Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
1
TRANSCEIVER FOR VIDEO, LANGUAGE AND TEXT INFORMATION
This invention relates to an apparatus for sending and
receiving video messages, voice messages, and text
messages over a telecommunications network.
EP 0 666 693 A1 discloses a videophone system
consisting of a PC workstation, a keyboard or mouse, a
display screen, a~camera, and an interface. In such a
system, an image is transmitted over an ISDN line to
the interface, from which it is transferred over a
suitable line to the PC, where it is displayed on the
associated screen. A camera mounted on the display
unit takes images of the user and passes these images
directly to the interface, which transmits them over
the ISDN line to another user. Such a videophone
system thus combines a videophone facility with a
conventional PC. Disadvantages of such a system are
that in order for the videophone to be ready for
service, the entire PC must be turned on, and that the
cost and complexity of the system are relatively high.
In addition, only an immediate indication of a video
telephone call, i.e., no recording, is possible.
Patent Application JP 3-201649 discloses an automatic
answering video telephone set. Such a videophone
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
2
system serves to answer an incoming call when the user
is absent. A message so received is recorded, and the
calling party is simultaneously informed that this
message is only being recorded. Such a system
requires, however, that both the calling party and the
called party have equipment which is ready to receive
such messages.
Accordingly, it-is an object of the invention to
provide an apparatus for sending and receiving video
messages which is composed of simple means and is
additionally capable of processing further messages of
other formats. Another object of the invention is to
improve the apparatus in such a way that the messages
can be recorded even if the called party does not take
them personally.
According to the invention, this is attained by the
teaching of claim 1.
One advantage of the invention is that on such an
apparatus for sending and receiving video messages, it
is also possible to display other messages, such as
messages coming from the Internet. Also, different
image standards can be displayed. Thus, such a system
is capable of displaying not only images of one
standard, but also images of a further standard.
Another advantage is that in the automatic answering
video telephone mode, a received image is stored in
one data format and can be outputted via the monitor
in any other data format.
Further advantageous aspects of the invention are
defined in claims 2 to 10.
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
3
A particular advantage results from the embodiment
claimed in claim 4, according to which information can
be added to a stored video message. This enables a
user to determine when a message was recorded and how
long it lasts.¢
According to claim 5, it is possible to inform a user
at a predetermined location about the reception of a
video message at his apparatus, which is located at
his home place, for example. He is thus enabled to
retrieve the video message at any time.
According to a further advantageous aspect of the
invention, which is claimed in claim 8, a video
message can be edited, i.e., provided with comments,
and forwarded to further users. These comments can be
added in the form of a text message or an additional
video message.
According to claim 9, a conventional television set
can be connected for displaying the video message.
The invention will become more apparent from the
following description of an embodiment when taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawing, whose
single figure is a schematic block diagram of an
apparatus for receiving and sending video messages,
voice messages, and text messages.
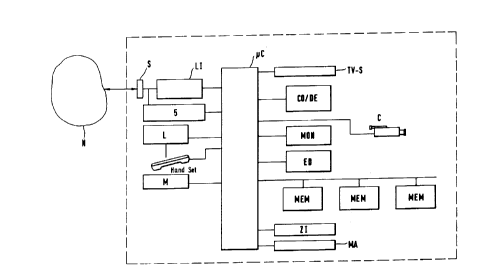
An apparatus for receiving and sending video messages,
voice messages, and text messages comprises an
interface S for interfacing the apparatus to a
telecommunications network N. Such a
telecommunications network N is the ISDN network, for
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
4
example. The interface S can be a standard interface.
It is also connected to a network interface LI for
adapting the apparatus to messages sent and received
at different transmission rates. This network
interface contains, for example, a modem which enables
the apparatus to process different data transfer
rates, namely up to several kb/s. Such a modem is
capable, for example, of processing data transfer
rates as occur in the Internet. In a further
development, this modem may be implemented as a
digital interface according to the ISDN standard.
Connected to the interface S and the network interface
LI is a power supply 5 for the apparatus, for example
a battery, so that the apparatus for receiving and
sending video messages is always ready for service.
The apparatus may further comprise a camera C for
picking up a video message. This camera C may be
integrated with the apparatus, but it may also be
connectable to the apparatus via a socket. The
apparatus for receiving and sending video messages
further includes a display screen MON for displaying a
video message and a text message. Furthermore, the
apparatus comprises a microphone M and a loudspeaker L
for picking up and reproducing a voice message or
speech associated with a video or text message. The
microphone M and the loudspeaker L may be combined in
a handset.
To store an incoming video message for later playback,
storage means MEM are provided in the apparatus for
storing the received video message. Also provided are
means ZI for adding information to the stored video
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
message. Such information may be, for example, the
time, the date, the length of the message, and further
information.
The apparatus further includes means MA for storing
the current location of a recipient. The recipient s
current location is stored in these means MA as a
number or as a list from which the number is selected,
so that upon receipt of a video message, a voice or
text message can be sent to the recipient s current
location to notify him of the presence of the video
message.
A recipient is thus kept informed as to whether a
message is waiting for him.
The apparatus further comprises a coder/decoder CODE
for converting an H.261-coded image to an MPEG-coded
image and vice versa. This coder/decoder DO/DE is
generally designed to convert a coded image of a first
standard to a coded image of a further standard.
Conversion of the H.320 standard to an MPEG standard
or similar standards is also possible. The following
sequence is conceivable: An H.261-coded image is
present; it may be present in two different formats.
This image is fed to a decoder, which transforms the
image back to the image plane. The decoded image is
passed to an MPEG encoder. MPEG covers a multitude of
image formats. Such a sequence is also possible in the
opposite direction, in which case attention must be
paid to the fact that in MPEG the frame frequency is
predefined.
In this connection it proves advantageous that a
CA 02267341 1999-03-24
6
receiving apparatus need not necessarily be compatible
with a sending apparatus in terms of image format.
The apparatus further comprises editing means ED for
editing a video message. This may include attaching
comments to the video message in the form of a text
message. Portions of the message may also be cut out
and then forwarded.
Since the means for converting an image of a first
standard to another standard also permit reproduction
of the image on a television set, the apparatus
includes an interface TV-S for connecting a television
set for reproducing the video message.
It is also important in the present invention that the
network interface LI adapts the apparatus to Internet-
type text messages and to voice messages from the ISDN
network. The network interface LI thus enables the
apparatus both to send and receive text messages over
the Internet and to send voice messages over the ISDN
network.
The following use of the apparatus for receiving and
sending video messages, voice messages, and text
messages is conceivable: The apparatus receives a
video message, stores it, and registers the presence
of a video message. A recipient is notified of the
presence of the message by sending him an E-mail over
the Internet. For the future is conceivable that the
video message can be forwarded to a recipient by video
transmission over the Internet.