Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98I19478 PCT/SE97/01811
A PRINTING AND SCANNING DEVICE FOR INTERNET AND FACSIMILE
CELLULAR SERVICES
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a mobile printing and scanning device. The
device is used for receiving and transmitting information via a cellular
network
and for scanning information from a paper and printing information on a
paper. The device can also be used for providing images scanned by an
electronic image generator.
PRIOR ART AND BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
In recent years there has been a strong increase in the demand for new
services using the cellular telephone networks being built, and which have
expanded enormously. Such demands includes the possibility of more
advanced hard-copying services.
The services today include the possibility of transmitting and receiving data
in
a mobile personal computer via a cellular network. The personal computer
can then also be equipped with a printer, integrated with the computer or
separate therefrom. Other hard-copying services commercially available is a
mobile hard-copy facsimile apparatus sold under the name "FX1 ", which is
developed and manufactured by System innovation. The facsimile apparatus
is designed for transmission via a cellular telephone network.
Thus, in the case where the primary desire is to obtain different kinds of
communications via a cellular network, the solutions available today are not
very well suited. For example, a laptop computer combined with a printer and
scanners is today quite expensive. Furthermore, such a combination is not
very practical to bring along due to its weight and size. Also, the standby
time
for such a combination is very limited due to the power consumption involved.
SUMMARY
It is an object of the present invention to provide a printing and / or
scanning
device, which can communicate and exchange information with other units via
a cellular network, and which can provide a number of different advanced
hardcopying services at a low cost.
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98/19478
PCT/SE97/01811
It is a further object of the present invention to provide a device, which
overcomes all the problems outlined above when a user wants to
communicate via a cellular network.
It is yet a further object of the invention to provide a small and low-cost
printing device which can access and search a global computer network.
These objects and others are obtained with a printing device comprising in
one single unit a printer and / or a scanner. The device also comprises a
microprocessor for handling the information flow inside the device, and a
searching means, such as a browser, whereby the printing device can access
and connect to an address in a global computer network. The device can then
be used for communication via a cellular network with other units only using
as man-machine intertace the printer and a keypad.
Possibly also a loudspeaker and light indication signals can be used for
providing a user with information. However, no LCD display is required, which
is a major advantage since this both saves space and costs.
The use of the device according to the invention provides a large number of
advantages in comparison to existing solutions according to the prior art.
Thus, by using a device as described herein, a large number of
communication services can be provided and utilised. Such services
includes: downloading and printout of any information available in a global
computer network such as the world wide web (WWW)) reception and
transmission of facsimiles, printout of electronic mail received in the user's
mailbox, and setting up one's own server which then can be accessed by a
third party via a cellular network, etc.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
The present invention will now be described in more detail by way of non-
limiting embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings) in
which:
- Fig. 1 is a schematic block diagram of a printing and scanning device.
- Fig. 2 shows the exterior of a preferred embodiment of the device in fig.1
interacting with a PC and a cellular telephone.
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98/19478 3 PC'T/SE97/01811
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
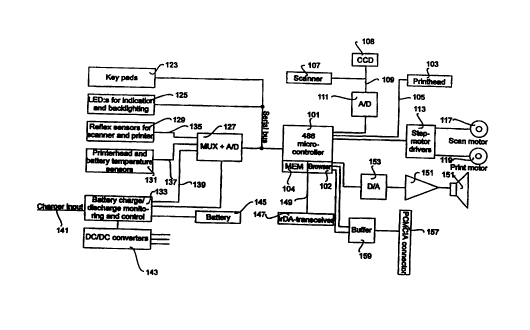
In fig. 1, a schematic block diagram of a printing device is shown. Thus, the
figure shows a control unit or microprocessor 101, in this example the
processor is a microprocessor compatible with a conventional 486-processor
manufactured by Intel Corporation. The processor 101 is connected to a
printing head 103 used for all printing operations initiated by the processor
101, via a tine 105. The microprocessor 101 is also connected to a scanner
107, which is used for scanning any kind of document to be transmitted as a
facsimile or stored in a memory 104 associated with the processor 101, via a
line 109 and a AID converter 111.
Furthermore, the processor 101 also controls step motors used for the printer
103 and scanner 107. This is pertormed by controlling the step motor drives
113 via the line 115. The step motor drives 113 then drive the scanner motor
and printer motor 117 and 119, respectively.
Further, the microprocessor 101 is connected to a serial bus 121. The serial
bus is also connected to a keypad 123, which is used for entering commands
to the microprocessor 101, light emitting diodes (LEDs) 125, which can be
used by the device for signalling different states of operation to a user, and
a
combined multiplexer and AID converter 127. The combined multiptexer and
AID converter is connected to reflex sensors 129 for the scanner and printer,
respectively) to printer head and battery temperature sensors 131, and to a
battery charge/discharge monitor and control unit 133, via lines 135, 137 and
139, respectively.
The unit 133 is used for monitoring the batteries and in response to the
monitor output signal obtained) for outputting a control signal, which is used
for control of the printing speed of the printer 103. Thus, by adapting the
printing speed to the battery capacity available, the printout quality can be
maintained as the batteries are discharged or exposed for changes in
temperature, which in turn will affect the output capacity from the battery.
The maintaining of quality is obtained by controlling the number of dots being
printed at the same time in such a manner that the state of charge of the
battery does not affect the printout quality. Also, by monitoring the battery
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98/19478 4 PCT/SE97J01811
charge, a light or sound signal is issued , or a message printout can be
initiated when a recharge of the batteries becomes necessary.
To the unit 133 a charger input 141, a DC/DC converter unit 143 and a
battery 145 are connected.
Moreover, the microprocessor 101 is connected to an IrDA transceiver 147
via a line 149, to a loud speaker 151 via a D/A converter 153 and an amplifier
155, and to a PCMCIA connector or PC-card slot 157 via a bi-directional
buffer 159.
The mobile printing device as shown in fig. 1 can perform a multitude of
different communication tasks. Thus, via the interface provided by the IrDA
transceiver, information can be received from or transmitted to another unit
such as a cellular telephone or a personal computer (PC) without having to
use any connection cables. In the case when a IrDA connection is not
possible or practised, a PC-card can instead be used. The PC-card is
inserted in the PCMCIA connector or PC-card slot 157, and allows for
communication via traditional telephone and LAN networks, such as for
example the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Thus, by entering a code via the key pad 123 of the device corresponding to
a specific address in a global computer network, such as the World Wide
Web (WWW), which address then preferably is printed on paper by the
printer head 103, and pressing an enter key, the information available at that
address or location in the WWW is transmitted to the printer device via a
cellular telephone and a cellular network, and printed out on paper. For this
purpose, i.e. searching a global computer network, the printing device is
equipped with a browser 102 located inside the controller 101.
In a similar manner an e-mailbox can be contacted and the electronic mail
received by the mailbox can be transmitted to the printer device and printed
directly on paper.
When the printed page is a page written in HTML code or a similar code
wherein links to other addresses in the WWW are indicated and included in
the page) each such link in that particular page is given an individual code
or
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98/19478 5 PCT/SE97/01811
number by the browser 102. The code or number is then preferably printed
both in association to the link on the page and/or as a footnote at the bottom
of the page printed by the printer, where also the complete address can be
printed.
If a user then wants to connect to any of the links indicated on the printed
page, he/she only needs to enter the code or number associated with that
particular link in order for the browser 102 inside the printing device to
look
up and connect to that address .
In the case when the links on the printed page are associated with a clickable
image, the numerical references to the links can be generated in two different
manners. As a first alternative each part of the clickable image can be
associated with a particular code which is printed next to that part of the
clickable image, i.e. basically the same procedure as described above, and
the corresponding address is printed as a footnote at the bottom of the page.
In another embodiment, a coordinate system is associated with the clickable
image, and by entering the coordinates corresponding to a link associated
with a particular part of the clickable image, that link is chosen and the
browser connects to the address given by that link.
Furthermore, the printing device can be used as a facsimile apparatus. In
such a case, the papers) which are desired to be transmitted are scanned by
the scanner 107 and the analogue signal output by the scanner is converted
to a digital bitstream in the AID converter 111. The digital signal is then
preferably transmitted via the IrDA transceiver 147 and a cellular network via
a cellular telephone interacting with the device via the IrDA interface 147.
The device is of course also capable of receiving facsimiles via the IrDA
interface 147. The received facsimiles are printed out directly on paper by
the
printer 103.
Also, the printing device can be used as a combined mobile printer/scanner,
interacting with a PC. The printer device can then provide all conventional
services provided by a conventional printer as well as by a conventional
scanner.
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98I19478
PCT/SE97/01811
In another preferred embodiment the micro processor 101 is also provided
with a memory 104 large enough for storing a number of scanned pages
scanned by the scanner or captured by the CCD or digital camera. In such an
embodiment the device can also act as a server to which other units can
connect and read and/or download the information stored in the memory. The
scanned or captured images can then be stored as HTML pages which can
be accessed via the WWW.
Also in yet another preferred embodiment, the scanner 107 is exchanged or
supplemented with an electronic image generator, such as a charge-coupled
device 108 (CCD) or a digital camera, whereby the image scanned by the
scanner does not need to be printed on paper, but instead can be an image
captured by the CCD 108.
In order to provide a user with more information indication LEDs 125 can as
mentioned above be lit by the processor 101. The printer device can also
output sound via the loud speaker 151.
In fig. 2, the exterior of a device housing in one single unit all the
components
and parts described above in conjunction with fig. 1, is shown at 201. The
figure also shows a cellular telephone 203 and a personal computer (PC)
205. The device 201 can communicate with the cellular telephone 201 and
the PC 205, via the IrDA intertaces shown at 207, 209 and 211. The
information received by the device is printed on paper by the printer 213, and
information can be transmitted or collected by a user by using the keypad 215
and the scanner 217 in a manner as described above in conjunction with
fig.1.
Hence, a device as described herein, provides a user with a very efficient and
powerful tool when he or she has to communicate. The device as described is
very small and has a low weight. The manufacturing cost will be very low
compared to other solutions providing similar services, such as a PC having a
printer and scanner connected thereto. This is primarily due to that no
graphical interface is required.
Furthermore, it is capable of unattended receipt of messages without any
power waste. The limiting factor in terms of standby time being determined by
CA 02270479 1999-04-29
WO 98I19478 ~ PCT/SE97/01811
the standby time for the mobile phone used for connecting to the cellular
network. The device is also mechanically rugged and robust, and involves
few moving parts and external connections. It is therefore suitable for
operations in a troublesome environment, such as low temperatures and high
vibrations.
Finally) the device has a simple user intertace only consisting of, in the
simplest embodiment, a keypad and a paper printout. Also, the device has a
low power consumption resulting in long recharge intervals.