Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 1 -
SYSTEM-ADAPTED ELASTIC MOUNTING
FOR A DIESEL GENERATOR
This invention relates to a mounting for an
internal combustion engine connected in driving rela-
tion to a machine, such as a diesel engine driving an
electric generator, wherein the internal combustion
engine and the generator are supported on a supporting
frame by first spring elements and the supporting frame
is mounted on a foundation by second spring elements.
In the engine driven generator unit disclosed
in German Patent document GM 79 32 802, an air receiver
by which the internal combustion engine draws in air
for combustion, is continued into the supporting frame
and the supporting frame has laterally extending air
inlet passages. Air guide vanes are inserted in the
appropriate part of the supporting frame in order to
absorb sound. This design is suitable for a reduction
of noise originating in the drawn-in combustion and
cooling air, but it does not bring about any advantages
with respect to a solid-borne-noise-insulating mounting
of the internal combustion engine connected to the
generator. One attempt to reduce solid-borne-noise
includes filling the supporting frame with concrete to
thus create an intermediate mass. Such a concrete
intermediate mass, however, brings about only condi-
tionally satisfactory results with respect to the insu-
lation of solid-borne noise.
It is an object of the invention to furnish a
mounting for an internal combustion engine connected to
a machine, such as a generator, which effects a marked
reduction in the solid-borne noise originating from the
internal combustion engine and the generator.
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 2 -
This object is achieved by providing a sup-
porting frame containing an acoustically efficient
intermediate mass for insulating solid-borne noise,
which intermediate mass includes at least two mutually
independent components. These two components effect a
marked reduction in the solid-borne noise originating
from the internal combustion engine and the driven
machine. one of the two components uses a material
having a high specific mass, while the second component
has a lower specific mass such as may be achieved by
use of a filler material.
The supporting frame is designed as a trough-
shaped steel structure having lateral box girders, the
intermediate mass being arranged at least in partial
regions of the box girders. These partial regions are
chambers that are arranged in distributed fashion in
the box girders. One component of the intermediate mass
is inserted into the chambers and the second component
is inserted into the regions of the box girders lying
between the chambers.
The two components of the intermediate mass
are preferably sheet-metal stacks and sand. The sheet-
metal stacks have a higher specific mass relative to
sand and are screwed together with tension rods and lie
in the chambers on the box-girder base plate. The
tension rods are spaced from the box-girder side walls
and from the chamber side walls. A small intermediate
space is left between the box-girder side walls and the
chamber side walls on the one hand and the sheet-metal
stacks on the other, into which intermediate space
rubber sheets can be inserted. Fine-grained, dry-
calcined sand is filled into the remaining regions of
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 3 -
the box girders. The metal sheets themselves are
protected against rusting.
The first spring elements are attached, pref-
erably screwed, to the sheet-metal stacks. The spring
elements are covered at the internal-combustion-engine
end and at the generator end by a frame designed in the
shape of a trough. This frame contributes to the mutual
alignment of the attachments of the spring elements, in
particular upon setting-down of the internal combustion
engine and the generator and the frame also serves to
reduce the emission of airborne sound in the foundation
region.
The trough bottom, which closes the entire
supporting frame from below, is, like the frame, pref-
erably fabricated from sound-deadening sheet metal and
thus serves as a shield against amplified emission of
airborne noise in the foundation region. This sound-
deadening sheet metal is further a steel sheet coated
with a bituminous material.
Finally, the internal combustion engine and
the generator are enclosed by a housing arranged on the
supporting frame.
Further advantages of the invention can be
inferred from the description of the drawings, in
which:
Figure 1 shows a diesel engine driven genera-
tor unit on a supporting frame;
Figure 2 shows a supporting frame having an
additional housing enclosing the diesel engine driven
generator unit;
Figure 3 is a perspective view of part of the
supporting frame;
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 4 -
Figure 4 is a perspective view of the com-
plete supporting frame;
Figure 5 is a longitudinal section through
the supporting frame of Figure 6;
Figure 6 is a top view of the supporting
frame; and
Figures 7a to 7c are cross sections through
the supporting frame of Figure 6.
In Figure 1, an internal combustion engine 1
drivingly connected to an electric generator 2 by an
elastic coupling is mounted on a supporting frame 4 by
first spring elements 3 (Figure 3), and the supporting
frame 4 is mounted on a foundation, not shown, by
second spring elements S.
The internal combustion engine 1 is, for
example, a 12 cylinder diesel internal combustion
engine of V design having a power of approximately 1300
kW and a weight of about 5000 kilograms or a 16-
cylinder diesel internal combustion engine of V design
having a power of approximately 1750 kW and a weight of
approximately 6500 kilograms. The electric generator 2
is appropriately adapted to the power of the internal
combustion engine 1 and has, in the first case, a power
of 1800 kW at a weight of 6500 kilograms and, in the
second case, a power of approximately 2400 kW at a
weight of 7400 kilograms. These diesel engine driven
generator units are designed primarily for diesel-
electric propulsion of a ship. A plurality of these
units can be provided in a ship in order to furnish the
requisite propulsive power. Because the diesel engine
generator units are the principal noise producers in
ships using these units for ship propulsion, this
mounting is designed to insulate the solid-borne noise.
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 5 -
Accordingly, the mounting must be carefully designed
and, as shown in Figure 2, the internal combustion
engine 1 and the generator 2 should be enclosed by a
housing 6. In Figure 2, the housing is shown partly
open.
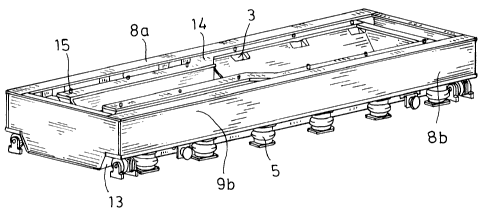
Figure 3 shows the supporting frame 4 in a
partly assembled condition and Figure 4 shows the sup-
porting frame 4 completely assembled. The supporting
frame 4 has lateral box girders 8a, 8b, to which
inwardly protruding chambers 12a, 12b are attached.
Sheet-metal stacks 7a, 7b lying on the box-girder base
plate 10, which are approximately 40mm thick, are
inserted into these chambers, the first spring elements
3 being attached to said sheet metal stacks. Between
the chambers 12a, 12b, the box girders 8a, 8b are
filled with fine-grained dry-calcined sand 18. Between
the sheet-metal stacks 7a, 7b on the one hand and, on
the other, the box-girder side walls 9a, 9b and the
remaining chamber side walls, an intermediate space of
approximately 3mm is left, which space can be filled
with rubber sheets. As shown in Figure 4, a frame 14 is
laid on the spring elements, which, like the trough
bottom 13, consists of 10mm thick sound-deadening sheet
metal (sandwich sheet) or also only of 10mm thick steel
sheet. On the one hand, this frame 14, likewise
designed in trough shape, aligns the fastening bolts 15
at the internal-combustion-engine end and at the
generator end, and it also contributes, in particular,
to further stiffening and reducing the emission of air-
borne noise.
Figure 6 is a top view of the supporting
frame 4, the frame 14 not yet being assembled in this
view. Figures 5 and 7a to 7c show the respectively
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 6 -
identified cross sections. In supplement to the fore-
going description, it can be inferred from this figure
that the chambers 12a, 12b are connected to one another
by means of ribs 16a, 16b. These ribs 16a, 16b are
connected to the trough bottom 13 and include rein-
forcements 17a, 17b on the upper free end. From Figures
7a to 7c, in particular, it can be inferred how the
sheet metal stacks 7a, 7b are screwed together with
four or, respectively, six tension rods 11 and arranged
in the chambers 12a, 12b.
In acoustical terms, this system satisfies
the following criteria:
A rigid-body mode lower than 20 hertz is
achieved. This criterion, in combination with the
spring constants of the first spring elements 5, deter-
mines the required mass (mZ) of the intermediate mass
plus housing mass (mk). The total mass is thus calcu-
lated as m = mZ + mk. For the 12-cylinder engine, mZ is
approximately 10,300 kilograms, mk is approximately
2,420 kilograms, and thus m is approximately 12,720
kilograms. For the 16-cylinder engine these valves are
mZ = 11,940 kilograms, mk = 2,560 kilograms, and m
14,500 kilograms. The first spring elements 3 are,
moreover, designed such that the first characteristic
frequency here lies around 500 hertz and the second
characteristic frequency around 1000 hertz. The second
spring elements 5 are designed such that the first
characteristic frequency here lies around 136 hertz.
The number of the first and second spring elements 3, 5
is ten for the 12-cylinder engine and twelve for the
16-cylinder engine. Thus, a fictive matching frequency
(dynamic rigidity) of some 8 hertz is achieved between
the diesel generator unit and the supporting frame,
CA 02260432 1999-01-26
- 7 -
while in the lower region a characteristic frequency of
3 hertz is achieved between the supporting frame and
the foundation.