
acid, maleic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, salicylic acid,
sorbic acid and lactic acid, and sulphonic acids, such as, for example,
p-toluenesulphonic acid, 1 ,5-naphthalenedisulphonic acid, and furthermore saccharin and
1 5 thiosaccharin.
Other preferred compounds according to the invention are adducts of salts of metals of
main groups II to IV and sub-groups I and II and IV to VIII of the Periodic Table of
the Elements and those 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic (thio)esters of formula (I) in which
R', R2 and Q each have those meanings which have been mentioned as being preferred
for these radicals.
Salts of copper, zinc, m~ng~nese, magnesium, tin, iron and nickel are particularly
preferred in this context. Suitable anions of these salts are those which are derived from
acids which lead to physiologically acceptable adducts. Particularly preferred acids of
this type are, in this context, the hydrohalic acids, such as, for example, hydrochloric
acid and hydrobromic acid, furtherrnore phosphoric acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid.
Some of the 1,2,3-thi~ olecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula (I) usable according
to the invention are known (cf. DE-A-2 728 523j.
' CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei,en Countries
- 15 -
The 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula
Nt/
N~ ~~C (Ia)
S
in which
s
R4 represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, straight-
chain or branched halogenoalkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical
or different halogen atoms or
represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two radicals may in each case be
mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
con~i~ting of halogen, cyano, nitro, straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to
6 carbon atoms, straight-chain or branched alkoxy having 1 to 6 carbon atoms,
straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms and 1 to
5 identical or different halogen atoms and halogenoalkoxy having 1 to 6 carbon
atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different halogen atoms,
R5 represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, where
these radicals are mono- to trisubstituted by dialkylamino having 1 to 4 carbon
atoms in each alkyl moiety, dialkylaminopropargyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms
in each alkyl moiety, halogenoalkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5
identical or different halogen atoms, alkoxycarbonyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms
in the alkoxy moiety, cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkenyl
having 3 to 6 carbon atoms and the radical of the formula
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 16 -
CH3 O
-R , in which
o
R represents alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or represents optionally
halogen-substituted phenyl,
s
or
R5 represents cycloalkyl having 3 to 8 carbon atoms or cycloalkenyl having 3 to 8
carbon atoms, where these radicals may contain an oxo group and may be
mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 8 carbon atoms,
halogenoalkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different
halogen atoms and cycloalkyl having 3 to 8 carbon atoms in the cycloalkyl
moiety and 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkyl moiety~5
or
R5 represents a radical of the formula
~C4Hg-tert. , ~ ,
CH3 CH3 F
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries - 17 -
=CHO, ~o~ 3
~o~ ~30~ 3 "~
~CH2~ -CH2~ , -CH2~3 CH3
Cl Cl
~3 CH2~Cl CH2 3CI
S -CH2~ -CH2~0CH3 ~ -CH2~OCF3
-CH2~3 , -CH2~ -CH2 OCF3
-CH2~oCF3 -CH2~ -CH2~ C4Hg-tert.
' CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 18 -
-CHz~ -CH,~CF, -CH2~ \~
-CH2~30~ '~OC,Hg-tert., CH CH C4Hg-tert.,
CH3 CF3 CF3
-CH2 CH2~-CH -CH2-CH2~ ' -CH
CH3 CH3
S or ~'~3CI
-CH
~) Cl
or
R5 represents the grouping A-Ar, where
A represents straight-chain or branched alkanediyl having 3 or 4 carbon
atoms, alkenediyl having 2 to 4 carbon atoms or alkinediyl having 2 to
4 carbon atoms; or represents -CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-O-,
represents -CH,-CH2-S-, represents -CH-CH2-O-or represents
CH3
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 19 -
-CH-CH2-O-, where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the
C2H5
radical Ar,
or
represents -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- or -CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
S where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar,
or represents -CH2--C--N- or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2-CH2, where
the nitrogen atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 represents alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of
halogen, cyano, nitro, carbamoyl,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulphinyl or alkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 to 6 carbon
atoms,
respectively straight-chain or branched halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy,
halogenoalkylthio, halogenoalkylsulphinyl or halogenoalkylsulphonyl
having in each case 1 to 3 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or different
halogen atoms;
straight-chain or branched alkoxycarbonyl having I to 6 carbon atoms in
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 20 -
the alkoxy moiety;
phenoxy, heterocyclyl having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two
nitrogen atoms, heterocyclylmethyl having 5 or 6 ring members and one
or two nitrogen atoms and heterocyclyloxy or heterocyclylmethyloxy
having 5 or 6 ring members and one or two nitrogen atoms, where the
four last mentioned substituents may themselves be mono- to
trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of halogen, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and
halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 identical or
different halogen atoms,
and
Q represents oxygen or sulphur,
or
R4 represents n-propyl,
R5 represents ethyl and
Q represents oxygen,
their acid addition salts and metal salt complexes are novel.
R4 preferably represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having l to 4 carbon
atoms, halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine
and/or bromine atoms, or
represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two radicals may in each case be
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 21 -
mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, straight-chain or
branched alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, straight-chain or branched alkoxy
having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to
S fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms and halogenoalkoxy having 1 or 2
carbon atoms and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms.
R5 preferably represents straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, where these radicals are mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of dialkylamino having 1 to 3 carbon
atoms in each alkyl moiety, dialkylaminopropargyl having 1 to 3 carbon atoms
in each alkyl moiety, halogenoalkoxy having 1 to 3 carbon atoms and 1 to 5
fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms, alkoxycarbonyl having 1 or 2 carbon
atoms in the alkoxy moiety, cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkenyl
having 5 or 6 carbon atoms and the radical of the formula
CH3 O
~N-R , in which
~/
o
R represents alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or represents optionally
halogen-substituted phenyl,
or
R5 preferably represents cycloalkyl having 3 to 7 carbon atoms or cycloalkenyl
having 3 to 7 carbon atoms, where these radicals may contain an oxo group and
may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the
group consisting of straight-chain or branched alkyl having 1 to 8 carbon atoms,
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries - 22 -
halogenoalkyl having 1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or
bromine atoms and cycloalkylalkyl having 3 to 7 carbon atoms in the cycloalkyl
moiety and 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkyl moiety,
S or
R5 preferably represents a radical of the formula
~C4Hg-tert., ~
CH3 CH3 F
~ 3CHo, ~o~ ~O~=~CI .
~~~ '~30~ o~N
~3CH2~ -CH2~ , -CH2 ~3CH
-CH2 ' -CH2~CI . -CH2~ ~ Cl
-CH2~3 CH2~30cH3 -CH ~OCF3
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries - 23 -
CH2~ , CH2~NO,, OCF2,
-CH2 ~OCF3 , ~CH2~ -CH2' ~ C4Hg-tert.,
-CH2~ -CH,~CF,, -CH,~ \~
-CH2~3 ~CF3 ~OC~Hg~tert ' -cH2-CH2~C4Hg~tert~
CH3 CF3 CF3
S -CH2-CH2~CH -CH2-CH2~ -CH ~=~
CH3 CH3
or -CH Cl
\~3C
or
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 24 -
R5 preferably represents the grouping -A-Ar, in which
l H3
A represents -CH2-lCH-CH2- . -CH-IC- or -CH2-C-C-, or
CH3 CH3
represents -CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-S-,
represents -CH-CH2-O- or represents -CH-CH2-O-,
CH3 C2H5
where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- or-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2--C--N- or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2-CH2 where the
nitrogen atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl,
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, nitro, carbamoyl,
respectively straight-chain or branched alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulphinyl or alkylsulphonyl having in each case 1 to 4 carbon
atoms,
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 25 -
halogenoalkyl, halogenoalkoxy, halogenoalkylthio,
halogenoalkylsulphinyl or halogenoalkylsulphonyl having in each case
1 or 2 carbon atoms and 1 to 5 fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine atoms,
alkoxycarbonyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkoxy moiety,
phenoxy, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl, pyridyloxy,
pyridylmethyloxy, pyrimidyloxy, pyrazinyloxy or pyridazinyloxy, where
each of these substituents may itself be mono- to trisubstituted by
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of fluorine,
chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl.
Q in the formula (Ia) likewise preferably represents oxygen or sulphur.
1 5 Furthermore
R4 likewise preferably represents n-propyl if
R5 represents ethyl and
Q represents oxygen.
R4 particularly preferably represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl,
isobutyl, sec-butyl or tert-butyl, or
particularly preferably represents phenyl or naphthyl, where these two radicals
may in each case be mono- to tetrasubstituted by identical or different
substituents from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine,
cyano, nitro, methyl, ethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, trichloromethyl, trifluoromethyl,
trichloromethoxy and trifluoromethoxy.
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 26 -
R5 particularly preferably represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl, where
these radicals are mono- or disubstituted by dimethylamino, diethylamino,
3-dimethylamino- 1 -propargyl, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy,
difluorochloromethoxy, trifluoroethoxy, 1,3-difluoro-2-propoxy,
methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, cyclohexyl, cyclohexenyl and/or the radical
of the formula
CH3 O
~N-R , in which
\~
o
R represents methyl, ethyl, phenyl or chlorophenyl,
or
R5 particularly preferably represents cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl,
cyclopentenyl, cyclohexenyl, cycloheptenyl or cycloheptatrienyl, where these
radicals may contain an oxo group and may be mono- to trisubstituted by
identical or different substituents from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
trifluoromethyl, n- and i-propyl, n-, i-, s- and t-butyl, 1-, 2-, 3- and neopentyl,
1-, 2-, 3- and 4-(2-methylbutyl), 1-, 2- and 3-hexyl, 1-, 2-, 3-, 4- and 5-(2-
methylpentyl), 1-, 2- and 3-(3-methylphenyl), 2-ethylbutyl, 1-, 3- and 4-(2,2-
dimethylbutyl), 1- and 2-(2,3-dimethylbutyl), 2,4,4-pent-2-yl, cyclohexylmethyl
and 2-cyclohexyl-2-propyl,
or
R5 particularly preferably represents a radical of the formula
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries - 27 -
~C4Hg-tert., ~
CH3 CH3 F
~3CHo, ~ ~ ~O~CI,
~30~ o~N
~CH2~ -CH2~3 -CH2~CH3
S -CH2~ -CH2~3CI, -CH2 <~--Cl
-CH2~ CF3 , -CH2~0CH3 , -CH2 OCF3
-CH2~ -CH2~ -CH2--~OCF3
Cl
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 28 -
-CH2~0CF3, -CH2~--CF3, ~C4Hg-tert.,
-CH2~F -CH2~CF,, -CH2~ \[3
-CH2~ ~CF3 ~OC4Hg-tert. . -CH2-CH2~ C4Hg-tert.
C~ CF3 CF3
-CH2-CH2~cH3, -CH2-CH2~ , -CH
CH3 CH3
or ~ Cl
-CH Cl
or
R5 particularly preferably represents the grouping -A-Ar, in which
CH3
A represents -CH2- ICH-CH2-, -CH-C- or -CH2-C--C-, or
CH3 CH3
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 29 -
represents -CH2-O, represents -CH2-CH2-O-, represents -CH2-CH2-S-,
represents -CH-CH2-O- or represents -CH-CH2-O-,
CH3 C2H5
where the hetero atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar, or
represents -CH2-CH2-O-CH2- or-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-O-CH2-,
where the -O-CH2- group is in each case attached to the radical Ar,
or represents -CH2--C--N- or -CH2-CH2-O-CH2-cH2
where the nitrogen atom is in each case attached to the radical Ar and
R3 represents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl,
and
Ar represents phenyl which may be mono- to trisubstituted by identical or
different substituents from the group consisting of
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, nitro, carbamoyl, methyl, ethyl,
n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, methoxy,
methylthio, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, methoxycarbonyl,
ethoxycarbonyl, phenoxy, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridylmethyl,
pyridylmethyloxy, pyridyloxy, pyrimidyloxy, pyrazinyloxy and
pyridazinyloxy, where each of these substituents may itself be mono- to
trisubstituted by identical or different substituents from the group
consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, trichloromethyl
and trifluoromethyl.
Q in the formula (Ia) likewise particularly preferably represents oxygen or sulphur.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 30 -
Furthermore
R4 likewise particularly preferably represents n-propyl if
R5 represents ethyl and
Q represents oxygen.
1,2,3-thi~ 7olecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula (Ia) and acid addition salts and
metal salt complexes thereof can be prepared by reacting 1,2,3-thi~ 7olecarboxylic
acid derivatives of the formula
N~
N~ ~X (II)
o
in which
R4 is as defined above and
X represents halogen
with (thio)alcohols of the formula
H-Q-R5
in which
Q and R5 are each as defined above,
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 31 -
if a~ropl;ate in the presence of an acid binder and if appropliate in the presence of a
diluent,
and, if appropriate, an acid or a metal salt is added to the resulting compounds of the
formula (Ia).
It is also possible to prepare the rern~ining 1 ,2,3-thi~ 7Olecarboxylic (thio)esters of the
formula (I) by the above process.
The 1,2,3-thi~ 7olecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula (I) usable according to the
invention may, if desired, be obtained as mixtures of different possible isomeric forms,
in particular in the form of stereoisomers. The invention relates both to the pure isomers
and to any mixtures thereof.
If 4-methyl-1,2,3-thi~ 7Ole carbonyl chloride and 4-trifluoromethylben_yl alcohol are
used as starting materials, the course of the process according to the invention can be
illustrated by the following equation:
O OH
Base
- HCI
N~S~--~( CF3
The formula (II) provides a general definition of the 1,2,3-thiadiazolecarboxylic acid
derivatives required as starting materials for carrying out the process according to the
invention. In this formula (II), R4 preferably or in particular has those meanings which
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 32 -
have already been indicated in connection with the description of the compounds of the
formula (Ia) according to the invention as being preferred or as being particularly
preferred for R4. X preferably represents chlorine.
S The 1~2~3-th~ 7olecarboxylic acid derivatives of the formula (II) are kno~vn or can
be prepared by processes known per se (cf. DE-A-2 728 523 or J. Heterocyclic Chem.
1976, 301).
The formula (III) provides a general definition of the (thio)alcohols furthermore required
as starting materials for carrying out the process according to the invention. In this
formula (III), Q and R5 each preferably or in particular have those meanings which have
already been indicated in connection with the description of compounds of the formula
(Ia) according to the invention as being preferred or as being particularly preferred for
Q and Rs.
The (thio)alcohols of the formula (III) are known reagents of organic chemistry.
Suitable acid binders for carrying out the process according to the invention are all
customary inorganic and organic bases. Preference is given to using alkaline earth metal
or alkali metal hydrides, hydroxides, amides, alkoxides, acetates, carbonates orbicarbonates, such as, for example, sodium hydride, sodium amide, sodium methoxide,
sodium ethoxide, potassium tert-butoxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide,potassium acetate, calcium acetate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, potassium
bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate, furthermore basic ammonium compounds, such as
ammonium hydroxide, ammonium acetate or ammonium carbonate, and tertiary amines,such as trimethylamine, triethylamine, tributylamine, N,N-dimethylaniline, N,N-
dimethyl-benzylamine, pyridine, N-methylpiperidine, N-methylmorpholine, N,N-
dimethylaminopyridine, diazabicyclooctane (DABCO), diazabicyclononene (DBN) or
diazabicycloundecene (DBU).
Suitable diluents for carrying out the process according to the invention are all
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 33 -
customary inert organic solvents. Preference is given to using aliphatic, alicyclic or
aromatic hydrocarbons, such as, for example, petroleum ether, hexane, heptane,
cyclohexane, methylcyclohexane, benzene, toluene, xylene or decalin; halogenatedhydrocarbons, such as, for example, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, dichloromethane,
chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane or trichloroethane; ethers, such as
diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, methyl t-amyl ether, dioxane,
tetrahydrofuran, 1,2-dimethoxyethane, 1,2-diethoxyethane or anisole; ketones, such as
acetone, butanone, methyl isobutyl ketone or cyclohexanone; nitriles, such as
acetonitrile, propionitrile, n- or i-butyronitrile or benzonitrile; amides, such as N,N-
1 0 dimethylformamide,N,N-dimethylacetamide,N-methylformanilide,N-methylpyrrolidone
or hexamethylphosphoric triamide, esters such as methyl acetate or ethyl acetate;
sulphoxides, such as dimethyl sulphoxide; sulphones, such as sulpholane.
When carrying out the process according to the invention, the reaction temperatures can
lS be varied within a relatively wide range. In general, the reaction is carried out at
tempela~llres between -20~C and +180~C, preferably at temperatures between 20~C and
1 30~C.
The process according to the invention is usually carried out under atmospheric
pressure. However, it is also possible to operate under elevated or reduced pressure.
When carrying out the process according to the invention, generally 0.5 to 10 mol,
preferably 0.8 to 3 mol, of (thio)alcohol of the formula (III) are employed per mole of
the 1 ,2,3-thi~ 7~-1ecarboxylic acid derivative of the formula (II). The reaction is carried
out and worked up by known methods (cf. Plel)~d~ion Examples).
The 1,2,3-thi~ 701ecarboxylic (thio)esters of the formula (I) or (Ia) can be converted
into acid addition salts or metal salt complexes.
For preparing acid addition salts of compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia), preference is
given to those acids which have already been mentioned in connection with the
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 34 -
description of the acid addition salts usable according to the invention as being
preferred acids.
The acid addition salts of the compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia) can be obtained in
S a simple manner by customary salt-forming methods, for example by dissolving a
compound of the formula (I) in a suitable inert solvent and adding the acid, for example
hydrochloric acid, and they can be isolated in a known manner, for example by filtering
off, and, if appropliate, purified by washing with an inert organic solvent.
For plepalillg metal salt complexes of the compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia),preference is given to those salts of metals which have already been mentioned in
connection with the description of the metal salt complexes usable according to the
invention as being preferred metal salts.
The metal salt complexes of the compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia) can be obtained
in a simple manner by customary methods, for example by dissolving the metal salt in
alcohol, for example ethanol, and addition to compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia).
Metal salt complexes can be isolated in a known manner, for example by filtering off,
and, if appropriate, purified by recryst~lli7~tion.
The active compounds usable according to the invention have a strong resistance-inducing activity in plants. They are therefore suitable for generating resistance in plants
against attack by unwanted microorg~nicmc.
Resistance-inducing compounds in the present context are substances which are capable
of stimulating the defence system of plants in such a way that the treated plants, when
subsequently inoculated with unwanted microorganisms, are largely resistant against
these microorg~ni.cmc.
In the present case, unwanted microorg~nicmc are phytopathogenic fungi, bacteria and
viruses. Thus, the compounds according to the invention can be employed to generate
' CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 35 -
resistance in plants against attack by the abovementioned harmful or~nism~ for acertain period after the treatment. The period for which resistance is generated generally
extends over 1 to 10 days, preferably 1 to 7 days, after the treatment of the plants with
the active compounds.
In addition to the resistance-inducing activity, the active compounds usable according
to the invention also have strong microbicidal activity, and they are also employed in
practice for the direct control of unwanted microorg~nisms The active compounds are
suitable for use as crop protection agents, in particular as fungicides.
In crop protection, unwanted microorg~nisms include fungi from the classes of the
Plasmodiophoromycetes, Oomycetes, Chytridiomycetes, Zygomycetes, Ascomycetes,
Basidiomycetes, Deuteromycetes.
Bactericides are employed in crop protection for controlling Pseudomon~ ccae,
Rhizobiaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, Corynebacteriaceae and Streptomycetaceae.
Some pathogens causing fungal and bacterial diseases which come under the generic
names listed above are mentioned as examples, but not by way of limitation:
Xanthomonas species, such as, for example, Xanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae;
Pseudomonas species, such as, for example, Pseudomonas syringae pv. Iachrymans;
Erwinia species, such as, for example, Erwinia amylovora;
Pythium species, such as, for example, Pythium ultimum;
Phytophthora species, such as, for example, Phytophthora infestans;
Pseudoperonospora species, such as, for example, Pseudoperonospora humuli or
Pseudoperonospora cubensis;
Plasmopara species, such as, for example, Plasmopara viticola;
Bremia species, such as, for example, Bremia lactucae,
Peronospora species, such as, for example, Peronospora pisi or P. brassicae;
Erysiphe species, such as, for example, Erysiphe graminis;
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 36 -
Sphaerotheca species, such as, for example, Sphaerotheca fuliginea;
Podosphaera species, such as, for example, Podosphaera leucotricha;
Venturia species, such as, for example, Venturia inaequalis;
Pyrenophora species, such as, for example, Pyrenophora teres or P. graminea
(conidia form: Drechslera, syn: Helminthosporium);
Cochliobolus species, such as, for example, Cochliobolus sativus
(conidia form: Drechslera, syn: Helminthosporium);
Uromyces species, such as, for example, Uromyces appendiculatus;
Puccinia species, such as, for example, Puccinia recondita;
Sclerotinia species, such as, for example, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum;
Tilletia species, such as, for example, Tilletia caries;
Ustilago species, such as, for exarnple, Ustilago nuda or Ustilago avenae;
Pellicularia species, such as, for example, Pellicularia sasakii;
Pyricularia species, such as, for example, Pyricularia oryzae;
Fusarium species, such as, for example, Fusarium culmorum;
Botrytis species, such as, for example, Botrytis cinerea;
Septoria species, such as, for example, Septoria nodorum;
Leptosphaeria species, such as, for example, Leptosphaeria nodorum;
Cercospora species, such as, for example, Cercospora canescens;
Alternaria species, such as, for example, Alternaria brassicae; and
Pseudocercosporella species, such as, for example, Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides.
The fact that the active compounds are well tolerated by plants at the concentrations
required for controlling plant diseases permits the treatment of aerial parts of plants, of
propagation stock and seeds, and of the soil.
The active compounds usable according to the invention can be employed particularly
successfully for controlling rice diseases, such as Pyricularia species, or diseases in
viticulture and fruit and vegetable growing, such as, for example, Uncinula species, and
they can also be employed very successfully against cereal diseases such as powdery
mildew.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 37 -
Depending on their particular physical and/or chemical properties, the active compounds
can be converted to the customary formulations, such as solutions, emulsions,
suspensions, powders, foams, pastes, granules, aerosols and microencapsulations in
polymeric substances and in coating compositions for seeds, and ULV cool and warm
fogging formulations.
These formulations are produced in a known manner, for example by mixing the active
compounds with extenders, that is liquid solvents, liquefied gases under pressure, and/or
solid carriers, optionally with the use of surfactants, that is emulsifiers and/or
dispersants, and/or foam formers. If the extender used is water, it is possible to use for
example organic solvents as auxiliary solvents. Essentially, the following are suitable
as liquid solvents: aromatics such as xylene, toluene or alkylnaphthalenes, chlorinated
aromatics or chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzenes, chloroethylenes
or methylene chloride, aliphatic hydrocarbons such as cyclohexane or paraffins, for
example petroleum fractions, alcohols such as butanol or glycol and their ethers and
esters, ketones such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone or
cyclohexanone, strongly polar solvents such as dimethylformamide or dimethyl
sulphoxide, or else water. Liquefied gaseous extenders or carriers are to be understood
as meaning liquids which are gaseous at standard temperature and under atmospheric
pressure, for example aerosol propellants such as halogenated hydrocarbons, or else
butane, propane, nitrogen and carbon dioxide. Suitable solid carriers are: for example
ground natural minerals such as kaolins, clays, talc, chalk, quartz, attapulgite,
montmorillonite or diatomaceous earth, and ground synthetic minerals such as highly
disperse silica, alumina and silicates. Suitable solid carriers for granules are: for
example crushed and fractionated natural rocks such as calcite, marble, pumice, sepiolite
and dolomite, or else synthetic granules of inorganic and organic meals, and granules
of organic material such as sawdust, coconut shells, maize cobs and tobacco stalks.
Suitable emulsifiers and/or foam formers are: for example nonionic and anionic
emulsifiers, such as polyoxyethylene fatty acid esters, polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol
ethers, for example alkylaryl polyglycol ethers, alkylsulphonates, alkyl sulphates,
arylsulphonates, or else protein hydrolysates. Suitable dispersants are: for example
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 38 -
lignin-sulphite waste liquors and methylcellulose.
Tackifiers such as carboxymethylcellulose and natural and synthetic polymers in the
form of powders, granules or latices, such as gum arabic, polyvinyl alcohol and
polyvinyl acetate, or else natural phospholipids such as cephalins and lecithins and
synthetic phospholipids can be used in the formulations. Other additives can be mineral
and vegetable oils.
It is possible to use colorants such as inorganic pigments, for example iron oxide,
titanium oxide and Prussian Blue, and organic dyestuffs such as alizarin dyestuffs, azo
dyestuffs and metal phthalocyanine dyestuffs, and trace nutrients such as salts of iron,
manganese, boron, copper, cobalt, molybdenum and zinc.
The formulations generally comprise between 0.1 and 95 per cent by weight of active
compound, preferably between 0.5 and 90%.
The active compounds usable according to the invention can be used as such or in their
formulations also mixed with known fungicides, bactericides, acaricides, nematicides
or insecticides in order thus, for example, to widen the spectrum of action or to prevent
development of resistance. In many cases, synergistic effects are achieved, i.e. the
activity of the mixture exceeds the activity of the individual components.
Examples of suitable co-components in mixtures are the following compounds-
Fwlgicides:
2-aminobutane; 2-anilino-4-methyl-6-cyclopropyl-pyrimidine; 2',6'-dibromo-
2-methyl-4 '-trifluoromethoxy-4 ' -trifluoro-methyl- 1 ,3-thiazole-5 -carboxanilide;
2,6-dichloro-N-(4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)benzamide~E)-2-methoxyimino-N-methyl-2-(2-
phenoxyphenyl)acetamide, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulphate; methyl-(E)-2-{2-[6-(2-cyano-
phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yloxy]-phenyl}-3-methoxyacrylate; methyl-(E)-methoximino
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
~ Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 39 -
[alpha-(o-tolyloxy)-o-tolyl] acetate; 2-phenylphenol (OPP), aldimorph, al1lplopylfos,
~nil~7ine, ~7~conazole,
benalaxyl, benodanil, benomyl, binapacryl, biphenyl, bitertanol, blasticidin-S,
bromuconazole, bupirimate, buthiobate,
calcium polysulphide, captafol, captan, carbendazim, carboxin, quinomethionate,
chloroneb, chloropicrin, chlorothalonil, chlozolinate, cufraneb, cymoxanil,
cyproconazole, cyprofuram,
dichlorophen, diclobutrazole, diclofluanid, diclomezine, dicloran, diethofencarb,
difenoconazole, dimethirimol, dimethomorph, diniconazole, dinocap, diphenylamine,
dipyrithione, ditalimfos, dithianon, dodine, drazoxolon,
edifenphos, epoxiconazole, ethirimol, etridiazole,
fenarimol, fenbuconazole, fenfuram, fenitropan, fenpiclonil, fenpropidin, fenpropimorph,
fentin acetate, fentin hydroxide, ferbam, ferimzone, fll1~7in~m, fludioxonil, fluoromide,
fluquinconazole, flusilazole, flusulfamide, flutolanil, flutriafol, folpet, fosetyl-aluminium,
fthalide, fuberidazole, furalaxyl, furmecyclox,
gu~7~tine,
hexachlorobenzene, hexaconazole, hymexazole,
im~7~1il, imibenconazole, iminoctadine, iprobenfos (IBP), iprodione, isoprothiolane,
k:~ug~mycin, copper prepalalions, such as: copper hydroxide, copper naphthenate,copper oxychloride, copper sulphate, copper oxide, oxine-copper and Bordeaux mixture,
mancopper, mancozeb, maneb, mepanipyrim, mepronil, metalaxyl, metconazole,
methasulfocarb, methfuroxam, metiram, metsulfovax, myclobutanil,
nickel dimethyldithiocarbamate, nitrothal-isopropyl, nuarimol,
ofurace, oxadixyl, oxamocarb, oxycarboxin,
pefurazoate, penconazole, pencycuron, phosdiphen, pimaricin, piperalin, polyoxin,
probenazole, prochloraz, procymidone, propamocarb, propiconazole, propineb,
pyrazophos, pyrifenox, pyrimethanil, pyroquilon,
quintozene (PCNB),
sulphur and sulphur preparations,
tebuconazole, tecloftalam, tecnazene, tetraconazole, thiabendazole, thicyofen,
thiophanate-methyl, thiram, tolclofos-methyl, tolylfluanid, triadimefon, triadimenol,
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 40 -
triazoxide, trichlamide, tricyclazole, tridemorph, triflumizole, triforine, triticonazole,
validamycin A, vinclozolin,
zineb, zlram.
R~ es:
bromopol, dichlorophen, nitrapyrin, nickel dimethyldithiocarbamate, kasugamycin,octhilinone, furancarboxylic acid, oxytetracyclin, probenazole, streptomycin, tecloftalam,
copper sulphate and other copper preparations.
Insecticides/Acaricides/Nematicides:
abamectin, acephate, acrinathrin, alanycarb, aldicarb, alphamethrin, amitraz, avermectin,
AZ 60541, azadirachtin, azinphos A, azinphos M, azocyclotin,
Bacillus thuringiensis, 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(tri-
fluoromethyl)- 1 H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, bendiocarb, benfuracarb, bensultap,
betacyfluthrin, bifenthrin, BPMC, brofenprox, bromophos A, bufencarb, buprofezin,
butocarboxim, butylpyridaben,
cadusafos, carbaryl, carbofuran, carbophenothion, carbosulfan, cartap, chloethocarb,
chlorethoxyfos, chlorfenvinphos, chlorfluazuron, chlormephos, N-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)-
methyl]-N'-cyano-N-methyl-ethanimidamide, chlorpyrifos, chlorpyrifos M, cis-
resmethrin, clocythrin, clofentezine, cyanophos, cycloprothrin, cyfluthrin, cyhalothrin,
cyhexatin, cypermethrin, cyromazine,
deltamethrin, demeton M, demeton S, demeton S-methyl, diafenthiuron, diazinon,
dichlofenthion, dichlorvos, dicliphos, dicrotophos, diethion, diflubenzuron, dimethoate,
dimethylvinphos, dioxathion, disulfoton,
edifenphos, emamectin, esfenvalerate, ethiofencarb, ethion, ethofenprox, ethoprophos,
etrimphos,
fenamiphos, fena7aquin, fenbutatin oxide, fenitrothion, fenobucarb, fenothiocarb,
fenoxycarb, fenpropathrin, fenpyrad, fenpyroximate, fenthion, fenvalerate, fipronil,
fl~ 7in~m, fluazuron, flucycloxuron, flucythrinate, flufenoxuron, flufenprox, fluvalinate,
fonophos, formothion, fosthi~7~te, fubfenprox, furathiocarb,
HCH, heptenophos, hexaflumuron, hexythiazox,
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 41 -
imidacloprid, iprobenfos, is~ophos, isofenphos, isoprocarb, isoxathion, ivermectin,
lambda-cyhalothrin, lufenuron,
malathion, mecarbam, mervinphos, mesulfenphos, metaldehyde, methacrifos,
methamidophos, methidathion, methiocarb, methomyl, metolcarb, milbemectin,
S monocrotophos, moxidectin,
naled, NC 184, nitenpyram
omethoate, oxamyl, oxydemethon M, oxydeprofos,
parathion A, parathion M, permethrin, phenthoate, phorate, phosalone, phosmet,
phosphamidon, phoxim, pirimicarb, pirimiphos M, pirimiphos A, profenophos,
promecarb, propaphos, propoxur, prothiofos, prothiophos, prothoate, pymetrozin,
pyrachlophos, pyridaphenthion, pyresmethrin, pyrethrum, pyridaben, pyrimidifen, pyri-
proxifen,
quinalphos,
salithion, sebufos, silafluofen, sulfotep, sulprofos,
tebufenozide, tebufenpyrad, tebupirimphos, teflubenzuron, tefluthrin, temephos, terbam,
terbufos, tetrachlorvinphos, thiafenox, thiodicarb, thiofanox, thiomethon, thionazin,
thuringiensin, tralomethrin, triarathen, tri~ophos, tri~uron, trichlorfon, triflumuron,
trimethacarb,
vamidothion, XMC, xylylcarb, zetamethrin.
It is also possible to admix other known active compounds, such as herbicides, or
fertilizers and growth regulators.
The active compounds usable according to the invention can be used as such or in the
form of their commercial formulations or the use forms prepared therefrom, such as
ready-to-use solutions, suspensions, wettable powders, pastes, soluble powders, dusts
and granules. They are used in the customary manner, for exarnple by wetting, spraying,
atomizing, broadcasting, foaming, brushing-on and the like. It is further possible to
apply the active compounds by the ultra-low volume method or to inject the preparation
of active compound, or the active compound itself, into the soil. The seeds of the plants
can also be treated, if appropriate.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
~ Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 42 -
In the treatment of parts of plants, the active compound concentrations in the use forms
can be varied within a substantial range. They are, in general, between 1 and 0.0001%
by weight, preferably between 0.5 and 0.001% by weight.
S In the treatment of seed, amounts of active compound of from 0.001 to 50 g, preferably
0.01 to 10 g, are generally required per kilogram of seeds.
In the treatment of the soil, active compound concentrations of from 0.00001 to 0.1%
by weight, preferably from 0.0001 to 0.02% by weight, are required at the site of action.
The active compounds according to the invention are also active against plant, hygiene
and stored-product pests, and also, in the veterinary medicine sector, against animal
parasites (ectoparasites), such as ixodid ticks, argasid ticks, scab mites, trombiculid
mites, flies (stinging and sucking), parasitic fly larvae, lice, hair lice, bird lice and fleas.
These parasites include:
From the order of the Anoplurida, for example, Haematopinus spp., Linognathus spp.,
Pediculus spp., Phtirus spp., Solenopotes spp.
From the order of the Mallophagida and the sub-orders Amblycerina and Ischnocerina,
for example, Trimenopon spp., Menopon spp., Trinoton spp., Bovicola spp.,
Werneckiella spp., Lepikentron spp., D~m~lin~ spp., Trichodectes spp., Felicola spp.
From the order Diptera and the sub-orders Nematocerina and Brachycerina, for example,
Aedes spp., Anopheles spp., Culex spp., Simulium spp., Eusimulium spp., Phlebotomus
spp., Lutzomyia spp., Culicoides spp., Chrysops spp., Hybomitra spp., Atylotus spp.,
Tabanus spp., Haematopota spp., Philipomyia spp., Braula spp., Musca spp., Hydrotaea
spp., Stomoxys spp., Haematobia spp., Morellia spp., Fannia spp., Glossina spp.,Calliphora spp., Lucilia spp., Chrysomyia spp., Wohlfahrtia spp., Sarcophaga spp.,
Oestrus spp., Hypoderma spp., Gasterophilus spp., Hippobosca spp., Lipoptena spp. and
Melophagus spp.
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 43 -
From the order of the Siphonapterida, for example, Pulex spp., Ctenocephalides spp.,
Xenopsylla spp. and Ceratophyllus spp.
From the order of the Heteropterida, for example, Cimex spp., Triatoma spp., Rhodnius
spp. and Panstrongylus spp.
From the order of the Blattarida, for example, Blatta orientalis, Periplaneta americana,
Blattela germanica and Supella spp.
From the sub-class of the Acaria (Acarida) and the orders of the Meta- and
Mesostigmata, for example Argas spp., Ornithodorus spp., Otobius spp., Ixodes spp.,
Amblyomma spp., Boophilus spp., Dermacentor spp., Haemophysalis spp., Hyalomma
spp., Rhipicephalus spp., Dermanyssus spp., Raillietia spp., Pneumonyssus spp.,
Sternostoma spp. and Varroa spp.
From the order of the Actinedida (Prostigmata) and Acaridida (Astigmata), for example
Acarapis spp., Cheyletiella spp., Ornithocheyletia spp., Myobia spp., Psorergates spp.,
Demodex spp., Trombicula spp., Listrophorus spp., Acarus spp., Tyrophagus spp.,
Caloglyphus spp., Hypodectes spp., Pterolichus spp., Psoroptes spp., Chorioptes spp.,
Octodectes spp., Sarcoptes spp., Notoedres spp., Knemidocoptes spp., Cytodites spp. and
Laminosioptes spp.
They have outstanding activity for example against Musca domestica and Lucilia
cuprina larvae.
The active compounds usable according to the invention are also suitable for controlling
arthropods which attack agricultural livestock, such as, for example, cattle, sheep, goats,
horses, pigs, donkeys, camels, buffalo, rabbits, chickens, turkeys, ducks, geese, honey
bees, other domestic ~nim~l~, such as, for example, dogs, cats, cage birds, aquarium
fish, and so-called experimental ~nim~ such as, for example, hamsters, guinea-pigs,
rats and mice. By controlling these arthropods, it is intended to reduce mortality and
decreased performance (in meat, milk, wool, hides, eggs, honey and the like), so that
more economical and simpler animal keeping is made possible by using the active
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 44 -
compounds according to the invention.
In the veterinary sector, the active compounds usable according to the invention are
used in a known manner by enteral ~lmini~tration, for example in the form of tablets,
capsules, drinks, drenches, granules, pastes, boluses, the feed-through method,
suppositories, by parenteral ~lmini~tration, such as, for example, by means of injections
(intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous, intraperitoneal and the like), implants, by
nasal application, by dermal ~lmini~tration, for example in the form of dipping or
bathing, spraying, pouring-on and spotting-on, washing, ~lnctin~, and with the aid of
shaped articles which comprise active compound, such as collars, ear tags, tail marks,
limb bands, halters, marking devices and the like.
When ~llmini~tered to livestock, poultry, domestic ~nim~ and the like, the active
compounds can be used as formulations (for example powders, emulsions, flowables)
which comprise the active compounds in an amount of 1 to 80% by weight, either
directly or after dilution by a factor of 100 to 10,000, or they may be used in the form
of a chemical bath.
The preparation and the use of the active compounds usable according to the invention
is illustrated by the examples below.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 45 -
P~eparation Examples
Example 1:
N~ o ~~
A solution of 6.5 g (39.6 mmol) of 4-t-butylbenzyl alcohol and 15 ml of triethylamine
in 100 ml of toluene is admixed with 5.5 g (33.8 mmol) of 4-methyl-1,2,3-thi~ 7O1e-
5-carbonyl chloride and stirred at 100~C for 18 hours. After cooling, the reaction
mixture is admixed with water. The organic phase is separated off, dried over
magnesium sulphate and evaporated. The oil that remains is subjected to a Kugelrohr
distillation. 6.7 g (68% of theory) of 4-t-butylbenzyl 4-methyl-1,2,3-thi~ 7ole-S-carboxylate are obtained as an oil of boiling point 200~C at 0.1 mbar.
Example 2:
Il ~" S~
A solution of 4 g (22.2 mmol) of 4-t-butylbenzenethiol and 10 ml of triethylamine in
60 ml of toluene is admixed with 3.5 g (21.5 mmol) of 4-methyl-1,2,3-thi~ 7O1e-
5-carbonyl chloride and stirred at 100~C for 18 hours. After cooling, the reaction
mixture is admixed with water. The organic phase is separated off, dried over
magnesium sulphate and evaporated. The oil that remains is subjected to a Kugelrohr
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 46 -
distillation. 4.0 g (61% of theory) of 4-t-butylbenzyl 4-methyl-1,2,3-thi~ 7O1e-5-thiocarboxylate are obtained as a yellow oil of boiling point 210~C at 0.1 mbar.
Similarly to Examples 1 and 2, and according to the procedures in the description, the
compounds listed in Table 1 below are obtained.
N~
o
Table 1:
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
3 -C3H7 ~ ~c2Hs bp: O.lmb
90~C
4 -C6Hs 0 \ ~Hc3H )lH NMR
3 7,89-7,27 (9H);
CH
3 5,31; 1,33 (9H)
-CH3 O ~o~ ~, bp: O,lmb
~0~ 2200C
6 -CH3 ~--~--~Hc3H )IH NMR
~/ CH3 4,54 (2H); 3,04
(2H); 1,31 (9H)
7 -CH3 ~ \ ~ bp: Olmb
-- \=/ 190~C
~ CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 47 -
Ex. Rl Q R2 phys. data
No.
8 -CH3 O Cl )lH NMR
5,52 (2H); 7,58-
F J~ 7,21 (3H)
9 -CH3 O \~O~O~ )lH NMR
33; 7,38-6,98
(9H)
-CH3 O H3C )lH NMR
~CH3 3,09 (2H); 4,43
~J (2H); 2,37 (6H);
H3C 6,88 (2H); 2,26
(3H)
11 -CH3 O ~, bp: 0., mb
180~C
~/--OCF3
12 -CH3 ~ / ~ ~ H~< lbpgo 'Cb
13 -CH3 o ~S~ bp: 0, mb
~CI 190~C
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- I,e A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 48 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
14 -CH3 O CH3 o )lH NMR
~N ~CI 4,76 (2H); 5,96-
1~ \~ 5,83 (2H); 1,37
J O (3H)
-CH3 O CH3 bp: 0 ~ mb
/~CH3
CH3
16 -CH3 O CH3 o )lH NMR
4,74 (2H); 1,34
~_ ~N--C2H5 (3H)
o
17 -CH3 O ~, )lH NMR
W~ 5,38 (2H); 7,49
(4H)
18 -CH3 o ~CI )lH NMR
W~CI 5,39 (2H); 7,79-
7,47 (3H)
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 49 -
Ex. Rl Q R2 phys. data
No.
19 -CH3 O Cl )lH NMR
5,43 (2H); 7,47-
~CI 7,29 (3H)
-CH3 ~ ~,~ bp: 0.l mb
W~OCH3 200~C
21 -CH3 O I )lH NMR
C~ 'CI
22 -CH3 ~ ~ )lH NMR
ll 5,52; 7,72 (lH);
CI~CF3 7,58 (2H)
23 -CH3 O F )lH NMR
~F 5,55 (2H)
F~CF3
24 -CH3 ~ ~,~CI bp: o I mb
W\OCF3 190~C
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 50 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
-CH3 O F )lH NMR
~F 5,48 (2H)
F /~--' F
26 -CH3 O ~ mp.: 101~C
W' NO2
27 -CH3 O ~ )lH NMR
5,43 (2H); 7,68-
~--CF3 7,46 (4H)
28 -CH3 O ~, bp: 0, mb
~CH3 170~C
29 -CH3 ~ ~ ~H, bp 0, mb
-CH3 ~ H3C )lH NMR
\ ~ 1,50; 5,50 (lH);
\~/ 4,12 (2H); 7,32-
6,89
31 -CH3 O ~ OCF3 bp: 0 l mb
~ 190~C
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 51 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
32 -CH3 O ~Br bp: 0, mb
~\OCF3 200~C
33 -C2Hs 0~"~o~ bp: 02mb
W W 210~C
34 -C2H5 0 ~ ~CcHHc3~H3 2bO0~~Cmb
-CH3 O ~ N~CF3 ~)lH NMR
5,40 (2H); 8,28-
Cl 7,21 (6H)
36 -C3H7 O ~CHC3H3 200~C
37 -C3H7 O ~,~ bp: 02mb
W~OCF3 1 80~C
38 -C3H7 ~ /\~ bp: 0.2 mb
W'CI 190~C
39 -CH3 O ICH3 bp: 0, mb
/\~ CH3 1 50~C
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 52 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
-C6H5 O ICH3 )lH NMR
/\~ CH3 3,65; 2,57; 2,35
(6H)
41 -C3H7 O ICH3 bp: 0.l mb
/\~ CH3 160~C
42 -CH3 OH3C CH )lH NMR
~ ~ 4,88 (lH); 0,73
43 -CH3 OH3C CH3 bp: o.l mb
210~C
3 CH3
44 -CH3 O ~O~ 2bP00~~Cmb
-CH3 OH3C CH3 bp: 0 ~ mb
/ C2Hs 180~C
,~
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 53 -
Ex. R' QR2 phys. data
No.
46 -CH3 O~~~ )lH NMR
W'cl 4,68 (2H); 4,27
(2H); 7,27-7,24
(2H); 6,86-6,83
(2H)
47 -CH3 O /\O~CH2F )lH NMR
CH2F 4,51 (2H); 3,98
(2H); 4,6 (2H);
4,45 (2H)
48 -CH3 O /~o~CF3 JlH NMR
4,52 (2H); 3,96
(2H); 3,93 (2H)
49 -CH3 O ,~ bp: 0, mb
,~ 180~C
-CH3 O IC2Hs )lH NMR
\/~o~N~ 4,48 (2H); 3,74
(2H); 3,50 (2H);
3,66 (2H); 7,21-
6,64 (SH); 1,14;
2,39
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
~ Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 54 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
51 -CH3 ~ ~~~ )lH NMR
2H); 4,35 (2H);
COOCH3 3 89; 8,01 (2H);
6,94 (2H)
52 -CH3 O ~O~ ~lH NMR
l~ 4,51 (2H); 3,78
(2H); 4,59 (2H)
53 -CH3 o ~O~CF3 )lH NMR
4,72 (2H); 4,34
(2H)
54 -CH3 O CH3 )lH NMR
CH3 7,46 (2H); 7,13
CH3 (2H); 1,34 (9H)
-CH3 O ~O~ mp.: 119~C
56 -CH3 O ~3 C4Hg-tert. , mp.: 161 ~C
57 -CH3 O ~ ~lH NMR
' 7,29-7,04 (7H)
CH3 CH3
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 55 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
58 -CH3 O F )IH NMR
_ ~ 7,49-6,84 (3H)
F
59 -CH3 O ~3CHO, mp.: 99-100~C
-CH3 O ~ ~ mp.: 91~C
61 -CH3 O H3C,~CH3 )lH NMR
~N~ 4,45; 4,95 1 09
Cl (2H)
62 -CH3 O ~ mp.: 91~C
63 -CH3 O ~= ~ mp.: 56-57~C
~Y
H3C CH3
64 -CH3 O ~ N~ )IH NMR, 2,36
~ \ ~ I J (2H); 3,02 (3H)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 56 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
-CH3 O ~3, ~CI mp.: 120-121~C
66 -CH3 O ~ mp.: 81~C
~CHO
67 -CH3 O ~O ~ mp.: 166-167~C
68 -CH3 O = )lH NMR
\~ 2,90 (3H); 5,02
(2H)
69 -CH3 O CH(CH3)2 )lH NMR
~o~ 2,93 (3H); 4,02
~/ (2H); 4,68 (2H)
CH(cH3)2
-CH3 O ~~ )lH NMR
\~/ 2,87 (3H); 4,17
(2H); 4,49 (2H)
71 -CH3 ~ \ /~ )lH NMR
~/ 2,88 (3H); 4,24
(2H); 5,63-5,68
(2H)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 57 -
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
72 -CH3 O Cl mp.: 35~C
\~CI
73 -CH3 O CH3 mp.: 55~C
~0~
C(CH3)3
74 -CH3 O CH3 mp.: 44~C
/~~\~CI
CH3
-CH3 O CF3 )lH NMR
2,94 (3H); 3,14
\~/ (2H); 4,57 (2H)
76 -CH3 O CF3 )lH NMR
1,71 (3H); 2,96
CH3\~/ (3H); 6,14 (lH)
77 -CH3 O CF3 )lH NMR
/~ 2,97 (3H); 4,95
(lH)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 58 -
Ex. R' Q R~ phys. data
No.
78 -CH3 ~ CH3 )lH NMR
\~ ~ 1,81 (6H); 2,30
CH3 N--CH3 (6H); 2,96 (3H);
CH3 3,29 (2H)
79 -CH3 O CF3 )lH NMR
2,98 (3H); 4,19
C2H5 (2H); 5,40 (1 H)
-CH3 O CH3 mp.: 38-40~C
~~~
81 -CH3 ~ /~~'C2H )lH NMR
O 1,31 (3H); 3,00
(3H); 4,28 (2H);
4,86 (2H)
82 -CH3 O CH3 )lH NMR
~3OCH3 2,77 (3H)
CH3
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
59
Ex. R' Q R2 phys. data
No.
83 -CH3 O fi~ mp.: 106~C
-CH2--CH2 0~
~<
O--CH2
c~CI
84 -CH3 O F bpo Imb 200~C
-CH--CH2 O~
CH3 F
-CH3 O ~ bpo,mb: 210~C
-CH--CH2 O~
CH3 C4Hg-tert
86 -CH3 O ~ bpo,mb: 200~C
- CH--CH2 O ~ OCF3
CH3
*) The lH NMR spectra were recorded in deuterochloroform (CDC13) or hexa-
deuterodimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO-d6) using tetramethylsilane as internal standard.
Stated is the chemical shift as ~ value in ppm for the radical R2.
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 60-
Use Examples:
Example A
Pyricularia test (rice) / protective
Solvent: 12.5 parts by weight of acetone
Emulsifier: 0.3 parts by weight of alkylaryl polyglycol ether
To produce a suitable preparation of active compound, 1 part by weight of activecompound is mixed with the stated amount of solvent and the concentrate is diluted
with water and the stated amount of emulsifier to the desired concentration.
To test for protective activity, young rice plants are sprayed with the active compound
preparation to run off point. S days after the treatment, the plants are inoculated with
an aqueous spore suspension of Pyricularia oryzae. The plants are subsequently placed
in a greenhouse at 100% relative atmospheric humidity and 25~C.
The extent of the disease is evaluated 4 days after the inoculation. 0% means anefficacy which corresponds to that of the control, while an efficacy of 100% means that
no infection is observed.
In this test, the compounds listed in Examples 9, 17-19, 21-25, 29, 30, 32, 34 and 35
exhibit, at an active compound concentration of 0.025% by weight in the spray liquor,
an efficacy of at least 70%.
. - CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 61 -
Table A
Pyricularia test (rice) / protective
Active compound Active compoundEfficacy in %
concentration in the
spray liquor in %
Accordin~ to the invention:
0,025 70
o~:3
~0~
S~
N~N~ CH3
(9)
~_,~CI 0,025 80
N~N CH3
(17)
~ /~CI 0,025 70
S Cl
N~N~--CH
(18)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- - 62 -
Table A (continued)
Pyricularia test (rice) / protective
Active compound Active compound Efficacy
concentration in the in %
spray liquor in %
/~ 0,025 90
N~N CH3
(19) Cl
0,025 80
o~O~ ~3Cl
S~
N~N CH3
(21)
Cl
~_ ~) CF3 0,025 80
N~N CH3
(22) F F
~_ CF3 0,025 80
N~N CH3
(23)
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 63 -
Table A (continued)
Pyricularia-Test (rice) / protective
Active compound Active compound Efficacy
concentration in the in %
spray liquor in %
Cl
~ ,/~O~CF3 0,025 70
N~N CH3
(24) F F
~_ ~ F 0,025 70
N~N CH3
(25)
~ O o ~ C(CH3)3
S~ 0,025 80
N~N CH3
(29)
CH3 0,025 70
S~O ~~
N~N CH3
(30)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 64 -
Table A (continued)
Pyricularia-Test (rice) / protective
Active compound Active compound Efficacy
concentration in the in %
spray liquor in %
~or~~~
N~N CH3
(32)
C(CH3)3 0,025 90
N~N CH3
(34)
CF3
Nh~ 0,025 90
~0/ {~~ Cl
N~N CH3
(35)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 65 -
Example B
Pynculana test (nce) / systemic
Solvent: 12.5 parts by weight of acetone
Emulsifier: 0.3 parts by weight of alkylaryl polyglycol ether
To produce a suitable prepalalion of active compound, 1 part by weight of activecompound is mixed with the stated amount of solvent and the concentrate is diluted
with water and the stated amount of emulsifier to the desired concentration.
To test for systemic properties, 40 ml of the active compound plepal~lion are poured
onto standard soil in which young rice plants were grown. 7 days after the treatment,
the plants are inoculated with an aqueous spore suspension of Pyricularia oryzae. The
plants then remain in a greenhouse at a temperature of 25~C and a relative atmospheric
humidity of 100% up to the evaluation.
The extent of the disease is evaluated 4 days after the inoculation. An efficacy of 0%
means that the infection corresponds to that of the control and an efficacy of 100%
means that no infection is observed.
In this test, the compounds listed in Examples 9, 17, 18, 22-25, 29, 30, 32 and 35
exhibit, at a concentration of 100 mg of active compound per 100 cm2, an efficacy of
more than 65%.
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
- Le A 31 406-Foreign Countries
- 66 -
Table B
Pyricularia test (rice) / systemic
Active compounds Application rate inEfficacy
mg of active compoundin %
per 100 cm2
Accordin~ to the invention:
0~
,~ \~/ 100 67
~0/~=~
S~
N~N ~ CH3
(9)
~ o/~3CI
S~ 100 90
N~N~--CH3
(17)
~ ~ ~ Cl 100 90
N~N CH3
(18)
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 67 -
Table B (continued)
Pyricularia test (rice) / systemic
Active compounds Application rate inEfficacy
mg of active compoundin %
per 100 cm2
~_ CF3 100 70
N~N CH3
(22)
S ~ ~ F 100 70
N~N CH3
(23)
_~ O,CF3 100 80
N~N CH3
(24)
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 68 -
Table B (continued)
Pyricularia test (rice) / systemic
Active compounds Application rate inEfficacy
mg of active compound in %
per 100 cm2
O ~ 100 80
S F F
N~N~--CH3
(25)
C(CH3)3 100 90
N~N CH3
(29)
CH3
~_o> \o~ 100 90
N~N CH3
(30)
- . CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 69 -
Table B (continued)
Pyricularia test (rice) / systemic
Active compounds Application rate in Efficacy
mg of active in %
compound
per 100 cm2
O~CF3 100 80
N~N CH3
(32)
CF3
100 80
~ ~_C~o~cl
N~N CH3
(35)
. CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 70 -
Example C
Uncinula test (grapevine) / protective
Solvent: 47 parts by weight of acetone
Emulsifier: 3 parts by weight of alkylaryl polyglycol ether
To produce a suitable ~ rdldlion of active compound, 1 part by weight of active
compound is mixed with the stated amounts of solvent and emulsifier, and the
concentrate is diluted with water to the desired concentration.
To test for protective activity, young plants are sprayed with the active compound
preparation to run off point. After the spray coating has dried on, the plants are dusted
with conidia of the fungus Uncinula necator. The plants are subsequently placed in a
greenhouse at 23 to 24~C and at a relative atmospheric humidity of about 75%.
Evaluation is carried out 14 days after the inoculation. An efficacy of 0% means that
the infection corresponds to that of the control, and an efficacy of 100% means that no
infection is observed.
In this test, the active compound listed in Example 11 exhibits, at an active compound
concentration of 25 ppm in the spray liquor, an efficacy of more than 80%.
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 71 -
Table C
Uncinula test (grapevine) / protective
Active compound Efficacy in % at an active compound
concentration of 25 ppm in the spray
liquor
Accordin~ to the invention:
~ ~ CF3
N~N CH3
(11)
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 72 -
Example D
Test with flies (Musca domestica)
Test ~nim~ Musca domestica, Reichswald strain (OP, SP, carbamate-resistant)
Solvent: 35 parts by weight of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether
Emulsifier: 35 parts by weight of nonylphenol polyglycol ether
To produce a suitable formulation, three parts by weight of active compound are mixed
with seven parts of the abovementioned solvent-emulsifier mixture, and the resulting
emulsion concentrate is diluted with water to the respective desired concentration.
2 ml of this active compound preparation are pipetted onto filter paper dishes
(0 9.5 cm) situated in Petri dishes of corresponding size. After the filter discs have
dried, 25 test animals are transferred into the Petri dishes and covered.
The activity of the active compound preparation is determined after 24 hours. 100%
means that all the flies have been killed; 0% means that none of the flies have been
killed.
In this test, the active compounds listed in Examples 24, 27 and 32 exhibit, at a
concentration of 1000 ppm in the active compound preparation, an efficacy of 100%.
- CA 02239710 1998-06-04
- Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 73 -
Table D
Test with flies (Musca domestica)
Active compound Active compound Efficacy in %
concentration in the
plepalalion in ppm
Accordin~ to the invention:
Cl 1000 100
O\CF3
N~N CH3
(24)
N~N CH3
(25)
Br
~ ~ ~ 1000 100
S~
N~N /'--CH
(32)
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
-
Le A 31 406-Foreign Countries
- 74 -
Example E
Blowfly lan~ae test / Development-inhibitory action
Test ~nim~ Lucilia cuprina larvae
Solvent: 35 parts by weight of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether
Emulsifier: 35 parts by weight of nonylphenol polyglycol ether
To produce a suitable preparation of active compound, three parts by weight of active
compound are mixed with seven parts by weight of the abovementioned mixture, andthe resulting emulsion concentrate is diluted with water to the respective desired
concentration.
About 20 Lucilia cuprina res. larvae are introduced into a test-tube which contains about
1 cm3 of horse meat and 0.5 ml of the active compound preparation. After 48 hours, the
activity of the active compound preparation is determined. The test-tubes are transferred
in a beaker having a bottom covered with sand. After a further 2 days, the test-tubes are
removed and the pupae are counted.
The activity of the active compound prepalalion is deterrnined by the number of the
flies that have hatched after 1.5 times the development time of an untreated control.
100% means that none of the flies have hatched; 0% means that all the flies havehatched normally.
In this test, the active compound listed in Example 32 exhibits, at a concentration of
1000 ppm in the active compound preparation, an efficacy of 100%.
CA 02239710 1998-06-04
Le A 31 406-Forei~n Countries
- 75 -
Table E
Blowfy larvae test / development inhibitory action
Active compound Active compound Efficacy
concentration in the in %
preparation in ppm
Accordin~ to the invention:
sr 1000 100
S ~ ~/~ CF3
N~N CH3
(32)