Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02240889 1998-06-17
PAVEMENT COMPOSITE MATERIAL WITH ELASTIC SURFACE LAYER
AND PRODUCTION METHOD THEREOF
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
FIELD OF THE INVENTION:
The present invention relates to a pavement composite
material, more specifically to a pavement composite material
having elasticity and permeability, effectively utilizing wastes
of rubber or plastic, and production method thereof.
DESCRIPTION OF THE RELATED ART:
As a known example of a pavement composite material
having elasticity and permeability, one comprising an upper
layer material produced by the compression molding of rubber or
plastic chips as the aggregate and a thermosetting urethane
resin as the binder, and a lower layer material made from a
permeable concrete after the solidification molding, bonded with
each other by an epoxy adhesive, can be presented.
However, since the upper layer material and the lower
layer material are bonded after the solidification molding in
the production of such a conventional pavement composite
material, a problem is involved in that a sufficient adhesive
force cannot be obtained between a rugged lower layer material
surface to be bonded and the upper layer material, resulting in
peel-off.
A method of applying an adhesive on the rugged surface
of the lower layer material so as to improve the adhesive force
by the fixing effect can be considered. However, due to the
need of a large amount of the adhesive, an adhesive layer is
formed between the upper layer material and the lower layer
material, and thus a problem is involved in that the
permeability is lost even though the adhesive force can be
improved.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, an
-1-
CA 02240889 2001-07-20
object of the present invention is to provide a pavement
composite material having elasticity and permeability,
where an upper layer having rubber or plastic chips as the
aggregate and a lower layer material made from a permeable
concrete are strongly bonded without losing the
permeability, and a production method thereof.
A pavement composite material of the present invention
comprises a lower layer material made from a permeable
concrete, and an upper layer material comprising a mixture
of 50 to 90% by weight o.f rubber or plastic chips having a
1.0 mm to 10.0 mm particle size and 50 to loo by weight of
a thermosetting resin, bonded via a thin adhesive layer
having a 50 to 100 cent_Lpoise viscosity. A production
method thereof comprises a step of applying an adhesive
having a 50 to 100 centipoise viscosity on a permeable
concrete block after solidification molding, a step of
accommodating the concrete block in a heat press mold, a
step of injecting a mixture of 50 to 90o by weight of
rubber or plastic chips having a 1.0 to 10.0 mm particle
size and 50 to loo by weight of a thermosetting resin on
the upper surface of the' concrete block applied with the
adhesive, and a step of a heat compression molding after
clamping the heat press mold.
Since the rubber o~_- plastic chips to be used as the
aggregate for the upper :Layer material have a 1.0 to 10.0
mm particle size and the' mixture ratio of the aggregate and
the thermosetting resin is 50 to 90% by weight and 50 to
- 2 -
CA 02240889 2001-07-20
loo by weight respectively, an upper layer having both
strength and permeabilit=y can be obtained.
Further, since the adhesive to be applied on the
surface to be bonded of the lower layer material has a 50
to 100 centipoise visco:~ity and the upper layer material
mixture is placed thereon for the heat compression molding,
a thin adhesive layer having a sufficient adhesion strength
and an appropriate permeable gap can be provided, and thus
a pavement composite material comprising an elastic surface
layer with a permeability and a good adhesion can be
obtained.
- 2a -
CA 02240889 1998-06-17
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a pavement
composite material according to one embodiment of the present
invention, and
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing a production
process of a pavement composite material of the present
invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Embodiments of the present invention will be explained
with reference to the accompanied drawings.
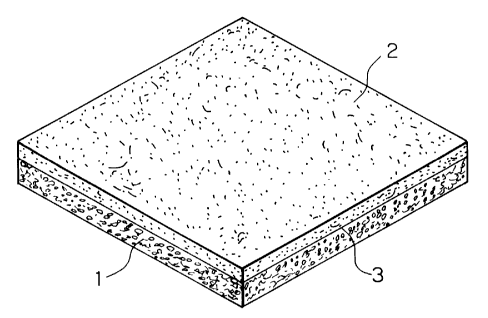
As shown in FIG. 1, a pavement composite material
according to one embodiment of the present invention comprises
an upper layer material 2 integrally bonded onto a lower layer
material 1 made from a permeable concrete block with an adhesive
3. The upper layer material 2 comprises a mixture of 50 to 90
by weight of rubber or plastic chips having a 1.0 to 10.0 mm
particle size and 50 to 10 % by weight of a thermosetting resin.
The adhesive 3 has a 50 to 100 centipoise viscosity. With the
upper layer material 2 and the adhesive 3, an elastic surface
layer is formed with sufficient elasticity and permeability on
the lower layer material 1.
A production method of the pavement composite material
will be explained. After applying the adhesive 3 having a 50 to
100 centipoise viscosity on the upper surface of the lower layer
material 1 made from a permeable concrete block after the
solidification molding with a roll coater, the concrete block is
accommodated in a heat press mold 4 as shown in FIG. 2. A
mixture of 50 to 90 o by weight of rubber or plastic chips
having a 1.0 to 10.0 mm particle size and 50 to 10 % by weight
of a thermosetting resin is injected on the adhesive 3 on the
upper surface of the lower layer material 1 so as to be heat
press-molded for bonding the upper layer material and the lower
layer material integrally.
As mentioned above, since the rubber or plastic chips
-3-
CA 02240889 1998-06-17
to be used as the aggregate for the upper layer material have a
1.0 to 10.0 mm particle size and the mixture ratio of the
aggregate and the thermosetting resin is 50 to 90 o by weight
and 50 to 10 ~ by weight respectively, an upper layer having
both strength and permeability can be obtained.
Further, since the adhesive to be applied on the
surface to be bonded of the lower layer material has a 50 to 100
centipoise viscosity and the upper layer material mixture is
placed thereon for the heat compression molding, a thin adhesive
layer having a sufficient adhesion strength and an appropriate
permeable gap can be provided. According to an experiment, with
an adhesive with a less than 50 centipoise viscosity, it was
learned that the adhesion force was deteriorated. On the other
hand, with an adhesive with more than 100 centipoise viscosity,
the adhesion force was improved, however, an adhesion layer was
formed so as to lose the permeability.
Hereinafter a further specific example will be
described. To the upper surface of a lower layer material 1
made from a permeable concrete block after the solidification
molding using rubbles having a 5 to 10 mm particle size as the
aggregate, 200 g/m2 of an adhesive 3 having a 50 to 100
centipoise viscosity (such as the concrete impregnating adhesion
applying material Bond E200P produced by Konishi Corp.) was
applied with a roll coater. After drying for 60 minutes at an
ordinary temperature, it was accommodated in a press mold 4.
A mixture of 50 to 90 a by weight of rubber chips
having a 1.0 to 10.0 mm particle size obtained by crushing waste
tires and 50 to 10 % by weight of a thermosetting resin (such as
Bandex TT-1221 produced by Dainippon Ink Corp.) was injected
thereon. After flattening the surface, a lid was put on and
bolted. After applying a heat treatment for 10 minutes with a
110 to 150 °C furnace temperature, it was left at a room
temperature for cooling. Then the mold was released.
Accordingly, a pavement composite material comprising
an elastic surface layer having elasticity and permeability with
-4-
CA 02240889 1998-06-17
a sufficient adhesion strength can be obtained utilizing a waste
material such as rubber or plastic.
-5-