Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
1
DEVICE AND METHOD FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN A DATA NETWORK
AND A TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a communication node between
data networks and public telecommunications networks.
STATE OF THE ART
Such a communication node between data and telecommunications
networks is disclosed in, for example, WO 94/24803. This
document describes such a node in a multimedia communication
system. The object of the node is to enable communication
between users using different types of terminals, such as
Common telephones, personal computers and workstations.
The published international patent application WO 87/078001
describes a node constituting an electronic mailbox. The object
is for the mailbox to be able to receive and store electronic
mail sent fram different types of sources, such as telephones,
2-0 computers and fax machines. Messages may have been translated
before they reach the mailbox. The electronic letters may
subsequently be retrieved from different types of terminals.
i
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
2
Some different types of network architecture for establishing a
link between data networks and telecommunications networks are
described comprehensively in a report of a final thesis at
Lulea Institute of Technology: "Functional Distribution between
Co-operating Networks", Bodin and Andreasson. The report
briefly describes the design of a node between data networks
and telecommunications networks, used to demonstrate the
ordering of telephony services from a computer. A user is
enabled to order telephony services presented on the computer
screen via pages in HTML format. The node consists of a
computer with an off-the-shelf software platform.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention attacks the problem of simplifying the
use of telecommunications services for a user by offering a
solution with which such telecommunications services in public
and private telecommunications networks may be made accessible
through a computer. In particular this applies to the ordering
from a computer of the set-up of a telecommunications
connection between an A subscriber and a B subscriber.
The telecommunications services of today are becoming more and
more advanced. The new services are perceived as difficult to
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
3
use since conventional telephones are only provided with a
primitive keypad allowing the user to enter commands or provide
data. The telephone also has very limited possibilities for
providing visual information.
With the new services, the need also arises to be able to adapt
some of the services according to the user's desires. Thus the
need for several alternative solutions for exchanging
information with the user is further increased.
Another problem is avoiding having to equip the user's computer
with special software to enable the ordering of
telecommunications services from it. It should be sufficient
for the computer to be provided with prior art software for
communication, and said software should also be useful for
other purposes than for ordering telephony services.
A further problem is that the user should have access to
personal stored information concerning telecommunications
services even if he/she moves geographically and changes
computer and telephone equipment.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
4
A purpose of the present invention is thus to enable a user to
order telecommunications services, especially connection of
calls, by means of a computer, in a way that is simple for the
user and to provide subscriber related data that can be used
for this purpose, and to give access to these
telecommunications services and this user related data even if
the user moves geographically and to another telephone and/or
computer.
A service node is provided, constituting a link between the
data network and the telecommunications network. The service
node has an interface to a telephone exchange through which
public and private telecommunications networks can be accessed.
The service node also has a WWW interface through which a
communication connection to a computer can be established
through a data network using the HTTP protocol. The computer is
equipped with a WWW browser and receives data in HTML format
from the service node. The data is presented on a screen
connected to the computer, in the form of pages comprising,
among other things, active fields. A-'user requests a service
using said active fields by means of the computer. The service
node receives the request for a telephony service or
programming of subscriber related data from the computer in
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
order for the data to be registered by the service node. The
service node performs the requested service and sends the
result to the computer in a new HTML page, which is presented
to the user on the screen.
5
The service node is comprised of a web server, a personal
assistant and a service node selector. The personal assistant
constitutes a control and supervision part of the service node
and communicates both with the service node selector and the
web server.
The personal assistant handles various subscriber services.
The personal assistant controls the service node selector,
which is connected to telecommunications and mobile
telecommunications networks.
The personal assistant can, by means of the service node
selector, make outgoing calls, receive calls and interconnect
incoming and outgoing calls.
The personal assistant stores information associated with a
user. The user can retrieve and store personal information by
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 6 PCT/SE97/01719
means of a computer telecommunications terminal of his/her
choice or.
A user can log in to the service node from a computer with a
WWW browser. The web server handles the communication with the
computer by transmitting WW4J pages in the mark-up language
HTML, said pages being presented on the user's computer. The
user may enter commands using active fields in the presented
HTML page. The commands are transmitted to the web server using
the HTTP protocol. The commands are forwarded by the web server
to the personal assistant.
The personal assistant makes sure the command is executed. The
result is then transmitted to the web server, which generates a
new HTML page presenting the result of the command to the user.
The invention makes it possible to simplify the user control of
telephony services by means of a computer.
The invention may be utilized by several users as the protocol
used for communication with the service node is found in most
network connected computers. Programs such as WWW browsers are
widely deployed in network connected computers.
.,. .
CA 02270046 2004-10-08
7
The invention enables the storage of data associated with a
user in a central node. This data is accessible to the user and
may be changed even if the user moves to a different location
and uses different terminals. The stored data may be used when
a telephone connection with a B subscriber is being set up.
Accordingly, in one aspect, the invention provides a
service node constituting a link between a computer network,
in which the HTTP protocol is used, and at least one
telecommunications network. The service node is used to
request a telecommunications service from an A subscriber's
computer through the data network. The service node
comprises: a web server for providing for an A subscriber to
authenticate for communication with said computer through the
computer network using the HTTP protocol. A service node
selector is connected to at least one telecommunications
network to set up two separate connections in the
telecommunications network, one of which connects a
telecommunications terminal belonging to the A subscriber and
the other connecting a telecommunications terminal belonging
to a B subscriber, in order to subsequently interconnect the
two connections. A personal assistant device has a
communication connection to the service node selector, said
personal assistant constituting the unit handling the request
for a communication service and ensuring it is performed by
controlling the service node selector at least partly in
dependence of pre-programmed user data.
CA 02270046 2004-10-08
7a
The invention will in the following be described in more detail
by way of preferred embodiments and with reference to the
enclosed drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. I shows a protocol stack known per se, used in the
Internet
Fig. 2 shows a schematic block diagram of units comprised in
the communication system of which the invention is part.
Figures 3, 4, 5 are sequence diagram of the signalling between
the parts of the system.
Figure 6 is a flow chart of the method for connection.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
8
DESCRIPTION OF THE ANNEX
The annex contains the complete syntax of the application
protocol which constitutes part of the invention.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The Internet is an important precondition for the applicability
of the present invention and will therefore be described
briefly here. The Internet in this context means any data
network using a protocol stack having an Internet Protocol (IP)
layer. Upon the IP another protocol, the Transmission Control
Protocol (TCP) is used. These two protocol layers are shown in
Figure 1. The IP protocol may be used in different types of
physical data networks, hence Figure 1 does not show the
protocols below the IP layer. Also, different protocols for
different types of applications may be added on top of the TCP
layer. Figure 1 shows the HTTP protocol on top of the TCP,
since this protocol is used in the application of the present
invention.
On the HTTP protocol data can be transferred in the mark-up
language Hyper Text Meta Language (HTML). In a computer PC, for
example, a personal computer or a mainframe computer with user
terminals, with WWW browser software, for example Netscape
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
9
Navigator or Mosaic, received data is presented according to
its HTML format on the screen in the form of pages comprising
pictures, graphics and text. The presented HTML pages also
comprise so called active fields by means of which the users
can request different types of services. The active fields are
made up of buttons, fields for entering text, and hypertext
links. The user may, for example using a mouse connected to the
computer, move a cursor over the page to place it on a button
or a hyper text link and then press a mouse button. This will
in the following be referred to as clicking a button or a hyper
text link, respectively. In this way a command is transferred
to another computer, a so called web server connected to the
data network, on the HTTP protocol. The command may cause a new
HTML page to be transmitted to the user's computer PC where it
is presented, or a search for information to be started in a
database. The result of said search will be presented to the
user on a new HTML page.
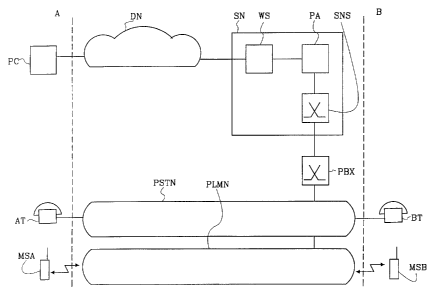
Figure 2 is an overview of the communication system in which
the method according to the invention is applied. The apparatus
according to the invention is comprised of a service node SN.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 1 p PCT/SE97/01719
The service node SN has a WWW interface for communication in
data networks using the HTTP protocol. The service node SN has
another interface towards a telephone exchange, which is shown
in Figure 2 as a private branch exchange PBX, but may also be
another type of exchange. Through the exchange PBX connections
may be established in public or private telecommunications
networks. It is also possible to connect the service node SN
directly to a telecommunications network without an exchange
therebetween. In the description below only the case in which
the communication with a telecommunications network is set up
through an exchange is shown. In Figure 2 two public
telecommunications networks are shown: a conventional Public
Services Telephone Network (PSTN) and a cellular mobile
telecommunications network PLMN. It is also possible to connect
to other types of telecommunications networks than the ones
shown in Figure 2, such as Integrated Services Digital Network
(ISDN) or private telecommunications networks. To each of the
telecommunications networks a number of telephones, mobile
telephones, telefaxes and other types of telecommunications
terminal are connected. Figure 2 only shows one telephone AT
and one mobile telephone MSA belonging to an A subscriber, and
a telephone BT and a mobile telephone MSB belonging to a B
subscriber.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
11
The A subscriber also has access to a computer PC. The computer
PC may be a personal computer with units for user communication
such as a screen, a mouse and a keyboard, or a mainframe
computer having a user terminal. The computer is provided with
a WWW browser and connected to a data network in which the
TCP/IP and HTTP protocols are used, in a conventional way.
Figure 2 shows this data network as a cloud referenced as DN.
The service node SN is comprised of three parts: a web server
WS, a personal assistant PA and a service node selector SNS.
The web server handles the communication with the computer PC
by generating HTML pages, which are then transferred to the
computer through the data network DN. The user requests a
service using the above described active fields in these pages.
When the A subscriber has entered text or clicked a button or a
hypertext link, a command specifying the requested service is
sent from the computer PC to the web server WS, using the HTTP
protocol. The web server transfers the command on to the
personal assistant PA. The web server WS and the personal
assistant communicate by means of an application protocol. The
application protocol uses TCP/IP for transport and thus
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 12 PCT/SE97/01719
constitutes a protocol layer on top of TCP/IP. The protocol
implies that commands and other information being exchanged
between different computers use an established syntax in order
to be interpreted in the same way in the different computers.
This means that computers having different operating systems
and software written in different programming languages, can
communicate with each other. In this way the web server WS and
the personal assistant PA, both constituting parts of the
present service node, may be computers from different vendors.
The complete syntax of the application protocol is described in
the annex.
The personal assistant PA is the control unit of the service
node. The personal assistant handles the command transmitted
from the computer PC and makes sure it is executed. If the
command from the computer PC, received by the personal
assistant PA implies that a service is to be performed in one
of the telecommunications networks PSTN, PLMN, the personal
assistant PA orders the service node selector SNS to set up a
connection with the appropriate network. The personal assistant
then performs the steps required to perform the requested
service. The command from the computer PC received by the
personal assistant PA may also imply that the personal
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
.13
assistant PA is to provide or store information, for example
programming of user data. When the personal assistant PA has
performed, or failed in performing, a requested service, the
. personal assistant PA transmits the result to the web server,
which enters the result into an HTML page and forwards it to
the computer PC, which presents it to the A subscriber.
The service node selector SNS is able to set up connections to
the telecommunications networks PSTN, PLMN, upon orders from
the personal assistant PA. The service node selector is also
able to connect to existing connections, upon orders from the
personal assistant. As described below, this function will be
utilized in the present method.
The commands exchanged between the computer PC, the telephone
AT of the A subscriber, the web server WS of the service node,
the personal assistant PA of the service node, the service node
selector SNS of the service node, the private branch exchange
PBX, the public network PSTN and the telephone BT of the B
subscriber, when a service is requested by the A subscriber,
are shown in Figures 3, 4 and 5.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
~.4
Figure 3 shows the login procedure to the service node SN. The
user has first retrieved a presentation page from the service
node SN, using his computer PC. In this page, the user enters
his identity and password in fields intended for this
information. This data is then transmitted to the web server WS
with a login request. The request is approved after the web
server has checked and verified the identity and password by a
query to the personal assistant PA. The web server WS then
transmits a new page to the computer PC comprising an index of
available services and data, a so called index page.
In the obtained index page, the user clicks on a hypertext link
to request user programming in the personal assistant PA.
Programming of user data involves the A subscriber changing or
adding information related to the user, which is stored in the
personal assistant PA. Programming of user data is necessary
for the personal assistant to know what telecommunications
terminal the A subscriber intends to use. If the A subscriber
wishes to change the telecommunications terminal, this is done
by reprogramming the user data in the personal assistant. The A
subscriber can also register the names and identities of other
telecommunications subscribers, with photos if desired, to
facilitate the ordering of telephone services. This data can
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98119445 PCT/SE97/01719
thus constitute a personal telephone directory for the A
subscriber. It is also possible to register telecommunications
commands in the personal assistant to facilitate their use.
Names, identities and other information registered can be used
5 as hypertext links or active fields, when presented to the user
on an HTML page, to facilitate making calls or using the data
in another way.
Figure 4 shows signal sequences in user programming when the A
10 subscriber changes his own telephone AT. The request is
transferred through the data network DN to the web server WS
which in turns forwards the request to the personal assistant
PA. The personal assistant, in which the user data is stored,
transmits a set of parameters to the web server WS. The web
15 server enters the parameters into an HTML page and transmits
the page to the computer PC. In the present example the A
subscriber wishes to change his telephone. If the identity of
the new telephone is already stored in the personal assistant
PA and registered on the parameter page, the A subscriber can
enter a new telephone by, for example, clicking on the
hypertext link of the new telephone. If the telephone to which
the A subscriber wishes to change is not registered, the
identity of the new telephone, the A number, is entered in a
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98!19445 16 PCT/SE97/01719
field intended for this information on the parameter page. The
request for a new A number is received by the web server WS,
which forwards the request to the personal assistant PA. The
personal assistant registers the new A number and then
transmits a new set of data to the web server. The web server
WS enters this data in a new parameter page in HTML format
which is transmitted to the computer PC. The telephone to which
the service node SN will connect the A subscriber's calls is
then presented to the A subscriber on the screen of the
computer PC.
The A subscriber can retrieve the index page stored in the
computer PC after login. The user requests the set-up of a
telephone connection between his own telephone AT and a B
subscriber's telephone, for example by typing in the B number
in a field on the index page intended for this information. It
is, however, easier for the user if the B number is already
stored in the above described personal telephone directory. The
telephone directory may either have come with the index page or
be retrieved to the computer PC in HTML format from the
personal assistant PA through the web server WS in the same way
as the data page. From the telephone directory the A subscriber
requests a call by, for example, on his computer, clicking on a
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
17
hypertext link with the B subscriber's name. Figure 6 shows the
procedure when a call is made. In the first block 1 the A
subscriber requests the B subscriber to be called, from his
computer PC, in any of the above described ways. Figure 5 shows
the signalling sequence when a call is made. The request to
call the B subscriber is transferred from the computer PC to
the web server WS, which forwards the request to the personal
assistant PA, which is also shown in step 2 in Figure 6.
The personal assistant PA orders the service node selector SNS
to call the A subscriber's telephone AT. The service node
selector calls the telephone AT through the exchange PBX and
the public network PSTN, corresponding to step 3 in Figure 6.
When the A subscriber has answered, by lifting the hook of the
telephone AT, step 4, the connection is set up between the
personal assistant and the A subscriber through the public
telecommunications network PSTN, the exchange PBX and the
service node selector SNS. The personal assistant PA then
orders the service node selector to call the B subscriber's
telephone BT. The service node selector SNS sets up a
connection to the B subscriber's telephone in the same way as
with AT, as represented by step 5. When the B subscriber has
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 PCT/SE97/01719
1B
answered, in step 6, the personal assistant PA orders the
service node selector SNS to connect the two connections. In
this way a connection between the two telephones AT and BT is
established, see step 7 in Figure 6.
The procedure would have been interrupted after a certain
period of time if one of the parties had not answered, see
steps 4 and 6. The personal assistant PA transfers the result
of the set-up, or the failed set-up, to the web server WS,
which transfers it, in HTML format, to the computer PC, where
it is presented to the A subscriber. This is shown in the final
step 8 in Figure 6.
The method for connection set-up described above can also take
place in modified ways. The set-up of connections for calling
the A subscriber and the B subscriber, respectively, can take
place in a different order than the one described above, and
independently of whether or not the other party has answered
the call. Interconnection of the two connections can be made
even if one of the parties has not answered the call.
For example, in a modified embodiment, the connection between
the service node and a B subscriber may be established
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 19 PCT/SE97/01719
independently of whether or not the call made to the A
subscriber's telephone was answered.
The method can also be modified to let the B subscriber be
called before the A subscriber.
In another modified embodiment the connection to the A
subscriber and the connection on which the B subscriber's
telephone is being called, are interconnected.
A further modification, for the case when the B subscriber
answers the call first, consists of the service node
interconnecting the connection to the B subscriber and the
connection on which the A subscriber's telephone is being
called. For the cases when the B subscriber is the first to
answer the call, the service node provides a spoken message
that a call is being made from another subscriber.
The service node SN also handles incoming connections to the A
subscriber if call forwarding has been set up from the called
identity to the service node SN.
CA 02270046 1999-04-27
WO 98/19445 2 ~ PCT/SE97101719
The A subscriber can, in the desired order and after logging in
to the service node SN, reprogram user related data or request
a telecommunications service, such as call set-up. Other
telecommunications services handled by the service node SN are,
for example, electronic mail, transmission or reception of
telefax, whereby the service node functions as a mailbox for e-
mail, fax and voice messages.