Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 TECHNICAL FIELD
2 This invention relates to the rams used in a wellhead production
3 blowout preventer.
4 BACKGROUND ART
The invention has to do with improving the rams in a known oilfield
6 wellhead assembly component known as a high temperature production
7 blowout preventer (hereafter "BOP").
8 This type of BOP is commonly used in connection with thermal
9 pumping wells. With such wells, a sucker rod string is reciprocated or
rotated
to drive a downhole pump, which lifts the produced fluid to the surface
through
11 a tubing string in the course of the production cycle. The well is also
used to
12 inject steam in the course of the steaming cycle.
13 The BOP is equipped with rams that can be advanced horizontally to
14 seal around the vertical polish rod of the rod string, to prevent the
upward
escape of fluid.
16 More particularly, the BOP comprises a cross-shaped housing forming
17 a vertical bore and a pair of coaxial, horizontal ram bores intersecting
the
18 vertical bore from each side. The BOP is commonly positioned in the
19 wellhead assembly between the tubing head and the flow tee. The BOP
vertical bore therefore forms part of the wellhead assembly fluid passageway.
21 A ram is positioned in each ram bore. Each ram usually comprises
22 a cylindrical back plate, a top retainer plate, a bottom retainer plate and
a
23 T-shaped seal element sandwiched between the plates. The components
24 are held together by cap screws. The assembly is illustrated in prior art
Figures 1 - 2.
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 As stated, the ram bores extend into or join with the vertical bore. The
2 bore surfaces combine at their intersection to form sealing areas. A screw
3 jack or like means is used to apply mechanical force to each ram back plate
to
4 advance the rams toward each other into sealing engagement. The inner end
faces of the retainer plates and the seal element each form a semi-circular,
6 vertically-directed groove. Thus, when the polish rod of the rod string is
7 present in the vertical bore and the rams are closed, the ram ends encircle
8 and press against it to effect a seal. At the same time, the seal element is
9 compressed by the retainer plates pushing back against the back plate,
thereby effecting an axial seal along the two sides of each ram and a
11 circumferential seal. The pressure in that portion of the wellhead assembly
12 fluid passageway below the rams is prevented from reaching that portion of
13 the passageway above the rams.
14 There are problems associated with the rams just described.
Firstly, when the two rams are pressed together, the protruding seal
16 elements contact first and act to spread the front ends of the retainer
plates.
17 The retainer plates begin to cant and can become jammed. The rams then are
18 difficult to withdraw.
19 Secondly, during steaming, steam can get behind the rams and, in cold
weather, can condense and freeze. The BOP may then be impossible to
21 operate and it becomes necessary to bring a steam truck to the site to heat
22 the wellhead and thaw the ice. This is expensive and time-consuming to do.
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 It is therefore one objective of the invention to alter the design of the
2 ram so that its tendency to get jammed is reduced or eliminated. It is
another
3 objective to modify the ram so that steam condensate behind the ram can
4 escape back into the wellhead to reduce or prevent the build-up of ice
behind
the ram.
6 It is also an objective of the invention to improve the life of the seal.
7 The key difference that achieves this is the way force is applied to the
seal
8 element. In the prior art, force is applied to the seal only from the front
face.
9 The seal element is forced upward and downward to meet the retainer plates.
The seal is typically manufactured from laminated sheets of asbestos or
11 graphite and the direction of the laminations are parallel to the ram bore.
The
12 force on the seal element works to expand the seal and separate the seal
13 lamianted sheets. The invention has been designed to compress the seal
14 element in a way that will reduce delamination.
16 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
17 The invention is directed to a wellhead production BOP ram, having
18 front and rear ends, and comprises:
19 ~ substituting a generally L-shaped retainer plate for the prior art
bottom and back plates (this retainer plate hereafter being referred
21 to as the "rear retainer plate");
22 ~ adopting a generally L-shaped configuration for the seal element;
23 ~ forming the other retainer plate (referred to as the "front retainer
24 plate") so that its inner surface is also generally L-shaped;
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 ~ whereby, when the plates and seal element are assembled with the
2 seal element sandwiched between the inner surfaces of the plates,
3 they form a full bore body which conforms to the surface of the ram
4 bore;
~ acutely angling, relative to the axis of the bore, at least one of the
6 front portions of the retainer plate inner surfaces so that, when the
7 front plate is driven rearwardly, there is both radial and axial
8 compression of the seal element arising from a wedging action. In
9 a preferred embodiment, the front retainer plate is on the top and
the rear retainer plate is on the bottom and the front portions of their
11 inner surfaces are parallel and upwardly inclined relative to the axis
12 of the bore;
13 ~ staggering the vertical alignment of the front end surfaces of the
14 components so that those of the front retainer plate and seal
element protrude beyond that of the rear retainer plate. Preferably
16 the front end of the seal element protrudes beyond the front end of
17 the front retainer plate which, in turn, protrudes beyond the front
18 end of the rear retainer plate; and
19 ~ preferably orienting the front and rear retainer plates at top and
bottom of the ram, respectively, and forming the bottom of the outer
21 longitudinal surface of the rear retainer plate to provide a
22 longitudinally extending groove for draining steam condensate, from
23 behind the ram, back into the wellhead.
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 By modifying the ram in this manner, the following advantages are
2 obtained:
3 ~ the L-shaped design ensures that the rear retainer plate is rigidly
4 supported around its circumference at its rear end by the BOP
housing and this rigidity extends to the front portion of the retainer
6 plate, so that the latter will not cant downwardly when extended into
7 the vertical bore of the BOP and pressed against the polish rod. In
8 addition, the rear retainer plate now provides a rigid anvil against
9 which the front retainer plate may downwardly and rearwardly
compress the seal element, thereby attaining a good longitudinal
11 seal and reducing the likelihood that the front retainer plate will
12 cant;
13 ~ in addition, the L-shaped design extends to the seal element which
14 means that the seal does not extend to the base of rear retainer
plate" making it possible for the drainage groove to extend along
16 the bottom surface of the plate;
17 ~ the angling of one or more of the front portions of the inner
18 surfaces, coupled with the front end protrusion of the front retainer
19 plate relative to that of the rear retainer plate, also leads to a
desired wedging effect which assists in reducing canting of the front
21 retainer plate and assists in improved seal element compression;
22 and
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 ~ with the new design, as the ram assembly is advanced, wedging of
2 the two retainer plates acts to force the laminated sheets together
3 and keep the seal element compressed, thus extending the life of
4 the seal. This shape also allows the use of very brittle materials
that will fail under any loading but compression.
6
7 DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
8 Figure 1 is an exploded perspective view of a prior art ram used in
9 production wellhead BOP's;
Figure 2 is a sectional side view showing the ram of Figure 1
11 assembled;
12 Figure 3 is an exploded perspective view showing a ram in accordance
13 with the invention;
14 Figure 4 is a rear end view of the ram of Figure 3;
Figure 5 is a sectional side view taken along lines A-A and B-B of
16 Figure 4, showing the staggering of the front surfaces and the angling of
the
17 front portions of the inner surfaces of the retainer plates; and
18 Figure 6 is a sectional side view of a BOP having a pair of rams in
19 accordance with the invention, shown in the closed position sealing against
the polish rod of a sucker rod string.
._
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
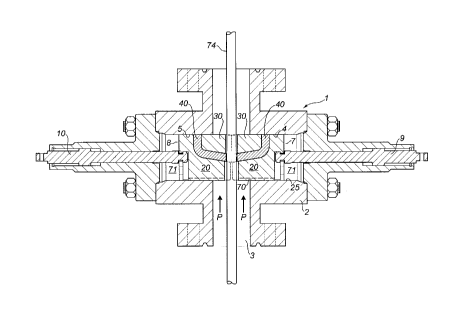
2 Having reference to Figure 6, a production blowout preventer 1
3 comprises a cross-shaped housing 2 forming a vertical bore 3 and a pair of
4 coaxial horizontal ram bores 4,5. The ram bores 4,5 intersect with the
vertical
bore 3 and form sealing areas.
6 A pair of generally cylindrical rams 7,8 are located within the ram bore
7 4,5. Screw jacks 9,10 extend through plugs 11,12 threaded into the outer
8 ends of the ram bores 4,5. The screw jacks 9,10 can be turned to advance or
9 retract the rams 7,8 into or out of the vertical bore 3.
Each of the cylindrical rams 7, 8 comprises a generally L-shaped, rear
11 retainer plate 20 having an arcuate longitudinal outer surface 21 and an L-
12 shaped inner surface 22 having front and rear portions 23, 24. The outer
13 surface 21 conforms with the cylindrical surface 25 of the ram bore in
which it
14 is positioned. The rear retainer plate therefore has a close sliding fit in
the
ram bore. A pair of bolt holes 26 extend through the upright, full bore
16 diameter section 27 of the rear retainer plate 20. In the embodiment shown,
17 each rear retainer plate 20 is positioned at the base of the ram of which
it
18 forms a part.
19 Each ram 7,8 further comprises a front retainer plate 30. The plate 30
has an arcuate, longitudinal outer surface 31 and a generally L-shaped inner
21 surface 32. The inner surface 32 has front and rear portions 33,34. A pair
of
22 bolt holes 35 extend longitudinally inward from the inner surface rear
portion
23 34.
24 The retainer plates 20, 30 will normally be formed of steel.
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 A generally L-shaped seal element 40 is sandwiched between the inner
2 surfaces 32, 22 of the front and rear retainer plates 30, 20. The seal
element
3 40 is formed of material commonly used for this purpose in production BOP
4 rams, such as asbestos or graphite combined with a bonding agent. A pair of
bolt holes 41 extend through the upright portion 42 of the seal element 40, in
6 register with the bolt holes 26, 35 of the rear and front retainer plates
20, 30.
7 The front portions 33, 23 of the inner surfaces 32, 22 are equally
8 acutely angled relative to the longitudinal axis of the ram bores 4,5. Each
9 front retainer plate 30 therefore has a tapered or wedge-like configuration.
The inner and outer surfaces 43, 44 of each seal element 40 conform
11 with the inner surfaces 32, 22 of the retainer plates 30, 20.
12 A pair of bolts 50 extend through the bolt holes 26, 41 and 35 to tie
13 together the rear retainer plate 20, seal element 40 and front retainer
plate 30.
14 This will be visible in Figures 3 - 5. The bolts 50 each have threads 51 on
one end and a center section 52 with larger diameter than the threaded end,
16 creating a shoulder 53, at the back end of the hreads. This shoulder 53
17 contacts a shoulder 54, in the front retainer palte 30, fixing the two
pieces
18 together. A separate shoulder 55 at the head of the bolt and a shoulder 56
in
19 the rear retainer plate 20 limit the movement of the front retainer palte
30
forward but allow movement rearwardly a limited amount, in order to
21 compress the seal element 40.
<-:
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 The front faces 60, 61 and 62 of the front retainer plate 30, seal
2 element 40 and rear retainer plate 20, respectively, are staggered; that is
the
3 seal element protrudes further forward than the front retainer plate which,
in
4 turn, protrudes further forward than the rear retainer plate. Each of the
faces
60, 61, 62 forms a central, vertical, semi-circular groove 63 for extending
6 around the rod string polish rod 74.
7 In operation, the jacks 9, 10 are actuated to bias the rams 7, 8
8 forwardly toward each other. As the seal elements 40 contact and press
9 against each other or the polish rod, the front retainer plate 30 is pressed
rearwardly. As it moves, its inner surface 43 compresses the seal element 40
11 downwardly and rearwardly against the inner surface 22 of the rear retainer
12 plate 20. The front surfaces 61 seal against each other and the seal
element
13 outer surfaces 44 seal against the ram bore surfaces 25, both
longitudinally
14 and circumferentially.
In a preferred feature, a longitudinally extending groove 70 is formed in
16 the bottom of the outer surface 21 of each rear retainer plate 20. These
17 grooves 70 connect the spaces 71 behind the rams 7, 8 with the vertical
fluid
18 production passageway 72 of the wellhead 73. Condensed steam in the
19 spaces 71 can drain into the passageway 72 to avoid ice build-up.
The assembly has been described with the rams 7, 8 having the rear
21 retainer plate 20 on the bottom. However the rams could be rotated to
22 position the rear retainer plates 20 on top. In addition, only one inner
surface
23 front portions 33, 23 needs to be angled to achieve the wedging effect.
24 Furthermore, the rams and ram bores have been described as being
cylindrical - however they can be ovalled as well. Finally, the rear retainer
.._ r_ ....._ _. _ _.._ _ _ _ __ ___ _ . _....
CA 02260655 1999-02-02
1 plate has been described as one piece - however it could also be formed in
2 two pieces. These modifications are considered to be within the scope of the
3 invention.
4 The foregoing description of a preferred embodiment of the invention
has been presented for purposes of illustration and description. It is not
6 intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise form
7 disclosed. Obvious modifications or variations are possible in light of the
8 above teachings. The embodiment provides the best illustration of the
9 principles of the invention and its practical application to thereby enable
one
of ordinary skill in the art to utilize the invention in various embodiments
and
11 with various modifications as are suited to the particular use
contemplated.
12 All such modifications and variations are within the scope of the invention
as
13 determined by the appended claims.