Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2243998 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | BIPOLAR SOI DEVICE HAVING A TILTED PN-JUNCTION, AND A METHOD FOR PRODUCING SUCH A DEVICE |
| (54) French Title: | DISPOSITIF A SEMI-CONDUCTEUR SUR ISOLANT AVEC JONCTION PN INCLINEE ET PROCEDE DE PRODUCTION DE CE DISPOSITIF |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | MARKS & CLERK |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1997-03-05 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1997-09-12 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/SE1997/000377 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 1997033319 |
| (85) National Entry: | 1998-07-22 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In a bipolar semiconductor-on-insulator transistor device (1) comprising an
emitter region (4), a base region (5), a collector region (2) and a collector
contacting region (6) in a semiconductor wafer, e.g. a monocrystalline silicon
wafer (2), on top of an insulator (3), the base-emitter and collector-base
junctions are tilted relative to the interface between the semiconductor wafer
(2) and the insulator (3). The device can be made by anisotropic etching in
order to produce a tilted surface (7) at an edge of the device or equivalently
a V-groove having tilted sidewalls. The base and emitter regions (5, 4) are
then produced by diffusing suitable donor and acceptor atoms into the material
inside the tilted surface. Such a bipolar semiconductor-on-insulator
transistor combines the high speed features of a lateral semiconductor device
and the high voltage features of a vertical semiconductor device.
Dispositif transistor bipolaire (1) à semi-conducteur sur isolant, comprenant une région d'émission (4), une région base (5), une région collectrice (2) et une région de contact de collecteur (6) sur une plaquette semi-conductrice telle qu'une plaquette de silicium monocristallin (2) sur un isolant (3). Les jonctions base-émetteur et collecteur-base sont inclinées par rapport à l'interface entre la plaquette semi-conductrice (2) et l'isolant (3). Le dispositif peut être réalisé par gravure anisotrope pour obtenir une surface inclinée (7) sur un bord du dispositif ou, de manière équivalente, une rainure en V présentant des parois latérales inclinées. Les régions base et émetteur (5, 4) sont ensuite élaborées par diffusion d'atomes appropriés donneurs et accepteurs dans le matériau contenu à l'intérieur de la surface inclinée. Un tel transistor bipolaire à semi-conducteur sur isolant combine les caractéristiques de vitesse élevée d'un dispositif à semi-conducteur latéral et les caractéristiques de tension élevée d'un dispositif à semi-conducteur vertical.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
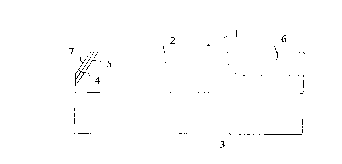
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2002-03-05 |
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2002-03-05 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2001-03-05 |
| Inactive: Single transfer | 1998-12-08 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Classification Modified | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-10-26 |
| Inactive: Courtesy letter - Evidence | 1998-10-06 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 1998-09-28 |
| Application Received - PCT | 1998-09-25 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1997-09-12 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2001-03-05 |
The last payment was received on 2000-03-03
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 1998-07-22 | ||
| Registration of a document | 1998-12-08 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 1999-03-05 | 1999-03-01 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2000-03-06 | 2000-03-03 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| TELEFONAKTIEBOLAGET LM ERICSSON |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| ANDREJ LITWIN |
| TORKEL ARNBORG |