Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
08 Rug 98 22:49 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.3
a FILE, Pl Tll1 ~ ,~~~r.,,,,"p
' T'r;~A~WL~"k'?T~~ '
Device for training the back muscles by the
transmission of oscillations to a sitting test subject
Description
The invention relates to a device with a seat
carrier for improving the spinal column muscles by
training these muscles with oscillations, without
extreme excursive movements.
Z0 A variety of training apparatus for improving
the function of the spinal column muscles are known. On
the one hand, these are devices on which the test
subject can train his muscle strength by executing more
or less fixed movements counter to adjustable means of
resistance. On the other hand, devices are known which
are distinguished by an unstable base which allows the
test subject to train his balance (Pezzy ball).
The complex link between specific training of
certain areas of the back muscles and the simultaneous
improvement in coordination and metabolic condition of
the affected tissues, muscles, intervertebral disks,
tendon and ligament structures, is employed in the
context of so-called riding therapy, such as is
described, for example, in the article "Neue Aspekte
zur Behandlung des Morbus Scheuermann mit
Hippotherapie" [New Aspects of Treatment of
Scheuermann's Disease by Hippotherapy] by A. Gottwald
et al., from Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie [Journal of
Orthopaedics] 119, (1981), pages 351 et seq., and in
the book "Reiten aus der Korpermitte. Pferd and Reiter
im Gleichgewicht" [Riding from the Centre of the Body.
Horse and Rider in Equilibrium] by S. Swift, published
by Raschlikon Verlag of Zurich, Stuttgart and Vienna,
1995.
These forms of therapy make use of the complex
transmission of movement impulses which are transmitted
from horses to their riders when riding at walking
pace. The therapeutic starting point is the
physiological back posture of the correctly seated
rider. This corresponds to the posture of the spinal
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
08 Rug 98 22:50 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.S
- 2 -
column demanded in back classes. The patient thus sits
in the saddle with physiological, muscle-stabilized
lordosis of the lumbar spinal column. The main points
of loading when sitting are the ischial bones. When
riding at a walking pace, the three-dimensional
oscillating rhythm of the horse's back is transmitted
to the patient.
The first component of movement is the pelvic
movement, induced by the gait of the horse, in the
frontal direction, with tilting and righting of the
pelvis. The lower lumbar spine is in this way forced to
constantly vary the adopted lordosis.
The second component of movement is a slight
lateral flexion, dependent on the pace, which always
affects the respective ischial tuberosity when the
lumbar spine is situated at the maximum point of its
lordotic curvature.
The third component of movement is an upward
and downward movement of the upper body along a
vertical axis which is tilted slightly forwards.
As regards the three abovementioned components
of movement, it should be noted that the rider
correctly seated in the saddle executes components of
movement 1 (t.ilting of the pelvis about the transverse
axis) and 3 (upward and downward movement along the
vertical axis tilted slightly forwards), but stabilizes
and thus checks the component of movement 2 (lateral
flexion of the pelvis) by reflex righting and
equilibrium reactions of the lumbar rotator muscles. It
is this very stabilizing reaction that is used, when
riding at a walking pace, for the purpose of training
the deep-lying monosegmental rotators, without building
up a rigid isometric tension field, similar to the
whole-body tension after BRUNKOW. As with the "lift-
free mobilization" by the method of KLEIN-VOGELBACH,
there are no maximum excursive movements, but only
small differentiated movements which, on lateral
flexion of the lower segments of the lumbar spinal
,,.
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
08 Rug 96 22:49 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.4
- 3 -
column, decisively influence the restoration of the
damaged nociceptive function.
EP 0 b12 542 A1 describes a panel with a seat
which are mounted on three uprights and are held
movably in a plurality of bearings and hinges. By means
of a motor with different crank discs and drive discs,
one or more of the legs are periodically moved about
three axes in a preferred direction. Hawever, because
of the fixed dimensions, the movements cannot be
individually controlled.
DE 39 41 498 A1 discloses a riding simulator in
the form of an imitation horse body in which the legs
of the horse body are driven by a main motor, the
difference in the movements being achieved by phase
adjustment devices. Here too, the individual components
of movement cannot be individually triggered.
The invention is based on the object of making
available a device of the type specified at the outset,
in which the multidimensional transmission of
oscillation impulses provides complex training effects
which are similar to those which occur in the various
forms of riding therapy, but which go beyond these on
account of the fact that the frequency and amplitude of
the various components of movement can be freely
controlled.
According to the invention, the object is
achieved by means of the fact that the seat carrier is
mounted so that it can move in a number of dimensions
about at least one pivot point, and the device has
drive means which are used to supply multidimensional
movement impulses to the seat carrier. By alternate
loading of the ischial bones of the person sitting on
the seat device, these movements trigger a lateral
flexion of the spinal column and additionally effect a
change in the tilt of the pelvis, so that the stability
and function of the spinal column muscles improve. A
possible turning effects a rotation along the
longitudinal axis of the spinal column. By means of a
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
08 Rug 98 22:50 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.6
- 4 -
parabolic movement, the body of the test subject is
accelerated below its centre of gravity.
It has proven advantageous if the spatial
positions of the pivot points for the movement impulses
in different directions are not the same.
An optimum adaptation to different persons can
be achieved if_ the drive means are designed in such a
way that the seat carrier can execute movement impulses
whose frequency and amplitude are adjustable.
A lateral flexion of the spinal column by
alternating right/left loading of the ischial bones of
the person sitting on the seat device is triggered if
the seat carrier is held so that it can tilt laterally
about its longitudinal axis.
This movement additionally causes a change in
the pelvic tilt of the person sitting on the seat
device if the seat carrier is held so that it can tilt
forwards.
Controllable rocking movements in the
longitudinal direction can be achieved if the seat
carrier can be swivelled about a pivot point forwards
and upwards along a circular path, in which case the
seat carrier remains horizontal.
Rotational impulses on the pelvis and the
spinal column can be achieved if the seat carrier can
be rotated about its vertical axis.
It has proven expedient for the device to have
a seat device in the shape of a riding saddle which can
execute tilting movements, adjustable in frequency and
amplitude, about its longitudinal axis, so that an
additional spreading of the legs takes place.
Rotations about the vertical axis of the seat
carrier with a base and an upright for supporting the
seat carrier can be executed if the drive means turn
the upright about its vertical axis.
The device can be used daily if it is designed
as an office chair, the seating surface of which being
provided with drive means.
.. ~
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
CA 02246625 2002-05-29
29628-1
It has proven advantageous if the device has a
base on which there is fixed an upright which bears a U-
shaped fork, if a shaft bent at right angles is mounted
rotatably between the ends of the fork, if an intermediate
5 support is fixed rotatably on the angled shaft part, and if
the seat carrier is arranged in the longitudinal direction
of the intermediate support and also mounted so that it can
rotate.
According to the invention, the device can have,
as the seat carrier, a seat device in the shape of a riding
saddle. This seat device can execute tilting movements,
adjustable in frequency and amplitude, about its
longitudinal axis (X-axis).
This seat device also executes tilting movements
about its transverse axis (Y-axis), the excursion of these
movements once again being adjustable in frequency and
amplitude. In addition, the seat device executes rocking
movements in the longitudinal direction, which movements
once again can be modified in frequency and amplitude.
Furthermore, the device can execute rotational movements
about its vertical axis (Z-axis).
According to one aspect, the invention provides a
device for training the back muscles with a seat carrier
characterized in that the seat carrier is mounted in at
least one pivot point and can move in a number of
dimensions, and that the device has drive means which are
used to supply multidimensional movement impulses to the
seat carrier for various movement components which can be
freely controlled with respect to frequency and amplitude.
The invention is explained in greater detail
hereinbelow with reference to the illustrative embodiments
i
CA 02246625 2002-05-29
29628-1
5a
which are represented in the drawing, in which:
Figure 1 shows a simplified representation of the
seat arrangement,
Figures 2 to 7 show sketches representing possible
movements of the seat arrangement, and
Figure 8 shows a perspective representation of a
device according to the invention.
In Figure 1, the seat device is shown in a
simplified manner as a barrel 1, so that the directions of
movement of the orthopaedic device according to the
invention can be illustrated more clearly. For information
purposes, the x-axis 2, the y-axis 3 and the z-axis 4 and
two pivot points 5 and 6 have been plotted.
08 Rus 98 22:51 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.8
- 6 -
The tilting movement is explained with
reference to Figures 2 and 3. The device is shown in a
side view. The x-axis 2 and thus the barrel 1 can be
tilted forwards and backwards about the lower pivot
paint 5.
The device i.s shown in a front view in Figures
4 and 5. The y-axis 3 and thus the barrel 1 can be
tilted laterally about the upper pivot point 6.
The device is once again shown in a side view
20 in Figures 6 and 7. A circular excursion takes place
about the upper pivot point 6, as the device is moved
in the direction of the x-axis 2, in which case it
remains on the horizontal. In this way, the body 1 is
given an additional movement in the direction of the z
axis 4.
According to the invention, the device can also
be turned additionally about the z axis 4.
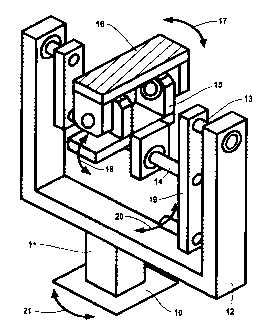
Figure 8 shows a device for generating a
controlled pattern of movement, with a base 10 on which
2Q there is fixed an upright 11 which bears a U-shaped
fork 12. A shaft 13 bent at right angles is mounted
rotatably between the ends of the fork. An intermediate
support 15 is mounted on the angled shaft part 14, on
which intermediate support 15 a seat, carrier 16 is
arranged in the longitudinal direction and is also
mounted so that it can rotate.
By means of the rotatable attachment of the
seat carrier 16 on the intermediate support 15, the
latter can be swivelled laterally about the x-axis 2,
as was shown with reference to Figures 4 and 5, so that
the y-axis 3 and thus the seat carrier 16 is tilted
laterally in the direction of the double arrow 17 by
drive means.
By tuning the intermediate support 15 on the
shaft part 14 by drive means, the x-axis 2 is tilted
according to t:he double arrow 18 and in accordance with
Figures 2 and 3.
The circular excursion of the seat carrier 16,
and thus of the device, as described with reference to
,., o
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
08 Rug 98 22:51 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.9
Figures 6 and 7, is achieved by pivoting the extended
lever 19 of the angled shaft 13 in the direction of the
double arrow 20. The drive means for swivelling the
seat carrier 16 can engage on this lever 19.
Moreover, the fork I2 can be turned about its
vertical axis, in the direction of the double arrow 21,
by means of drive means arranged in the base 10 or
upright 11.
The device shown in Figure 8 is expediently
covered with a lining (not shown) which lies tightly on
the seat carrier 16 so that the movement impulses are
transmitted to it. It can be provided with a seat
device in the shape of a riding saddle.
A foot holder can also be arranged rigidly on
the base 10 of the device, which, for example, allows a
person sitting on a saddle secured to the seat carrier
16 to place his feet thereon and so additionally
achieve a change in the position of flexion of the
hips. This foot holder rests in relation to the floor.
However, it can also be suspended in such a way as to
move freely.
For all these movements, which effect only a
small excursion in the directions illustrated, drive
means (not shown) are provided. According to the
invention, the movement impulses can be triggered by
electric motors, electromagnets, hydraulic devices or
the like. They can comprise a steady or impulse-type
movement.
The device described above is mounted so as to
be freely movable in all directions, namely so that it
can tilt laterally about the X-axis and Y-axis, on a
device that can travel in a circle along the X-axis, by
means of which the seat carrier 16 and the device
supporting it can additionally be moved upwards along
the Z-axis, and can be rotated about the Z-axis. All
these movements are effected by a drive which can be
adjusted in frequency and amplitude.
Such a device can be used in many ways for
therapeutic treatment in medical practices,
~.,.
CA 02246625 1998-08-14
08 Rus 98 22:51 RRe Rnn - Faigle - Kittel +49 9131 8129299 S.IU
_ g _
rehabilitation clinics or the like. Also, chairs and
other seating arrangements can be equipped with it so
that, for example, when doing writing work, while
sitting on an office chair equipped according to the
invention, the back muscles can be exercised without
interrupting work.
~ . ~
CA 02246625 1998-08-14