Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-1-
Wall module, in particular for vehicle bodies
The invention relatsa to a wall module according to the preamble
of claim 1.
A known wall module of this type (DE 43 O1 763 A1) comprises two
wall panels extending at least substantially parallel to each
other, between whiclh a filler with a heat and sound insulating
function is loosely installed. One of the wall panels is designed
as an extruded section with integral profiling elements within
its surface and consists of a light alloy, preferably aluminium.
The second wall panEal is designed as a plain top panel and con-
nected to supporting webs provided within the surface of the
first wall panel. The blunt side edges are used as welding flanks
for welding the module to adjacent or engaging edge profiles to
be j oined together . The supporting webs are located at a distance
from the side edges, so that strips of the heat insulating mater-
ial can be installed between the outer supporting Webs and the
edge profile as well as between adjacent supporting webs. This
construction has the disadvantage that the supporting webs and
their profiles provide only linear support between the wall pan-
els, while the edge profiles required for the lateral ends have
to be provided and :fitted as separate components.
The invention is based on the problem of providing by suitable
measures a wall module according to the preamble of claim 1 with
a stable structure while facilitating its installation.
This problem is solved by the characteristic features of claim
1. Advantageous emb~~diments are described in further claims.
In an embodiment of a wall module according to the invention, the
lateral termination in the area of the side edges is provided by
end webs which are :integral with and preferably at right angles
to the first wall panel represented by an extruded section and
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-2-
form a single piece: integrated with the outer edge zone to be
sealed. The end webs protect the core material, which is sensit-
ive to transverse loading, from mechanical damage) By matching
their design to local loading conditions, the end webs further
provide the possibility of achieving an optimum relationship
between the necessary rigidity and the weight of the installat-
ion. In the edge zone, the end web takes up the load acting on
the wall panel surface, keeping it away from the core material.
The filler may furtlher be designed as a core material providing
a mechanical support funr_tion, preferably a type of honeycomb
structure, the hollow axes of which lie at least approximately
at right angles to the wall panels, while their end faces are
fully attached to the wall panels, preferably by means of solder-
ing, if metal or mcatallixed honeycombs and/or wall panels are
involved. Other suit=able core materials are foams, in particular
rigid foams. Bonding. is a suitable alternative for soldering. The
outer edge zone of the second wall panel may be located on the
free end of the corresponding end web determining the distance
between the wall panels in accordance with the height of the core
material. The wall panels are thus evenly supported over their
entire surface by the core material and in the edge zone by the
end web. At the same time, the bulging of the panels is prevented
by the core material, which may, for instance, be installed
between the wall panels in. one piece. In this Way, it also serves
as a reinforcing means of low thermal conductivity.
The end webs may additionally be fitted with integral single-
piece retaining welu~s in or adjacent to the plane containing a
wall panel, said regaining webs being usefully prof filed for pos-
itive engagement wii~h diametrically opposed retaining webs or to
retain the welding pool if panels are to be welded to the sur-
rounding structure. The retaining webs on the end webs may be U-
shaped channel webs open 'towards the outside and extending par-
allel to the longitudinal direction of the end web. If the free
outer ends of the web legs are set back relative to the outer
surface of the adj acent wall panel, a corresponding retaining web
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-3-
of another wall module can provide a flush connection with the
adjacent wall panel.. For this purpose, each retaining web on an
end web projects be~~ond the corresponding end web in the plane
of the wall panels .in question and carries a meshing web, said
meshing webs facing each other. In this way, they can be brought
into engagement with the channel webs of a wall panel to be fit-
ted. Where channel 'webs are formed on the side of the end web
facing the core mat~arial, the end web itself may form the leg,
in particular the shortened leg, of the U-shaped channel. While
the free end of the e:nd web can be provided with a supporting web
lying below the surface of the second wall panel, it is set back
towards the associated wall panel by the depth of the channel in
the second embodiment, so that the second wall panel placed on
it is once again flush with the hook-shaped retaining web of any
adj acent component . The component to be connected need not always
be another wall module; it may be another structural component,
such as a window or door frame, a spar, beam or frame element or
the like. In the second embodiment with channel webs set back
into the panel surface, the end web forms a level end face of the
module side flank concerned.
The invention is described in detail below with reference to the
diagrammatic sketch of an embodiment, of which
Figure 1 is a perspective view of the body of a rail vehicle
made up oi: several wall modules;
Figure 2 is a partial cross-section through connected wall mod-
ules;
Figure 3 is a cross.-section through a vehicle body according to
Figure 1 showing the area of a window cutout; and
Figure 4 shows mod:Lf ied retaining means between two wal l mod-
ules.
A vehicle body 1 designed in particular for rail vehicles is made
up of several wall modules 2 of varying dimensions and shapes,
with openings 3, pre:Eerably between two wall modules 2, for wind-
ows, doors etc. being provided. Each plane or arched wall module
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-4-
2 consists of two air least substantially parallel wall panels 4
and 5, between which a core material 6 preferably designed as a
honeycomb with longitudinal axes lying at least approximately at
right angles to the plane of the closely fitting section of the
panel 4 or 5 is located. ~Jther suitable core materials are foam
or other mechanically supporting core materials or structures.
The end faces of the honeycomb core material 6 are permanently
fixed to the facing sides of the wall panels 4, 5 over their ent-
ire surface, for instance by means of hard soldering, bonding or
ultrasonic or laser welding. The method depends on the materials
used for the wall panels 4 and 5 and of the core material. A wall
panel 4 facing the .inside of the vehicle is, for instance. pre-
ferably designed as an extruded section of light alloy, in part-
icular aluminium, and may have superimposed or recessed C-shaped
or T-shaped, for instance ring-shaped, profiling elements 7 for
fitting vehicle components such as seats, luggage racks, linings,
ducts and the like. This first wall panel 4 may, however, also
be a moulded or inje~~tion moulded plastic part, for instance with
a fibre, in particular glass or carbon fibre, reinforcement. The
insides of the wall panels 4, 5, which face each other, are, in
particular in the area of overlap with the core material 6,
plain. The second wall panel 5, too, may be designed as a cor-
responding extruded section. Each wall panel may be provided with
two end webs 8, for instance on parallel side edges, so that end
webs 8 are provided on all four side edges, if one wall panel is
turned by 90~ relative to the other panel.
In order to connect wall panels to each other and, where requir-
ed, to the side-sill of the body substructure or to top chord
roofing members, the: first wall panel 4 only is provided with in-
tegral end webs 8 in the outer edge zones, these extending, in
particular, at right: angles to the adjacent sections of the wall
panels 4, 5. The end webs 8 block the lateral access to the space
holding the core material 6 between the wall panels 4 and 5. The
second, external wall panel 5 is fitted to the free end of the
end web 8. To obtain an adequate overlap, the free end of the end
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-5-
web 8 is provided wii~h a supporting web 9 lying below the surface
of the second wall F~anel 5 extending into the space holding the
core material 6.
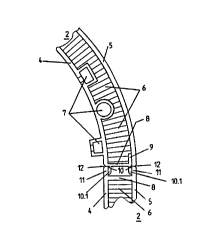
The end webs 8 sealing the enclosed space against the outside are
further provided with integral retaining webs 10 in or adjacent
to the plane containing one of the wall panels 4 or 5, said webs
being profiled for positive engagement with matching retaining
webs 11 on another wall module 2. These retaining webs 10, 11
extend over the length of the side edge of the wall modules 2.
The retaining webs 10 on ane end web 8 are designed as U-shaped
channel webs open towards the outside and extending parallel to
the longitudinal direction of the end web 8. In order to achieve
a flush connection between the meshing retaining webs 11 of an
adjacent wall module 2 and the wall panels 4 and 5 of the adjac-
ent wall module 2, the free outer ends 10.1 of the web legs are
set back relative to the outer surface of the adjacent wall panel
2 or relative to their own wall panels 4 or 5 respectively. The
other retaining web:a 11 on the end web 8 of the adj acent wal l
module 2 also lie in the plane of the wall panels 4, 5, extending
beyond the associated end web towards the adjacent wall panel 2.
Each of these retaining webs 11 has a meshing web 12, said mesh-
ing webs 12 facing each other for engagement with the retaining
webs 10 designed as channel webs. The meshing webs 12 match the
profile of the channel webs, resulting in a connection between
adjacent wall modules 2 which is at least substantially free from
play.
In a modified embodiment of the retaining means according to
Figure 4, the free longitudinal end of the end web 8 also forms
the free, in particular shortened set-back end 10.1 of the re-
taining web 10, which in this case is moulded into the wall panel
4 on the side of they end web 8 which faces the core material 6
and is represented b:~ the supporting web 9 and the adjacent edge
13 of the wall panel 5 lying on said web in the area of the ex-
ternal wall panel 5. In this way, the supporting web 9 also forms
CA 02266710 1999-03-23
-6-
the base of the channel web. The retaining webs 11 on the adjac-
ent wall panel 2 can remain unchanged. This embodiment offers the
advantage that the e:nd web 8 with the leg ends 10.1 provides for
a plain end face of the edge zone of the wall module 2 in quest-
ion, which makes it particularly suitable for edges 8.2 of window
and door cutouts 3.
The retaining webs 10 designed as channel webs and the retaining
webs 11 designed as:hooked webs are preferably located on oppos-
ite side edges of a wall panel 2. This enables one wall panel to
be attached to the other. It is further useful to fix the con-
nection at the retaining means 10, 11 after the assembly of the
wall modules 2, for instance by welding, bonding or other means.
A wall module of this type can be used not only for side walls,
but also for roof ar.~d floor sections, end walls and partitions,
and can be plane or arched (roof section 2.2). With floors 2.1,
it is particularly useful to design at least the lower wall panel
4.1 as an extruded section with downwards-projecting or integral
mounting profiles 7.1 for equipment such as motors, electrical
equipment and the 1 i:ke . Thi s f aci 1 i ty i s due to the f act that the
tension and compression resistant soldering/bonding of the panels
4, 5 with the core material results in a highly stable base plate
for high loads.