Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
Method and System for Monitoring the TranSportation and
Positioning of Moving Objects.
Specification
The invention relates to a method and system for
monitoring the transportation and positioning of moving
objects using a miniaturised high-frequency transmitter,
preferably a fixed frequency transmitter, preferably in
IC-card format.
From the unexamined German application DE 42 37 486 A1, a
device is known for recognising the theft of a vehicle,
especially a motor vehicle, a high frequency transmitter
being provided which is secured on or in the motor
vehicle. In the case where the vehicle is moved without
authorisation i.e. by operation by a stranger the
transmitter is activated whereupon a receiving system is
in the position to receive signals emitted from the high
frequency transmitter and to set off an alarm. The radius
of the beam from the high frequency transmitter, which is
located in the motor vehicle, is exceedingly small and
locating the vehicle itself is not possible.
In the device for determining the position of a moving
object according to DE 43 12 670 A1, a transmitter is
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
assigned to an object e.g. to a ship or to a land vehicle
In order to arrange for position detection very exactly
even in the near field region a differential-GBS-system~
i.e. satellite locating is fallen back on here. In fact,
locating of an object can take place thus relatively
exactly, however a transport route or transportation
progression control and hence identification of the
position of the objects is either not possible or only
possible at considerable cost over a local or regional
area. This is particularly true when a multiplicity of
objects is provided with a corresponding monitoring
device.
Likewise known are portable high frequency transmitters
for keyless entry systems, especially for vehicles where
the transmitter is designed in the format of a cheque
card. Therefore, DE 36 27 194 A1 discloses a transmitter
of the type of a transponder, which transfers high
frequency energy in the near field in order to open e.g.
the door of a motor vehicle or to allow a vehicle to
start.
According to US-PS 3,825,833, an electromagnetic
transmitter is known which is arranged camouflaged in a
key or similar. The transmitter is only activated in the
case of danger, i.e. it is not connected until a
corresponding manual handling of a current supply circuit
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
takes place. Then the short range of the transmitter can
be increased quasi indirectly via transponder stations.
The transmitter described in the US Patent specification
serves predominantly for sending out an emergency signal,
the location itself being secondary. A similar emergency
signal transmitter is portrayed in the unexamined German
application document DE 38 19 057 A1.
Furthermore, it has already been proposed to provide
vehicles, of higher price ranges especially, with a
transmitter so that a satellite-supported bearing is
possible in the case of a theft or other loss. Because of
the fact that the equipment required for locating is
relatively demanding and expensive, the use of systems of
this type has up till now only been effective for the high
value products mentioned. In the case of a cheap
configuration of high frequency transmitters, which is
entirely possible owing to a progressive miniaturisation
and reasonably-priced electronic components, the basic
problem resides in allocation if a multiplicity of objects
is provided with transmitters of this type.
Proceeding from the aforementioned, the object of the
invention is to offer a method and a system for monltoring
the transportation and positioning of moving objects, also
comprising persons or animals, by means of a miniaturised
high frequency transmitter, said system allowing any
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
objects, persons or similar to be located in a
particularly simple manner by falling back upon, as far as
receivers are concerned, already available components or
networks, as a consequence of which increased security is
assured when transporting goods and also people. It is at
the same time the object of the invention to improve the
logistics of transportation by optimising the transport
routes from data obtained while being able to make more
precise predictions about the arrival time of goods and
merchandise at their destination.
The solution to the object of the invention is achieved
with a method according to the teaching according to
Patent Claim 1 and also with a system with the features
according to ~atent Claim 4, the dependent Claims
comprising at least useful developments and further
developments.
With the method according to the invention for monitoring
the transportation and positioning of moving objects, e.g.
transport pallets, packets, containers, vehicles of all
types, people, animals and also smaller articles such as
luggage a miniaturised high frequency transmitter is
attached to the pertinent object in as undetachable a
manner as possible or being removable only by destruction.
It may be noted at this point that the attached,
miniaturised high frequency transmitter is fixed to the
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
S
pertinent object in such a manner that said transmitter
can be removed after use without destruction by authorised
persons by means of a special tool. Separation of the
high frequency transmitter by unauthorised persons is
admittedly only possible in a destructive manner. By
recording the last message of the transmitter,
abnormalities can be detected. After clearing of the high
frequency transmitter, a data telegram is sent at pre-set,
if necessary programmable intervals of time, the data
telegram defining the object unequivocally.
This definition is given by a special code which
characterises for example the owner, the transportation
goods, the carrier and similar. In addition, the data
telegram contains information which permits verification
with respect to the permissibility of a monitoring
inquiry.
The sent data telegrams are picked up by receiver
stations. These receiver stations are, in a particularly
preferred manner, devices of GSM-, DECT- or a similar
telecommunication network and/or devices of geostationary
location satellites. ~referably, monitoring of
transportation and positioning is carried out in the local
and regional area using radio cells of a telecommunication
network. In the continental monitoring area, on the other
hand, geostationary location satellites are fallen back
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
upon. Especially when monitoring shipping routes, use of
geostationary location satellites has proved to be
especially advantageous.
The respective receiver data of both the radio cells of
the telecommunication network and the geostationary
location satellites proceed to a central computer,
locating of the respective transmitter location and hence
of the object being possible from the receiver data. Thus
the transportation route of an object can be followed via
several radio cells and retraced without needing to have
special monitoring or receiving devices created.
Detection of the speed of the transport vehicle can result
from monitoring of the transport route and the time and
the possibility exists of determining excess driving
periods or too long rest or break times and the pertinent
location.
The recorded positioning or transport route data of the
respective object are then transmitted upon inquiry and
identification of the person being asked by pre-setting
and checking of a code word which corresponds at le~st in
part to the data telegram. This transmission to the
authorised receiver, e.g. the carrier who is interested in
where the sent merchandise is located can be realised via
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
regional and continental data communication ne~works e.g.
the Internet in a cheap manner.
The recording of data for a multiplicity of objects is
achieved by and with the mentioned central computer which
is used at the same time for calculating and billing of
costs per inquiry.
In a development of the invention, the transport route and
the transportation progression are reconstructed from the
stored, recorded data, the speed of transportation and a
provisional time of arrival at the destination being
calculable from the available data.
In order to reduce the quantity of data being recorded in
or with the central computer, storing only occurs when a
change in position can be established on reception.
In the system according to the invention for monitoring
transporting and positioning of moving objects a
miniaturised fixed frequency transmitter, preferably in an
IC card format or in a comparable handy format is fallen
back upon. The fixed frequency transmitter had an
identification marking which can be read manually or by a
machine and transmits a data telegram after clearance at
pre-set intervals, said telegram containing amongst other
things the identification code.
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
Furthermore, the system comprises a radio cell receiver
network, preferably of a telecommunication operator and/or
a satellite-supported location device for receiving data
telegrams.
In the system there is used a central computer which is
connected to the radio cell reception network and/or the
satellite-supported location device and which records the
received signals of the same identification code relative
to the location in a corresponding data set so that upon
authorised access to the central computer, the transport
progression and the respective position of the object or
objects can be accessed.
The fixed frequency transmitter used in the system and in
an IC card format is designed as a so-called "tag" and
comprises means for secure attachment to the object, as a
result of which unauthorised removal can be largely
excluded.
In a preferred embodiment of the high frequency
transmitter used in the system this transmitter has a
receiving part for remote-control clearance and/or
switching from a sleep-mode to the transmission state so
that a totally energy-saving operation and hence an
adequate life-span of the independent transmission unit
can be achieved.
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
Because of the embodiment of the high frequency
transmitter as a fixed frequency transmitter which only
operates in the frequency area being used by normal
telecommunication operators or satellite location systems,
expensive tuning devices, i.e. electronically tuned
oscillators or similar may be dispensed with so that the
costs of producing the transmitter, especially with
correspondingly large-scale manufacturing can be kept
down. Because of the programmable type of intermittent
operation of the transmitter energy consumption is small,
as a consequence of which the useful life-span is
increased in association with the remote-control clearance
option.
On the basis of the fact that only authorised persons, who
are seeking to make an inquiry, have access to the system
for monitoring transportation and positioning, the demands
of data protection and other entrepreneurial interests are
taken into account.
As far as application is concerned, the central computer
is operated or administered by a special server which
releases the desired, stored position data or the
transport progression after identifying the inquirer. In
order to keep the amount of data to be handled to a
manageable quantity information is not only stored solely
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
when a change in position of the objects has been
established but also non-accessed data is deleted after a
pre-set length of time when no changes in position have
been established.
In one design of the invention, the inquirer, i.e. the
client of the service system is informed about the
transport progression and the present state or stopping
location not only in co-ordinates but rather a graphical
representation is achieved by using cartographic
superimposition, the respective positions reached being
provided with additional information such as the day and
time.
The possibility exists, by means of a group identification
code, of using the system according to the invention for
larger carriers, car rentals or railway operators in order
to put the latter in the position of being able to obtain
an overview of the respective positions of the vehicles or
similar quickly and comprehensively.
The invention is explained subsequently in greater detail
with reference to an embodiment, given by way of example
and with the additional help of a Figure.
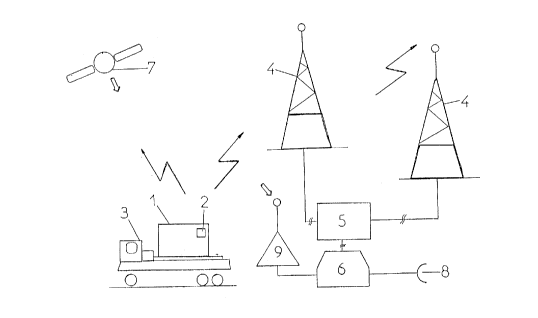
Fig. 1 hereby shows a principal representation of the
system for monitoring the transportation and positioning
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
11
of moving objects in the example of a container 1 which
is located on a motor vehicle 3.
As shown, there is secured on the container 1, for example
at one point where normally a piece of freight
documentation is located, a fixed frequency transmitter 2
in the format of an IC card. The transmitter contains an
identification marking either in plain text or in so-
called BAR code.
This marking is registered by the carrier and is a
component of the freight goods documentation. This means
a corresponding marking is allocated to all freight, in
the present case the container 1.
The data telegram emitted from the transmitter 2 after
being given clearance contains an individual code which
serves to identify the transmission signal and hence the
container 1.
When the container 1 located on the motor vehicle 3 is
moved locally or regionally on corresponding traffic
routes the high frequency signals, which are transmitted
at pre-set intervals of time, are picked up by the radio
cell receiver antennae 4 of a GSM or DECT network operator
and supplied to a processing station 5 which is a
component of the available network. From the processing
CA 022~2997 1998-11-06
station 5, the information can then be selected which
corresponds to the radio cell transition when the motor
vehicle 3 with the container 1 and the transmitter 2
moves. The transport progression can be reconstructed
from registration of this radio cell transition and
monitoring of the position is achieved.
For this purpose, the processing station 5 remains in
contact via a data line with a central computer 6 of the
system for monitoring transportation and positioning.
This central computer 6 has a further interface for
picking up data from a receiver 9 for satellite-supported
location devices 7. These satellite-supported location
devices 7, which can for example be part of a GPS
navigation device, enable position monitoring in areas
which are not supplied or are only inadequately supplied
by a telecommunication radio cell networki this is true
for example for sea routes or air transportation.
An access interface 8 of the central computer 6 now
enables inquiry about data for monitoring transportation
and/or positioning by someone authorised to do so, in the
present case the carrier who knows the identification
code. The person with authorised access can ln pre-set
intervals of time, for example in times of light traffic,
download the relevant information for the pertinent
objects from the central computer 6 via a data network in
.
CA 022~2997 l998-ll-06
13
order to enter said information in the person's own
computer system for documentation, control and detection
purposes, especially for possible insurance cases. The
data stored in the central computer 6 are automatically
deleted after a pre-set time to limit the volume of the
data; only data about changes in movement or positioning
of the respective object being transferred into the
memory, likewise with a view to reducing the amount of
data.
The transportation speed can be detected from the stored
data stock and the arrival time of the object or objects
at a pre-set destination can be determined a priori.
Reference Number List
1 Container
2 High frequency transmitter
3 Motor vehicle
4 Radio cell receiver antenna
Processing station
6 Central computer
7 Satellite-supported location device
8 Access interface
9 Receiver