Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
DESCRIPTION
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR THE CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION OF PLASTICS SLEEVES
The invention is based on known plastics sleeves, envelopes or jackets,
which are manufactured in such a way that two webs of a long plastics sheet
are placed on one another, the two webs e.g. being obtained by the folding
round of a single sheet. The said webs are then e.g. horizontally conveyed
with the aid of driven rollers and stopped in a cycle corresponding to the
length of the finished plastics sleeve. During the stoppage a longitudinal
weld, transverse weld, optionally a perforation and a separation or cutting
are carried out. This takes place with the aid of welding dies, hole punch-
ing dies or cutting knives movable on the plane of the webs. After carrying
out these processes it is necessary to reaccelerate the sheet web. This
production procedure leads to the efficiency of such installations being
limited.
The problem of the invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for
producing plastics sleeves, in which the efficiency can be increased and/or
the costs of the production plant decreased.
For solving this problem the invention proposes a method having the features
of claim 1 and an apparatus having the features of claim 17. Further
developments of the invention form the subject matter of dependent claims,
whose wording, like that of the abstract) is made into part of the content
of the present description by reference.
Through producing the transverse weld during movement, the installation for
conveying the plastics webs no longer has to be stopped and then reacceler-
ated. Even if the conveying speed of the webs does not increase compared
with that of known installations, there is an increase in the efficiency of
a plant or installation for plastics web production. The welding of the two
sheets in the transverse direction and in which case a double weld can be
involved, can be brought about in different ways. Whereas in the prior art
the plastics sleeves are produced in their own longitudinal direction, it is
now also possible to position the plastics sleeves transversely to the
longitudinal direction of the sheet web, so that the overall installation
can be made shorter.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
-
According to a further development of the invention, during movement the
webs can also be welded together along at least one longitudinal edge. This
makes it possible to so orient the plastics sleeves that their own longi-
tudinal direction coincides with the longitudinal direction of the webs, so
that the apparatus parts responsible for the supply of the plastics sheet
and the conveying away of the finished plastics sleeves do not require
modification compared with known installations. It is also possible to
start with two separate plastics webs) which are then welded together along
both longitudinal edges.
According to a further development of the invention, longitudinal welding
can e.g. be carried out by a welding wheel, which is rotated about an axis
parallel to the web surface and perpendicular to the conveying direction of
the webs with a peripheral speed corresponding to the linear speed of the
webs. Thus, the welding wheel runs on the continuously moved on plastics
sheets and thereby brings about a heating and consequently welding.
It is in particular possible to provide on the opposite side of the web a
similar wheel, which rotates in the opposite rotation direction about a
parallel rotation axis and with which cooperates the welding wheel. The two
wheels enclose the sheet between them and the second wheel can either be
constructed as a countermember or also as a welding wheel. As a function of
the heating procedure, there need be no contact between the welding wheel,
the sheet and the countermember. On contact with the sheet and the welding
wheel, the countermember can be driven and carried along by the welding
wheel. It can have a size different from that of the welding wheel.
According to a further development of the invention, the transverse welding
is performed by a welding jaw or die, which is moved jointly with the plas-
tics webs to the welding position. The welding die can carry out the weld-
ing operation, e.g. as a result of heating. The welding die can in this
case cooperate with a counterdie positioned on the opposite side of the webs
and moved therewith to the welding position. This opposite die can also be
an independent welding die or a countermember, against which the upper weld-
ing die presses the plastics sheet.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
- 3 -
The movement of the welding die and/or counterdie can e.g. take place along
a closed movement path, said movement e.g. taking place with the aid of
chains or toothed belts.
According to the invention the welding die used for producing the transverse
weld can simultaneously perform a separating weld, so that ttte transversely
directed separation can also be carried out for separating the individual
plastics sleeves from the welding die.
It is also possible according to the invention for the webs to be separated
with a knife running transversely to the conveying direction and which is
moved together with the webs at the separation point and optionally cooper-
ates with a countermember on the opposite side of the webs.
According to a further development of the invention, the knife and/or
countermember can be moved in opposing directions along a circular path.
This circular path approaches the sheeting, until the actual separation or
cut takes place at the contact point.
If the plastics sleeves are to have a perforation or hole system along one
edge enabling filing in files, according to the invention the webs are
provided with such a perforation or hole system during conveying.
The perforations can in particular be made with a hole punching die moved
together with the webs and which cooperates with a bottom die located on the
opposite side of the webs and moved with the latter.
If the holes are to be made along the longitudinal edge of the webs, accor-
ding to the invention the hole punching dies are located on the circumfer-
ence of a jointly rotating perforating wheel.
Here again the hole punching die and/or bottom die can be contrarotated
along a closed path, particularly along a circular path.
The apparatus proposed by the invention and having the features of claim 17
is able, per unit of time, to produce a larger number of plastics sleeves
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
- 4 -
than is possible in the prior art. The installation can also have a partic-
ularly simple construction, because the high forces occurring through the
deceleration of the conveying device and its reacceleration are
avoided.
The longitudinal welding device can have a welding wheel) whzch is rotated
at a peripheral speed corresponding to the linear speed of the webs and
which cooperates with a counterwheel rotating in the opposite rotation
direction and located on the opposite side of the sheeting.
According to the invention, the transverse welding device can have a trans-
versely positioned welding die, which is moved along a closed path parallel
to itself with a peripheral speed corresponding to the linear speed of the
webs and which cooperates with an oppositely movable countermember posi-
tioned on the opposite side of the sheeting.
This movement along a closed path can e.g. take place with the aid of
chains guided around at least two gears or toothed belts guided round guide
members. Over a certain distance the welding die then moves parallel to the
sheet webs and can weld the latter.
According to a further development of the invention, the welding die and/or
countermember can be moved about a fixed axis, so that they are moved along
a circular path.
If the plastics sleeves are to have holes, according to the invention the
apparatus can have a device for producing a system of holes in the sheeting
during conveying.
According to a further development, this device can have a wheel provided
with at least one hole punching die, which is driven about an axis parallel
to the sheeting and perpendicular to the conveying direction at a peripheral
speed corresponding to the conveying speed. This wheel then makes a perfor-
ation along the conveying direction or a row of holes transversely to said
conveying direction.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
- 5 -
In particular, the perforating device can be a wheel with at least one hole
synchronously contrarotated about a parallel axis on the opposite side of
the sheeting and which has a position corresponding to that of the hole
punching die and in which the latter engages.
If the row of holes is to be at right angles to the conveying direction of
the plastics webs, the hole punching die can be positioned along a line
parallel to the rotation axis of the wheel and this also applies with
respect to the holes.
However, if the row of holes is to be parallel to the longitudinal direction
of the plastics webs, the hole punching dies and holes can be positioned
along a circumference of the corresponding member.
Further features, details and advantages of the invention can be gathered
from the following description of a preferred embodiment of the invention
and the attached drawings, wherein show:
Fig. 1 In highly simplified form, an installation for performing the
method proposed by the invention.
Fig. 2 A plan view of an apparatus for producing plastics sleeves.
Fig. 3 A plan view of a modified apparatus.
Fig. 4 A known plastics sleeve for explaining the operation of the
apparatus proposed by the invention.
The apparatus shown in highly simplified form in fig. 1 is used for produc-
ing individual plastics sleeves from two flat) superimposed sheet webs.
The sheet webs can be separate or interconnected along a longitudinal edge.
In the simplified representation the two sheet webs are shown as a single
web 1) which runs horizontally and is located in one plane. For its convey-
ing with a continuous, constant speed) it is possible to provide conveying
rollers) which are rotated. This is not shown in detail. The conveying
direction in fig. 1 is from left to right in the direction of arrow 2.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
- 6 -
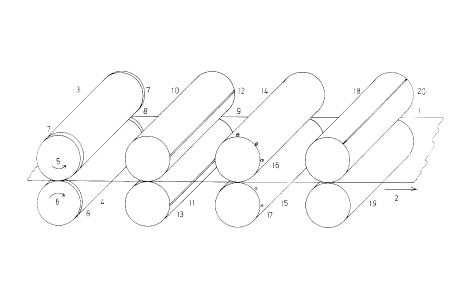
Considered in the conveying direction, the apparatus has two rollers 3, 4,
which in the represented embodiment have the same size, i.e. the same length
and same circumference. Each of the two rollers 3, 4 is rotatable about an
axis, the two axes being parallel to one another. These rollers 3, 4 are so
positioned that they enclose the sheet web 1 between them and are in contact
with said web. For example, the upper roller 3 is rotated in the direction
of arrow 5 and carries with it the lower roller 4 in the direction of the
arrow 6. It is also possible, as a result of the pressure which they exert
on the sheet web 1, for the rollers to be moved by said web 1. It is also
possible to have a self-contained drive for both rollers, which takes place
in synchronized manner to the conveying of the sheet web 1. In the vicinity
of the front end, the roller 3 contains a strip 7, which is constructed as a
welding wheel and is e.g. electrically heated. This electrically heated
area, on rolling on the sheet web 1, leads to a heating of the latter and
consequently to a welding of the two plastics sheet layers forming the sheet
web 1. The opposite roller 4 has a similar strip 8, which is either also
constructed as a welding wheel or which merely acts as a countermember. Dur-
ing the conveying of the sheet web 1 the two strips 7, 8 carry out a longi-
tudinal welding of the two layers forming the sheet web 1. As a function of
the nature of the plastics sleeve to be produced, such strips can also be
located at the opposite end of the two rollers 3, 4, so as to be able to
bring about a longitudinal welding of the trailing edge 19 of the plastics
sheet 1 in fig. 1.
In the conveying direction according to arrow 2, following the rollers 3, 4
is provided a second roller pair 10, 11, which are once again contrarotat-
able about two parallel axes. Rotary driving can take place by a self-
contained drive. The upper roller 10 of this roller pair contains a strip
12, which is parallel to the rotation axis over the entire width of the
sheet web 1 and can be constructed as a welding die and then, if it contacts
the web 1 during the rotary movement, performs a transversely directed weld
of the plastics sheet. On the opposite roller 11, i.e. positioned below the
web 1, is provided a corresponding counterdie 13, which is once again either
in the form of a countermember, against which welding is carried out, or as
an independent welding die.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
_ 7 _
Thus, a transverse weld on the two layers forming the plastics web 1 can be
carried out with the aid of the roller pair 10, 11. As in the case of the
longitudinal weld, it can here again be a double weld seam.
In the conveying direction of the web 1 following the roller pair 10, 11 is
provided a further roller pair 14, 15 in the same way as the'roller pair
10, 11. At the leading end of the upper roller 4 in fig. 1 are provided in
the embodiment shown four hole punching dies 16, whilst at the opposite end
of the lower roller 15 are provided four holes 17. In the case of a
synchronous contrarotation of the two rollers 14, 15, the hole punching dies
16 engage in the holes 17 and thereby perforate the sheet. The mutual spac-
ing of the hole punching dies 16 and their orientation with respect to the
transverse weld made by the welding die 12 is such that the holes are made
at standardized points along the edge of the plastics sleeve.
The roller pair 14, 15 is followed by a final roller pair 18, 19, which is
once again arranged and driven in a similar way to the preceding roller
pairs. Along a periphery parallel to the rotation axis the upper roller 18
is provided with a knife 20, which cuts the web 1 during rotation. The
lower roller 19 contains a countermember, e.g. an edge on the border of a
depression. In the position shown in fig. 1 it is impossible to see said
depression. The knife 20 cuts the finished plastics sleeves from the web 1.
The apparatus shown in the drawing operates with a constant, continuous
conveying on of the plastics web 1, so that at no time during production is
it necessary to stop the conveying process.
Fig. 2 shows on a smaller scale a plan view of the arrangement according to
fig. 1 with the corresponding rollers. The first roller 3, i.e. to the left
in fig. 1, performs the longitudinal weld with the aid of the welding wheel
7 located on its one or on both ends. The roller is provided at both ends
with an axle journal 21) which can be used for the mounting support of the
roller 3 and for driving the same, but no details are shown.
The following roller 10 for producing the transverse weld, the roller 14 for
producing the perforation and the roller 18 for separating the plastics
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
_ g _
sleeves 22 from the web 1 are mounted in the same way. All the rollers can
be constructed so that they cooperate in the conveying of the sheet 1. This
can e.g. be brought about by a corresponding surface design. It is
obviously also possible for the conveying of the web 1 to be carried out by
other, not shown conveying rollers. In this case the devices for carrying
out the different processes can be somewhat differently constructed, as
shown in simplified form in fig. 3. Here the welding wheels 7 for producing
the longitudinal weld are positioned on a shaft 23, which only brings about
the rotation of the two welding wheels 7. The welding die 12 is located on
the circumference of two wheels 24, so that it is even possible to omit the
shaft. The welding die produces the transverse weld 25.
If the row of holes 26 is only to be made along one edge or border of the
web 1, the corresponding wheel having the hole punching dies 16 can also be
positioned on a single shaft 21. The knife 20) which transversely com-
pletely separates or cuts the sheet web is again arranged in a similar man-
ner to the welding die 12.
Fig. 4 shows a plastics sleeve, as can be produced by the method proposed in
the present invention. Along its one longitudinal edge the plastics sleeve
28 contains two parallel longitudinal welds 29, which leave between them a
free space in which a strip can be placed. In the prior art said longitud-
inal weld 29 is produced in such a way that it represents a weld in the
longitudinal direction of the cohesive sheet web 1. However, this is
unnecessary according to the invention. The longitudinal weld 29 of the
plastics sleeve 28 can also be a transverse weld 25 of the sheet web 1. In
this case the hole punching dies 16 are arranged along a straight line
parallel to the rotation axis of the roller 14. The same applies regarding
the holes 17 in the lower roller 15.
The weld 30 forming the lower edge of the plastics sleeve 28) which forms
the transverse weld in the prior art, can then be the longitudinal weld.
The two welds 29 can be simultaneously produced with the aid of a single
device, either with a welding wheel 7, which produces two welds in juxta-
posed manner) or with a welding die 12, which contains two welding wires.
CA 02262225 1999-02-15
- 9 -
Material welding can take place ultrasonically and not only by a heat
contact process.