Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
1
PROCEDURE AND SYSTEM FOR TIC SETTING UP OF CALLS
The present invention relates to a procedure as defined in the preamble of
claim 1
and to a system as defined in the preamble of claim 10 for the setup of
specially rated calls
between two predetermined subscriptions: Moreover, the invention relates to
the setting up of
a specially rated call between said subscriptions.
Call setup in a telephone network is normally based on a number selection made
by a
calling subscriber, in other words, a calling subscriber selects via his/her
terminal equipment
the subscriber number of a called subscription, on the basis of which the
switchboard and ex
change system of the telephone network connects the calling subscriber with
the called sub-
scriber. In the case of this kind of normal call setup, the calling subscriber
pays fox the calls
he/she has made a price in accordance with the general tariffs valid at the
time.
In the existing telephone network, a known practice is to use service numbers
com
mon to all callers, for instance the so-called free numbers starting with 9800-
, 0800- or 9700-,
and the chargeable service numbers starting with 0700-, 9600- or 0600-, and
e.g. the short
numbers used for number inquiries. However, such service numbers are not
actual subscriber
numbers, but the calls made to these numbers are redirected by the switchboard
and exchange
system of the telephone network to actual subscriber numbers behind the
service numbers.
2o When calling such a number, the calling subscriber does not know the
connected subscriber's
number because the number is changed and the call is redirected in the
telephone network. In
the call setup chain, the service number is a so-called C-number. Calls to
such service num-
bers are usually either free or rated at a price substantially higher than
normal call tariffs.
The object of the present invention is to achieve in the telephone network a
new type
of procedure and system for call control and to meet a need observed recently
in the telecom
munication business for calls especially between certain predeterlninable
subscriptions. A
further object of the present invention is to present a procedure that allows
said calls to be set
up using a predetermined call number common to all subscribers, on the basis
of which the
calls can also be assigned a price below normal tariffs. Such calls could be
e.g. calls made
3o within a family or a small enterprise e.g. between a wired network
subscription and and/or an
optional number of mobile subscriptions. In this case, the specially rated
telephone communi-
cation would comprise calls from a specified wired network subscription to a
specified num-
ber of mobile telephone subscriptions and vice versa, calls between specified
mobile tele-
phone subscriptions and also between wired network subscriptions.
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
2
A further object of the invention is to achieve a service in which the
customer
is able to define a pair or set of desired subscriptions between which the
calls are
invoiced at a price below the normal tariff
As for the features characteristic of the present invention, reference is made
to the claims.
In the procedure of the invention, a specially rated call, generally cheaper
than the normal tariff, is set up between two subscriptions. According to the
inven-
tion, the subscriptions are predetermined and the procedure is implemented as
fol-
lows. First, a common call number differing from the subscriber number is
reserved
to for all subscriptions. The common call number may consist of two parts and
have the
form ABCDER, where the prefix part ABCDE is a digit series common to all,
while R
is an integer in the set [0, 1, ..., I~]. Further, a subscriber number pair
between two
subscriber numbers is formed, between which a specially rated call is set up,
and the
number pair is stored by means of a storage device. The number pair can
preferably be
stored in a suitable database or an equivalent component in the telephone
network.
After this, calls to the common call number are directed to a checking device,
by
means of which the second subscriber number corresponding to the subscriber
number
of the calling subscription is determined. Finally, the call is connected to
the subscrip-
tion corresponding to the second subscriber number. Finally, invoicing data
deter-
2o mined on the basis of the common call number is given to the invoicing
system, so
that a price preferably lower than the normal call price will be charged for
the call.
The advantages of the present invention as compared with prior art include
the fact that the system does not require any substantial system changes in
the tele-
phone network. In addition, calls between predetermined subscriptions can be
rated
according to a special tariff and the charges can be easily and flexibly
included in the
normal invoicing.
Moreover, the invention allows the same tariffs to be applied to calls in
either
direction, i.e. from a mobile station to a wired network subscription or vice
versa, or,
on the other hand, the price may be different depending on direction.
Furthermore, the
3o invention makes it possible to offer the customer a specially rated data
connection for
communucation between a pair or set of computers.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the pair of subscriber
numbers to be considered is selected on the basis of a suffix part of a common
call
number. Further, subscriber numbers entitled to specially rated calls are
stored in a
database and the calling subscriber's right to specially rated calls is
verified via refer-
ence to the database on the basis of the calling subscriber's subscriber
number.
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
3
There are several alternative solutions for forming a subscriber number pair.
A subscriber number pair can be established between a wired network
subscription
and a mobile communications network subscription. In addition, a subscriber
number
pair can be established between a wired network subscription and several
mobile
communications network subscriptions, in which case the subscriber number pair
is
assigned a separate common call number in which the sufl'lx part determines
the
subscriber number pair to be considered so that a call made from the wired
network
subscription is directed on the basis of the suffx part of the common call
number to
the subscription corresponding to the mobile subscriber number defined in the
sub-
1o scriber number pair and a call made from each mobile subscriber number is
directed to
the subscriber number corresponding to the wired network subscriber number
defined
in the subscriber number pair. This makes it possible to form a kind of
specially rated
group in which a specially rated call can be made from a wired network
subscription
to several mobile network subscriptions and from each mobile subscription in
the
i5 group to one and the same wired network subscription. Furthermore, it is
possible to
establish a subscriber number pair among a set comprising a wired network
subscriber
number and a plurality of mobile network subscriber numbers so that a call
made from
any one of the subscriber numbers to the common call number is directed on the
basis
of the suffix part of the common call number to the subscription corresponding
to the
2o second subscriber number corresponding to the calling subscriber number in
the set of
subscriber numbers. This again provides the possibility to form a kind of
specially
rated network comprising a number of subscriptions which can be selected
either from
a wired network or from a mobile communications network and between which it
is
possible to establish specially rated number pairs according to free
selection.
25 Moreover, the present invention relates to a system for setting up a
specially
rated call between two predetermined subscriptions in a telephone network,
which
may comprise a mobile communications network, a wired telephone network, some
other telecommunications network or a combination of these, between two
subscrip-
tions. According to the invention, the system comprises a storage device in
which, in
3o addition to the predetermined subscriber number pairs and the corresponding
common
call number, it is also possible to store a Iist of subscriber numbers
entitled to specially
rated calls. In addition, according to the invention, the system comprises
means for
receiving the subscriber number of the calling subscription in connection with
the
setup of a call to the common call number and for determining the second
subscriber
35 number corresponding to the calling subscriber number on the basis of the
number
pair data stored in the storage device. The telephone network preferably
comprises an
intelligent network switching centre, in which case the means for receiving
the sub-
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
4
scriber number of the calling subscription and determining the subscriber
number pair
corresponding to the subscriber number are disposed in the intelligent network
switching centre.
In. a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the storage device com-
prises a first database which contains the subscriber numbers entitled to
specially rated
calls, and a second database which contains the subscriber number pairs
between
which a specially rated call is to be set up when the common call number is
called.
In an embodiment of the invention, the intelligent network switching centre is
disposed in a mobile communications network, in which case a call to the
common
lo call number is directed to the intelligent network switching centre of the
mobile
communications network. On the other hand, the intelligent network switching
centre
may be disposed in the wired telephone network, in which case a call to the
common
call number is directed to the intelligent network switching centre of the
wired tele-
phone network. Moreover, the system comprises an invoicing system, which is
con-
nected to the intelligent network switching centre or some other suitable
component,
such as a telephone exchange.
In an embodiment of the system, one of the databases contains a number of
common call numbers and the subscriber number pair corresponding to each
common
call number so that the first subscriber number in each subscriber number pair
is the
2o same wired network subscriber number and the second subscriber number is a
mobile
communications network subscriber number. Reference is here made to the above
description of a specially rated group.
In another embodiment, the other database contains a number of common
call numbers and the subscriber number pair corresponding to each common call
number so that the first and second subscriber numbers in each subscriber
number pair
are selected from a set of subscriber numbers comprising a wired network
subscriber
number and a mobile communications network subscriber number. Reference is
here
made to the above description of a specially rated group.
As a summary of the above, let the following be noted. When the number of
3o subscriptions per customer is limited to two, the common call number for
all custom
ers is the same, e.g. 020100. When this number is dialled, the call is
directed to the
wired network subscription specified in the subscriber number pair when the
call is
made from a mobile station, and vice versa. When the number of subscriptions
con
nected to the system by a customer is greater than two, the common call number
comprises a prefix part which is the same for all customers and on the basis
of which
the telephone network exchange recognizes the service call of intelligent
network calls
and specially rated calls, and a suffix part which is an integer and which,
via the
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/230$1 PCT1FI96/00672
intelligent network, determines the desired individual subscription among the
sub-
scriptions selected to be included in the system by the customer. In this case
it is
preferable that the suffix part indicating the wired network subscription is 0
and the
sui~x part identifying other subscriptions is an integer selected from the set
[0, l, ...,
s NI.
A service as achieved by the procedure and system of the invention can be
included in the service agreement made with the customer. The dealer selling
the
subscription may also open the service via his/her terminal or by calling the
teleopera-
tor's service number or customer service via an automatic apparatus
recognizing tone
l0 frequency signals or via a corresponding customer server. A service ordered
via a
service number and an automatic apparatus is ready for use on the next
weekday,
provided that the order has been made from the subscription to which the
service is to
be added, because in this way the subscriber number or identity or A-ID of the
sub-
scription in question can be signalled. For the sake of clarity, let it be
stated that an A-
TI7 is always given in mobile communication and in the wired network when the
subscription is digital. This limitation encountered in the wired network is
the only
restriction to the connection of the service and if the subscription pair or
set desired
by the customer includes such a wired network subscription which does not
signal an
A-ID, such a subscription can only function as a subscription receiving calls
in the
2o system of the invention. Having joined the system, a customer may change
the num-
bers in the pair or set of subscriptions he/she has selected or cancel it by
making a call
to the system service number.
In the following, the invention is described in detail by the aid of a few em-
bodiment examples by refernng to the attached drawings, in which
Fig. 1 presents a diagram representing a system according to the invention,
Fig. 2 presents a diagram representing a control arrangement according to
the invention for directing calls to an intelligent network; and
Fig. 3 represents a method according to the invention for the storage of
number pairs.
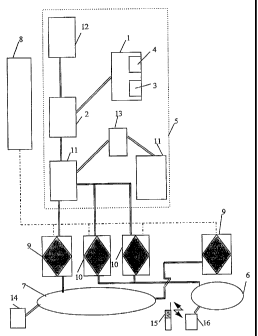
The system presented in Fig. 1 comprises a public telephone network 7,
PSTN (Public Switched Telecommunications Network) and a number of telephone
exchanges 9, PTX (Public Telephone Exchange) connected to it. In addition, the
system comprises a mobile communications network 6, MCN (Mobile Communica-
tions Network), and a number of mobile services switching centres 10, MSC
(Mobile
Services Switching Centre) connected to it. An essential part of the system is
an
intelligent network 5, IN (Intelligent Network), which is connected to the
public
telephone network 7 and/or to the mobile communications network 6 e.g. via an
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
6
interconnecting network. The intelligent network 5 comprises, e.g. in
accordance with
the CCITT definition (IN Conceptual Model) a service switching point 11, SSP
(Service Switching Point), through which the intelligent network is connected
to the
public telephone network 7 PSTN or 6 MCN, a service control point 2 SCP
(Service
s Control Point) which contains the Logic associated with the control of the
services, i.e.
the service control functions, and which is usually also provided with a
service data-
base 1 SDF (Service Data Function) which contains information including the
cus-
Comer and network data needed for the services, a service management system 12
SMS (Service Management System) which contains the required functions for the
to creation and control of services, and an intelligent peripheral device or
peripheral
computer 13.
The SSP 11 is functionally a part of a wired network or mobile communica-
tions network exchange or it is integrated with an exchange PTX 9 or MSC 10.
When
a caller makes a call to a common call number ABCDER, which constitutes an
essen-
15 tial feature of the present invention, where R is an integer from the set
[0, 1, ..., NJ,
the SSP 11 recognizes an IN need on the basis of the beginning or prefix part
ABCDE
of the called number and transmits an IN request to the other IN components.
Moreover, the SSP 11 contains a service switching function SSF (Service
Switching
Function) and a function CCAF (Call Control Agent Function) associated with
the
2o control of the calling subscriber's selection. Functionally, the SCP 2
controls the
implementation of IN services by issuing commands to other functions,
including SSF,
CCAF, SRF and SDF, as necessary for the service. The SMS 12 contains a service
management point SMP (Service Management Point), a service creation point SCEP
(Service Creation Environment Point), which also comprises a service creation
func-
25 tion SCEF (Service Creation Environment Function) for the definition,
development
and testing of services, and a service management function SMF (Service Manage
ment Function) which is used to control the supply and implementation of
services.
The intelligent peripheral device or computer IP 13 contains special auxiliary
func
tions SRF (Special Resource Function) used to implement e.g. voice
announcements,
3o voice recognition and speech processing.
In the following, the invention is described by the aid of a preferred embodi-
ment by referring to Fig. 1. In this embodiment, the calling master
subscription is a
wired network 7 subscription and the receiving slave subscription is a mobile
com-
munications network 6 subscription and vice versa. '
35 Referring to Fig. l, the wired network subscription and the terminal 14 con-
nected to it communicates via a wired connection with a public telephone
exchange
PTX 9, which transmits the calls in the wired network PSTN 7 and further to
other
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCT/FI96/00672
7
telecommunications networks and vice versa. Further, via a base station I6
with a
limited base station area and via a mobile communications network MCN 6, the
mobile station 15 usually communicates with a mobile communications switching
centre MSC 10, which transmits the calls in the mobile communications network
MCN and further to other telecommunications networks and vice versa.
When a caller dials a number in the wired telephone network 7, the sub-
scriber number or identity or A-II? of the calling subscription is fed into
the telephone
network, on the basis of which information the calling subscription can be
unambigu-
ously determined. In a mobile communications network 7, e.g. an authentication
1o centre (AUC or AR), a home location register HLR (Home Location Register)
or a
visitor location register VLR (Visitor Location Register) identifies the
caller or calling
subscriber, and, together with the calling subscriber's subscriber number and
the
dialled number, unambiguous identification data, such as the international
mobile
subscriber identity IMSI, which consists of the mobile subscriber's national
mobile
subscriber identity NMSI and the mobile country code MCC, is fed into the
mobile
communications network. Moreover, the information fed into the network
comprises
the mobile subscriber identification number MSIN, by means of which the mobile
subscriber can be identified within the area of the mobile communications
network,
the temporary mobile subscriber identity TMSI, which is a temporary identifier
as-
2o signed to the mobile subscriber by the visitor location register to allow
identification
of the subscriber, and the international mobile station equipment identity to
allow
identification of the mobile station. The calling subscriber number and the
identifica-
tion data for the calling subscriber and/or the calling subscriber's mobile
station
constitute the calling subscriber identity or A-ID.
In this connection it is to be noted that the creation of invoicing records
and
their input to the invoicing system 8 is usually handled by the telephone
exchanges
PTX 9 or MSC Z 0, and when an intelligent network (IN) architecture is used,
the
selections given, especially selections requiring IN support, are routed via
one or
more intelligent network service switching points I l, to one of which the
telephone
3o exchanges PTX or MSC are connected. It is also to be noted that there is
nothing to
prevent the telephone exchanges PTX 9 or MSC 10 of all or at least the digital
com-
munication systems from being used as service switching points SSP 11.
Furthermore,
an SSP 11 may also function in a telephone network as a router to systems
connected
to or communicating with the telephone network, such as a customer service
system
or CSS, which is usually implemented as a voice service computer CVAP (Central
Voice Application Platform), (not shown).
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/23081 PCTJFI96/00672
8
To join a system according to the invention as a user, the subscriber dials
the
service number of the system via the terminal equipment he/she wants to
include in
the system. When this is done, the system according to the invention is
supplied with E
the calling subscriber identity data or A-ID, which is stored in a first
database SDF 3
in the SCP 2 or in a database equipment 1 capable of data communication with
it.
This database SDF 3 therefore contains the A-ID information for all
subscriptions that
have joined the system.
In response to the calling subscriber identity information, a customer- and/or
calling subscription-specific file or register corresponding to the A-B3 as
shown in
1o Fig. 3 is created in a second database DB 4 in the SCP 2 or in database
equipment I
communicating with it. Preferably the customer-specific subscriber numbers are
stored
in this file or register in the form of a table. Further, Fig. 3 shows a
subscriber number
pair 123456 and 333444 defined as numbers corresponding to each other and
020100
as the common call number for this number pair. In a corresponding manner,
both
1s numbers can be assigned further paired numbers by entering the desired
numbers into
the 0-fields in the table.
The numbers stored in the customer-specific file or register are those sub-
scriber numbers that are intended to form a pair or set of numbers for
specially rated
calls, which means that in addition to the master subscriber number at least
one slave
2o subscriber number is stored in the register. When the number of
subscriptions stored
is two, the common call number for calls from any one of the subscriptions in
the pair
to the other subscription in the pair is always the same and preferably of the
format
ABCDEO, in which case either the dialled number as a whole or its prefix part
AB-
ODE will activate the intelligent network control and the last digit 0 of the
dialled
25 number together with the A-ID given into the network will function as an
inquiry key
and activate a search to find the second number of the pair in the second
database DB
4 in the database equipment I and further under control of the intelligent
network S
cause the call to be connected via the SSP 11 to the subscription
corresponding to the
second subscriber number while at the same the invoicing system 8 is supplied
with
3o invoicing data for the specially rated call.
When the number of customer-specific or small-enterprise-specific subscrip-
tions is more than two, the common call number is of the format ABCDER, where
R
is an integer and dependent on the number of subscriptions to be combined. The
prefix part ABODE of the selection will activate the intelligent network
control 5 and
35 the last selection R together with the A-1D given into the network will
function as an
inquiry key and activate a number search to find the second number of the pair
in the
second database DB 4 in the database hardware and further under control of the
CA 02241107 1998-06-19
WO 97/Z3081 PCT/FI96/00672
9
intelligent network 5 cause the call to be connected via
the SSP 11 to the relevant
subscription while at the same the invoicing system 8 is
supplied with invoicing data
for the specially rated call.
After the user A-ID has been stored in the first database
SDF 3 and after the
s desired subscriber numbers have been stored in the customer-
andJor calling-
subscriber-specific register or file in the second database
DB 4, in which second
database 4 and register the A-ID together with the common
call number functions as a
search key, the system of the invention is ready for use.
When the user calls the prede-
termined common call number via the network exchange PTX
9 or MSC 10, the user
to is identified automatically by the telephone network exchange.
The communication
system takes care of the signalling associated with the
call. In the case of a call be-
tween an intelligent network {IN) exchange 5 and a PTX 9
or MSC 10 exchange, the
signalling follows a protocol consistent with e.g. the SS7,
TUP, ISUP, TCP/IP, X400,
XS00, X25 or similar standard.
15 Referring to Fig. 2, further preferred possibilities of
application of the inven-
tion are now described. A call to the common call number
is directed from the tele-
phone network of the subscriber exchange, either a wired
network 7 telephone ex-
change 9 or a mobile communications network 6 exchange 10,
to which the subscrip-
tion is connected, either using the dialled number directly
or using an intermediate
2o number to be assigned during the call setup, to an intelligent
network 5, which is
connected either to the wired network 51, alternative A,
or to a mobile communica-
tions network 52, alternative B. The intermediate number
may be a prefix added
before the selection given from the calling subscription
or the selection may be re-
placed with a different number. Further, in the intelligent
network element performing
2s the service, the service can be identified either directly
by the selection given or by the
calling subscriber's identity. Moreover, the service can
be so implemented that, when
the call is made from a wired network, the intelligent network
51 connected to the
wired network 7 is used, and correspondingly when the call
is made from a mobile
communications network, the intelligent network 52 connected
to the mobile commu-
3o nications network 6 is used.
The invention is not limited to the embodiment examples
presented above,
but many variations are possible within the framework of
the inventive idea defined by
the claims.