Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
1~ llS~'/06029
I J~ 3 1 ~T J997
TRIPLE LUMEN CATHETER
TECHNICAL FIELD
1. Field of the Invention
This invention has to do with triple lumen catheters (multiple lumen
catheters). More specifically, the invention involves triple lumen catheters that
are used for blood dialysis, for monitoring of tempora~ ~ circulatory fluids and of
central venal pressure (CVP), etc. Even more specifically has to do with the
structure of triple lumen catheters that are used to allow easy blood extractionduring blood dialysis.
o 2. Description of the Prior Art
Examples of triple lumen catheters used for blood dialysis include the
inventions disclosed in Patent Disclosure Report Hei 2-209159, Patent
Disclosure Report Hei 1-23142, and the United States Patent Report 5,221,256.
The triple lumen catheter disclosed in Patent Disclosure Report Hei 2-
S 209159 (Conventional Example 1), as is shown in Figure 3(a), has a main body21 comprising a tapered tip part 21 a and three lumens 22, 23, and 24, and three
connecting tubes (not shown) that co n"ect respectively to the three lumens 22,
23, and 24 that are equipped in the base part of the main unit 21. Moreover, two- lumens, 22 and 23, of these three lumens, as shown in Figure 3(b), are formed
20 by a dividing wall 22b that is equipped lengthwise and across the inner lumen of
main unit 21, where, as shown in Figure 3(a), both lumens 22 and 23 are
covered on their tip ends by inserts 25 and 26 that are equipped on the inside
near the tips, where the side walls of lumens 22 and 23 at the base side of these
inserts 25 and 26 have multiple openings 22a and 23a to allow the lumen to
extract or return blood fluids, where the remaining lumen 24 is fabricated by a
through hole from the base part to the tip part in the center of main unit 21 and
within the dividing wall 21 b, and where guide wire 27 passes into this circulatory
fluid lumen.
When blood dialysis is performed using the triple lumen catheter 20
structured in this way, the catheter is placed within the blood vessel using guide
~as~p,l~c~
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07 ~ ,T~S ~ 7 / 06 o 29
P~/ J 3 1 OCT 1997
wire 27 that passes through circulation fluid 24 of main unit 21 of the triple lumen
catheter 20, a tube connected to the extraction lumen 22 is connected to the
blood removal side of the dialysis circuit, and a tube connected to the return
lumen 23 is connected to the blood delivery side of the dialysis circuit. However,
s when the blood dialysis begins, the blood flows into extraction lumen 22 fromopening 22a in extraction lumen 22, is sent to the dialysis circuit, is receivedfrom the dialysis circuit by the blood retum lumen 23, where it flows back into the
blood vessel through openings 23a through retum lumen 23 to form a dialysis
circuit.
o The triple lumen catheter disclosed in Patent Disclosure Report Hei 1-23142 (Conventional Example 2) is an intravenous catheter. As shown in Figure
4, from the central part of catheter 30 there extends a three-leg inner wall 30athat divides the catheter into three separate independent inner lumens 31, 32,
and 33, where one of these three inner lumens, inner lumen 31, extends to the
tip of catheter 30, while the other two inner lumens 32 and 33 end with their
respective openings 32a and 32b equipped in the side walls of catheter 30, and
are covered by valves 34 and 35 at the tip part side. Furthermore, these three
innef lumens 31, 32, and 33 extend beyond the base part of catheter 30 and are
attached to inner lumen adaptors (not shown in the Figure) for connecting their
respe~,ti-/e bases to circulation fluid equipment, etc.
1\1oreover, using the guide wire that is inse, led into inner lumen 31,
caU,eter 30 is inserted into the blood vessel where it is secured, and then after
the guide wire is removed from inner lumen 31, the inner lumen adaptors that areconnected to the respective inner lumens 31, 32, and 33 are connected to fluid
delivery devices, CVP monitoring equipment, etc., and thus it is possible to inject
the patient with fluid materials through inner lumen 31, etc., at the same time as
performing CVP monitoring and/or simultaneously taking blood from the patient's
vein.
The triple lumen catheter disclosed in United States Patent Report 5,221,
256 (Conventional Example 3) as shown in Figure 5, has a tapered tip part 41 a,
a main body 41 comprising three lumens 42, 43, and 44, and three connecting
tubes (not shown) equipped at the base part of main unit 41 and that connect,
F~
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07 ~f~
9 7/06029
J 3 i OCT 19~7
respectively, to the three lumens 42, 43, and 44, where two lumens 42 and 43 of
these three lumens are formed by a separator wall 41 b that is established
crosswise and in the axial direction in the inner lumen of main unit 41, where
lumen 42 is formed between the base part of main unit 41 and openings 42a that
s is established in the side wall, where this lumen 42 serves as a blood extraction
lumen, where lumen 43, which serves as the blood return lumen, is formed
extending from the base part of main unit 41 through the tip part opening 41 c,
and where the remaining lumen 44, which serves as a circulation fluid lumen is
formed in the dividing wall 41 b of main unit 41 on one edge of that wall,
o extending from the base part to opening 44a that is established in the side wall
of main unit 41.
Moreover, the guide wire that is inse, lecl into circulation fluid lumen 44 is
used to insert triple lumen catheter 40 into the blood vessel, where it is held, and
while blood dialysis is performed by connecting to a dialysis circuit connectionS tubes that connect with extraction lumen 42 and retum lumen 43, the blood fromthe dialysis circuit, which was delivered to the dialysis circuit by flowing through
extraction lumen 42 from the opening 42a in extraction lumen 42, flows through
return lumen 43 and is delivered into the blood vessel through tip opening part
41c.
DISCLOSURE OF INVENTION
Rec~use, as is shown in Figure 3(b) openings 22a in the extraction lumen
22 in the triple lumen catheter 20 of Conventional Example, 1 as described
above, is on the top side of the side wall of main unit 21, or in other words,
because the opening is biased to be on only one side of the lumen, then, for
2s example, when blood analysis is performed, the force delivered to the inside of
extraction lumen 22, or in other words, the suction force when opening 22a,
which is extracting blood, is close to the blood vessel wall, will cause the space
between the blood vessel inner wall and main unit 21 to become narrow,
resulting in problems such as inadequate blood extraction flow, and ultimately,
with a situation where opening 22a becomes affixed to the inner wall of the blood
vessel resulting in faulty blood extraction.
, . . ~ ~ . _ . ...
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
US97/06029
\f~ 3 1 OCT 1997
Furthermore, similar to Conventional Example 1, in the triple lumen
catheter 30 of Conventional Example 2, the opening part 32a of inner lumen 32,
which serves as the extraction side, is equipped with a bias that points to onlyone side of the side wall of catheter 30, and thus the suction will concentrate on
only one side so opening part 32a may become affixed to the inside wall of the
blood vessel which may result in the occurrence of extraction problems.
On top of this, even in the triple lumen catheter 40 of Conventional
Example 3, blood extraction for blood dialysis is pei rOI med through opening 42a
in extraction lumen 42 that is established with a bias to only one side in the side
10 wall of main unit 41, and thus, similar to Conventional Example 1, the blood
. extraction will cause suction, which will cause opening part 42a to become
- affixed to the inner wall of the blood vessel, resulting in blood extraction
problems, etc.
This invention was created to solve problems such as described above for
IS the purpose of providing a high-reliability triple lumen catheter able to prevent
with certainty constricted extraction blood flows and e,~l,a~lion problems, etc.through preventing the blockage of extraction openings resulting from the
extraction suction force.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the form of e",L,odi",ent of this
invention with the ~ssoci~ted A-A cross-se~liG"al diagram and B-B cross-
sectional diagram.
Figure 2 is an expanded cross-sectional diagram of important parts of
Figure 1.
Figure 3 is an expanded cross-sectional view and a C-C cross-sectional
diagram of the important parts of a conventional triple lumen catheter.
Figure 4 is an expanded cross-sectional view and a D-D cross-sectional
diagram of the impo, lant parts of another conventional triple lumen catheter.
Figure 5 is an expanded cross-sectional view and a E-E cross-sectional
30 diagram of the important parts of yet another conventional triple lumen catheter.
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07 ~ C ¦~ S 9 7 / O 6 O 2 9
PEt~ 3 i O~T I99
MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
The triple lumen catheter of this invention has a N o. 1 lumen and a N o. 2
lumen that have a constricted diameter tip part and that are fabricated by a
separating wall equipped in the axial direction on the inside, and is equipped
with a N o. 3 lumen that is parallel to the No. 1 lumen and N o. 2 lumen where
said N o. 3 lumen is equipped on the inside of the side wall so as to connect tothe outside through a tip opening part that is equipped on said tip, where either
said No. 1 lumen or said N o. 2 lumen has at least one pair of opposing side wall
openings that connect to the outside and that are perpendicular to the side walls
of one of the lumens, and by the provision of a side opening that is perpendicular
to the side wall of the other lumen.
Moreover, the triple lumen catheter of this invention is not only proved
with a separating wall that causes one of the two lumens, the N o. 1 lumen or the
N o. 2 lumen, have a larger cross-sectional area than the other lumen of the pair,
s but also the lumen with the larger aoss-sectional area is equipped with at least
one pair of mutually opposing side openings.
Moreover the triple lumen catheter of this invention has a thick wall part
that extends from said wall part at the position that is opposite to the dividing
wall on the inside of either one of the lumens, the N o. 1 lumen or the N o. 2
lumen, where said N o. 3 lumen being equipped within this thick wall part.
Moreover the triple lumen catheter of this invention is equipped with a soft
tip that comprises a cutting head conical head part that has a wider diameter atits base side, two extending parts that cover the tip side of the lumen that
extends from the base part of said head part to the tip region of the side
2s openings of the N o. 1 and No. 2 lumens described above, is equipped with a
through hole that is connected to the tip part of said No. 3 lumen and that is
fabricated running along the conical surface of said head part to the tip opening
part equipped in said head part, and is structured with a catheter tip part wherein
said soft tip extension parts fit into said No. 1 and No. 2 lumens and where said
No. 3 lumen connects to said through hole.
In this way, by making either the No. 1 lumen or the N o. 2 lumen larger in
cross-sectional area than the cross-sectional area of the other lumen, and by
., , . . , ~ , . . .
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07 ~ ~ ~ S ~ 7 1 ~ 6 0 2 9
~P~ ' 3 1 ~T 19g7
establishing in the side walls of the lumen with the larger cross-sectional area at
least one pair of mutually opposing side openings that flow to the outside, it is
possible to not only prevent the occurrence of inadequate extraction blood flow
and blood extraction problems by preventing the blockage of the opening by the
s side openings contacting the blood vessel inner wall causing blockage by the
inner wall, preventing this by extracting blood on both sides of the catheter rather
than concenlrating the extraction suction force on one side of the calheter whenusing as the extraction lumen in blood dialysis the lumen equipped with the pairof side openings, but also to perform a highly stabile, high-volume blood
o extraction for blood dialysis.
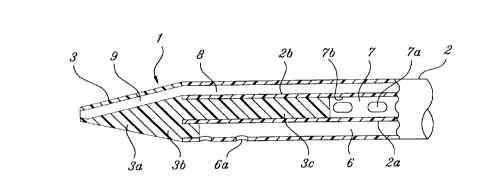
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a form of embodiment of this invention
where cross-sectional diagram A-A, cross-sectional diagram B-B, and Figure 2
shows expanded cross-sectional views of ilnpGl tar,t parts of Figure 1. In thesefigures, 1 is a triple lumen catheter, comprising a cylindrical main unit 2 that has
s three lumens 6, 7, and 8 and is made from a synthetic resin material such as, for
example, polyurell ,a"e, a soft tip 3 structured at the tip of said triple lumencatheter 1 and made from a synthetic resin material such as, for example,
polyurethane, and a connection part 4 that is fabricated in a single unit with the
base part of main unit 2 and which is equipped with, for example, connection
tubes that connect to dialysis circuits, etc., and which are made of synthetic resin
materials such as, for example, polyuretl ,ane.
The main unit 2 of triple lumen catheter 1, as is shown in Figures 1 (b) and
(c) is e~ ~irped with a dividing wall 2a that extends downward from the center of
main unit 2 and also in the axial direction, where this main unit 2 is divided by
this dividing wall 2a into nearly semicircular halves that form lumens 6 and 7
where one of these lumens, lumen 6, is the blood send lumen for the blood
dialysis and is equipped with side opening 6a, which opens to the outside, in the
tip part side of the side wall of the conical side wall of main unit 2, while the other
lumen, lumen 7, has a larger cross-sectional area than the cross-sectional area
of lumen 6, and is the lumen for blood extraction for the blood dialysis that isequipped with at least 1 pair of side openings 7a that open to the outside and
that are equipped further towards the base side of main unit 2 than the side
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
PGT/lJ~ ~ 7/06029
~P~ 3 1 OCT ~99~
opening 6a of lumen 6, and that open on opposite sides of the arc of main unit 2.
Moreover, in a position opposite from dividing wall 2a on the inner wall of lumen
7 there is a convex part 7b that protrudes to dividing wall 2a and which forms athick part on the inner wall of main unit 2, where within this thick wall part 2b is
s formed a lumen 8, which is circular in cross section with an inner diameter that is
nearly the same as the outer diameter of a guide wire (not shown), where this
lumen 8 is the circulation fluid lumen that is used for circulation fluid and for CVP
monitoring, etc. Furthermore, at the base part of main unit 2, No. 1, No. 2, andNo. 3 connecting tubes 5a, 5b, and 5c are connected to lumens 6, 7, and 8,
o respectively, through a connector 4.
As is shown in Figure 2, soft tip three is equipped with a head part 3a that
is conical with a wider diameter at the base, and extension parts 3b and 3c thatare structured with the same shape as the cross-sectional shape of lumens 6
and 7 respectively and that extend to near the tip parts of side openings 6a ands 7a of lumens 6 and 7 from the base part of head part 3a, where these extensionparts 3b and 3c not only block the tip sides of lumens 6 and 7 by fitting into
lumens 6 and 7, but also head part 3a is formed into a single unit with the tip part
side of main unit 2, structuring the tip part of triple lumen catheter 1. Moreover, in
head part 3a is equipped through hole 9 that is fabricated along the outside wall
of head part 3a until tip opening part 3b that is established in head part 3a and
that connects to the tip part of lumen 8, and which has about the same diameter
as the inner diameter of lumen 8, and thus lumen 8 opens into through hole 9
when soft tip 3 is joined with the tip part side of main unit 2.
No. 1 and No. 2 connection tubes 5a and 5b, as shown in Figure 1 (a) are
structured from a flexible tube 1 Oa that is made from, for example, a silicone or a
soft synthetic resin material such as polyurethane, and which has a connector
1 Ob that connects at its tip to the dialysis circuit connector, and a clamp 1 Oc that
can pinch of and close this flexible tube 10a, where the No. 3 connecting tube 5c
is structured from a soft tube 11 a made from, for example, silicone or a flexible
synthetic resin material such as polyurethane, and which has a connector 11 b
that is connected to the connector of circulation fluid equipment, etc., along with
a clamp 11 c that is able to pinch off and close this flexible tube 1Oa.
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
- - PG-U~97/06029
' 3 1 OCT ~997
If the form of embodiment structured in this way is used for blood dialysis,
the guide wire that is inserted into the blood vessel is inserted into through hole
9 and lumen 8 through tip opening part 3d in soft tip 3 of triple lumen catheter 1,
and using this guide wire, etc., triple lumen catheter 1 is inserted into the blood
vessel, where it remains. Following this, the guide wire is removed from lumen 8,
etc., and after soft tube 11 a is pinched off by clip 11 c if No. 3 connection tube 5c,
connector 1 Ob of No. 1 connector tube 5a is connected to the supply side of thedialysis circuit, connector 1 Ob of No. 2 connector tube 5b is connected to the
extraction side of the dialysis circuit, and dialysis begins.
o When the blood dialysis begins, the blood fluids flow into lumen 7 from
side openings 7a that open into lumen 7, and are sent to the dialysis circuit, and
the blood flyids from the dialysis circuit are sent into through lumen 6 and into
the blood vessel through side openings 6a that opens into lumen 6. At this time,the blood fluids are drawn into lumen 7 through the 1 pair or more of side
lS openings 7a that are equipped opposite each other in the side walls of main unit
2, or in other words, are drawn in from two dirrerenl directions.
After the blood has been dialyzed, then if the triple lumen catheter 1 is
maintained within the blood vessel, connector 1 Ob of the No. 1 connector tube
5a, and connector 1 Ob of the No. 2 connector tube 5b are removed from the
dialysis circuit, lumens 6 and 7 are flushed with a heparin saline solution, and a
heparin lock is created.
In this way, the blood extraction in the blood dialysis is performed through
at least 1 pair of side openings 7a that are established opposite each other in
the side walls of main unit 2 and that open into lumen 7, or in other words, theblood extraction is performed through side openings 7a that are established in
two different directions relative to lumen 7, and thus the suction force on sideopenings 7a does not concer,lrate in a single~~irection as it did in the past (i.e.
the direction where the side openings are), but rather there is suction on both
sides, making it possible to maintain main body 2 with stability in nearly the
center of the blood vessel. Using this process, it is possible to prevent
inadequate blood extraction due to the space between the inner wall of the bloodvessel and main unit 2 becoming constricted when the force of the suction of the
~ ~ --'' 77~ e~
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
PCr/lJS 9 7/ 06 0 29
IP~~ 3 1 0CT 1997
blood fluids causes side opening 7a to move near to the inner wall of the blood
vessel, and making it possible to prevent side opening 7a from becoming stuck
to the inner wall of the blood vessel which leads to problems with failed blood
extraction. This makes it possible to obtain a highly reliable triple lumen catheter
1 that is able to produce a stable and secure blood extraction.
Moreover, be~use the cross section of lumen 7 is formed larger than the
cross section of lumen 6 it is possible to obtain an increased blood extraction
flow, not only making it possible to reduce the load on the patient, but making it
possible to perform smooth, rational dialysis because it is possible to extract
o blood with certainty using the pair of opposing side openings 7a provided.
Furthermore, by fabricating lumen 8 in the thick wall part 2b of main unit 2
it becomes possible to position the pair of side openings 7a equipped in the side
walls of main unit 2 at nearly 180 degrees opposite each other, making it
possible to make the side openings 7a larger, thus making it possible to secure
the extraction blood flow, and making it possible to prevent the blood vessel
walls from obstructing the blood vessel.
Moreover, while the form of embodiment described above was explained
assuming the tip part of triple lumen catheter 1 was structured from soft tip 3, soft
tip 3 may also be fabricated as a single unit with main body 2, or the triple lumen
catheter 1 tip part may be structured from the tip part of main unit 2.
As described above, the triple l~men catheter of this invention has a No. 1
lumen and a No. 2 lumen that have a constricted diameter tip part and that are
fal,ri~led by a separaling wall equipped in the axial direction on the inside, and
is equipped with a No. 3 lumen that is parallel to the No. 1 lumen and No. 2
lumen where said No. 3 lumen is equipped on the inside of the side wall so as toconnect to the outside through a tip opening part that is equipped on said tip,
where either said No. 1 lumen or said No. 2 lumen has at least one pair of
opposing side wall openings that connect to the outside and that are
perpendicular to the side walls of one of the lumens, and by the provision of a
side opening that is perpendicular to the side wall of the other lumen. Thus it is
possible to prevent inadequate blood extraction due the side opening move near
to the inner wall of the blood vessel, and making it possible to prevent the side
CA 022~1227 1998-10-07
PCT/lJS 9 7 / 06 0 29
~ IP~J"~~ 3 ~ OCT 1997
opening from becoming stuck to the inner wall of the blood vessel which leads toproblems with failed blood extraction, thus making it possible to obtain a highly
reliable triple lumen catheter 1 that is able to produce a stable and secure blood
extraction.
Moreover, the triple lumen catheter of this invention is not only proved
with a separating wall that causes one of the two lumens, the No. 1 lumen or theN o. 2 lumen, have a larger cross-sectional area than the other lumen of the pair,
but also the lumen with the larger cross-sectional area is equipped with at least
one pair of mutually opposing side openings, making possible to obtain a triple
o lumen catheter capable of an increased blood extraction flow, not only making it
possible to reduce the load on the patient, but making it possible to perform
smooth, rational dialysis because it is possible to extract blood with certaintyusing the pair of opposing side openings 7a provided.
Moreover the triple lumen catheter of this invention has a thick wall part
s that extends from said wall part at the position that is opposite to the dividing
wall on the inside of either one of the lumens, the N o. 1 lumen or the No. 2
lumen, where said N o. 3 lumen being equipped within this thick wall part. This
makes it possible to secure a large extraction blood flow, and makes it possibleto prevent with certainty the side openings from being obstructed by the blood
20 vessel side walls.
Moreover the triple lumen catheter of this invention is equipped with a soft
tip that comprises a cutting head conical head part that has a wider diameter atits base side, two extending parts that cover the tip side of the lumen that
extends from the base part of said head part to the tip region of the side
2s openings of the N o. 1 and N o. 2 lumens described above, is equipped with a
through hole that is connected to the tip part of said N o. 3 lumen and that is
fabricated running along the conical surface of said head part to the tip opening
part equipped in said head part, and is structured with a catheter tip part wherein
said soft tip extension parts fit into said N o. 1 and N o. 2 lumens and where said
30 N o. 3 lumen connects to said through hole. This makes it possible to use a
simple structure that does not require a separate insert to be put into the lumen,
etc. in order to prevent dead space in the lumen, and makes it possible to
CA 02251227 1998-10-07
9 7/0602
p Q~iJ~ 3 ~ O~T t3
11
structure into conical shapes the soft tips that have been provided at the tips of
conventional catheters, thus making it possible to obtain a triple lumen catheter
that greatly reduces the amount of labor by making the soft tip more secure.
rRl~rr~ 5~