Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
Fl~ rfl~t~T~"~A~ E~.
e~ ttANSLATlON
DR. KARL THOMAE GMBH Case 5/1203-FL
D-88397 BIBERACH Foreign text
Carboxylic acid derivatives, medicaments comprising these
compounds, their use and processes for their production
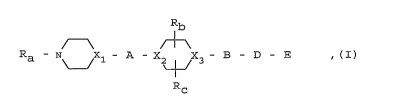
The present invention relates to carboxylic acid derivatives
of the general formula
; ~
Rb
~ rh
R - N Xl - A - X X3- B - D - E ,(I)
Rc
their tautomers, their stereoisomers, including their
mixtures, and their salts, in particular their salts with
physiologically tolerated acids or bases, which ha~e useful
pharmacological properties, preferably aggregation-inhibiting
actions, medicaments comprising these compounds and their use,
and processes for their production.
In the above general formula I
Ra is a hydrogen atom, a C1_5-alkyl or phenyl-C1_3-alkyl group,
in which in each case the alkyl moiety can be substituted by a
carboxyl, C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, N-C1_3-alkylamino-
carbonyl, N,N-di(C1_3-alkyl)aminocarbonyl, vinyl or ethynyl
group or alternatively, if the abovementioned substituents are
not on an a-carbon atom adjacent to a nitrogen atom, by a
hydroxyl, C1_3-alkoxy, amino, C1_3-alkylamino or
di(C1_3-alkyl)amino group, or is a radical which can be cleaved
in vivo,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
Rb and Rc, which can be identical or different, in each case
are a hydrogen atom or the side chain of a natural D- or L-
~-amino acid, and their esters and ethers,
A is an -HCRl-HCR2-, -CO-HCR1-, -HCRl-CO-, -NR3-HCR1-,
-HCR1-NR3-, -NR2-CO-, -CO-NR2-, -O-CO-, -CO-O-, -O-HCR1- or
-CHR1-O- group, in which
R1 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl or
phenyl group,
~ ~
R2 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_3-alkyl or phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl
group and
R3 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_3-alkyl, phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
Cl_3-alkylcarbonyl or C1_5-alkylsulphonyl group,
X1, X2 and X3, which can be identical or di~erent, in each
case are a nitrogen atom or a methine group, it additionally
in each case being possible in the abovementioned heterocyclic
rings in which X2 or X3 or X2 and X3 are each a nitrogen atom
for a methylene group linked to a ring nitrogen atom to be
replaced by a carbonyl group,
B is a 3-piperidinylene, 4-piperidinylene or 1,4-piper-
azinylene group, in which in each case a methylene group
adjacent to a nitrogen atom can be replaced by a carbonyl
group, it additionally being possible for a 1,4-piperazinylene
group to be substituted by Rb and Rc, and Rb and Rc being
defined as mentioned above, or a phenylene, cyclohexylene,
pyridinylene, pyridazinylene, pyrimidinylene or pyrazinylene
group,
D is an -O-R1CR4-CO-, -NR3-HCRl-CO-, -NR3-CH2CH2CO-, -CHzCO-,
-CHRlCH2CO- or (-0-)2CH-CO- group, in which
R1 and R3 are defined as mentioned above and
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
~ ' .
- 3
R4 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl, hydroxy-C1_3-alkyl,
carboxy-Cl_3-alkyl, Cl_3-alkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
C3_~-cycloalkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkyl, phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
phenyl, pyridyl-C1_3-alkyl or pyridyl group,
and E is a hydroxyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to
6 carbon atoms, a phenylalkoxy group in which the alkoxy
moiety can contain 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a cycloalkoxy group
having 3 to 9 carbon atoms in which the cycloalkyl moiety
having 5 to 8 carbon atoms can additionally be substituted by
one or two alkyl groups each having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a
cycloalkoxy group having 5 to 8 carbon atoms in which in the
cycloalkyl moiety a methylene group in the 3- or 4-position is
replaced by an oxygen atom or by an imino group which is
optionally substituted by an alkyl, phenylalkyl or
phenylalkoxycarbonyl group, in which the alkyl and alkoxy
moiety can each contain 1 to 3 carbon atoms, or by an alkanoyl
group having 2 to 6 carbon atoms, and the cycloalkyl moiety
can additionally be substituted by one or two alkyl groups
each having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, or is a cycloalkenyloxy group
in which the cycloalkenyl moiety can contain 4 to 7 carbon
atoms, an alkenyloxy, phenylalkenyloxy, alkynyloxy or
phenylalkynyloxy group with the proviso that a bond to the
oxygen atom does not start ~rom a carbon atom which carries a
double or triple bond and in which the alkenyl and alkynyl
moiety can each contain 3 to 5 carbon atoms, a
cycloalkylalkoxy group in which the cycloalkyl moiety can
contain 3 to 8 carbon atoms and the alkoxy moiety 1 to 3
carbon atoms, a bicycloalkoxy group having a total o~ 8 to 10
carbon atoms, which in the bicycloalkyl moiety can
additionally be substituted by one or two alkyl groups each
having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a 1,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1-
isobenzo~uranyloxy group or an R7-CO-O-(R5CR6)-O group, in
which
R5 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_6-alkyl, C3_7-cycloalkyl or
phenyl group,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
R6 is a hydrogen atom or a C1_6-alkyl group and
R7 is a Cl_5-alkyl, C1_5-alkoxy, C5_7-cycloalkyl or
C5_7-cycloalkoxy group,
or E is an ~-amino group of a natural D- or L-amino acid and
their esters.
The expressions "a phenyl group" or "a phenylene group"
mentioned in the definition of the above radicals is in each
case in particular understood as meaning a phenyl or phenylene
group which is optionally mono-, di- or trisubstituted by
~ fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine atoms, by C1_3-alkyl,
trlfluoromethyl, nitro, amino, C1_3-alkylamino,
di(C1_3-alkyl)amino, C1_4-alkanoylamino, hydroxyl, C1_3-alkoxy,
carboxyl, C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl, C3_7-cycloalkoxycarbonylalkoxy,
hydroxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkoxy, Cl_3-alkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkoxy,
aminocarbonyl, C1_3-alkylaminocarbonyl or di(C1_3-alkyl)-
aminocarbonyl groups, it being posisble for the substituents
to be identical or different,
the esters of a natural ~-amino acid are understood as meaning
its C1_6-alkyl, C2_6-alkenyl, C5_7-cycloalkyl, phenyl or phenyl-
C1_3-alkyl esters such as the methyl, ethyl, n-propyl,
isopropyl, tert-butyl, allyl, phenyl or benzyl ester,
the ethers of the side chain of a natural D- or L-~-amino acid
are understood as meaning its C1_5-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl,
phenyl or C4_7-cycloalkyl ether and
a radical which can be cleaved in vivo is understood as
meaning an alkanoyl group having a total of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms, a benzoyl, allyloxycarbonyl, C1_5-alkoxycarbonyl or
phenyl-C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl group such as the formyl, acetyl,
propionyl, butanoyl, pentanoyl, hexanoyl, benzoyl, allyloxy-
carbonyl, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, propoxycarbonyl,
isopropoxycarbonyl, butoxycarbonyl, tert-butoxycarbonyl,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
pentoxycarbonyl, hexoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, phenyl-
ethoxycarbonyl or phenylpropoxycarbonyl group.
Preferred compounds of the above general formula I are those
in which
R~ is a hydrogen atom, a C1_5-alkyl or phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl group
in which in each case the alkyl moiety can be substituted by a
carboxyl, C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, N-C1_3-alkylamino-
carbonyl, N,N-di(C1_3-alkyl)aminocarbonyl, vinyl or ethynyl
group or alternatively, if the abovementioned substituents are
~ not on an a-carbon atom adjacent to a nitrogen atom, by a
hydroxyl, C1_3-alkoxy, amino, Cl_3-alkylamino or
di(C1_3-alkyl)amino group, or is a radical which can be cleaved
in vivo,
Rb and Rc, which can be identical or different, are each a
hydrogen atom or the side chain of a natural D- or L-a-amino
acid, and their esters and ethers,
A is an -HCRl-HCR2-, -CO-HCR1-, -HCR1-CO-, -NR3-HCR1-,
-HCR1-NR3-, -NR2-CO-, -CO-NR2-, -O-CO-, -CO-O-, -O-HCR1- or
-CHR1-O- group, in which
.
R1 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl or
phenyl group,
R2 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl or phenyl-C1_3-alkyl
group and
R3 is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl,
C1_3-alkylcarbonyl or C1_~-alkylsulphonyl group,
X1, X2 and X3, which can be identical or different, are each a
nitrogen atom or a methine group, it additionally in each case
being possible in the abovementioned heterocylic rings in
which X2 or X3 or X2 and X3 are each a nitrogen atom for a
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 6 --
methylene group linked to a ring nitrogen atom to be replaced
by a carbonyl group,
B is a 3-piperidinylene, 4-piperidinylene or 1,4-piper-
azinylene group in which in each case a methylene group
adjacent to a nitrogen atom can be replaced by a carbonyl
group, it additionally being possible for a 1,4-piperazinylene
group to be substituted by Rb and Rc, and Rb and Rc being
defined as mentioned above, or a phenylene, cyclohexylene or
pyridazinylene group,
D is an -O-R1CR~-CO-, -NR3-HCRL-CO-, -NR3-CH2CH2CO-, -CH2CO-,
-CHRlCH2CO- or (-0-)2CH-CO- group, in which
R1 and R3 are defined as mentioned above and
R4 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_3-alkyl, hydroxy-Cl_3-alkyl,
carboxy-Cl_3-alkyl, Cl_3-alkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
C3_7-cycloalkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkyl, phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
phenyl, pyridyl-Cl_3-alkyl or pyridyl group,
and E is a hydroxyl, Cl_6-alkoxy, C3_9-cycloalkoxy, phenyl-
Cl_3-alkoxy or R7-CO-O-(R5CR6)-O- group, in which
~ R5 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_6-alkyl, C3_7-cycloalkyl or
phenyl group,
R6 is a hydrogen atom or a Cl_6-alkyl group and
R7 is a Cl_5-alkyl, Cl_5-alkoxy, C5_7-cycloalkyl or
C5_7-cycloalkoxy group,
the expressions A "a phenyl group" or "a phenylene group"
mentioned in the definitions of the above radicals in each
case in particular being understood as meaning a phenyl or
phenylene group which is optionally mono-, di- or
trisubstituted by ~luorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine atoms,
by Cl_3-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino, Cl_3-alkylamino,
di(Cl_3-alkyl)amino, C1_4-alkanoylamino, hydroxyl, Cl_3-alkoxy,
carboxyl, Cl_3-alkoxycarbonyl, C3_7-cycloalkoxycarbonylalkoxy,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 7 --
hydroxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkoxy, Cl_3-alkoxycarbonyl-Cl_3-alkoxy,
aminocarbonyl, C1_3-alkylaminocarbonyl or di(C1_3-alkyl)-
aminocarbonyl groups, it being possible for the substituents
to be identical or dif~erent,
the esters o~ a natural ~-amino acid are understood as meaning
its C1_6-alkyl, C2_6-alkenyl, C5_7-cycloalkyl, phenyl or phenyl-
C1_3-alkyl esters such as the methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-
propyl, tert-butyl, allyl, phenyl or benzyl ester,
the ethers of the side chain of a natural D- or L-~-amino acid
~ are understood as meaning its C1_5-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl,
phenyl or C4_~-cycloalkyl ether and
a radical which can be cleaved in vivo is understood as
meaning an alkanoyl group having a total of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms, a benzoyl, allyloxycarbonyl, C1_5-alkoxycarbonyl or
phenyl-C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl group such as the formyl, acetyl,
propionyl, butanoyl, pentanoyl, hexanoyl, benzoyl,
allyloxycarbonyl, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl,
propoxycarbonyl, isopropoxycarbonyl, butoxycarbonyl, tert-
butoxycarbonyl, pentoxycarbonyl, hexoxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl, phenylethoxycarbonyl or phenylpropoxy-
carbonyl group,
their tautomers, their stereoisomers, including their
mixtures, and their salts.
Particularly pre~erred compounds of the above general ~ormula
I are those in which
Ra is a hydrogen atom, a C1_3-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl,
C1_5-alkoxycarbonyl or phenyl-C1_3-alkoxycarbonyl group,
Rb and Rc, which can be identical or dif~erent, are each a
hydrogen atom or the side chain of a natural D- or L-~-amino
acid, and its esters and ethers,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
A is a -CH2CH2-, -CO-CH2-, -CH2-CO-, -CH2-NR3-, -NR3-CH2-,
-NH-CO-, -O-CO- or -CH2-O- group, in which
R3 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_3-alkyl, phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
C1_3-alkylcarbonyl or Cl_5-alkylsulphonyl group,
Xl, X2 and X3, which can be identical or different, are each a
nitrogen atom or a methine group, it additionally in each case
being possible in the abovementioned heterocylic rings in
which X2 or X3 or X2 and X3 are each a nitrogen atom for a
methylene group linked to a ring nitrogen atom to be replaced
by a carbonyl group,
B is a 4-piperidinylene group or a 1,4-piperazinylene group in
which a methylene group adjacent to a nitrogen atom can be
replaced by a carbonyl group, it additionally being possible
for the abovementioned 1,4-piperazinylene groups to be
substituted by a carboxymethyl or Cl_5-alkoxycarbonyl group, or
is a 1,3- or 1,4-phenylene group which is optionally
substituted by an E-CO-CH2- group, E being defined as below,
or a 1,4-cyclohexylene or 2,5-pyridazinylene group,
~ D is an -O-R1CR4-CO-, -CH2CO-, -CHRlCH2CO-,-NR3CH2CO- or
(-0-)2CH-Co- group, in which
R3 is defined as mentioned above,
Rl is a hydrogen atom or a Cl_3-alkyl group and
R4 is a hydrogen atom, a Cl_3-alkyl, hydroxy-Cl_2-alkyl,
carboxymethyl, benzyl, chlorobenzyl or phenyl group,
.
and E is a hydroxyl, Cl_6-alkoxy, C3_9-cycloalkoxy or phenyl-
Cl_3-alkoxy group,
the esters of a natural ~-amino acid in the definition of the
abovementioned radicals being understood as meaning its
Cl_ç-alkyl, C2_6-alkenyl, C5_7-cycloalkyl, phenyl or phenyl-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
g
Cl_3-alkyl esters such as the methyl, ethyl, n-propyl,
isopropyl, tert-butyl, allyl, phenyl or benzyl ester and
the ethers of the side chain of a natural D- or L-a-amino acid
being understood as meaning its Cl_5-alkyl, phenyl-Cl_3-alkyl,
phenyl or C4_7-cycloalkyl ether,
their tautomers, their stereoisomers, including their
mixtures, and their salts.
Very particularly preferred compounds of the above general
~ formula I are those in which
Ra is a hydrogen atom, a benzyl, Cl_5-alkoxycarbonyl or
benzyloxycarbonyl group,
Rb and Rc, which can be identical or dl~ferent, are each a
hydrogen atom or the side chain of a natural D- or L-a-amino
acid, and its esters and ethers,
A is a -CH2CH2-, -CO-CH2-, -CH2-CO-, -CH2-NR3-, -NR3-CH2--or
-NH-CO- group, in which
~ R3 is a hydrogen atom, a methyl, benzyl, acetyl or
- n-butylsulphonyl group,
Xl, X2 and X3, which can be identical or different, are each a
nitrogen atom or a methine group, it additionally in each case
being possible in the abovementioned heterocylic rings in
which X2 or X3 or X2 and X3 are each a nitrogen atom for a
methylene group linked to a ring nitrogen atom to be replaced
by a carbonyl group,
B is a 4-piperidinylene group or a 1,4-piperazinylene group in
which a methylene group adjacent to a nitrogen atom can be
replaced by a carbonyl group, it additionally being possible
for the abovementioned l,4-piperazinylene groups to be
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 10 --
substituted by a carboxymethyl or C1_5-alkoxycarbonyl group, or
is a 1,3- or 1,4-phenylene group which is optionally
substituted by an E-CO-CH2- group, E being defined as below,
or a 1,4-cyclohexylene or 2,5-pyridazinylene group,
D is an -O-R1CH-CO-, -O-(CH3CCH3)-CO-, -CH2CH2CO-,
-(CHCH3)CH2CO-,-NR3CH2CO- or (-0-)2CH-CO- group, in which
R3 is defined as mentioned above and
R1 is a hydrogen atom, methyl, 2-hydroxyethyl, carboxy-
methyl, benzyl, chlorobenzyl or phenyl group,
and E is a hydroxyl, C1_6-alkoxy, C3_9-cycloalkoxy or phenyl-
C1_3-alkoxy group,
the esters of a natural ~-amino acid in the definition of the
abovementioned radicals being understood as meaning its
C1_6-alkyl, C2_6-alkenyl, C5_7-cycloalkyl, phenyl or phenyl-C1_3-
alkyl esters such as the methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl,
tert-butyl, allyl, phenyl or benzyl ester and
the ethers of the side chain of a natural D- or L-~-amino acid
being understood as meaning its C1_5-alkyl, phenyl-C1_3-alkyl,
phenyl or C4_7-cycloalkyl ether,
their tautomers, their stereoisomers, including their
mixtures, and their salts.
For example, the following particularly preferred compounds of
the general formula I may be mentioned:
(1) 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[Z-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
plperazlne,
(2) 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazin-2-one,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
(3) 1-[3,4-di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine,
(4) 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine,
(5) trans-1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-methylmethylamino]cyclohexane,
(6) 1-(trans-4-carboxymethyloxycyclohexyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one,
(7) 1-[4-(1-carboxybenzyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine,
their C1_4-alkyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl esters, their
stereoisomers, including their mixtures, and their salts,
but in particular the compounds
1-(4-cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine and
~ 1-[3,4-di(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
and their salts.
a) To prepare a compound of the general formula I in which Ra
is defined as at the beginning and E is a hydroxyl group or E,
with the exception of the hydroxyl and R7-CO-O-(R5CR6)-O- group,
is as defined at the beginning and R~ is a hydrogen atom:
conversion of a compound of the general formula
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
R ' - N x1 - A - X X3- B - D - E~ ,(II)
Rc
in which
R," Rc~ A, B, D and Xl to X3 with the proviso are as defined in
the beginning that E' has the meanings mentioned for E at the
beginning and Ral is a protective radical for an imino group
which can be removed by means of hydrolysis, treatment with an
~ acid or base, thermolysis or hydrogenolysis or
Ral has the meanings mentioned for R~ at the beginning and E'
is a group which can be converted lnto a hydroxyl group by
means of hydrolysis, treatment with an acid or base,
thermolysis or hydrogenolysis,
into a compound of the generaI formula I, in which Ra is as
defined at the beginning and E is a hydroxyl group or E, with
the exception of the hydroxyl and R7-CO-O-(R5CR6)-O- group, is
as defined at the beginning and R~ is a hydrogen atom.
As protective groups for a hydroxyl group of a carboxyl group,
for example, the functional derivatives of a carboxyl group
~ such as its unsubstituted or substituted amides, esters,
thioesters, trimethylsilyl esters, orthoesters or iminoesters
can be converted into a carboxyl group by means of hydrolysis,
esters with tertiary alcohols, e.g. the tert-butyl ester, can
be converted into a carboxyl group by means of treatment with
an acid or thermolysis and
.
esters with aralkanols, e.g. the benzyl ester, can be converted
into a carboxyl group by means of hydrogenolysis.
The hydrolysis is expediently carried out either in the
presence of an acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid,
CA 02244860 l998-07-29
- 13 -
phosphoric acid, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, tri-
fluoroacetic acid or their mixtures or in the presence of a
base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or potassium
hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as water, water/methanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, methanol, ethanol,
water/tetrahydrofuran or water/dioxane at temperatures between
-10 and 120~C, e.g. at temperatures between room temperature
and the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture.
Under the abovementioned reaction conditions, N-acylamino or
Cl_5-alkoxycarbonylamino groups which may be present, such as an
N-trifluoroacetylamino or tert-butyloxycarbonylamino group, can
be converted into the corresponding amino groups.
If E' in a compound of the general formula II is, for example,
the tert-butyloxy group and/or Ra~ is the tert-butyloxy-
carbonyl group, these groups can also be removed by treatment
with an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid,
p-toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid,
phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric acid, if appropriate in an
inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, benzene,
toluene, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, preferably
at temperatures between -10 and 120~C, e.g. at temperatures
~ between 0 and 60~C, or alternatively thermally, if appropriate
in an inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform,
benzene, toluene, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane and preferably in
the presence of a catalytic amount of an acid such as
p-toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid or
polyphosphoric acid, preferably at the boiling temperature of
the solvent used, e.g. at temperatures between 40 and 120~C.
Under the abovementioned reaction conditions, N-tert-
butyloxycarbonylamino groups which may be present can be
converted into the corresponding amino groups.
If E' in a compound of the formula II is, for example, the
benzyloxy group and/or Ra~ is the benzyl group, these groups
can also be removed hydrogenolytically in the presence of a
CA 02244860 l998-07-29
- 14 -
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/carbon in a suitable
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial
acetic acid, ethyl acetate, dioxane or dimethylformamide,
preferably at temperatures between 0 and 50~C, e.g. at room
temperature, and at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar. During
the hydrogenolysis, other radicals can simultaneously be
converted, e.g. a nitro group into an amino group, a benzyloxy
group into a hydroxyl group and an N-benzylamino,
N-benzylimino, N-benzyloxycarbonylamino or
N-benzyloxycarbonylimino group into a corresponding amino or
imino group.
.
b) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which X2 is a nitrogen atom and A is an -HCR1-HCR2-,
-CO-HCR1- or -HCR1-CO- group:
reaction of a compound of the general formula
Rb
,~
H - X2 ~ X3 - B - D - E , (III)
Rc
~ in which
Rb, Rc, X3, B, D and E are as defined at the beginning and
X2 is a nitrogen atom, with a compound of the general formula
Ral - N~ X1- A' - Z1 ,(IV)
in which
X1 is as defined at the beginning, and
Ra'/ with the exception o~ the hydrogen atom, has the meanings
mentioned for R~ at the beginning or is a protective radical
for an imino group,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 15 -
A' is -HCR1-HCR2-, -C0-HCR1- or -HCR1-CO- group, R1 and R2 being
as defined at the beginning, and
Z1 is a hydroxyl group or a nucleofugic leaving group such as a
halogen atom, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodlne atom, a
sulphonic acid ester group, e.g. a methanesulphonyloxy or
p-toluenesulphonyloxy group, an imidazolyl, triazolyl or
4-nitrophenyloxy group and, if appropriate, subsequent removal
of a protective radical used.
The reaction is preferably carried out in a solvent such as
methanol, ethanol, methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran,
~ toluene, dioxane, dimethyl sulphoxide or dimethylformamide, if
appropriate in the presence of an inorganic or of a tertiary
organic base or if appropriate in the presence of an agent
which dehydrates or activates the acid, at temperatures between
-30 and 200~C.
The reaction of a carboxylic acid of the general formula IV is
optionally carried out in a solvent or solvent mixture such as
methylene chloride, dimethylformamide, benzene, toluene,
chlorobenzene, tetrahydrofuran, benzene/tetrahydrofuran or
dioxane or in an appropriate amine of the general formula III,
if appropriate in the presence of a dehydrating agent, e.g. in
the presence of isobutyl chloroformate, tetraethyl ortho-
carbonate, trimethyl orthoacetate, 2,2-dimethoxypropane,
tetramethoxysilane, thionyl chloride, trimethylchlorosilane,
phosphorus trichloride, phosphorus pentoxide, N,N'-dicyclo-
hexylcarbodiimide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/N-hydroxy-
succinimide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/1-hydroxybenzo-
triazole, 2-(lH-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium
tetrafluoroborate, 2-(lH-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-
tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate/1-hydroxybenzotriazole,
N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole or triphenylphosphine/carbon
tetrachloride, and if appropriate with addition of a base such
as pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, N-methylmorpholine or
triethylamine, expediently at temperatures between 0 and
150~C, preferably at temperatures between 0 and 100~C.
CA 02244860 l998-07-29
- 16 -
The reaction of a compound of the general formula IV in which
Z1 is a nucleofugic leaving group is preferably carried out in
a solvent such as methylene chloride, acetonitrile,
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, toluene, dimethylformamide or
dimethyl sulphoxide, if appropriate in the presence of a base
such as sodium hydride, potassium carbonate, potassium tert-
butoxide or N-ethyldiisopropylamine, at temperatures between
-20 and 100~C, preferably at temperatures between 0 and 60~C.
The subsequent removal of a protective radical used is
expediently carried out hydrolytically either in the presence
of an acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, tri-
fluoroacetic acid or their mixtures or in the presence of a
base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or potassium
hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as water, water/methanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, methanol, ethanol, water/
tetrahydrofuran or water/dioxane, at temperatures between -10
and 120~C, e.g. at temperatures between room temperature and
the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture, or hydro-
genolytically in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst such
as palladium/carbon in a suitable solvent such as methanol,
~ ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate,
dioxane or dimethylformamide, preferably at temperatures
between 0 and 50~C, e.g. at room temperature, and at a
hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar.
c) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which A is an -NR3-C0- group and X2 is a nitrogen atom:
reaction of a compound of the general formula
-
CA 02244860 l998-07-29
- 17 -
Rb
H X2 ~ X3 B D E ,(III)
C
in which
Rb, Rc~ X3, B, D and E are as defined at the beginning and
X2' is a nitrogen atom, with a compound of the general formula
R ' - N ~ ~ ~ - NR2 -C~z2 ,(V)
in which
R2 is as defined at the beginning,
Ral, with the exception of the hydrogen atom, has the meanings
mentioned for Ra at the beginning or is a protective radical
for an imino group and
Z2 is a nucleofugic leaving group such as a halogen atom, e.g.
a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom, an imidazolyl, triazolyl
or 4-nitrophenyloxy group or
Z2~ together with R2, is a further carbon-nitrogen bond and, if
appropriate, subsequent removal of a protective radical used.
--
The reaction is preferably carried out in a suitable solvent,
such as methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran, toluene, dioxane,
dimethyl sulphoxide or dimethylformamide, if appropriate in
the presence of an inorganic or of a tertiary organic base or
if appropriate in the presence of a dehydrating agent, at
temperatures between -30 and 200~C.
The reaction of a compound of the general formula V in which
Z2 is a nucleofugic leaving group, or with an isocyanate of
the general formula V, is preferably carried out in a solvent
such as methylene chloride, acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane, toluene, dimethylformamide or dimethyl sulphoxide, if
appropriate in the presence of a base such as sodium hydride,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
,
- 18 -
potassium carbonate, potassium tert-butoxide or N-ethyl-
diisopropylamine, at temperatures between -20 and 100~C,
pre~erably at temperatures between 0 and 60~C.
The subsequent removal of a protective radical used is
expediently carried out hydrolytically either in the presence
of an acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid,
trifluoroacetic acid or their mixtures or in the presence of a
base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or potassium
hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as water, water/methanol,
~ water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, methanol, ethanol,
water/tetrahydrofuran or water/dioxane, at temperatures
between -10 and 120~C, e.g. at temperatures between room
temperature and the boiling temperature of the reaction
mixture, or hydrogenolytically in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/carbon in a suitable
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial
acetic acid, ethyl acetate, dioxane or dimethylformamide,
preferably at temperatures between 0 and 50~C, e.g. at room
temperature, and at a hydrogen pressure ~rom 1 to 5 bar.
d) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which D is an -O-RlCR4-CO- group:
reaction of a compound of the general formula
Rb
~ rh
R ' - N Rc ,(VI)
in which
R~, Rc, A, B and X1 to X3 are as defined at the beginning and
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 19 --
Ra~ with the exception of the hydrogen atom, has the meanings
mentioned for RA at the beginning or is a protective radical
for an imino group, with a compound of the general formula
Z3-RlCR4-CO-E ,(VII)
in which
Rl, R4 and E are as defined at the beginning and
Z3 is a leaving group such as a halogen atom, e.g. a chlorine
or bromine atom, or alternatively, if B is one of the
phenylene groups mentioned at the beginning, a hydroxyl group
~ and, if appropriate, subsequent removal of a protective
radical used.
The reaction is expediently carried out in a solvent such as
methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethyl
sulphoxide, dimethylformamide or acetone, if appropriate in
the presence of a reaction accelerator such as sodium or
potassium iodide and preferably in the presence of a base such
as sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate or in the presence
of a tertiary organic base such as N-ethyldiisopropylamine or
N-methylmorpholine, which can simultaneously also serve as a
solvent, or if appropriate in the presence of silver carbonate
or silver oxide or in the presence of an azodicarboxylic acid
diester and of a phosphine at temperatures between -30 and the
boiling temperature of the solvent used, but preferably at
temperatures between -10 and 80~C.
If Z3 is a hydroxyl group, the reaction is pre:Eerably carrled
out in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether, tetrahydro-
furan, dioxane, diglyme, benzene or toluene in the presence of
an azodicarboxylic acid diester such as diethyl azodi-
carboxylate and of a phosphine such as triphenylphosphine, at
temperatures between -20~C and the boiling temperature of the
solvent used.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
- 20 -
The subsequent removal of a protective radical used is
expediently carried out hydrolytically either in the presence
of an acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, phos-
phoric acid, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, trifluoro-
acetic acid or their mixtures or in the presence of a base
such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or potassium
hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as water, water/methanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, methanol, ethanol,
water/tetrahydrofuran or water/dioxane, at temperatures
between -10 and 120~C, e.g. at temperatures between room
temperature and the boiling temperature of the reaction
~ mixture, or hydrogenolytically in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/carbon in an suitable
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial
acetic acid, ethyl acetate, dioxane or dlmethylformamide,
preferably at temperatures between 0 and 50~C, e.g. at room
temperature, and at a hydrogen pressure from 1 to 5 bar.
e) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which B is a 3-piperidinylene, 4-piperidinylene or
1,4-piperazinylene group, it additionally being possible to
substitute a l,4-piperazinylene group by Rb and Rc, in which Rb
and Rc are defined as mentioned above, and D is an ethylene
group:
reaction of a compound of the general formula
Rb
R - N Xl - A - X X3 - B' - H ,(VIII)
RC
in which
R;, to Rc, Xl to X3 and A are as defined at the beginning and
B' is a 3-piperidinylene, 4-piperidinylene or 1,4-pipera-
zinylene group, with a compound of the general formula
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 21 -
CH2=CH2-CO-E ,(IX)
in which
E, with the exception of the hydroxyl group, is as defined at
the beginning.
The reaction is preferably carried out in a solvent such as
methanol, ethanol, methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran,
toluene, dioxane, dimethyl sulphoxide or dimethylformamide, if
appropriate in the presence of a tertiary organic base such as
N-ethyldiisopropylamine or N-methylmorpholine, at temperatures
between -30 and 150~C, but preferably at temperatures between
0 and 100~C.
f) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which the radicals B and X3 are linked with one another via
a carbon-nitrogen or nitrogen-carbon bond:
reductive amination o~ a compound of the general formula
~ Ra ~ N x1 - A - X2 U ,(X)
Rc
with a compound of the general formula
B~ - D - E ,(XI)
in which
Ra to Rc, X1, X2, A, D and E are as defined at the beginning,
U is a carbonyl group and
B" is a 3-piperidinylene, 4-piperidinylene or
1,4-piperazinylene group, it additionally being possible to
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 22 -
substitute a l,4-piperazinylene group by Rb and Rc, in which Rb
and Rc are defined as mentioned above, or
U is an imino group and
B" is a cyclohexanone group.
The reductive amination is preferably carried out in the
presence of a complex metal hydride such as sodium borohydride,
lithium borohydride, sodium cyanoborohydride, zinc borohydride,
sodium triacetoxyborohydride or borane/pyridine, expediently at
a pH of 1-7, if appropriate in the presence of a dehydrating
agent such as molecular sieves or titanium (IV) isopropoxide
and at room temperature or with hydrogen in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst, e.g. in the presence of palladium/
carbon, at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar, preferably at
temperatures between 20~C and the boiling temperature of the
solvent used.
g) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which E, with the exception o~ the hydroxyl group, is as
defined at the beginning:
reduction of a compound of the general formula
R - N Xl - A - X X - B - D - OH ,(XII)
Rc
in which
Ra to Rc, Xl to X3, A, B and D are as de:Eined at the beginning,
or their reactive derivatives, with an alcohol of the general
formula
HO - Rd ,(XIII)
or with its formamide acetal
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 23 -
or o~ a compound of the general ~ormula XII with a compound o~
the general formula
Z4 - R ,(XIV)
in which
Rd is an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a phenylalkyl
group in which the alkyl moiety can contain 1 to 3 carbon
atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3 to 9 carbon atoms in which
the cycloalkyl moiety having 5 to 8 carbon atoms can be
additionally substituted by one or two alkyl groups each
having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to
8 carbon atoms in which in the cycloalkyl moiety a methylene
group in the 3- or 4-position is replaced by an oxygen atom or
by an imino group which is optionally substituted by an alkyl,
phenylalkyl or phenylalkoxycarbonyl group in which the alkyl
and alkoxy moiety can each contain 1 to 3 carbon atoms, or by
an alkanoyl group having 2 to 6 carbon atoms, and the
cycloalkyl moiety can additionally be substituted by one or
two alkyl groups each having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a
cycloalkenyl group in which the cycloalkenyl moiety can
contain 4 to 7 carbon atoms, an alkenyl, phenylalkenyl,
alkynyl or phenylalkynyl group, with the proviso that no bond
to the oxygen atom starts ~rom a carbon atom which carries a
~ double or triple bond and in which the alkenyl and alkynyl
moieties can each contain 3 to 5 carbon atoms, a
cycloalkylalkyl group in which the cycloalkyl moiety can
contain 3 to 8 carbon atoms and the alkyl moiety 1 to 3 carbon
atoms, a bicycloalkyl group having a total o~ 8 to 10 carbon
atoms, which in the bicycloalkyl moiety can additionally be
substituted by one or two alkyl groups each having 1 to 3
carbon atoms, or a l,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1-isobenzo~uranyloxy
group,
Re has the meanings mentioned ~or Rd above and is additionally
an R7-CO-O-(R5CR6)-O- group, in which
R5 to R7 are as de~ined at the beginning, and
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
'
- 24 -
Z4 is a leaving group such as a halogen atom, e.g. a chlorine
or bromine atom.
The reaction with an alcohol of the general formula XII is
expediently carried out in a solvent or solvent mixture such
as methylene chloride, benzene, toluene, chlorobenzene,
tetrahydrofuran, benzene/tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, but
pre~erably in an alcohol of the general formula XII, if
appropriate in the presence of an acid such as hydrochloric
acid or in the presence of a dehydrating agent, e.g. in the
presence of isobutyl chloroformate, thionyl chloride,
trimethylchlorosilane, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid,
methanesulphonic acid, p-toluenesulphonic acid, phosphorus
trichloride, phosphorus pentoxide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbo-
diimide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide,
N,NI-carbonyldiimidazole, N,N'-thionyldiimidazole, triphenyl
phosphine/carbon tetrachloride or triphenylphosphine/diethyl
azodicarboxylate, if appropriate in the presence of a base
such as potassium carbonate, N-ethyldiisopropylamine or
N,N-dimethylaminopyridine, expediently at temperatures between
0 and 150~C, preferably at temperatures between 0 and 80~C.
~ With a compound of the general formula XIV, the reaction is
expediently carried out in a solvent such as methylene
chloride, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethyl sulphoxide,
dimethylformamide or acetone, if appropriate in the presence
of a reaction accelerator such as sodium or potassium iodide
and preferably in the presence of a base such as sodium
carbonate or potassium carbonate or in the presence of a
tertiary organic base such as N-ethyldiisopropylamine or
N-methylmorpholine, which can simultaneously also serve as a
solvent, or if appropriate in the presence of silver carbonate
or silver oxide at temperatures between -30 and 100~C, but
preferably at temperatures between -10 and 80~C.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 25 -
h) For the preparation of a compound of the general formula I
in which A is an -HCRl-NH- group:
reduction of a compound of the general formula
Rb
R ~ ~ xl- A~- X X3- B - D - E ,(XV)
Rc
~ in which
R~ to Rc, Xl to X3, B and D are as defined at the beginning and
A" is an -HCRl-N= group, in which Rl is as defined at the
beginning.
The reduction is preferably carried out in the presence of a
complex metal hydride such as sodium borohydride, lithium
borohydride, sodium cyanoborohydride, zinc borohydride, sodium
triacetoxyborohydride or borane/pyridine, expediently at a pH
of 1-7, if appropriate in the presence of a dehydrating agent
such as molecular sieves or titanium(IV) isopropoxide and at
room temperature or with hydrogen in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst, e.g. in the presence of palladium/
carbon, at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar, preferably at
temperatures between 20~C and the boiling temperature of the
solvent used.
If, according to the invention, a compound of the general
formula I is obtained which contains an imino group, this can
be converted by means of subsequent alkylation or acylation
into the desired alkylated or acylated compound of the general
formula I.
The subsequent alkylation is optionally carried out in a
solvent or solvent mixture such as methylene chloride,
dimethylformamide, benzene, toluene, chlorobenzene,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
- 26 -
tetrahydrofuran, benzene/tetrahydrofuran or dioxane using an
alkylating agent such as an appropriate halide or sulphonic
acid ester, e.g. using methyl iodide, ethyl bromide, dimethyl
sulphate or benzyl chloride, if appropriate in the presence of
a tertiary organic base or in the presence of an inorganic
base, expediently at temperatures between 0 and 150~C,
preferably at temperatures between 0 and 100~C, or using an
appropriate carbonyl compound such as formaldehyde,
acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde or acetone in the presence of a
complex metal hydride such as sodium borohydride, lithium
borohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride, expediently at a pH of
6-7 and at room temperature or in the presence of a hydro-
genation catalyst, e.g. with hydrogen in the presence of
palladium/carbon, at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar. The
methylation, however, can also be carried out in the presence
of formic acid as a reducing agent at elevated temperatures,
e.g. at temperatures between 60 and 120~C.
The subsequent acylation is carried out using an appropriate
reactive carboxylic acid derivative such as the acid halide,
i~ appropriate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as
methylene chloride, dimethyl~ormamide, benzene, toluene,
chlorobenzene, tetrahydro~uran or dioxane, if appropriate in
the presence of a tertiary organic base or in the presence of
an inorganic base or using an appropriate carboxylic acid in
the presence of a dehydrating agent, e.g. in the presence of
isobutyl chloro~ormate, thionyl chloride, trimethylchloro-
silane, phosphorus trichloride, 2-(lH-benzotriazol-1-yl)-
1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate, N,N'-dicyclo-
hexylcarbodiimide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/N-hydroxy-
succin;mide or 1-hydroxybenzotriazole and if appropriate in
the presence of 4-dimethylaminopyridine, N,N'-carbonyl-
diimidazole or triphenylphosphine/carbon tetrachloride,
expediently at temperatures between 0 and 150~C, preferably at
temperatures between 0 and 80~C.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 27 -
In the reactions described above, reactive groups which may be
present such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, alkylamino or imino
groups can be protected during the reaction by customary
protective groups which are removed again after the reaction.
For example, a suitable protective radical for a hydroxyl
group is the trimethylsilyl, acetyl, benzoyl, tert-butyl,
trityl, benzyl or tetrahydropyranyl group,
protective radicals for a carboxyl group are the trimethyl-
silyl, methyl, ethyl, tert-butyl, benzyl or tetrahydropyranyl
group and
a protective radical for an amino, alkylamino or imino group
is the formyl, acetyl, trifluoroacetyl, methoxycarbonyl,
ethoxycarbonyl, tert-butoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl,
benzyl, methoxybenzyl or 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl group, for the
imino group additionally the methyl group and for the amino
group the phthalyl group.
The possible subsequent removal of a protective radical used
is carried out, for example, hydrolytically in an aqueous
solvent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water, acetic acid/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presence of an
acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric acid or
sulphuric acid or in the presence of an alkali base such as
sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide or by means of ether
cleavage, e.g. in the presence of iodotrimethylsilane, at
temperatures between 0 and 120~C, preferably at temperatures
between 10 and 100~C.
The removal of a benzyl, methoxybenzyl or benzyloxycarbonyl
radical, however, is carried out, for example, hydro-
genolytically, e.g. with hydrogen in the presence of a
catalyst such as palladium/carbon in a solvent such as
methanOl, ethanol, isopropanol, ethyl acetate or glacial
acetic acid, if appropriate with addition of an acid such as
~ = ~ = = _ _ _
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 28 -
hydrochloric acid, at temperatures between 0 and 100~C, but
preferably at temperatures between 20 und 60~C, and at a
hydrogen pressure of 1 to 7 bar, but preferably of 3 to 5 bar.
The removal of a tert-butyl or tert-butyloxycarbonyl radical
is preferably carried out by treatment with an acid such as
trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid or by treatment with
iodotrimethylsilane, if appropriate using a solvent such as
methylene chloride, dioxane, methanol or ether.
~ The removal of a trifluoroacetyl radical is preferably carried
out by treatment with an acid such as hydrochloric acid, if
appropriate in the presence of a solvent such as acetic acid
or methanol at temperatures between 50 and 120~C or by
treatment with sodium hydroxide solution, if appropriate in
the presence of a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or methanol
at temperatures between 0 and 50~C.
The removal of a methyl group from a methylimino group is
preferably carried out in the presence o~ 1-chloroalkyl
chloro~ormates such as 1-chloroethyl chloroformate, preferably
in the presence of a base such as 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)-
naphthalene in the presence of a solvent such as methylene
s chloride, 1,2-dichloroethane, toluene or dioxane at
temperatures between 0 and 150~C, preferably at temperatures
between 20~C and the boiling temperature of the reaction
mixture, and subsequent treatment with an alcohol such as
methanol at temperatures between 20~C and the boiling
temperature of the alcohol used.
The removal of a phthalyl radical is preferably carried out in
the presence of hydrazine or o~ a primary amine such as
methylamine, ethylamine or n-butylamine in a solvent such as
methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, toluene/water or dioxane at
temperatures between 20 and 50~C.
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
Furthermore, the compounds of the general formula I obtained,
as has already been mentioned at the beginning, can be
separated into their enantiomers and/or diastereomers. Thus,
for example, cis/trans mixtures can be separated into their
cis and trans isomers, and chiral compounds into their
enantiomers.
Thus, for example, the cis/trans mixtures obtained can be
separated by chromatography into their cis and trans isomers,
the compounds of the general formula I obtained which occur in
racemates can be separated by methods known per se (see
Allinger N. L. and Eliel E. L. in "Topics in Stereochemistry",
Vol. 6, Wiley Interscience, 1971) into their optical antipodes
and compounds of the general formula I having at least
2 stereogenic centres can be separated on the basis of their
physico-chemical differences according to methods known per
se, e.g. by chromatography and/or fractional crystallization,
into their diastereomers which, if they are obtained in
racemic form, can then be separated into the enantiomers as
mentioned above.
The separation of enantiomers is preferably carried out by
column separation on chiral phases or by recrystallization
from an optically active solvent or by reaction with an
optically active substance forming salts or derivatives such
as, for example, esters or amides with the racemic compound,
in particular acids and their activated derivatives or
alcohols, and separation of the diastereomeric salt mixture or
derivative obtained in this way, for example on the basis of
different solubilities, it being possible to liberate the free
antipodes from the pure diastereomeric salts or derivatives by
the action of suitable agents. Particularly useful, optically
active acids are, for example, the D and L forms of tartaric
acid or dibenzoyltartaric acid, di-o-tolyltartaric acid, malic
acid, mandelic acid, camphorsulphonic acid, glutamic acid,
aspartic acid or quinic acid. A suitable optically active
alcohol is, for example, (+)- or (-)-menthol and a suitable
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 30 -
optically active acyl radical in amides is, for example, (+)-
or (-)-menthyloxycarbonyl.
In addition, the compounds of the formula I obtained can be
converted into their salts, in particular for pharmaceutical
use into their physiologically tolerated salts with inorganic
or organic acids. Suitable acids for this purpose are, for
example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid or maleic acid.
.
Additionally, the novel compounds of the formula I thus
obtained, if these contain a carboxyl group, can if desired
then be converted into their salts with inorganic or organic
bases, in particular for pharmaceutical use into their
physiologically tolerated salts. Suitable bases here are, for
example, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, arginine,
cyclohexylamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine and tri-
ethanolamine.
The compounds used as starting substances are known from the
literature in some cases or they are obtained according to
processes known from the literature (see Examples I to XXIII).
j
As already mentioned at the beginning, the novel carboxylic
acid derlvatives of the general formula I and their salts, in
particular their physiologically tolerated salts with
inorganic or organic acids or bases, have useful properties,
in particular useful pharmacological properties, in addition
to an antiinflammatory and antiosteoclastic action, in
particular antithrombotic, antiaggregatory and antitumour or
antimetastatic action.
For example, the compounds o~ the general formula I were
investigated for their biological actions as follows:
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
1.
- 31 -
1. Inhibition of the binding of 3H-BIBU 52 to human platelets:
A suspension of human platelets in plasma is incubated with
3H-BIBU 52 [= (3S,5S)-5-[(4'-amidino-4-biphenylyl)oxymethyl]-
3-[(carboxy)methyl]-2-pyrrolidinone[3-3H-4-biphenylyl]], which
replaces the ligand 12sI-fibrinogen known from the literature,
(see DE-A-4,214,245) and various concentrations of the
substance to be tested. The free and bound ligand is separated
by centrifugation and determined quantitatively by
scintillation counting. From the measurements, the inhibition
of 3H-BIBU 52 binding by the test substance is determined.
To do this, donor blood is taken from an antecubital vein and
anticoagulated with trisodium citrate (final concentration
13 mM). The blood is centrifuged at 170 x g for 10 minutes and
the supernatant platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is removed. The
residual blood is rapidly centrifuged once more to obtain
plasma. The PRP is diluted 1:10 with autologous plasma. 750 ul
are incubated with 50 ml of physiological saline solution,
100 ul of test substance solution, 50 ul of 14C-sucrose
(3700 Bq) and 50 ul o~ 3H-BIBU 52 (final concentration: 5 nM)
at room temperature for 20 minutes. To measure the non-
specific binding, instead of the test substance, 100 ul of
BIBU 52 (final concentration: 30 ~M) is employed. The samples
are centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 20 seconds and the
supernatant is removed. 100 ul thereof are measured to
determine the free ligand. The pellet is dissolved in 500 ul
of 0.2N NaOH, and 450 ul are mixed with 2 ml of scintillator
and 25 ul of 5N HCl and measured. The residual plasma still
remaining in the pellet is determined fro~ the 14C content, the
bound ligand from the H measurement. After subtraction of the
non-specific binding, the pellet activity is plotted against
the concentration of the test substance and the concentration
for a 50% inhibition of binding is determined.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 32 -
2. Antithrombotic action:
Methodology
Platelet aggregation is measured according to the method of
Born and Cross (J. Physiol. 170, 397 (1964)) in platelet-rich
plasma of healthy subjects. To inhibit clotting, the blood is
treated with sodium citrate 3.14~ in the volume ratio 1:10.
Collagen-induced aggregation
.
The course of the decrease in the optical density of the
platelet suspension is measured photometrically and recorded
after addition of the aggregation-inducing substance. From the
angle of inclination of the density curve, the aggregation
rate is deduced. The point on the curve at which the greatest
light transmission is present serves for the calculation of
the optical density.
The amount of collagen is chosen to be as low as possible, but
of course such that an irreversibly running reaction curve
results. Commercially available collagen from Hormonchemie,
Munich is used.
Before the addition of collagen, the plasma is incubated at
37~C with the substance for 10 minutes in each case.
From the measured values obtained, an ECso which relates to a
50% change in the optical density in the sense of an
inhibition of aggregation is determined graphically.
The following table contains the results found:
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 33 --
SubstanceFibrinogen bindingInhibition of platelet
(Example No.) test aggregation
IC50[nM] EC50[nM]
150 120
1(1) 360 370
1(3) 47 110
1(7) 260 240
1(22) 260 370
7(1) 200 250
~ 7(6) 150
Additionally, the compounds of Examples 2, 9, 9(1), 9(2) and
2(4) in Rhesus monkeys after oral administration of 1 mg/kg
exhibit high plasma levels over a period o~ more than 8 hours.
The novel compounds are well tolerated, since, for example,
after intravenous administration of 100 mg/kg of the compound
according to the invention of the above examples to the mouse
it was not possible to observe any toxic side effects.
On account of their inhibitory action on cell-cell or cell-
matrix interactions, the novel carboxylic acid derivatives of
the general formula I and their physiologically tolerated
salts are suitable for the control or prevention of illnesses
in which relatively small or relatively large cell aggregates
occur or cell-matrix interactions play a part, e.g. in the
control or prevention of venous and arterial thromboses, of
cerebrovascular disorders, oi~ pulmonary embolisms, of cardiac
infarct, of arteriosclerosis, of osteoporosis and of
metastasization of tumours and of the therapy of genetically
related or alternatively acquired disorders of the
interactiOns of cells with one another or with solid
structures~ Furthermore, they are suitable for concomitant
therapy in thrombolysis with fibrinolytics or vascular
interventions such as transluminal angioplasty or
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 34 -
alternatively in the therapy of states of shock, of psoriasis,
of diabetes and of inflammations.
For the control or prevention of the abovementioned illnesses,
the dose is between 0.1 mg and 30 mg/kg of body weight,
preferably 1 mg to 15 mg/kg of body weight, with up to
4 administrations per day. To this end, the compounds of the
formula I prepared according to the invention, if appropriate
in combination with other active substances such as
thromboxane receptor antagonists and thromboxane synthesis
inhibitors or their combinations, serotonin antagonists, a
-receptor antagonists, alkyl nitrates such as glyceryl
trinitrate, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, prostacyclin and its
analogues, fibrinolytics such as tPA, prourokinase, urokinase,
streptokinase, or anticoagulants such as heparin, dermatan
sulphate, activated protein C, vitamin K antagonists, hirudin,
inhibitors of thrombin or other activated clotting factors,
together with one or more inert customary excipients and/or
diluents, e.g. with maize starch, lactose, cane sugar,
microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl-
pyrrolidone, citric acid, tartaric acid, water, water/ethanol,
water/glycerol, water/sorbitol, water/polyethylene glycol,
propylene glycol, stearyl alcohol, carboxymethylcellulose or
fat-containing substances such as hard fat or suitable
mixtures thereof, in customary pharmaceutical preparations
such as tablets, coated tablets, capsules, powders,
suspensions, solutions, sprays or suppositories.
The following examples are intended to illustrate the
invention in greater detail:
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
Preparation of the starting materials:
Example I
1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
trifluoroacetate
a) l-(tert-Butyloxycarbonyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine
A solution of 52.4 g (0.24 mol) of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
in 50 ml of dioxane is added dropwise at 0~C with stirring to
a solution of 35.6 g (0.2 mol) of 4-hydroxyphenylpiperazine in
300 ml of dioxane and 300 ml of water. After addition is
complete, the reaction mixture is allowed to warm to room
temperature and is stirred further overnight at this
temperature. The solution is then concentrated to a small
volume in vacuo and acidified to pH 3 using potassium hydrogen
sulphate. The mixture is extracted with ethyl acetate, and the
combined extracts are dried over sodium sulphate and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is crystallized
from ether and dried.
Yield: 38 g (68% of theory),
Rf: O. 40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
~ b) l-(tert-Butyloxycarbonyl)-4-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)piperazine
20.5 g (0.15 mol) of potassium carbonate are added with
stirring at room temperature to a solution of 38 g (0.137 mol)
of l-(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine in
150 ml of dry dimethylformamide and the mixture is stirred for
a further 45 minutes. 23.0 g = 14.2 ml (0.15 mol) of methyl
bromoacetate are then added with further stirring and the
mixture is stirred further overnight. The solution is then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the'residue is
partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The combined
organic phases are dried over sodium sulphate and concen-
trated The residue which remains is triturated with ether,
filtered of~ with suction and dried.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 36 -
Yield: 35.7 g (75% of theory),
Melting point: 102-104~C
Rf: 0. 65 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9.5:0.5)
c) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoro-
acetate
A solution of 35.7 g (0.1 mol) of 1-(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)-
4-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine in 190 ml of
trifluoroacetic acid and 190 ml of methylene chloride is
allowed to stand for 3 hours at room temperature. After this
~ time, the solution is concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is crystallized from ether, filtered off with suction
and dried.
Yield: 38 g (quantitative),
Melting point: 106-108~C
R~: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Example II
1-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-yl)-2-methane-
sulphonyloxyethane
a) 2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-yl)ethanol
A solution of 100 g (0.812 mol) of 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyridine
in 1 l of 50% strength acetic acid is exhaustively
hydrogenated over 10 g of platinum dioxide at room temperature
and a hydrogen pressure of 50 psi. The catalyst is filtered
off with suction and the solution is concentrated to dryness
in vacuo. The oily residue of 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperidine
acetate which r~m~;n~ is dissolved in 500 ml of dioxane and
500 ml of water, adjusted to pH 10 with lON sodium hydroxide
solution and treated with a solution of 177.2 g (0.812 mol) of
di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in 200 ml of dioxane. The mixture is
stirred overnight at room temperature, diluted with water and
extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases are
dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
s
- 37 -
purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel column,
ethyl acetate/cyclohexane = 1:2 and 1:1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 44.3 g (24~ of theory),
Rf: O . 40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
b) l-(l-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-yl)-2-methane-
sulphonyloxyethane
28 ml (0.193 mol) of triethylamine are added to a solution of
44.3 g (0.193 mol) of 2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-
~ yl)ethanol in 200 ml of methylene chloride. 15 ml (0.193 ml)
of methanesulphonyl chloride are then added dropwise with ice-
cooling and stirring and the mixture is allowed to stand
overnight at room temperature after addition is complete. It
is then treated with water, the organic phase is separated off
and the aqueous phase is extracted once more with methylene
chloride. The combined organic phases are dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue which remains is
crystallized from petroleum ether.
Yield: 51 g (86% of theory),
Melting point: 76-78~C
Rf: O . 30 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/cyclohexane = 1:1)
~ Example III
1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-2-one hydro-
chloride
a) Ethyl 4-nitrophenoxyacetate
125.4 g (0~9 mol) of 4-nitrophenol are dissolved in 1000 ml of
absolute dimethylformamide and, after addition of 150.6 g
(0.9 mol) of dried potassium carbonate, the solution is
stirred at room temperature for 45 minutes. 150.6 g = 100 ml
(0.9 mol) of ethyl bromoacetate are then added dropwise with
stirring and the suspension is then heated at an oil bath
temperature of 80~C for 5 hours. The heating is switched off
and the suspension is stirred for a further 15 hours, the
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 38 -
reaction mixture slowly coming to room temperature. The
undissolved inorganic salts are filtered off with suction and
the filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue
is partitioned between ethyl acetate and water. The organic
phase is extracted with water a further 2 times and then dried
over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated. The residue
is triturated with petroleum ether and filtered off with
suction. 192.0 g (95% of theory) of the desired product are
obtained, which is processed further without further
purification.
R~: 0.80 (silica geli methylene chloride)
b) Ethyl 4-aminophenoxyacetate
144.9 g (0.643 mol) of methyl 4-nitrophenoxyacetate are
exhaustively hydrogenated over 1.5 g of palladium on carbon
(10% strength) at room temperature and under a hydrogen
pressure of 50 psi in 1500 ml of ethyl acetate. The catalyst
is filtered off with suction and the filtrate is concentrated
to dryness in vacuo. The residue is triturated with petroleum
ether and filtered of~ with suction.
Yield: 123.4 g (98% of theory),
R~: 0.26 (silica gel; methylene chloride)
~ c) Ethyl 4-(2,2-diethoxyethylamino)phenoxyacetate
-~ A solution of 20 g (0.102 mol) of ethyl 4-aminophenoxyacetate,
18.5 ml (0.123 mol) of bromoacetaldehyde diethyl acetal and
21.4 ml (0.123 mol) of N-ethyldiisopropylamine in 60 ml of dry
dimethylformamide is heated at 100~C for 30 hours and then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is partitioned
between ethyl acetate and water, and the organic phase is
washed with water, dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
The residue is purified by means of chromatography on a silica
gel column, cyclohexane/ethyl acetate - 4:1 being used as
eluent.
_
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 39 -
Yield: 18.05 g (57% of theory),
Mass spectrum: M+ = 311
Rf: 0.78 (sillca gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
d) Ethyl 4-[N-(benzyloxycarbonylglycyl)-N-(2,2-diethoxyethyl)-
amino]phenoxyacetate
A mixture of 6 g (0.0193 mol) of ethyl 4-(2,2-diethoxyethyl-
amino)phenoxyacetate, 4.03 g (0.0193 mol) of N-benzyloxy-
carbonylglycine, 3.2 ml (0.029 mol) of N-methylmorpholine and
7.1 g (0.0193 mol) of 2-(1~-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-
~ tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate in 150 ml of drytetrahydrofuran is stirred overnight at room temperature and
then heated at reflux temperature for 8 hours. The mixture is
then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
partitioned between saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate solution and ethyl acetate and the aqueous phase is
extracted twice more with ethyl acetate. The combined organic
phases are dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel
column, cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 9.69 g (quantitative) of oil,
Mass spectrum: M+ = 502
Rf: 0.42 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
!
e) 4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperazin-5-en-2-one
2 g of p-toluenesulphonic acid are added to a solution of
9.6 g (0.019 mol) of ethyl 4-[N-(benzyloxycarbonylglycyl)-N-
(2,2-diethoxyethyl)amino]phenoxyacetate in 200 ml of toluene
and the mixture is heated at 75~C for 4 hours. It is
concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is
partitioned between saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate solution and ethyl acetate. The aqueous phase is
extracted twice more with ethyl acetate. The combined ethyl
acetate extracts are dried and concentrated to dryness in
vaCuo. The crude residue (7 g) is purified by means of
chromatography on a silica gel column, ethyl acetate/
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 40 -
cyclohexane = 1:1 being used as eluent. After evaporation, the
residue is crystallized from ether/petroleum ether.
Yield: 1.64 g (21% of theory),
Melting point: 85-88~C
Rf: 0.60 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/cyclohexane = 1:1)
f) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-2-one hydro-
chloride
1.6 g (0.0039 mol) of 4-benzyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazin-5-en-2-one are exhaustively
hydrogenated at room temperature and under a hydrogen pressure
of 50 psi over 1 g of palladium on carbon (10% strength) in
100 ~l of ethyl acetate after addition of an equimolar amount
of hydrochloric acid. After removal of the catalyst and
concentration of the filtrate in vacuo, the residue is
triturated with ether, filtered off with suction and dried.
Yield: 0.97 g (77% of theory),
Melting point: 163-168~C
Rf: 0.45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example IV
1-[4-(2-Methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]piperazine
a) Methyl 4-nitrocinn~m~te
A suspension of 50 g (0.258 mol) of 4-nitrocinn~mic acid and
5 ml of conc. sulphuric acid in 1200 ml of methanol is heated
at reflux temperature for 10 hours. After cooling, the solid
is filtered off with suction and dried.
Yield: 51.1 g (96% of theory),
Melting point: 135-138~C
Rf: 0.9 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) Methyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)propionate
50 g (0.241 mol) of methyl 4-nitrocinnamate are exhaustively
hydrogenated at room temperature and 50 psi hydrogen pressure
over 5 g of palladium on carbon (10% strength) at catalyst in
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 41 -
1000 ml of ethyl acetate. The catalyst is filtered off and the
filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
crystallized from ether/petroleum ether.
Yield: 40.5 g (94% of theory),
Melting point: 52-54~C
R~: 0.75 (silica gel; ~ethylene chloride/methanol = 9.5:0.5)
c) 4-Benzyl-1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]piperazine
A mixture of 3 g (0.0167 mol) of methyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)-
propionate, 4.5 g (0.0167 mol) of bis(2-chloroethyl)benzyl-
amine and 7.57 g (10 ml)(0.059 mol) of N-ethyldiisopropylamine
in 60 ml of absolute ethanol is heated at reflux temperature
for 20 hours. The mixture is then concentrated to dryness in
vacuo and the residue is purified by chromatography on a
silica gel column, methylene chloride/methanol = 50:1 being
used as eluent.
Yield: 2.9 g (51% of theory),
Melting point: 56-58~C
Rf: 0.80 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
d) 1-[4-(2-Methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]piperazine
2.9 g (0.0083 mol) of 4-benzyl-1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)-
phenyl]piperazine are exhaustively hydrogenated at room
t temperature and under a hydrogen pressure o~ 45 psi over 1 g
of palladium on carbon (10% strength) in 100 ml of methanol.
The catalyst is filtered off with suction and the filtrate is
concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 2.2 g (78% of theory) of resin,
Rf: 0.13 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Example V
.. . .
1-(3,4-Dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
a) 3,4-Dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxynitrobenzene
A mixture o~ 10 g (0.0645 mol) of 4-nitropyrocatechol, 12.8 ml
(0.1354 mol) of methyl bromoacetate and 18.7 g (0.1354 mol) of
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
,. .
- 42 -
potassium carbonate in 100 ml of dry dimethylformamide is
heated at 80~C with stirring for 5 hours. It is then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is
partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The aqueous phase
is extracted twice more with ethyl acetate. The combined
organic extracts are dried and concentrated in vacuo. The
residue is triturated with ether and filtered o~f with
suction.
Yield: 11.4 g (59% of theory),
R~: 0.85 (silica gel; methylene chloride)
.
b) 3,4-Dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxyaniline hydrochloride
11.4 g (0.0381 mol) of 3,4-dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxynitro-
benzene are exhaustively hydrogenated at room temperature and
under a hydrogen pressure of 50 psi in 160 ml of methanol over
2 g of palladium on carbon (10% strength) in the presence of
40ml of lN hydrochloric acid. The catalyst is filtered off,
the filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the
residue is triturated with acetone and filtered off with
suction.
Yield: 10.96 g (94% of theory),
R~: 0.65 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
~ c) 4-Benzyl-1-(3,4-dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
A suspension of 4 g (0.013 mol) of 3,4-dimethoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyaniline hydrochloride, 3.5 g (0.013 mol) of bis(2-
chloroethyl)benzylamine and 5.09 g (6.74 ml)(0.039 mol) of
N-ethyldiisopropylamine in 50 ml of absolute ethanol is heated
to reflux with stirring for 20 hours, a clear solution
resulting. After concentration to dryness in vacuo, the
residue which remains is purified by chromatography on a
silica gel column, methylene chloride/methanol = 50:1 being
used as eluent.
Yield: 1.3 g (23% of theory) of oil,
R~: 0.15 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
., ~
- 43 -
d) 1-(3,4-Dimethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
1.25 g (0.0029 mol) of 4-benzyl-1-(3,4-dimethoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine are exhaustively hydrogenated under
a hydrogen pressure of 50 psi over 1 g of palladium on carbon
as catalyst in 100 ml of methanol at 50~C. The catalyst is
filtered off with suction and the filtrate is concentrated to
dryness in vacuo. The residue is reacted further without
purification.
Yield: 0.7 g (71% of theory) of resin,
Rf: 0.11 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
.
Example VI
1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-ylacetic acid
a) Piperidin-4-ylacetic acid
75 g of 4-pyridylacetic acid hydrochloride are treated with
750 ml of glacial acetic acid (50~ strength), 6 g of platinum
dioxide are added and the mixture is hydrogenated at 3 bar and
room temperature ln the course o~ 3 hours. The catalyst is
filtered off with suction and the mother liquor is concen-
trated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is triturated with
acetone and filtered off with suction. It is washed twice with
~ acetone and once with ether.
Yield: 71.7 g (92% of theory) of white substance,
Melting point: 150-153~C
b) 1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-ylacetic acid
A solution of 24.3 g (0.11 mol) of di-tert-butyldicarbonate in
20 ml of tetrahydrofuran is added dropwise to a solution of
20 g (0.11 mol) of piperidin-4-ylacetic acid in 250 ml of lN
sodium hydroxide solution and the mixture is allowed to stand
at room temperature overnight. It is then neutralized with
250 ml of lN hydrochloric acid and extracted three times with
methylene chloride. The combined organic phases are dried and
evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The oily residue is
cry5tallized from petroleu~ ether.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 44 -
Yield: 19 g (70% of theory),
Melting point: 97-99~C
Example VII
1-Benzyl-4-carboxymethylpiperazine
a) 1-Benzyl-4-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperazine
4.9 g = 6.7 ml (0.048 mol) of triethylamine and 7.4 g = 4.6 ml
(0.048 mol) of methyl bromoacetate are added to a solution of
~ 8.5 g (0.048 mol) of 1-benzylpiperazine in 100 ml of methanol
and the mixture is stirred overnight at room temperature. It
is then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
partitioned between saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate solution and ethyl acetate and the aqueous phase is
extracted again with ethyl acetate. The combined organic
extracts are dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 10.4 g (87% of theory) of oil,
Rf: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) 1-Benzyl-4-carboxymethylpiperazine
83.8 ml of lN sodium hydroxide solution are added to a
solution of 10.4 g (41.9 mmol) of 1-benzyl-4-methoxycarbonyl-
methylpiperazine in 120 ml of tetrahydrofuran and 60 ml of
water and the mixture is stirred for 4 hours at room
temperature. 83.8 ml of lN hydrochloric acid are then added
and the mixture is concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is treated three times with absolute ethanol, which is
distilled off in vacuo each time. The residue which remains is
stirred with methylene chloride/methanol = 1:1, then the
precipitated, organic solid is filtered off and the filtrate
is concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 7.3 g (74% of theory),
Melting point: 190-192~C
R~: 0.16 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 4:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 45 -
Example VIII
4-Carboxymethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperazine
a) 4-Benzyloxycarbonylmethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)piperazine
4.6 g = 3.2 ml (0.02 mol) of benzyl bromoacetate are added to
a solution of 9.6 g (0.02 mol) of 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoroacetate and 6.1 g = 8.4 ml
~ (0.06 mol) of triethylamine in 150 ml of methanol, and the
mixture is heated at reflux temperature for 8 hours and
allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. The solution
is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is
partitioned between saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate
solution and ethyl acetate. The aqueous phase is extracted
once more with ethyl acetate. The combined ethyl acetate
extracts are dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue which remains is purified by means of chromatography
on a sillca gel column, methylene chloride which contains 2%
methanol being used as eluent.
Yield: 3.2 g (40% of theory),
Melting point: 93-94~C
Rf: 0.80 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) 4-Carboxymethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperazine
Prepared from 4-benzyloxycarbonylmethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine by hydrogenation over palladium on
carbon (10% strength) analogously to Example 5, but without
hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 2.2 g (92% of theory),
R~: 0.09 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 46 -
Example IX
1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine
trifluoracetate
a) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-
piperazine
A solution of 10 g (0.0485 mol) of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-
methylpiperazine in 50 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid is
heated at 180~C ~or 10 hours in an autoclave and then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue which remains is
dissolved in 100 ml of dioxane/water = 1:1. A pH of 11 is set
using lON sodium hydroxide solution, a solution of 11 g of
di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in 15 ml of dioxane is added
dropwise with ice-cooling and the mixture is stirred overnight
at room temperature. It is then concentrated to dryness in
vacuo. The residue is crystallized from methanol/ether. The
crystals are filtered off with suction and washed with ether.
Yield: 8.09 g (57% of theory),
R~: 0.45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-2-methylpiperazine
A suspension of 6 g (0.0205 mol) of 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine, 2.4 ml (0.0246 mol) o~
methyl bromoacetate and 3.4 g (0.0246 mol) of potassiu~
carbonate in 50 ml of dimethylformamide is heated at 100~C for
6 hours and, after cooling, concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
The residue is partitioned between ethyl acetate and water and
the aqueous phase is extracted once more with ethyl acetate.
The combined ethyl acetate extracts are concentrated to
dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified by means o~
chromatography on a silica gel column, ethyl acetate/cyclo-
hexane being used as eluent. After evaporation, the residue is
crystallized from ether/petroleum ether.
Yield: 6 g (80% o~ theory),
Me l t ing po int: 62-65~C
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 47 -
c) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine
trifluoroacetate
6 g (0.0165 mol) of 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-methoxy-
carbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine are dissolved in
20 ml of methylene chloride and 20 ml of trifluoroacetic acid.
This solution is allowed to stand at room temperature for
4 hours and is then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is treated three times with acetone and concentrated
to dryness in vacuo each time. The residue which remains is
~ triturated with ether and filtered off with suction.
Yield- 8.95 g (quantitative),
Melting point: 140-143~C
R~: 0.22 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example X
2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)ethyl bromide
A solution o~ 1.0 g of 1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazine and
0.7 g (0.005 mol) of N-ethyldiisopropylamine in 5 ml of
1,2-dibromomethane is allowed to stand at room temperature for
- 3 days and then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue
is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel column,
methylene chloride which initially contains 1% and then 2% of
methanol being used as eluent.
Yield: 0.6 g (38% of theory),
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 293/295
R~: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 48 -
Example XI
1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine hydrochloride
a) Methyl 4-aminophenylacetate hydrochloride
7.6 g = 4.7 ml of thionyl chloride are added dropwise with
stirring at -10~C to -20~C to 100 ml of methanol and the
mixture is then stirred for half an hour at -20~C. 8.0 g
(0.053 mol) of 4-aminophenylacetic acid are added to this
solution at -20~C, and it is stirred for a further 2 hours at
-20~C and then overnight at room temperature. The solution is
concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is triturated
with petroleum ether and filtered off with suction.
Yield: 9.0 g (84~ of theory),
Melting point: 194-196~C
Rf: 0.85 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) 4-Benzyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine
Prepared from methyl 4-aminophenylacetate hydrochloride,
bis(2-chloroethyl)benzylamine and N-ethyldiisopropylamine
analogously to Example IVc.
Yield: 1.8 g (55% of theory),
Melting point: 73-75~C
Mass spectrum: M = 324
Rf: 0.7 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9.5:0.5)
c) 1-(4-Methyloxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared by hydrogenation of 4-benzyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methylphenyl)piperazine over palladium on carbon (10%
strength) analogously to Example IVd.
Yield: 1.5 g (quantitative) of oil,
Rf: O . 10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9.5:0.5)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 49 --
Example XII
(S)-1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-
piperazin-2-one
a) Ethyl 4-(2,2-diethoxyethylamino)phenoxyacetate
A solution of 10 g (0.051 mol) of ethyl 4-aminophenoxyacetate,
8.5 ml (0.056 mol) of bromoacetaldehyde diethyl acetal and
9.8 ml (0.056 mol) of N-ethyldiisopropylamine in 30 ml of dry
dimethylformamide is heated at 100~C for 30 hours. After
~ cooling, the mixture is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and
the oil which remains is partitioned between ethyl acetate and
water. The organic phase is washed with water, dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified by
means of chromatography on a silica gel column, cyclohexane/
ethyl acetate = 1:1 being used as eluent. After evaporation,
9 9 g (62% of theory) of an almost colourless oil remain.
Rf: O . 70 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 1:1)
b) Ethyl 4-[N-(benzyloxycarbonyl-O-methyl-L-tyrosyl)-2,2-
diethoxyethylamino]phenoxyacetate
A solution of 2.1 g (67 mmol) of ethyl 4-(2,2-diethoxyethyl-
amino)phenoxyacetate, 2 g (61 mmol) of benzyloxycarbonyl-O-
methyl-L-tyrosine, 0.73 ml (67 mmol) of N-methylmorpholine and
0.9 ml (67 mmol) of isobutyl chloroformate in 50 ml of dry
dimethylformamide is allowed to stand overnight at room
temperature and then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is partitioned between 0.5 molar potassium hydrogen
sulphate solution and ethyl acetate. The organic phase is
dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue which
remains is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel
column, ethyl acetate/cyclohexane = 1:2 being used as eluent.
After evaporation, 3.3 g (87% of theory) of an almost
colourless oil remain.
Rf: O . 60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 1:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 50 -
c) (S)-4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)piperazin-5-en-2-one
A solution of 3.3 g (53 mmol) of ethyl 4-[N-(benzyloxy-
carbonyl-O-methyl-L-tyrosyl)-2,2-diethoxyethylamino]phenoxy-
acetate in 15 ml of trifluoroacetic acid is allowed to stand
overnight at room temperature and then concentrated to dryness
in vacuo. The residue is partitioned between saturated,
aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and ethyl acetate.
The ethyl acetate phase is dried and concentrated to dryness
in vacuo. The residue which remains is purified by means of
chromatography on a silica gel column, ethyl acetate/
cyclohexane = 1:2 being used as eluent. After evaporation, 3.6
g (76% of theory) remain as almost colourless oil.
Rf: 0.50 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
d) (S)-1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl-
piperazin-2-one
Prepared by hydrogenation of 1.7 g (82 mmol) of (5)-4-benzyl-
oxycarbonyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxy-
benzyl)piperazin-5-en-2-one over palladium on carbon (10%
strength) analogously to Example IVd.
Yield: 1.2 g (98% of theory) of oil,
Melting point: 93-94~C
: 0.05 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
~ ,
Example XIII
1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-butyl-
oxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyleneamino]cyclohexane
a) 4-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)cyclohexanone
13 ml (78.9 mmol) of tert-butyl bromoacetate are added
dropwise at room temperature with stirring to a mixture of
15.0 g (78.8 mmol) of 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexanone and
12.4 g (90 mmol) of potassium carbonate in 100 ml of dimethyl-
formamide and the mixture is additionally stirred overnight.
It is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is
- CA 02244860 1998-07-29
1~ ~
- 51 -
partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The organic phase
is dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
crystallized from cyclohexane.
Yield: 17.5 g (73% of theory),
Melting point: 78-80~C
Rf: 0. 50 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate 2:1)
b) 1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyleneimino]cyclohexane
A mixture of 4.57 g (15 mmol) of 4-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
~ methyloxyphenyl)cyclohexanone, 3.21 g (15 mmol) of l-(tert-
butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-ylmethylamine and 10 g of
molecular sieve 3A in 100 ml of tolene is stirred overnight at
room temperature. 0.75 g of l-(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)-
piperidin-4-ylmethylamine are then added again and the mixture
is stirred for a further 8 hours at 60~C and then overnight at
room temperature. The molecular sieve is filtered off and the
filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 8.85 g of crude product.
Example XIV
4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]-1-(4-
1 hydroxyphenyl)piperidine
. .
a) l-Benzyl-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]piperidine
4.71 g (0.108 mol) of a 55% strength sodium hydride/oil
suspension are added to a solution of 20 g (0.1 mol) of
N-benzyl-4-hydroxypiperidine in 300 ml of dry tetrahydrofuran
and the mixture is stirred for 4 hours at room temperature.
~fter this time, a suspension of 29.3 g (0.1 mol) of 1-(1-
tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl-2-methanesulphonyloxy-
ethane in 30 ml of tetrahydrofuran is added, and the mixture
is additionally stirred for 2 days at room temperature and
then partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The organic
phase is dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
,~ ~
- 52 -
residue is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel
column, methylene chloride/methanol (30:1) and (10:1) being
used as eluent.
Yield: 16.6 g (42% of theory) of orange oil,
Rf: O .17 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 15:1
b) 4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-
piperidine
8.04 g (21 mmol) of 1-benzyl-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]piperidine are exhaustively
hydrogenated analogously to Example 5 over palladium hydroxide
on carbon in methanol.
Yield: 6.21 g (99~ of theory).
c) 1-(4-Benzyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methoxy]piperidine
A mixture of 600 mg (2 mmol) of 4-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)methoxy]piperidine, 526 mg (2 mmol) of
4-benzyloxybromobenzene, 314 mg (2.8 mmol) of potassium tert-
butoxide, 23 mg (0.04 mmol) of bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-
palladium(O) and 24 mg (0.08 mmol) of tri-o-tolylphosphine in
20 ml of toluene is heated at reflux temperature for 6 hours
under nitrogen. After cooling, the mixture is partitioned
between water and ethyl acetate, and the organic phase is
dried and evaporated to dryness. The residue which remains is
purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel column,
cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 2:1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 420 mg (44% of theory,
Rf: 0.35 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate 2:1)
d) 4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]-
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine
540 mg (1.1 mmol) of 1-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]piperidine are
exhaustively hydrogenated analogously to Example 5 on
palladium on carbon (10% strength) in methanol.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 53 -
Yield: 410 mg (93% of theory) of viscous oil,
Rf: O. 60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example XV
1-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
a) l-Benzyl-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine
Prepared from l-(l-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl-
2-methanesulphonyloxyethane and l-benzylpiperazine analogously
to Example 3.
Yield: 21 g (90% of theory),
Rf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
b) l-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazine
Prepared ~rom l-benzyl-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-piperi-
din-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine by exhaustive hydrogenation over
palladium on carbon (10% strength) analogously to Example 5.
Yield: 12.4 g (95% of theory) of oil,
Rf: O.I9 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example XVI
l-(trans-4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazin-2-one
a) Methyl 4-trans-[N-(benzyloxycarbonylglycyl)-N-(2,2-
diethoxyethyl)amino]cyclohexyloxyacetate
Prepared from N-benzyloxycarbonylglycine, methyl 4-trans-2,2-
diethoxyethylaminocyclohexyloxyacetate and 2-(lH-benzotriazol-
l-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate analogously
to Example IIId.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 54 -
Yield: 2.42 g (93% of theory) of viscous oil,
Rf: 0. 75 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
b) 4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-1-(trans-4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
cyclohexyl)piperazin-5-en-2-one
Prepared ~rom methyl 4-trans-[N-(benzyloxycarbonylglycyl)-
N-(2,2-diethoxyethyl)amino]cyclohexyloxyacetate and
trifluoroacetic acid analogously to Example IIIe.
Yield: 1.33 g (68% o~ theory) of resin,
~ Rf: O . 55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
c) 1-(trans-4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazin-2-
one
Prepared by hydrogenation o~ 4-benzyloxycarbonyl-1-(trans-
4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazin-5-en-2-one
analogously to Example IIIf.
Yield: 780 mg (90% o~ theory) of oil,
Rf: O . 45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example XVII
. ,..)
4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-1-
(piperidin-4-yl)piperazine
a) 1-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
Prepared ~rom 1-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine, 1-benzylpiperidin-4-one and sodium cyanboro-
hydride analogously to Example 11.
Yield: 4.27 g (91% o~ theory),
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 55 -
Rf: O . 45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
b) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-1-
(piperidin-4-yl)piperazine
Prepared by hydrogenation of 1-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-[2-
(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine over
palladium on carbon (10% strength) analogously to Example 5.
Yield: 1.55 g (87% of theory),
Rf: O . 38 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
~ ammonia = 4:1:0.25)
I
Example XVIII
trans-4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-1-
(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexane
a) trans-4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexanol
Prepared from 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexanone and sodium
borohydride analogously to Example 10.
Yield: 3.9 g (68% of theory),
Rf: 0.34 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 15:1)
b) trans-4-(4-Benzyloxyphenyl)cyclohexanol
mixture o~ 3.9 g (0.02 mol) of trans-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-
cyclohexanol, 2.4 ml (0.02 mol) of benzyl bromide and 3.45 g
(0.025 mol) of potassium carbonate in 30 ml of dimethylform-
amide is stirred at room temperature for one day, heated to
70~C for one hour and then, after cooling, poured slowly with
stirring into 200 ml of water. The precipitated crystals are
filtered off and drled.
Yield: 5.07 g (89~ of theory) of white crystals,
R~: 0.45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 15:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 56 -
c) trans-1-(4-Benzyloxyphenyl-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane
Prepared from trans-4-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)cyclohexanol and
~ tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl-2-methanesulphonyl-
oxyethane analogously to Example XIVa.
Yield: 1.3 g (39% of theory),
Rf: 0.55 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 2:1)
d) trans-4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexane
Prepared by hydrogenation of trans-1-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclo-
hexane on palladium on carbon (10% strength) analogously to
Example 5.
Yield: 850 mg (81% of theory),
Rf: O . 45 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 2:1)
Example XIX
[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]cyclo-
hexan-4-one
a) 4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-
cyclohexane ethylene ketal
Prepared from 4-hydroxycyclohexane ethylene ketal and
1-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl-2-
methanesulphonyloxy-ethane analogously to Example XIVa.
Yield: 6.2 g (27% of theory) of oil,
Rf: O . 35 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
b) [(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]cyclohexan-
4-one
A solution of 8.5 g (0.024 mol) of 4-[(1-tert-butyloxy-
carbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane ethylene ketal in
120 ml of glacial acetic acid and 30 ml of water is heated at
65~C for 5 minutes. After cooling, it is partitioned between
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 57 -
saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and ethyl
acetate. The aqueous phase is extracted a further three times
with ethyl acetate. The combined organic extracts are dried
and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified
by means of chromatography on a silica gel column,
cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 2:1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 4 g (54% of theory),
Melting point: 48-52~C
Rf: 0.50 (silica geli cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
Example XX
1-(3-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoroacetate
a) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine
Prepared by acidic hydrolysis of 1-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazine
with concentrated hydrochloric acid and subsequent reaction of
the 1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine prepared in this way with
di-tert-butyl dicarbonate analogously to Example IXa.
Yield: 6.5 g crude (quantitative) of oil,
Rf: O . 60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia =--9:1:0.1)
.
b) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-(3-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)piperazine
Prepared from 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-
piperazine, ethyl bromoacetate and potassium carbonate
analogously to Example IXb.
Yield: 3.9 g (46% o~ theory) o~ amorphous solid,
Rf: 0.85 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
c) 1-(3-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine tri~luoro-
acetate
Prepared ~rom 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-1-(3-ethoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine and trifluoroacetic acid
analogously to Example IXc.
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 58 -
Yield: 3 g (74% of theory), amorphous solid
R~: 0.15 (silica gel; cyclohexane/ethyl acetate = 1:1)
Example XXI
- (S)-4-[1-(2-Ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxycarbonyl-
methyl-2-oxo-piperazinyl]piperidine
a) (S)-1-(2-Ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
2-oxo-piperazine
~ 44 g of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide are
l added with stirring and cooling with ice to a solution of
0.8 g of N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-8-alanine ethyl ester and 1 g
of 8-methyl N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-aspartate in 20 ml of
methylene chloride. This mixture is stirred further for
10 minutes with ice-cooling and then for 50 minutes at room
temperature. 20 ml of water and 10 ml of a 5% strength aqueous
potassium hydrogen sulphate solution are added with further
stirring. The organic phase is separated off and the aqueous
phase is extracted with 20 ml of methylene chloride. The
combined organic phases are washed with water, dried over
sodium sulphate and concentrated to dryness under reduced
pressure. The residue which remains (1.3 g) is allowed to
stand overnight at room temperature in 2.5 ml of trifluoro-
~ acetic acid and 0.5 g of p-toluenesulphonic acid is then added
and the mixture is stirred for 4 hours at 70-75~C. After
cooling, the toluene solution is washed with aqueous sodium
hydrogen carbonate solution and concentrated to dryness under
reduced pressure. The residue is purified by means of
chromatography on a silica gel column, ethyl acetate/cyclo-
hexane = 1:1 being used as eluent. After evaporation, the
residue (0.9 g) is dissolved in 25 ml of ethanol und
exhaustively hydrogenated with hydrogen over 0.3 g of
palladium on carbon (10~ strength). The catalyst is filtered
off and the filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
0.9 g of a colourless oil r~m~; n.s,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 59 -
b) (S)-l-Benzyloxycarbonyl-4-[1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-
3-isopropyloxycarbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]piperidine
2 g (0.0083 mol) of N-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidone and
2.27 g (0.0083 mol) of (S)-1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-
methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazine are dissolved in 40 ml
of absolute ethanol and, after standing at room temperature
for 2 hours, 3.4 g (0.016 mol) of triacetoxyborohydride,
2.8 ml (0.0092 mol) of titanium(IV) isopropoxide and 1.05 ml
of acetic acid are added at room temperature with stirring and
the mixture is stirred further overnight at room temperature.
It is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is
partitioned between ethyl acetate and sodium hydrogen
carbonate solution and the aqueous phase is extracted twice
more with ethyl acetate. The combined ethyl acetate phases are
dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
purified on a silica gel column, methylene chloride which
contains 2% or 3% methanol being used as eluent.
Yield: 1.64 g (66% of theory),
R~: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
c) (S)-4-[1-(2-Ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxycarbonyl-
methyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]piperidine
~ 0.8 g (1.5 mmol) of (S)-l-benzyloxycarbonyl-1-[1-(2-ethoxy-
J carbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxycarbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]-
piperidine are exhaustively hydrogenated at a hydrogen
pressure of 50 psi over 0.5 g of palladium on carbon (10%
strength) in 80 ml of ethanol. The catalyst is filtered off
with suction and the filtrate is concentrated to dryness in
vacuo.
Yield: 0.52 g (88% of theory), of oil,
R~: 0.10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 60 -
Example XXII
1-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)phenyl]piperazine
hydrochloride
a) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)piperazine
A solution of 16.5 g (0.067 mol) of 4-nitrophenylpiperazine in
500 ml of tetrahydrofuran is treated at room temperature and
with stirrlng with 148 ml of lN sodium hydroxide solution and
then with 17.7 g (0.081 mol) of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate. The
mixture is further stirred overnight at room temperature, then
the tetrahydrofuran is distilled off under reduced pressure
and the residue is extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined
ethyl acetate extracts are washed with water, dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is triturated
with ether, and the solid is filtered off with suction and
dried.
Yield: 17.4 g (83.6% of theory),
Melting point: 146~C
R~: 0.8 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9.5:0.5)
b) l-(4-Aminophenyl)-4-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazine
A solution of 10.7 g (0.035 mol) of 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
~ 1-(4-nitrophenyl)piperazine in 200 ml of ethyl acetate is
- exhaustively hydrogenated over 1 g of palladium on carbon (10%
strength) at room temperature and under a hydrogen pressure of
50 psi in 200 ml of ethyl acetate. After filtering off the
catalyst, the mother liquor is concentrated to dryness in
vacuo.
Yield: 9.6 g (100% of theory) of oil, which crystallizes,
Melting point: 92~C
R~: 0.41 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
c) l-(4-Acetaminophenyl)-4-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazine
2.8 g (0.01 mol) of 1-(4-aminophenyl)-4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperazine and 0.78 g = 0.7 ml (0.01 mol) of acetyl chloride
are dissolved in 50 ml of dry dimethylformamide, 1.3 g =
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 61 -
1.8 ml (0.013 mol) of triethylamine are added dropwise with
stirring and at room temperature and the mixture is stirred
further overnight. It is then concentrated to dryness in vacuo
and the residue is partitioned between ethyl acetate and lN
hydrochloric acid. The combined organic extracts are washed
with saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 2.0 g (62.0% of theory),
Melting point: 143~C
Rf: 0.49 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
.
d) 1-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)phenyl]-l-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperazine
0.74 g (6.6 mmol) of potassium tert-butoxide is added at room
temperature and with stirring to a solution of 2.0 g
(6.3 mmol) of 1-(4-acetaminophenyl)-4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperazine in 20 ml of dimethyl sulphoxide and the mixture is
stirred for a further 30 minutes. 1.0 g = 0.6 ml (6.3 mmol)of
methyl bromoacetate is then added dropwise with further
stirring and the mixture is stirred further overnight at room
temperature. After this time, it is poured onto water and
extracted with methylene chloride. The combined organic
extracts are washed successively with 0.5 molar potassium
hydrogen sulphate solution and saturated sodium hydrogen
-3 carbonate solution, dried and evaporated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 1.8 g (73.4% of theory),
Mass spectrum: M+ = 391
Rf: O . 55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
e) l-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)phenyl]-
piperazine hydrochloride
15 ml of ethereal hydrochloric acid are added to a solution of
1.77 g (4.5 mmol) of 1-[4-(N-acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
amino)phenyl]-4-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazine in 20 ml of
methanol and the mixture is allowed to stand at room
temperature for 5 hours. It is then concentrated to dryness in
vacuo.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 62 -
Yield: 1.5 g (quantitative) of oil,
Rf: O .13 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Example XXIII
1-[4-(N-n-Butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]piperazine hydrochloride
a) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-(4-n-butylsulphonylaminophenyl)-
piperazine
~ 2.8 g (0.01 mol) of 1-(4-aminophenyl)-4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperazine and 1.7 g = 1.4 ml (0.01 mol) of n-butanesulphonyl
chloride are dissolved in 50 ml of dry methylene chloride,
1.0 g = 1.0 ml (0.013 mol) of pyridlne is added dropwise with
stirring and at room temperature and the mixture is stirred
further overnight. It is then concentrated to dryness in vacuo
and the residue is partitioned between ethyl acetate and lN
hydrochloric acid. The combined organic extracts are washed
with saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
Yield: 3.9 g (quantitative) of oil,
Mass spectrum: M = 397
Rf: 0.52 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
b) 4-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl-N-methoxy-
carbonylmethylamino)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 4.0 g (0.01 mol) of 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
1-(4-n-butylsulphonylaminophenyl)piperazine, 1.3 g (0.011 mol)
of potassium tert-butoxide and 1.8 g = 1.1 ml (0.011 mol) of
methyl bromoacetate in 10 ml of dry dimethyl sulphoxide
analogously to Example XXIId.
Yield: 4.6 g (97.3% of theory) of oil,
Rf: 0.73 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
- CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 63 -
c) 1-[4-(N-n-Butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 3.0 g (6.4 mol) of 4-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]piperazine and 10 ml of ethereal hydrochloric acid in
10 ml of methanol analogously to Example XXIIe.
Yield: 2.6 g (quantitative) of oil,
Rf: O . 27 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Preparation of the final products:
.
Example 1
1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazine dihydrochloride
A solution o+~ 450 mg (1.2 mmol) ol- 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
dihydrochloride in 25 ml of 3N hydrochloric acid is allowed to
stand at room temperature for 5 hours and then concentrated to
dryness in vacuo. The solid residue which remains is
triturated with acetone, filtered of~ with suction and dried.
Yield: 400 mg (76% of theory),
Melting point: 258-260~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 348
Rf: O . 08 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
1 :
(1) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidln-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride.
Yield: 96% of theory of amorphous solid,
Mass spectrum: M+ = 361
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 64 -
Rf: 0.70 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/50% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(2) 1-[4-(2-Carboxyethyl)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 98% of theory,
Melting point: 268-271~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 346
~ Rf: 0.65 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/50% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(3) 1-[3,4-Di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[3,4-di(methoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine.
Yield: 99% of theory,
Melting point: 118-121~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 421
Rf: 0.65 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/50~0 strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(4) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)acetyl]-
piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-
[(piperidin-4-yl)acetyl]piperazine hydrochloride.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Melting point: 88-90~C
Mass spectrum: M = 361
Rf: 0.08 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 65 -
(5) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)amino-
carbonyl]piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-
[(piperidin-4-yl)aminocarbonyl]piperazine hydrochloride.
Yield: 91% of theory,
Melting point: 73-78~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 363
Rf: 0.18 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(6) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-piperazinyl)carbonyl-
methyl]piperazine
Prepared from l-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-
piperazinyl)carbonylmethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 62% of theory,
Melting point: 248-252~C
Mass spectrum: M = 362
Rf: O . 40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(7) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-4-
[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 83% o~ theory of amorphous solid,
Mass spectrum: M = 361
Rf: 0.70 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/5% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(8) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperazin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperazin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 78% of theory,
Melting point: 253-2S6~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 348
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 66 -
Rf: 0.07 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(9) 1-(4-Carboxymethylphenyl)-4-[2-(piperazin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperazin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 69% of theory,
Melting point: 235-238~C
Mass spectrum: M = 332
~ Rf: 0.35 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
! ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(10) (S)-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride
Prepared from (S)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-
(4-methoxybenzyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one
dihydrochloride.
Yield: 81% of +heory,
Melting point: 109-115~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 482
Rf: 0.55 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/5% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
~-~ (11) 1-[2,4-Di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[2,4-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(12) 1-[3,5-Di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[3,5-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 67 -
(13) 1-(3-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(3-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 98% of theory,
Melting point: 218-220~C
Mass spectrum: M = 347
Rf: 0. 20 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/ammonia =
2:1:0.25)
~ (14) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
oxycarbonyl]piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)oxycarbonyl]piperazine hydrochloride and
trifluoroacetic acid.
(15) 1-(2-Carboxybenzo-1,3-dioxol-5-yl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-(2-ethoxycarbonylbenzo-1,3-dioxol-5-yl)-4-
[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(16) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperidine hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperidine hydrochloride.
(17) 1-(4-Carboxymethylaminophenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethylaminophenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(18) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-2-(4-methoxybenzyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-(4-
methoxybenzyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one
hydrochloride.
=
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 68 --
(19) (S)-4-[1-(2-Carboxyethyl)-3-isopropyloxycarbonyl-2-oxo-
piperazinyl]-l-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperidine
hydrochloride
Prepared ~rom (S)-4-[1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxy-
carbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]-1-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperidine hydrochloride.
Yield: 83% oi~ theory, amorphous
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 467
R~: 0.65 (reversed-phase plate RP 18i methanol/5% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(20) (R)-2-Benzyl-1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(pipe-
ridin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared i~rom (R)-2-benzyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydro-
chloride.
(21) trans-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
methylamino]cyclohexane dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom trans-1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-4-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-
amino]cyclohexane and 6N hydrochloric acid/acetic acid = 1:1.
~ Yield: 98~6 of theory,
~-~ Melting point: 309-311~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 346
R~: 0.12 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(22) trans-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-methylmethylamino]cyclohexane dihydrochloride
Prepared i~rom trans-1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-methyl-
methylamino]cyclohexane and 6N hydrochloric acid/acetic acid =
1 : 1 .
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 69 -
Yield: 99% of theory,
Melting point: 123-126~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 360
Rf: 0.18 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(23) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy~piperidine hydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-(4-methyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]piperidine hydrochloride.
Yield: 99% of theory, amorphous solid
Mass spectrum: M+ = 348
Rf: 0.30 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(24) 1-[1-(2-Carboxyethyl)piperidin-4-yl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin trihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-[1-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine trihydrochloride.
Yield: 99% of theory,
Melting point: 341-345~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 352
Rf: 0.09 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
~ ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(25) trans-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy)]cyclohexane hydrochloride
Prepared from trans-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane hydrochloride and 6N
hydrochloric acid/acetic acid = 1:1.
Yield: 95% of theory,
Melting point: 242-245~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 348
R~: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 70 -
(26) trans-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-acetylmethylamino]cyclohexane hydrochloride
Prepared from trans-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-N-acetylmethylamino]cyclohexane hydro-
chloride and 6N hydrochloric acid.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 113-115~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ - 388
Rf: 0.35 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
.
(27) trans-1-(4-Carboxymethyloxypiperidino)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane ditrifluoroacetate
Prepared from trans-1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy-
piperidino)-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]cyclohexane and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: quantitative, of resin
Mass spectrum: M+ = 354
Rf: O . 10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
(28) 1-(3-Carboxymethyloxypyridazin-6-yl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[Z-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(3-methoxycarbonylmethyloxypyridazin-6-yl)piperazine.
Yield: 6% of theory,
Melting point: 265-270~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 350
Rf: 0.20 (silica ~el; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
(29) cis/trans-1-(4-Carboxymethylpiperazino)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared from cis/trans-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperazino)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride.
Yield: quantitative,
CA 02244860 l998-07-29
- 71 -
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 340
Rf: 0.13 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
(30) cis/trans-1-t4-(1-Carboxyprop-2-yl)piperazino]-4-
[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom cis/trans-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylprop-2-yl)-
piperazino]-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane
trihydrochloride.
Yield: 80% o~ theory,
Melting point: 90-110~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 368
R~: 0.15 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
(31) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyl-
amino]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~ro~ 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methylamino]piperidine dihydrochloride.
(32) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-methylmethylamino]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-N-methylmethylamino]piperidine
dihydrochloride.
(33) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-benzylmethylamino]piperidlne dihydrochloride
Prepared +-rom 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-N-benzylmethylamino]piperidine
dihydrochloride.
(34) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)amino-
methyl]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)aminomethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
- 72 -
(35) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidln-4-yl)-N-
benzylaminomethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-N-benzylaminomethyl]piperidine
dihydrochloride.
(36) 4-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-1-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
~ 1-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperidine dihydrochlorlde.
(37) 1-[4-(1,2-Dicarboxyethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-[4-(1,2-dimethoxycarbonylethoxy)phenyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(38) 1-[4-(1-Carboxy-2-phenylethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenylethyloxyphenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(39) 1-[4-(1-Carboxy-3-hydroxypropyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonyl-3-hydroxypropyl)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
(40) 1-[4-(1-Carboxy-2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methoxycarbonyl-
ethyloxy]phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
dihydrochloride.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 73 -
(41) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-~yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride.
(42) 1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine-2,5-dione hydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine-2,5-dione hydrochloride.
~ (43) 1-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-carboxymethylamino)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from l-[4-(N-acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride.
Yield: 78.3~ of theory,
Melting point: 118-121~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 388
Rf: 0.19 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(44) 1-[4-(N-n-Butylsulphonyl-N-carboxymethylamino)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonyl-
methylamino)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
dihydrochloride.
Yield: 75.9~ of theory,
Melting point: 104-105~C
Mass spectrum: M = 466
Rf: O . 22 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
f
"
- 74 -
Example 2
1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
A solution of 1.0 g (2.2 mmol) of 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxy-
carbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)piperazine in 20 ml of methanol and 30 ml of ethereal
hydrochloric acid is allowed to stand at room temperature for
5 hours. It is then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
solid residue which remains is triturated with acetone,
filtered off with suction and dried.
Yield: 900 mg (96% of theory),
Melting point: 225-227~C
Mass spectrum: M = 361
Rf: 0.08 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
2:
(1) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-2-one and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 92% of theory,
Melting point: 212-217~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 389
R~: 0.09 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(2) 1-[4-(2-Methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]piperazine and
tri~luoroacetic acid.
Yield: 96% of theory,
Melting point: 253-256~C (dec.)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 75 -
Mass spectrum: M+ = 359
Rf: 0.36 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(3) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)acetyl]piperazine hydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
acetyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 82% of theory,
Melting point: 98-99~C
' Mass spectrum: M+ = 375
Rf: 0.10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(4) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-4-[2-(pipe-
ridin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 27% of theory,
Melting point: 230-231~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 375
R~: 0.25 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
~ ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
_ . ,
(5) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperazin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Melting point: 210-212~C (sintering from 160~C)
Mass spectrum: M = 362
Rf: 0.13 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 76 -
(6) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)-4-[2-(piperazin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine and tri-
fluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Melting point: 238-242~C
Mass spectrum: M = 346
Rf: O . 25 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(7) (S)-1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxy-
benzyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydro-
chloride
Prepared ~rom (S)-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxy-
benzylpiperazin-2-one and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77% of theory, foam
Melting point: 212-217~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 509
Rf: 0.20 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(8) 1-[2,4-Di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
~,
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[2,4-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine and
trifluoroacetic acid.
(9) 1-[3,5-Di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[3,5-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine and
tri~luoroacetic acid.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
c
(10) 1-(3-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(3-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid in methanol.
Yield: 34% of theory,
Melting point: >270~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 361
Rf: 0. 65 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia 2:1:0.25)
.
(11) 1-(2-Ethoxycarbonylbenzo-1,3-dioxo-5-yl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(2-ethoxycarbonylbenzo-1,3-dioxo-5-yl)piperazine and
trifluoroacetic acid.
(12) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperidine hydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperidine and tri-
fluoroacetic acid.
.
(13) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethylaminophenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dlhydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine and tri-
fluoroacetic acid.
(14) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-(4-methoxybenzyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-l-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-(4-methoxy-
benzyl)piperazin-3-one and trifluoroacetic acid.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 78 -
(15) (S)-4-[1-(2-Ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxy-
carbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]-1-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperidine hydrochloride
Prepared from (S)-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]-4-[1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxy-
carbonylmethyl]-2-oxopiperazinyl]piperidine and trifluoro-
acetic acid.
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 495
Rf: 0.10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(16) (R)-2-Benzyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared from (R)-2-benzyl-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperazin-3-one and trifluoroacetic acid.
(17) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]piperidine hydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 195-198~C
~ Mass spectrum: M = 362
R~: 0.12 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(18) 1-(trans-4-Carboxylmethyloxycyclohexyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazlne dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(trans-4-carboxymethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazine and
conc. hydrochloric acid/water = 1:1.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 288-289~C (dec.)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 79 -
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 354
Rf: O.12 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(19) 1-(trans-4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(trans-4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)-
piperazin-2-one and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 80% of theory,
Melting point: 255-256~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 381
Rf: 0.26 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.25)
(20) 1-(1-Methoxycarbonylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine trihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(1-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)piperazine and
methanollc hydrochlorlc acld.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Melting point: 294-297~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 352
Rf: 0.20 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.25)
(21) 1-[1-(2-Methoxycarbonylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]-4-[Z-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazlne trlhydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[1-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]piperazine
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 97% of theory,
Melting point: 324-326~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 366
Rf: O . 37 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.25)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 80 -
(22) trans-[1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperi-
din-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane hydrochloride
Prepared from trans-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)cyclo-
hexane and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 86% of theory,
Melting point: 198-200~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 361
Rf: O . 10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(23) trans-1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperi-
din-4-yl)-N-acetylmethylamino]cyclohexane hydrochloride
Prepared from trans-[1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-acetyl-
methylamino]cyclohexane and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 90-92~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 402
Xf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.25)
(24) cis/trans-1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazino)-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared from cis/trans-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazino]-
cyclohexane and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 46% of theory,
Melting point: 218-228~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 353
Rf: O . 35 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
- CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.c ~
- 81 -
(25) cis/trans-1-[4-(2-Ethoxycarbonylethyl)piperazino]-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom cis/trans-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methyloxyJ-1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)piperazino]-
cyclohexane and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 98% o~ theory,
Melting point: 285-288~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 381
Rf: O . 20 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
.
(26) cis/trans-1-[4-(1-Methoxycarbonylprop-2-yl)piperazino]-
4-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared from cis/trans-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylprop-2-yl)piperazino]-
cyclohexane and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 90% o~ theory,
Melting point: 281-285~C
Mass spectrum: M = 381
Rf: O . 33 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(27) 1-[4-(1-Methoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperldin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 80% o~ theory,
Melting point: 265-270~C
Mass spectrum: M = 375
Rf: O . 25 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 82 -
(28) 1-[4-(2-Ethoxycarbonylprop-2-yloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylprop-2-yloxy)phenyl]piperazine
and ethereal hydrochlorlc acid.
Yield: 76% of theory,
Melting point: 260-266~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 403
Rf: O . 35 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
~ (29) 1-[4-(1-Methoxycarbonylbenzyl)phenyl]-4-[2-[piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylbenzyl)phenyl]piperazine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 76% of theory,
Melting point: 224-228~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 438
Rf: 0.27 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(30) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
~ 4-yl)methylamino]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methylamino]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperidine
and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(31) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
N-methylmethylamino]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared lrom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidln-4-yl)-
N-methylmethylamino]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperidine and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 83 -
(32) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)-N-benzylmethylamino]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
N-benzylmethylamino]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperidine and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(33) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)aminomethyl]piperidine dihydrochlorlde
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
aminomethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperidine
and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(34) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)-N-benzylaminomethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
N-benzylaminomethyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-
piperidine and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(35) 4-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-1-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-4-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperidine and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
_.~
(36) 1-[4-(1,2-Dimethoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(1,2-dimethoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
and tri~luoroacetic acid.
(37) 1-[4-(1-Methoxycarbonyl-2-phenylethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperldin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenylethyloxy)phenyl]-
piperazine and tri~luoroacetic acid.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 84 -
(38) 1-[4-(2-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-methoxycarbonylethyloxy)-
phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methoxycarbonylethyloxy)-
phenyl]piperazine and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(39) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-3-one hydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-3-one and
ethereal hydrochloric acid.
.
(40) 1-(4-Ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2,5-dione hydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-2,5-dione
and ethereal hydrochloric acid.
(41) 1-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-[4-(N-acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]-4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
piperazine.
~ Yield: 99.1% o~ theory,
Melting point: 198-199~C
Mass spectrum: M = 402
Rf: 0.25 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(42) 1-[4-(N-n-Butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochlorlde
Prepared ~rom 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
amino)phenyl]piperazine.
Yield: 85.2% o~ theory,
Melting point: 194-196~C
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 85 -
Mass spectrum: M = 480
Rf: 0.27 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
Example 3
4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
A solution of 4.8 g (0.01 mol) of 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
oxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoroacetate, 3.0 g (0.01 mol) of
1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methane-
sulphonyloxyethane and 3.9 g = 5.2 ml (0.03 mol) of N-ethyl-
diisopropylamine in 100 ml of methanol is heated at reflux
temperature for 24 hours. The methanol is then distilled off
in vacuo. The residue which remains is purified by
chromatography on a silica gel column, methylene chloride
which contains 3% methanol being used as eluent.
Yield: 2.1 g (46.6% of theory),
Melting point: 197-199~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 461
Rf: 0.55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
(1) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-2-one
Prepared from 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazin-
2-one hydrochloride and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-
4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 48% of theory,
Melting point: 94-96~C
Rf: 0.65 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 86 -
~2) 4-[2~ tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)phenyl~piperazine
and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methane-
sulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 56% of theory,
Melting point: 92-94~C
Rf: 0.75 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(3) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
~ 1-[3,4-di(methoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-[3,4-di(methoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
piperazine and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-
2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 30% of theory, of resin
Mass spectrum: M+ = 549
Rf: 0.70 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(4) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methylpiperazine
Prepared ~rom 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-
piperazine trifluoroacetate and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)-
piperidin-4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 70% of theory, of oil
Mass spectrum: M+ = 475
Rf: O . 55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(5) (S)-4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-
piperazin-2-one
Prepared from (S)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-3-(4-
methoxybenzyl)piperazin-2-one and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxy-
carbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 42% o+.~ theory, amorphous solid
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 87 -
Mass spectrum: M+ = 609
Rf: 0.25 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/cyclohexane = 1:1)
(6) 4-[2~ tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[2,4-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared ~rom 1-[2,4-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
piperazine and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-
2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
(7) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
-- 1-[3,5-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
~ Prepared ~rom 1-[3,5-di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
piperazine and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-
2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
(8) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(3-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
Prepared from 1-(3-ethoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-
methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 29% of theory,
Melting point: 80-82~C
Mass spectrum: M = 475
Rf: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(9) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethylaminophenyl)piperazine
Prepared ~rom 1-(4-ethoxycarbonylmethylaminophenyl)piperazine
and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methane-
sulphonyloxyethane.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 88 -
(10) (S)-1-[2~ tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
4-[1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyloxycarbonylmethyl-
2-oxopiperazinyl]piperidine
Prepared ~rom (S)-4-[1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-3-isopropyl-
oxycarbonylmethyl-2-oxopiperazinyl]piperidine and 1-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 26% o~ theory, amorphous solid
Mass spectrum: M+ = 594
Rf: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(11) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(trans-4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazin-2-one
Prepared +~rom 1-(trans-4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)-
piperazin-2-one and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-
4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 71~ o~ theory,
Mass spectrum: M = 481
Melting point: 85-87~C
Rf: O . 65 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(12) 1-[4-(N-Acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)phenyl]-
4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-[4-(N-acetyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]piperazine hydrochloride and 1-[(1-tert-butyloxy-
carbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
Yield: 34.8% of theory, o+.~ oil
Mass spectrum: M = 502
Rf: 0.6 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
(13) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl-N-methoxycarbonylmethylamino)-
phenyl]piperazine
Prepared +.~rom 1-[4-(N-n-butylsulphonyl- N-methoxycarbonyl-
methylamino)phenyl]piperazine hydrochloride and 1-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methanesulphonyloxyethane.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 89 -
Yield: 69.9% of theory, of oil
Mass spectrum: M~ = 580
R~: 0.77 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Example 4
4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)acetyl]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
A mixture of 1.5 g (0.062 mol) of 1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-ylacetic acid, 2.9g g (0.0062 mol) of 1-(4-
methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoroacetate,
1.9 g = 2.6 ml (0.0185 mol) of triethylamine and 2.0 g
(0.0062 mol) of 2-(lH-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyl-
uronium tetrafluoroborate in 100 ml of dry dimethylformamide
is stirred at room temperature overnight. It is then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue which remains
is partitioned between saturated, aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate solution and ethyl acetate and the aqueous phase is
extracted twice more with ethyl acetate. The combined organic
extracts are dried and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The
residue is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel
column, methylene chloride which contains 3~ methanol being
used as eluent.
Yield: 1.3 g (44% of theory), amorphous solid
R~: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
4:
(1) 4-[4-(1-Benzylpiperazinyl)acetyl]-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine
Prepared from 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
trifluoroacetate and 1-benzyl-4-carboxymethylpiperazine.
Yield: 45% of theory,
Melting point: 128-130~C
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 90 -
Mass spectrum: M+ = 466
Rf: O . 75 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(2) 4-[4-(1-Benzylpiperazinyl)carbonylmethyl]-1-(4-methoxy-
carbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
Prepared from 4-carboxymethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxy-
phenyl)piperazine and 1-benzylpiperazine.
Yield: 81% of theory,
Melting point: 95-96~C
Mass spectrum: M = 466
Rf: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol= 9:1)
Example 5
. .
1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-4-yl)-
aminocarbonyl]piperazine hydrochloride
2.0 g (4.3 mmol) of 4-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)aminocarbonyl]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine are
exhaustively hydrogenated at room temperature and under a
hydrogen pressure of 50 psi over 0.5 g of palladium on carbon
(10% strength) in 50 ml of methanol in the presence o~ 4.3 ml
~ of lN hydrochloric acid. The catalyst is filtered o~f, the
filtrate is concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue
is triturated with ether and filtered off with suction.
Yield: 1.5 g (84.8% of theory),
Melting point: 90-92~C
Mass spectrum: M = 376
Rf: 0.20 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
5:
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
-- 91 --
(1) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-piperazinyl)-
acetyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[4-(1-benzylpiperazinyl)acetyl]-1-(4-methoxy-
carbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine.
Yield: 96% o~ theory,
Melting point: 70-72~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 376
Rf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(2) 1-(4-Methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-piperazinyl)-
carbonylmethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 4-[4-(1-benzylpiperazinyl)carbonylmethyl]-1-(4-
methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine.
Yield: 96% o~ theory,
Melting point: 53-58~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 376
Rf: O . 10 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(3) 1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)oxycarbonyl]piperazine
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxycarbonyl]-1-(4-
~ tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine.
Example 6
4-[(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)aminocarbonyl]-1-(4-methoxy-
carbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
1.5 g (0.008 mol) o~ 1-benzyl-4-aminopiperidine are added at
0~C to a solution o~ 1.3 g (0.008 mol) of 1,1'-carbonyldi-
(1~2~4-triazole) in 100 ml of dry dimethylformamide and the
mixture is stirred ~or 30 minutes at 0~C and for 1 hour at
room temperature. 3.8 g (0.008 mol) o~ 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)piperazine tri~luoroacetate and 2.4 g = 3.3 ml
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 92 -
(0.024 mol) of triethylamine are then added, and the mixture
is heated for 2 hours at 80~C and stirred for a further
16 hours at room temperature. The solution is concentrated to
dryness in vacuo and the residue is partitioned between
saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and methylene
chloride. The aqueous phase is extracted twice more with
methylene chloride. The combined organic phases are dried and
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified by
chromatography on a silica gel column, methylene chloride
which contains 3% methanol being used as eluent.
Yield: 2.0 g (54% of theory),
~ Melting point: 140-141~C
Mass spectrum: M = 466
Rf: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 9:1)
Example 7
1-(4-Carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-piperazinyl)acetyl]-
piperazine
5.3 ml of a lN sodium hydroxide solution are added to a
solution of 0.6 g (1.3 mmol) of 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
methyloxyphenyl)-4-[(4-piperazinyl)acetyl]piperazine
dihydrochloride in 8 ml o~ tetrahydrofuran and 4 ml of water,
and the mixture is allowed to stand at room temperature for 3
~' hours. After this time, 5.3 ml of lN hydrochloric acid are
added and the solution is concentrated to dryness in vacuo.
The residue is treated three times with acetone and
concentrated to dryness each time. The residue which remains
is stirred with a mixture of methylene chloride/methanol =
1:1. The precipitated inorganic salts are filtered o+~f with
suction. The mother liquor is concentrated to dryness in
vacuo.
Yield: 52% of theory, amorphous foam
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 363
R~: 0.22 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 93 -
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
7:
(1) 1-(trans-4-Carboxymethyloxycyclohexyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one
Prepared from 1-(trans-4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxycyclohexyl)-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazin-2-one dihydrochloride.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 305-307~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 368
Rf: 0.15 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(2) 1-(1-Carboxymethylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-(1-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine trihydrochoride.
Yield: quantitative,
Melting point: 262-264~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 339
Rf: 0.065 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
(3) cis/trans-1-[4-(2-Carboxyethyl)piperazino]-4-[(piperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane trihydrochloride
Prepared from cis/trans-1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)-
piperazino]-4-[(4-piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclohexane
trihydrochloride and lithium hydroxide.
Yield: 58% of theory,
Melting point: 248-256~C
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 354
R~: 0.16 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 94 -
(4) 1-[4-(1-Carboxyethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
lithium hydroxide.
Yield: 79% of theory,
Melting point: 278-288~C
Mass spectrum: M = 361
Rf: 0.17 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
- (5) 1-[4-(2-Carboxyprop-2-yloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
Prepared from 1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylprop-2-yloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
lithium hydroxide.
Yield: 61% of theory,
Melting point: 262-265~C
Mass spectrum: M = 375
R~: 0.30 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 1:1:0.2)
(6) 1-[4-(1-Carboxybenzyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)-
~ ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylbenzyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and lithium
hydroxide.
Yield: 89% of theory,
Melting point: >250~C
Mass spectrum: M = 423
Rf: 0.12 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 95 -
Example 8
4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperazine
A solution of 1.63 g (3.4 mmol) of 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
oxyphenyl)piperazine trifluoroacetate, 1.0 g (3.4 mmol) of
2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)ethyl bromide and
1.32 g = 1.8 ml (10.2 mmol) of N-ethyldiisopropylamine in 5 ml
of methanol is allowed to stand at room temperature for
24 hours. The methanol is distilled off in vacuo and the
residue is purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel
column, methylene chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia = 99:1:0.1
being used as eluent.
Yield: 1.6 g (quantitative) of oil,
Mass spectrum: M = 462
R~: 0.55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
The following compound can be prepared analogously to Example
8:
(1) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine
~ Prepared ~rom 1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylphenyl)piperazine
hydrochloride and 2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperazin-4-yl)-
ethyl bromide.
Yield: 45% of theory,
Melting point: 161-180~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 446
R~: 0.37 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 96 -
Example 9
1-[3,4-Di(ethoxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Hydrogen chloride is passed into a suspension of 200 mg
(0.405 mmol) of 1-[3,4-di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperidine dihydrochloride in 50 ml of
absolute ethanol with stirring and cooling with ice until it
is saturated, a clear solution resulting. This solution is
allowed to stand at room temperature overnight and is then
~ concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is triturated
with acetone and filtered off with suction.
Yield: 0.2 g (83% of theory),
Melting point: 161-163~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 477
Rf: O . 35 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
9 :
(1) 1-[3,4-Di(isobutyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
~ piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared ~rom 1-[3,4-di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
isobutanol.
Melting point: 156-158~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: M = 533
Rf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(2) 1-[3,4-Di(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[3,4-di(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
cyclohexanol.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.
- 97 -
Melting point: 148-152~C
Mass spectrum: M = 585
Rf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
(3) 1-[3,4-Di[(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-[3,4-di[(carboxymethyloxy)phenyl]-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
cyclopentanol.
Melting point: 88-90~C
Mass spectrum: M = 557
Rf: O . 5 (silica geli methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.25)
Examplel 10
1-(4-Isobutyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine
20 ml of ethereal hydrochloric acid are added to a suspension
of 0.6 g (1.4 mmol) of 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-
(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride in 30 ml of
isobutanol and the ether is distilled off at 50~C. The mixture
,
is then heated for 12 hours at 130~C. The solution resulting
in this way is cooled and diluted with ether. The precipitated
solid is filtered off with suction and purified by means of
chromatography on a silica gel column, methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia = 4:1:0.2 being used as
eluent.
Yield: 250 mg (43.4% of theory),
Melting point: 137-139~C
Mass spectrum: M = 403
Rf: O . 30 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 98 -
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
1 0 :
(1) 1-(4-Cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperi-
din-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-4-
yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and cyclohexanol at 180~C.
Yield: 42% of theory,
Melting point: 248-250~C
Mass spectrum: M+ = 429
Rf: 0.40 (reversed-phase plate RP 18; methanol/50% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
(2) 1-(4-Cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperi-
din-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and cyclopentanol.
(3) 1-(4-n-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and n-butanol.
(4) 1-(4-Cycloheptyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperi-
din-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-4-[2-(piperidin-
4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and cycloheptanol.
(5) 1-(4-Cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-
4-[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 1-(4-carboxymethyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-
4-[2-piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride and
cyclohexanol.
Yield: 63% of theory, amorphous solid
Mass spectrum: M = 443
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
_ 99 _
Rf: 0.27 (reversed-phase plate RP18; methanol/5% strength
sodium chloride solution = 3:2)
Example 11
trans-1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methylamino]cyclohexane
0.23 g (6.1 mmol) of sodium borohydride is added in portions
at -18~C with stirring to a solution of 8.85 g (15 mmol) of
1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyleneimino]cyclohexane in
40 ml of dry methanol and the mixture is stirred for a further
2.5 hours at -15~C and then for 1 day at room temperature. The
solution is concentrated to dryness in vacuo, the residue is
partitioned between water and ethyl acetate, and the organic
phase is dried and evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The residue
which remains is purified by means of chromatography on a
silica gel column, methylene chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia =
9:1:0.1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 3.88 g (44~ of theory),
Melting point: 64-67~C
Mass spectrum: M = 502~ Rf: 0.47 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example 12
trans-1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-methylmethylamino]-cyclo-
hexane
160 ml (2 mmol) of formalin solution (37% strength) and 135 mg
(2 mmol) of sodium cyanoborohydride are added at room
temperature and with stirring to a solution of 502 mg (1 mmol)
of trans-1-(4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-
tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methylamino]cyclohexane
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 100 --
in 20 ml of methanol, and the mixture is stirred further for 1
hour and evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
purified by means of chromatography on a silica gel column,
methylene chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia = 19:1:0.1 and
9:1:0.1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 370 mg (72% of theory), of oil
Mass spectrum: M = 516
Rf: O. 60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
(1) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
l-(trans-4-carboxymethyloxycyclohexyl)piperazine
Prepared from 450 mg (2.6 mmol) of 4-carboxymethyloxycyclo-
hexanone, 770 mg (2.6 mmol) of 1-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine, 0.15 ml (2.6 mmol) of acetic
acid and 260 mg (3.9 mmol) of sodium cyanoborohydride in 30 ml
o+~ tetrahydro+~uran.
Yield: 28% of theory, foam
R~: 0.22 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.25)
-
(2) trans-1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxypiperidino)-
4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]cyclo-
hexane
Prepared +~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]cyclohexanone, 4-tert-butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy-
piperidine and sodium triacetoxyborohydride.
Yield: 9% of theory,
R~: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
-- 101 --
(3) cis/trans-4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperazino)cyclohexane
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]cyclohexanone, 1-methyloxycarbonylmethylpiperazine
and sodium triacetoxyborohydride.
Yield: 18% of theory, of oil
Rf: O.9O (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.2)
(4) cis/trans-4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]-1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)piperazino]cyclohexane
Prepared from 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]cyclohexanone, 1-(2-ethoxycarbonylethyl)piperazine
and sodium triacetoxyborohydride.
Yield: 85% of theory, of oil
Mass spectrum: M+ = 481
Rf: O . 45 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(5) cis/trans-4-([1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]-1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylprop-2-yl)piperazino]-
cyclohexane
Prepared ~rom 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]cyclohexanone, 1-(1-methoxycarbonylprop-2-yl)-
piperazine and sodium cyanoborohydride.
Yield: 13% of theory,
Melting point: 70-72~C
Rf: O . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example 13
4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-
1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)piperidine
Prepared from 400 mg (lmmol) of 4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)methyloxy]-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine,
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 102 -
0.1 ml (1 mmol) of methyl bromoacetate and 166 mg (1.2 mmol)
of potassium carbonate and 10 ml of dimethylformamide
analogously to Example XIIIa.
Yield: 340 mg (72% of theory),
Melting point: 77-79~C
Mass spectrum: M = 462
Rf: 0.60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 15:1)
The following compounds can be prepared analogously to Example
13:
~ (1) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-(1-methoxycarbonylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)piperazine
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(piperidin-4-yl)piperazine and methyl bromoacetate.
Yield: 85% of theory,
Melting point: 71-74~C
Mass spectrum: M = 452
Rf: 3 . 50 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(2) trans-4-[(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
methyloxy]-1-(4-methoxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)cyclohexane
Prepared from trans-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-
4-yl)methyloxy]-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexane and methyl
bromoacetate.
Yield: 82% of theory,
Melting point: 70-72~C
Mass spectrum: M = 461
Rf: 0.55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol = 15:1)
(3) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4-(1-methoxycarbonylethyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine and methyl 2-bromo-
propionate.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 103 -
Yield: 90% of theory, of oil
Rf: 0.30 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 2:1:0.1)
(4) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4-(2-ethoxycarbonylpropyloxy)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine and ethyl 2-bromoiso-
butyrate.
Yield: 47% of theory, of oil
: 0.60 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/ = 20:1)
(5) 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[4~ methoxycarbonylbenzyl)phenyl]piperazine
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine and methyl ~-bromophenyl-
acetate.
Yield: 93% of theory, of oil
Rf: O . 23 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 20:1:0.1)
Example 14
~ 4-[2-(1-tert-Butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-
1-[1-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]piperazine
A solution of 730 mg (1.9 mmol) of 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxy-
carbonylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-1-(piperidin-4-yl)piperazine and
0.18 ml (2 mmol) of methyl acrylate in 10 ml of methanol is
allowed to stand at room temperature overnight and is then
concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified by
means of chromatography on a silica gel colll~n, methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia = 19:1:0.1 being used as
eluent.
Yield: 840 mg (94~ of theory),
Melting point: 95-97~C
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 104 -
Rf: 0.55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example 15
.
trans-[1-(4-tert-Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-
butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-acetylmethylamino]cyclo-
hexane
A solution of 0.14 ml (2.0 mmol) of acetyl chloride in 5 ml of
methylene chloride is added dropwise with stirring and at
-10~C to a solution of 740 mg (1.5 mmol) of trans-1-(4-tert-
butyloxycarbonylmethyloxyphenyl)-4-[(1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yl)methylamino]cyclohexane and 0.3 ml (2.1 mmol)
of triethylamine in 50 ml of methylene chloride and the
mixture is allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. It
is washed with water and the organic phase is concentrated to
dryness in vacuo. The residue is purified by means of
chromatography on a silica gel column, methylene chloride/
methanol = 30:1 being used as eluent.
Yield: 690 mg (86% of theory), of resin
Mass spectrum: M = 544
Rf: O. 65 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
~ ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
Example 16
1-[4-(1-Methoxycarbonyl-3-hydroxypropyloxy)phenyl]-4-
[2-(piperidin-4-yl)ethyl]piperazine dihydrochloride
Prepared from 4-[2-(1-tert-butyloxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-
ethyl]-1-[4-(2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)phenyl]piperazine
and ethereal hydrochloric acid in methanol. The product is
contaminated with the corresponding lactone.
Melting point: from 220~C (dec.)
Mass spectrum: (M+H) = 406
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 105 -
~f: 0.22 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 4:1:0.2)
Example 17
Dry ampoule containing 2.5 mg o~ active compound per 1 ml
Composition:
Active compound 2.5 mg
Mannitol 50.0 mg
Water ~or injection purposes to 1.0 ml
Preparation:
Active compound and mannitol are dissolved in water. After
dispensing, the solution is ~reeze-dried. Dissolution to give
the ready-to-use solution is carried out using water ~or
injection purposes.
Example 18
Dry ampoule containing 35 mg o~ active compound per 2 ml
Composition:
Active compound 35.0 mg
Mannitol 100.0 mg
Water for injection purposes to 2.0 ml
Preparatlon:
Active compound and mannitol are dissolved in water. After
dispensing, the solution is freeze-dried. Dissolution to give
the ready-to-use solution is carried out using water ~or
injection purposes.
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 106 -
Example 19
Tablet containlng 50 mg of active compound
Composition:
(1) Active compound50.0 mg
(2) Lactose 98.0 mg
(3) Maize starch 50.0 mg
(4) Polyvinylpyrrolidone 15.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate2.0 mg
215.0 mg
Preparation:
(1), (2) and (3) are mixed and granulated with an aqueous
solution of (4). (5) is admixed to the dried granules. Tablets
are pressed ~rom this mixture which are biplanar with a bevel
on both sides and a breaklng notch on one side.
Diameter o~ the tablets: 9 mm.
Example 20
~ Tablets containing 350 mg of active compound
Composition:
(1) Active compound350.0 mg
(2) Lactose 136.0 mg
(3) Maize starch 80.0 mg
(4) Polyvinylpyrrolidone 30.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate4.0 mg
600.0 mg
-
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
.,
- 107 -
Preparation:
(1), (2) and (3) are mixed and granulated with an aqueous
solution of (4). (5) is admixed to the dried granules. Tablets
are pressed from this mixture which are biplanar with a bevel
on both sides and a breaking notch on one side.
Diameter of the tablets: 12 mm.
Example 21
Capsules cont~ining 50 mg of active compound
.~
Composition:
(1) Active compound 50.0 mg
(2) Maize starch, dry58.0 mg
(3) Lactose, powdered50.0 mg
(4) Magnesium stearate2.0 mg
160.0 mg
Preparation:
(1) is triturated with (3). This trituration is added to the
mixture of (2) and (4) with intensive mixing.
,--
This powder mixture is dispensed into hard gelatin capsules of
size 3 in a capsule dispensing machine.
Example 22
Capsules contalning 350 mg of active compound
Composition:
(1) Active compound 350.0 mg
(2) Maize starch, dry 46.0 mg
(3) Lactose, powdered30.0 mg
CA 02244860 1998-07-29
- 108 -
(4) Magnesium stearate 4.0 mg
430.0 mg
Preparation:
(1) is triturated with (3). This trituration is added to the
mixture of (2) and (4) with intensive mixing.
This powder mixture is dispensed into hard gelatin capsules of
size 0 in a capsule dispensing machine.