Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
"Machine for the production of metal sheet panels with bent edges"
* * * * *
DESCRIPTION
The present invention refers to a machine for the production of metal
sheet panels with bent edges, commonly referred to as panel machine.
In particular the invention refers to a panel machine equipped with a
single bending die to obtain metal sheets of generically rectangular shape
having edges that are bent one or more times at one or more of their four
sides, for example of the kind described in the US patent N. 4242898.
Panels of this type have a wide utilisation for example in the
manufacture of metal cabinets, refrigerators, washing machines, air
conditioners, shelving in general etc.
The known panel machines comprise a work plane where to lay the
metal sheet (panel) to be machined, a bending press provided with a bending
die and located frontally to the work plane, a mechanical hand mobile with
respect to the work plane to move the sheet to be machined during
machining, an automatic sheet feeder located laterally to the work plane and
comprising a carriage for the conveyance of the sheet from the feeder to the
work plane and for the removal of the bent sheet from the work plane once
the machining has been completed.
The conveyor carriage takes the sheet from the feeder and locates it on
the work plane; the mechanical hand takes the sheet substantially at its
centre and it moves it in such a way so as to position in turn each side to be
bent in correspondence of the bending press. Once the machining is
completed, the mechanical hand drops the sheet, and the carriage removes it
from the work plane.
Therefore, all the operations of the panel machine, in particular the
feeding of the sheet to be machined and the removal of the machined sheet,
are automated.
Because of the presence of the feeder and of the carriage, the machining
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
zone (that is the work plane) is substantially accessible from the outside
during machining, in order not to hinder the operations of the same carriage.
In order to meet the safety requirements imposed by the current
regulations, light scan devices (laser scanner or photocells) are provided
which stop the panel machine any time a human operator, or in any case a
not identified body, gets near the m~hining zone.
Such panel machines, although they are very efficient, are rather
complex to realise and as a consequence they are costly due exactly to the
high degree of automation.
In view of the state of the art described, object of the present invention
is to provide for a less complex and as a consequence less costly panel
machine and that would anyhow meet the safety requirement imposed by
the current regulations.
According to the present invention, such object is obtained by means of
a panel machine comprising a work surface for a sheet to be machined, a
bending press provided with a bending die and located frontally to the work
plane, a mechanical hand mobile as regards the work plane for the
displacement of the sheet during m~hining, characterised in that said work
plane is substantially enclosed inside a protection structure, said protection
structure comprising at least one opening for the access to the work plane for
the feeding to and the removal of the sheet from the work surface on behalf
of a human operator, and in that said at least one access opening is
associated to respective means for the interdiction of the access to the work
plane during machining.
According to a preferred form of embodiment, said interdiction means
consist of a door mounted on the protection structure in correspondence of
the access opening or openings, selectively openable by the human operator
for the feeding and removal of the sheet and closable during the machining
of the same sheet. The door or doors form physical barriers preventing the
access to the work plane when the machine is operating.
' CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
As an ~ltern~tive~ said interdiction means can consist in light scan
devices as photocells or laser scanners, serving the purpose to interrupt the
operation of the machine any time that, during machining, a non-
recognisable body tries to accede to the work plane through the access door
or doors.
The panel machine according to the invention is clearly less complex
than the known panel machines, since neither automatic feeder nor carriage
to convey sheets are provided. As a result of this, not only the panel machine
is less costly, but it is also possible to enclose the work plane inside a
protection structure (physical), consisting for example of a barrier made of
sheets preferably provided with windows, that would completely isolate the
m~hining zone for the metal sheets from the outside during the same
machining. The feeding and removal of sheets from the work plane is carried
out through the access opening or openings provided in the protection
structure by means of a human operator. The presence of said interdiction
devices in correspondence of the access opening or openings guarantees the
safety of the operator.
The characteristics and advantages of the present invention will be
rendered more evident by the following detailed description of a possible
embodiment thereof, illustrated as a non-limiting example in the enclosed
drawings, in which:
Figure 1 shows in a schematic axonometric view a panel machine
according to the present invention, surrounded by a protection structure;
Figure 2 is analogous to Figure 1, but with the protection structure
partially removed;
Figure 3 shows in a m~gnified scale the detail of a door to close an
access opening of the protection structure of the panel machine of Figure l;
Figure 4 is a section along a vertical median plane of the panel machine
of Figure l;
Figure 5 shows in detail an element for the centring of a sheet on the
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
work plane, with the respective mechanism of movement.
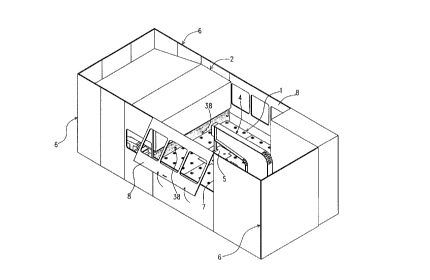
With reference to the drawings, in Figure 1 and 2 a panel machine
according to the present invention is shown. The panel machine comprises a
work plane 1 for a sheet to be machined 5, a bending press 2 provided with a
bending die (that will be described in detail later) positioned frontally to thework plane 1, a mechanical hand 4 mobile as regards the work plane 1 for
the movement of the sheet 5 during machining, and a protection structure 6,
consisting of sheets preferably provided with windows, that encloses the
work plane 1 with the mechanical hand 4, and the bending press 2. In this
example, inside the protection structure 6 two openings 7 for the access to
the m~hining zone are provided on opposite sides of the work plane, that
allow a human operator to introduce a sheet to be machined 5 on the work
plane 1 and to remove the sheet once the machining is completed. In the
example shown, the access openings are associated with respective doors 8,
that can be seen in a m~gnified scale in Figure 3, hinged to a supporting
frame (not shown for clearness reasons) in the protection structure 6 in such
a way so as to result to be turnable around respective horizontal axes.
Preferably, in order to facilitate the opening and closing of the doors 8,
conventional gas cylinders (not shown) can be provided.
In the example shown, the protection structure 6 comprises two
openings for the access to the work plane, so that the latter turns out to be
accessible from either sides; however, it could also be possible to provide for
a single access opening.
More details about the structure of the bending press 2 and the
mechanical hand 4, and the relative way of operating, are shown in Figures 4
and 5, that will now be described, in which for clearness reasons the
protection structure 6 is not shown.
In a known way, the mechanical hand 4 comprises a carriage globally
indicated by 9, conformed as an "arch press" mobile as regards the work
plane 1 through a longitudinal slit 3 of the same on rectilinear horizontal
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
guides 10 supported by a bed 11 which rests on the floor, said guides 10
extending perpendicular to the front of the bending press 2. A fluid
mechanical cylinder 50 causes the movement of the carriage 9 along the
guides 10 in the direction toward or away from the bending press 2. The
carriage 9 supports a hydraulic vice 12 with overlaid and coaxial lower and
upper jaws 13, 14 having flat and horizontal opposite walls suitable to clamp
between them the sheet to be machined, as shown in Figure 4. The lower jaw
13 is fixedly mounted on the upper end of a horizontal shaft 15 set into
rotation by a rotator 16 mounted on the lower part of the carriage 9 and
capable to confer the shaft 15 and the lower jaw 13 angular shift by 90~ and
180~ in one and in the opposite direction. The upper jaw 14 is fixedly
mounted to the lower end of a vertical shaft 17 tllrningly held in idle mode
by a bracket arm 51 held in turn in a slidingly vertical way by the end of the
upper part of the carriage 9. A fluid mechanical cylinder, not shown, causes
the lowering and lifting of the bracket arm 51, and therefore of the jaw 14, in
such a way as to respectively clamp the sheet to be machined 5 between the
jaws 13, 14 or to release the same sheet. The shaft 17 must idle in rotation
around its own axis, in order not to prevent the rotation of the sheet 5 by
means of the rotator 16, the jaw 14 having to co-operate with the jaw 13 in
order to clamp the sheet 5.
In addition, the mechanical hand 4 comprises a thrust mean 19, that can
also be seen in Figure 2 and shown in Figure 4 into two different operating
positions, globally mobile with the carriage 9 and also independently set in
motion by a respective fluid mechanical cylinder 52 and sliding in a slide
created in the lower part of the carriage 9. When the thrust mean 19 is in the
position of rest, it is substantially in correspondence of the throat of the arch
press 9; by moving forward along the slide toward the bending press 2 under
the action of the cylinder 52, the thrust mean 19 abuts against the back edge
of the sheet to be machined in such a way as to push the sheet 5 and to allow
its automatic correct positioning, as it will be described more in detail later.
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
The bending press 2 comprises a bearing structure having a substantially
"C" shaped section and comprising a lower wing 21 and an upper wing 22.
The lower wing 21 rests on the floor, while the upper wing 22 is hinged to
the lower wing 21 in correspondence of flanges 23 located on the back of the
latter, in such a way so as to result turnable around a horizontal axis
indicated by A. A cylinder-piston unit 24 produces the rotation of the upper
wing 2 around the axis A, being provided at least one vertical rod 25
(schematically indicated by dots and lines) which acts as a guide to the
movement of the upper wing 22. Frontally to the lower wing 21 a vertical
support 26 is fixed having a free flat and horizontal upper surface located at
the same level of the work plane 1, that forms a lower blank holder.
Frontally to the upper wing 22 an upper blank holder 27 is fixed in such a
way so as to extend vertically toward the bottom, that is provided with a free
flat lower surface suitable to co-operate with the upper surface of the lower
blank holder in order to clamp the sheet to be machined near the edge of the
same to be bent.
In the space comprised between the upper and lower wings 22, 21 a
bending blade holder 28 is housed, having a substantially "C" shape, in cross
section. The blade holder 28 comprises a lower arm 29 and an upper arm 30
which extend toward the front of the bending press 2. A lower bending blade
34 is fixed at the end of the lower arm 29, while an upper bending blade 35
is fixed to the upper arm 30. On the back, the blade holder 28 is hinged to a
torsion bar 31 in such a way so as to result as being turning around the axis
indicated by C. The torsion bar 31 is also turnable around the horizontal axis
indicated by B under the action of a fluid mechanical cylinder, of which only
the rod 32 is schematically shown in dots and lines. A fluid mechanical
cylinder (whose rod 33 is schematically shown in dots and lines) produces
the rotation of the blade holder 28 around the axis C. The combination of the
rotation of the torsion bar 31 around its own axis B, which determines the
position of the axis of rotation C of the blade holder 28, and the rotation of
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
the blade holder 28 around the axis C allows a great variety of movements to
the bending blades 34,35 in order to obtain bends with various angles both
upward and downward.
Frontally to the support 26 a known reference-bearing block 36 is
S mounted, that has a flat horizontal upper surface 37 at the same level of the
work plane 1 and inside of which reference elements 38 visible also in
Figures 1 and 2 are located. The block 36 is movable in a direction
perpendicular to the front of the bending press 2, so that it can move away
from or toward the same. In addition, the reference elements 38, normally
retractable inside the block 36 during the machining ofthe sheet, can project
in such a way so as to jut out from the surface 37. The reference elements 38
can also move in a direction parallel to the front of the bending press, in
such a way that they can mutually move toward or away from each other.
As shown in Figure 5, each reference element 38 (shown by a
continuous line in a position of rest, retracted and by dots and lines in the
operating position, projecting) is tllrningly supported by a respective
carriage 61 mounted on an endless screw 39, extending parallel to the front
of the bending press 2 and mortised on a pulley 62 which in turn is set in
rotation by a motor 60 through a belt 63. The carriage 61 can therefore move
in the direction parallel to the front of the bending press. Parallel to the
screw without end 39, a bar 64 exten(l~, which form the axis of rotation of
the reference element 38. A cylinder-piston unit 65, whose vertical rod 66 is
hinged to the reference element 38 while the cylinder is hinged to the
reference-bearing block 36 causes the rotation of the reference 38 around the
bar 64, in such a way so as to produce the projection or the retraction of the
reference element 38 from the reference bearing block 36.
The operation of the panel machine previously illustrated will be now
described.
Initially, the operator takes a sheet to be machined, opens the door 8 in
order to accede to the work plane 1, and positions the sheet to be machined
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
on the work plane, in a roughly central position. Therefore, the operator
closes the door 8 and he turns the panel machine on. The mechanical hand 4,
initially in a position distant from the bending press 2 and with the upper jaw
14 lifted, moves toward the bending press. In the meantime, the thrust mean
19 is activated by the relative cylinder 52, and moves along the relative slide
toward the front of the bending press 2, in such a way so as to abut against
the back edge of the sheet to be machined and to push the latter toward the
bending press. Simultaneously, the two retractable reference elements 38
project, so that the fore edge of the sheet, pushed by the thrust mean 19,
abuts against the same reference elements. The conformation of the
reference elements 38 is such as to allow the centring of the sheet to be
machined, in a direction parallel to the front of the bending press, whether or
not this has sheared corners. The possibility to move the reference elements
38 in a direction parallel to the front of the bending press allows the centringof sheets having variable dimensions. Therefore, the operator has not to
worry about positioning the sheet on the work plane in a precise manner.
At this point, the reference elements 38 retract, and the thrust mean 19
returns to its rest position, in such a way as not to represent an obstacle
during the following stages of the m~l~hinin~. .The upper jaw 14 lowers and
in co-operation with the jaw 13, it holds the sheet in a substantially central
position. Therefore, the mechanical hand moves the sheet forward, toward
the bending press. The upper wing 22 of the latter is lifted, so that the upper
blank holder is enough distant from the lower blank holder 26 to allow the
passage of the sheet. Once the latter has been introduced in the bending
press, the cylinder 24 produces the lowering of the upper wing 22 so that the
upper blank holder 27 presses against the lower blank holder 26, an edge of
the sheet to be machined projecting inside the bending press. At this point,
the cylinders whose rods are indicated by 32 and 33 in Figure 4 set in motion
the blade holder 28, whose bending blades 34 and 35 cause bending of the
edge of the sheet, in co-operation with the blank holder 26, 27. Once the
CA 0224~081 1998-08-13
edge of the sheet has been bent in the desirable way, the upper wing 22 of
the bending sheet is lifted, and the sheet released from the hold of the upper
blank holder 27. The mechanical hand 4 backs, removing the sheet from the
bending press and, if other edges of the sheet have to be bent, it carries out
S the rotation of the sheet by 90~ or 180~ by means of the rotator 16. When the
sheet has been rotated in the desired manner, the mechanical hand moves
forward again bringing the edge of the sheet to be machined inside the
bending press, and the operations described above are repeated.
At the end of the m~rhining of the sheet, the operator stops the machine,
he opens the door 8, and he removes the sheet from the work plane, he takes
a new sheet, he positions it on the work plane, he closes the door and turns
the machine on.