Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
. CA 02248487 1998-09-30
POWER CONTROL FOR MOBILE WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
This invention relates to power control mech~nicms for controlling signal
strength in a Mobile Wireless Commin~tion System, and in particular to the initial
5 power at which signals to and from mobile end-user devices and a fixed base station
should be transmitted.
In existing systems, a mobile end-user device seeking to initiate
communication with a base station broa~c~ctc a request signal at increasing power
levels until acknowledged by the base station. Likewise, a base station pages a mobile
10 end-user device at increasing power levels until the end-user device responds. In each
situation, one bro~dc~cting station in the communication system ramps the power until a
reasonable SNR is achieved by the second receiver. This ramping of power can lead to
a .sign~lling exchange procedure which can take sometime, since typically each station
is bro~clc~cting over a different channel (particularly in cellular radio telephone
15 systems). It can also lead to inte.~lel1ce between mobile end-user devices and to a loss
of signal quality of other users of the wireless communication system.
EP 682418 A2 describes a fast, closed loop power control for a mobile
radio telecommunication system, which is directed to the steady state operation of
closed loop power control. Such a system is common in "second generation" systems,
20 which are circuit switched wireless communication systems. A closed loop functions
only if both transceivers in a wireless colllmul~ication link are already synchronised and
exch~nging information. The power control algorithm makes use of this established bi-
directional link, to ~x~h~nge information on power levels. The received power ismeasured and the information fed back to the tr~ncmitter, allowing it to adjust its power
25 level to an optimal value.
Future wireless communic~tions systems will support a wide range of
services including packet services and, therefore, are likely to be highly dynamic. Thus,
the initial set up will be increasingly important, as COlllpdll d with the steady state, and
reasonable power levels must be reached imme~ tely. There is thus a need for power
30 control mech~nicms between stations in a mobile wireless co~ll,nullication system which
CA 02248487 1998-09-30
functions at start up and which decreases the time taken to establish an efficient power
level.
According to a first aspect of the invention there is provided a method of
establishing initial power control between a first and second station in a mobile wireless
5 communication system comprising:
transmitting from a first station a first set-up signal over a first channel
within said communication system;
receiving said first signal at a second station and transmitting, in
response, a second signal over a second channel within said cornmunication system;
receiving said second signal, at said first station, and transmitting, in
response, a third signal; and characterised in that
said second signal includes a measure of the Signal-to-Inlelr~,lellce ratio
(SIR) of said first signal as received at said second station
and further characterised in that
the power of said third signal is a~ sted, in response to the SIR measure
included in said second signal.
According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided appal~ s
for establishing initial power control between a first and second station in a mobile
wireless communication system compri~ing:
a first station in the communication system, having a transmitter for
transmitting a first set-up signal over a first channel within the communication system;
a second station in the communication system, having a receiver for
receiving the first signal and a trAn~mitt~r for transmitting a second signal over a second
channel within the colll.llullication system;
said first station having a receiver for receiving said second signal;
wherein a third signal is tr~ncmitte-l in response to said second signal;
and
characterised in that
said second station includes means to measure the Signal-to-IllL~,.r~,.ence
30 ratio (SIR) of the first signal as received at said second station and to include the SIR
measure in said second signal and further characterised in that
CA 02248487 1998-09-30
said first station includes means to adjust the power of the third signal, in
response to the SIR measure included in said second signal.
The third signal may include a measure of the SIR of the second signal,
as received at the first station. The second station may include means to adjust the
5 power of subsequent signals transmitted by the second station. The third signal may be
transmitted over a third channel in the communication system.
The stations may broadcast additional signals over the first, second or
third channels or over additional channels in the communication system. The first
station may be a base station and the first channel may be a broadcast control channel
10 (BCCH) over which a constant information signal is broadcast (the first signal). The
second station may be a mobile end-user station and the second channel may be a
random access channel (RACH) over which the mobile station transmits request to
~ sl~ signals (the second signal). The third signal may be a RACH request
acknowledgement (RA Ack), broadcast by the base station over an associated control
15 channel (FACH), the third channel.
Alternatively, the first channel may be a paging channel (PCH) over
which the base station pages (with the first signal) the mobile station. The mobile
station may respond with a page acknowledgement (Page Ack) over the random access
channel (the second signal and the second channel, respectively). The base station may
20 then respond to the Page Ack by tr~ncmitting data (the third signal) over the traffic
channel (TCH), the third channel.
An embodiment of the invention is described, by way of example, with
reference to the following figures, in which:
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of a cellular mobile communication
25 system according to the invention;
Figure 2 shows a flow diagram of a power control mech~ni~m according
to the invention;
Figure 3 shows another flow diagram of a power control mech~ni~m
according to the invention;
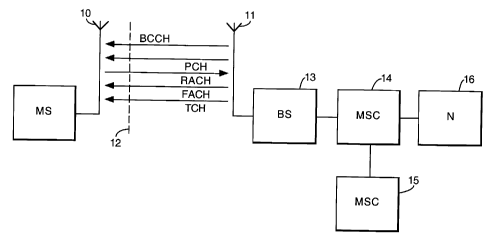
An end-user device (Mobile Station 1) may use any one of a number of
communication protocols to communicate with a base station 13, via ~nt~nn~e 10 and
CA 02248487 1998-09-30
11, across an air interface 12. In the following embodiment, the communication
protocol used in CDMA (code division multiple access). This enables the mobile
stations to communicate using a coded spread specll~ll signal with codes which are
almost uncorrelated, thereby providing a multiple access communications protocol in
S which the collisions are not destructive of other signals broadcast concullelllly. Once a
communication channel has been established between mobile station 1 and its closest
base station 13, the mobile switching centre 14 may establish a further connection to
another mobile switching centre 15 or to the public voice or data networks 16.
The base station contin~ ly bro~dc~ts information on the broadcast
10 control channel (BCCH) to all mobile stations within range. The BCCH information
includes various codes and control signals necessary for a mobile station to register into
the system and to clet~rrnine whether handover to another base station is a~propliate.
The base station may page the mobile station on the paging channel (PCH) or,
alternatively, the mobile station may request access to the system on the random access
15 channel (RACH). The base station and the mobile communicate over the traffic channel
(TCH), whilst the base station transmits feedb~cl~ control over the forward access
channel (FACH).
Figure 2 illu~ les a call to a mobile station, origin~ted by a base station,
which has arrived at the base station via the mobile switching centre. The base station
20 pages the mobile station on the paging ch~nnel; the mobile may detennin~ the
approximate power at which to respond from the power value of the BCCH. The
mobile measures the Signal-to-Interference ratio (SIR) of the paging signal and issues
an acknowledgement (Page Ack) including the BCCH SIR information on the RACH.
Thus the base station is immediately offered a measure of the PCH SIR and thus an
25 indication of a~plo~l;ate power levels at which to conduct further communication
exchanges. The base station measures the SIR of the Page Ack and transmits
information regarding the Page Ack SIR and traffic channel allocation to the mobile
station on the control channel (ACCH) in an RA Ack, at an a~plopl;ate power level.
The mobile station is thus given an indication of an al)propliate power level at which to
30 initiate co~ ication exchanges. Communication may then commence over the
traffic channel (TCH) and, as is known from the art, additional control bits on either the
~ CA 02248487 1998-09-30
FACH or in the TCH or both may indicate that a station should increase or decrease
s1gnal power.
Figure 3 illustrates a call ori~in~ted by a mobile station, to a base station.
The mobile station measures the SIR of the BCCH signal before initiating the call by
5 requesting to transmit a packet. The request is sent by the mobile station on the RACH
and includes information on the BCCH SIR measure. If the RACH request is received
by the base station, the base station decodes the request, extracting the SIR information
and is thereby given an indication of an appropl;ate power level at which to transmit
fi~ther signals on other channels. The base station also measures the SIR of the RACH
10 request and includes this information in the RACH request acknowledgement (RA Ack)
transmitted on the FACH. The mobile station is thereby given an indication of anappro~l;ate level at which to transmit further signals, particularly on the traffic channel.
The base station transmits a transmit permission (Tx Perm) on the FACH and the
mobile station replies by sending the first data packet on the TCH.
The foregoing is illustrative of the invention and similar embo-limentc
would be appalent to one skilled in the art. For example, another communicationsprotocol, such as TDM or FDMA may be used. The invention may be used in initiating
other types of communication bclween stations in a coll~.lu,.ications system.