Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
NOVEL FIRE STOP AND ITS USE
The present invention relates to devices for use in
making fire stops in buildings, and to a method of using the
devices.
Partitions in general, including walls, floors and
ceilings in buildings, may have holes in them for passage of
items such as vent pipes, drain pipes, plumbing pipes, gas
pipes, electrical wiring, conduits to contain electrical
telephone and computer wiring, optical fibre, air conditioning
ducts, heating ducts and the like. One hole may accommodate
one or several such items. Annular spaces between the hole and
the item passing through the hole create passages through which
heat and fire can spread, especially if a pipe collapses or
burns under the influence of heat. It is therefore desired to
provide means for filling or blocking these spaces to prevent
the spread of heat and fire through the holes. There are
devices and materials known for this purpose. These have the
disadvantages as they are cumbersome to apply, require tools
and skills for their installation, and may require use of metal
frames and screws or grout or caulking for their permanent
installation. They may require that a seal to prevent passage
of heat and fire is formed at the moment of installation. Such
devices and materials make re-entry to repair or to retro-fit
piping and cabling systems difficult. Furthermore, in many
cases subsequent visual inspection does not readily reveal
whether the device or material has been properly installed or
not.
It is an obJect of the present invention to alleviate
some or all of the above-mentioned disadvantages.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides a device that
comprises a material that intumesces on exposure to heat, a
patch of an adhesive connected to one surface of the
intumescent material and a liner that covers the adhesive and
is readily detachable from the adhesive by means of a pull, to
expose the adhesive.
- 1 -
CA 02271229 2007-01-24
60557-6097
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a firestop device comprising:
(a) intumescent material; (b) a container surrounding the
intumescent material; (c) adhesive arranged on the
container; and (d) a liner including a first portion
covering the adhesive, a second portion arranged in at least
partially overlapping relation with the liner first portion,
and a tab portion arranged adjacent the liner second
portion, whereby the tab can be pulled to release the liner
first portion from the adhesive to expose at least a portion
of the adhesive to adhesively bond the device at a desired
location.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided an elongate flexible firestop
device, comprising: (a) intumescent material; (b) a
container surrounding the intumescent material; (c) adhesive
arranged on the container; and (d) a liner including a first
portion covering the adhesive, a second portion arranged in
at least partially overlapping relation with the liner first
portion, and a tab portion arranged adjacent the liner
second portion, whereby the tab can be pulled to release the
liner first portion from the adhesive to expose at least a
portion of the adhesive to adhesively bond the device at a
desired location, wherein the device includes first and
second ends having means for holding the ends of the device
together, thereby to form an annulus.
-la-
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
In another aspect the invention provides a method of
providing a fire stop In a space between a hole in a partition
and an item passing through the hole, which method comprises
wrapping around the item a device as defined above, sliding the
device along the item into the hole and pulling on the pull tab
to expose adhesive and anchor the device permanently on the
item by means of the adhesive.
Description of Preferred Embodiments of the Invention
In the description of preferred embodiments that
follows, for purposes of illustration reference is made to a
pipe passing through a hole. It should be appreciated that the
pipe is merely representative of items that may pass through a
hole, and examples of such items are mentioned above.
When the device is in place in a hole and heat from
fire is encountered, the intumescent material swells markedly,
thereby blocking the hole and preventing passage of heat,
flame, smoke and the like. Suitable intumescent materials
include flexible fire barrier felts that are disclosed in
United States Patent No. 5,830,319, the disclosure of which is
incorporated by reference. The felt comprises an organic
polymeric binder, organic fibres having pendant hydroxyl
groups, for example cellulosic fibres, a heat absorbing
compound that is suitably an intumescent compound, for example
intercalated graphite, mica, perlite, vermiculite, hydrated
sodium silicate, and a phosphorus compound.
One such intumescent material that is suitable for
use in the present invention is a flexible fire barrier felt
that is available from 3M under the trade-mark Interam Ultra
GS. It is available in strips about 2 inches wide and about 'A
inch thick, in any length. When exposed to temperatures of at
least 300 F (149 C) it intumesces rapidly, expanding up to
approximately 25 times its original volume. It turns into a
hard char that impedes or prevents passage of heat, fire, smoke
and gases. The material exerts substantial pressures on items
in the hole so that it compresses piping and wiring materials,
thus further effecting a seal of the hole against fire, heat,
smoke and the like. It also releases chemically bound water
- 2 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
that helps to slow temperature rise.
In one simple embodiment of the invention, suitable
for use with small holes and small pipes, the patch of adhesive
is present directly on a surface of a strip of an intumescent
fire barrier felt. The liner is removed from the patch of
adhesive, the felt is flexed to permit it to be pushed into the
hole and the adhesive attaches either to the exterior surface
of the pipe or the interior surface of the hole, where it is
held permanently in place. In another simple embodiment the
intumescent felt strip is contained in a coating of, for
example, a plastic sheet, woven fabric or, preferably, aluminum
foil and the adhesive patch is on the coating. The intumescent
felt material and the adhesive are operatively connected to
each other via the coating, although not in direct physical
contact. The coating contains the intumescent material when it
first encounters heat and intumesces, so that the expanded
material remains contained in the hole and blocks the hole,
rather than perhaps being blown around by a fire draught and
leaving the hole unblocked. These embodiments are more suited
for use with small pipes, up to about 1 inch nominal diameter,
and small holes, up to about 1% inch nominal diameter.
For use with pipes larger than 1 inch and holes
larger than 1% inch it is preferred to enclose the intumescent
material in a container.
The container surrounding the intumescent material is
preferably flexible and has a certain degree of strength.
Suitable materials for the flexible container include plastics
materials and mention is made of polyolefins, particularly
polyethylene, which heat will melt and may assist in sealing.
Another flexible container material that can be used is a metal
foil, such as aluminum foil. Yet another material is a fabric,
for instance woven fibres of polyamide, polyester, polyolefin,
polyacrylate, glass or ceramic or the like. A preferred
container, particularly for more stringent conditions, is
composed of a thin aluminum sheet or foil attached to a fabric
or fiber reinforcing material made of, for instance, polyamide,
polyester, glass, ceramic or the like. Suitable materials
- 3 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
include fabric net reinforced aluminum foils with polyethylene
heat seal layer available from Alpha Associates, Inc., of
Woodbridge, New Jersey, U.S.A. particularly the foil available
under the designation Alpha Style 4413-VLS*.
To make a device for use with pipes sizes of about 1;,~
inch nominal and greater, the flexible container, when laid
flat, is normally elongate and in use is folded to bring one
end into contact with the other to form an annulus. In a
preferred embodiment the two ends are held in contact by some
means. The particular means for holding the ends is not
critical. Persons skilled in the art will be able to suggest
many possible means for this purpose, for instance a clip or
clamp, or tape, or Velcro. Preferred is an adhesive covered
with a detachable liner, so that the annulus can be readily
made simply by detaching the detachable liner and pressing the
two ends of the container together to be held by the adhesive.
The demands on this adhesive are not particularly stringent,
and suitable adhesives are available from 3M under the
designation Scotch* 467 HiPerformance Adhesive and 468
HiPerformance Adhesive.
A device of the invention can be made by taking a
sheet of the flexible material that will form the container.
The sheet should be of the approximate length required for the
maximum length of the container when flat, plus, if necessary,
an allowance for sealing at each end to enclose the intumescent
material. It should be of a width sufficient to encompass both
the width and the height of the unexpanded intumescent
material, plus again, if necessary, an allowance for sealing
along one edge. The material can then be folded over the
unexpanded intumescent material and sealed along one side and
both ends, to form the required enclosure. One suitable way of
doing this is by heat sealing, although it is again clear that
this could be done by many other means, for instance use of
adhesive or even stitching. The flexible container should not
be a tight fit over the intumescent material, so that when the
Trade-mark
- 4 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
intumescent material does swell some of that swelling is
accommodated before the flexible container becomes stressed by
the swelling. It is important that the flexible container
contain the intumescent material as it first swells on
encountering the heat, so that the intumescent material stays
in place and is trapped in the hole, surrounding the pipe that
passes through the hole. The container holds the swelling
material for at least this brief init ial period of t ime . Even
if a seal bursts or the container subsequently tears the
expansion of the intumescent material in the confined space
will hold at least the bulk of the expanded material in place
and form an effective fire stop.
In order to locate the device permanently around the
pipe and in a hole that is to be blocked, use Is made of the
patch of adhesive that is on one exterior surface of the
container. That adhesive can be on the surface that becomes
the inner surface when the device is formed into an annulus.
The installation of the device is not particularly critical,
provided that it adheres to the pipe, as the seal is not formed
on installation but is formed only when heat causes the
intumescent material to intumesce. On installation the device
is wrapped around a pipe to form an annulus, or collar, using
the adhesive or other sealing means at either end of the
container to form the annulus, then thrust into the hole.
Once the device is in the desired location a pull tab, which
attaches to or is integral with the liner on the adhesive patch
and projects from the hole, is pulled to remove the liner from
over the adhesive patch. During insertion of the device in a
hole there is usually some degree of friction between the inner
surface of the device and the pipe that tends to help in
holding the device in place before the exposure of the adhesive
patch to form the permanent bond. The adhesive then comes in
contact with the pipe and the device is held permanently by the
adhesive at the desired location. The pull tab and liner,
which at its one end is permanently attached to the container,
projects from the hole and serves as a flag or marker to
indicate that the device is in place. At this stage, or at any
- 5 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
subsequent inspection, the hole can readily be examined
visually to see that the device is in place in the hole, as
indicated by the flag. Adhesion between the strip of adhesive
on the inner surface of the annulus and the outer surface of
the pipe can also be checked, of course.
Also within the scope of the invention is a device
similar to that described in the immediately preceding
paragraph, but differing in having the adhesive patch on the
surface that becomes the outer surface when the device is
formed into an annulus. With this device the adhesive attaches
to the inside of the hole, rather than the exterior of the
pipe. One application of this device is in a partition wall
composed of studs faced on both sides with gypsum wallboard.
For effective fire-stopping it is necessary to use two fire
stops, one in each piece of wallboard, or to insert a sleeve
that extends through the two pieces of wallboard and spans the
gap that is equal to the width of the studs. In this case one
fire stop can be inserted in the sleeve, which is, for example,
of PVC or of 24 or 28 gauge sheet metal. The device can be
held in place by the adhesive patch adhering the outer surface
of the device to the inner surface of the sleeve.
As stated above, with the device of the invention the
seal to prevent passage of heat, smoke, flame, etc. is not
formed on installation, but is formed on exposure to heat
causing rapid expansion of the intumescent material. The
rapidly expanding intumescent material occupies whatever space
is available, so it accommodates awkward shapes with ease. For
instance, sometimes in a hole there is a pipe in which there is
an elbow or a coupling between two pipes of different diameter,
or two or more small pipes passing through one hole. These
create awkward shapes and present problems for fire stops
composed of rigid material and designed to form a seal
immediately on installation. They present no problem with the
fire stop of the present invention, however, as the intumescent
material expands into whatever shape of space is available to
form the required seal.
The intention is that the adhesion between a surface
- 6 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
of the fire stop device and the outer surface of the pipe, or
the inner surface of the hole, as the case may be, shall be
permanent, and shall therefore be able to withstand variations
in temperature, exposure to conditions of moisture, lack of
humidity, vibration, exposure to gases and any other condition
which might tend to reduce or break the adhesion. The demands
on this adhesive material are therefore greater than the
demands on the material Joining the two ends of the container
to form an annulus. If the latter adhesion should fail this is
of no effect, because the device is still retained in place.
In contrast, the adhesive holding the device to the pipe must
remain in place and should therefore have the capacity of
adhering to materials that have low surface energy. Suitable
adhesives are known, for instance, from U.S. Patents Nos.
5,602,221; 5,616,670 and 5,654,387 the disclosures of which are
incorporated herein by reference. One adhesive for this
purpose is available from 3M under the trade-mark Scotch 300LSE
HiStrength Adhesive. It should be borne in mind that fire stop
devices of the same construction might be used on pipes made of
many different materials, such as various plastic materials,
including but not limited to cellular core PVC (ccPVC), PVC,
crosslinked PVC (CPVC), fire resistant polypropylene (FRPP),
PVDF, ccABS and ABS, steel, galvanized steel, aluminum, copper
or mild steel which may have an anti-corrosive oil finish, or
be painted, and the adhesive should attach permanently and
firmly to any of these materials.
Pipes and conduits used in buildings tend to be of
certain nominal sizes. There is some variation in external
diameter, because diameters quoted are often internal diameters
and different pipes for different purposes have different wall
thicknesses. The outer diameters of pipes encountered in
buildings are clustered in various fairly narrow dimensional
ranges, however, and a device of appropriate size is made for
each range.
Alternatively, or in addition to sizing devices with
regard to the pipe size it is possible to size them with regard
to the hole size.
- 7 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
Usually in construction a hole to accommodate a pipe
passing through it is sized so that the diameter of the pipe is
about 50 to 80% of the diameter of the hole. In this case one
appropriately sized device of the invention is all that is
needed to form a fire stop. In some instances, however, it is
necessary to insert a fire stop where the hole is much larger
than the pipe. This is the case particularly when
retrofitting, when, say, a 3 inch pipe may have been removed
from a hole and in the retrofit a 1 inch pipe is passed through
the hole. In such a case it is possible to use two devices of
the invention. Immediately around the 1 inch pipe is placed a
device appropriately sized for 1 inch pipe, and around that
there is placed a second, larger device of the invention.
Alternatively the hole can be partially filled with some non-
combustible material, for example mineral wool.
As stated above, after installation of the device the
pull tab can serve as a flag. The flags can be coded to
indicate the size of the device, for instance with different
colours.
The invention is further illustrated in the
accompanying drawings showing, by way of example, preferred
embodiments of the invention, of which:
Figure 1 illustrates certain characteristics of a liner-
covered adhesive that are taken advantage of in some preferred
embodiments of the invention;
Figure 2 shows a flexible container in accordance with the
invention in plan view;
Figure 3 shows a device of the invention in longitudinal
section;
Figure 4 shows a device of the invention in cross section;
Figure 5 shows a device in process of installation; and
Figure 6 shows detail of a liner and pull tab.
Figure 1 shows a substrate 1 on the surface of which
is applied an adhesive material 2 covered with a liner 3 which
extends to form a pull tab 4. If a pull is exerted on the pull
tab in the direction indicated as 00 in the figure then the
shear force resisting removal of the pull tab will be very
- 8 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
great and it is more likely that the pull tab will tear than
that the adhesive will release. If the pull is in the
direction indicated as 90 , i.e., perpendicular to the surface
bearing the adhesive, then the force required to remove the
liner is considerably less. If the pull is in the direction
indicated as 180 the resistance to removal of the liner is
also less. The embodiment of the invention that is illustrated
in Figures 2 to 5 takes advantage of this phenomenon.
Figures 2, 3 and 4 show a device in accordance with
the invention before installation. A flexible container 5
encloses strips 10 of intumescent material, the container being
closed by a heat-sealed strip 7. At one end of the container
is a strip of adhesive 6, temporarily covered by a releasable
liner 6a, that will adhere to the other end of the container to
hold the two ends when the flexible container is formed into an
annulus. Attached to one surface of the flexible container is
a pull tab 8 that, over part of its length, act as a liner over
a patch of double-sided adhesive 9 that is on the surface of
the container that forms the inner surface when the container
forms an annulus. As can be seen from Figure 4, the liner and
pull tab 8 is looped over so that when a pull on the pull tab
in the direction of the arrow it is initially at about 180 to
the adhesive surface, so that the liner is released relatively
easily. As the point of attachment of the liner approaches the
edge of the flexible container then the angle approaches 90
and the resistance to release increases. As more of the liner
is removed the angle approaches 0 and the resistance to
release increases yet further as discussed above. At the point
that this further increase in resistance is encountered the
patch of adhesive that will contact the pipe is exposed. The
adhesive contacts and attaches to the pipe. The pull tab
extends from the hole and serves as a flag indicating that a
device has been inserted. The device will therefore remain in
place. It will be appreciated that its insertion has involved
no use of tools, no particular skills, no use of screws, grout
or caulking to hold it in place, and it is clearly very easily
capable of rapid visual inspection, to determine that it has
- 9 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
been installed properly.
The intumescent material inside the container is shown as
two strips of intumescent material 10. As stated above, each
device is designed for use with pipe of a particular size, and
the device shown in Figures 2, 3 and 4 is intended for pipe
whose external diameter is approximately 2 inches. The
intumescent material Interam Ultra GS is available in strips
that are approximately 2 inches wide and 1/8 of an inch thick.
For a device for use with 2 inch pipe two strips of this
material are used, one approximately 7 1/2 inches in length and
the other approximately 8 1/4 inches in length. The one is
laid on top of the other and the strips are free to move
relatively to each other, although they are, of course,
confined within the flexible container. The shorter length of
intumescent material is adJacent that side of the foil
container that, on its outer surface, bears the adhesive patch
9 and liner S. As the device is wrapped around a pipe the two
layers of intumescent material move relatively to each other to
accommodate the formation of the annulus. For 2 inch pipe, the
flexible container is formed from a sheet that is approximately
10 1/4 inches long by 7 inches wide, when laid flat. The two
layers of intumescent material are laid on this sheet. The
sheet is then folded over lengthwise to enclose the intumescent
material and heat-sealed along one edge, and to form seal 7 at
either end. Adhesive 6 and liner 6a are applied to the one end
and the adhesive patch 9 and liner 8 attached thereafter. For
4 inch pipe the flexible container is suitably about 19 1/2
inches long and contains four strips of the Interam Ultra GS
intumescent material, the shortest of which is about 14 3/8
inches long and the longest of which is about 17 inches long.
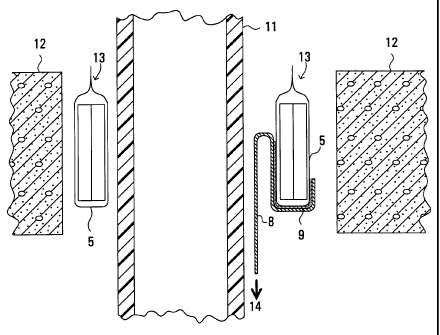
Figure 5 shows schematically the device in place
before removal of the liner 8. A pipe 11 extends through a
hole in a concrete wall 12. In the space between the exterior
surface of the pipe and the interior of the hole in the
concrete there is placed the device of the invention. As can
be seen, a pull on the liner in the direction of the arrow will
expose the adhesive which then attaches to the pipe. The liner
- 10 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
8 is not completely detached from the device but remains in
place and serves as a flag to indicate that the device has been
installed.
It is clear from the above description that the
adhesive that attaches the device of Figures 2 to 6 to the pipe
need not extend all around the inner circle of the annulus of
the adhesive. The area of the adhesive should be such that,
when in place, it occupies a sector of at least about 25
preferably about 50 . The size of this sector does depend to
some extent on the size and weight of the device and the pipe
around which it is to be wrapped. With a larger device and
larger diameter pipe the sector subtended by the adhesive patch
can be smaller. Particularly for use in a hole in a floor or
ceiling, where gravity will tend to pull on the device, the
amount and tenacity of the adhesive should be sufficient to
support the weight of the device permanently in a non-friction
mode, i.e., without reliance on friction, on a low energy
surface.
Figure 6 shows detail of a preferred embodiment of
the liner and pull tab 8, in its orientation after it has been
pulled from the adhesive patch 9. The liner and pull tab is
composed of a silicone release coated paper 15, i.e., paper
coated on both sides with low surface energy silicone so that
it will readily release from the adhesive patch 9. As the pull
tab 8 is to remain in place as a permanent flag or marker it is
necessary that it shall not release from the device as a whole.
To enhance the adhesion between the surface of the container 5
and the paper 15 there is used a double-sided adhesive,
available from 3M as Double Sided Adhesive 9731. This is
composed of a scrim, on one side of which is a layer 16 of
Scotch 300LSE HiSt rength Adhesive, which adheres well to the
silicone release coated paper 15. On the other side of the
scrim is a layer 15 of an acrylate adhesive that adheres well
to the fabric of container 5. At the other end of the strip of
paper 15 there is a strip of plastic sheet 18 that is attached
to the paper 15, again using 3M's Double Sided Adhesive 9731,
with the 300LSE HiStrength Adhesive in contact with the paper
- 11 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
15 and the acrylate in contact with the plastic sheet 18.
It will be appreciated that the invention can be
embodied in some ways different from that described above with
reference to the drawings. For instance, with larger pipe
diameter a larger device will be needed and there may be used 3
or 4 or even 5 or more strips of the 1/8 inch thick material
Interam Ultra GS. The intumescent material could be in
pulverulent form, rather than solid strip form. The manner of
sealing the flexible container to contain the intumescent
material is not critical, provided that the sealing material
does withstand the initial force to sufficient extent to ensure
that at least the bulk of the intumescent material remains in
place in the annulus between the pipe and the hole and does in
fact form a fire stop. The liner and pull tab may be formed of
the same material, or, of course, may be made of a composite of
several different materials. Suitable materials are sheet
plastic and paper, or a combination of the twof clearly the
selection of material for this purpose is not critical. The
liner and pull tab remain attached to the device, and this can
be done by means of adhesive, as described above, or the liner
can be anchored at its one extreme end by any other suitable
means, for instance stitching, or by making the flexible
container of a material which is shaped so that when it is
folded to enclose the intumescent material there is a tail
extending from one surface of the container material, which
tail can be folded over to cover the adhesive and serve as
liner and pull tab.
Another variant of the embodiment of Figures 2 to 6
is to dispense with the pull tab 8 and adhesive batch 9, and to
locate the adhesive along the lengthwise strip of the heat-
sealed area 7. The adhesive would be covered with a release
liner until used. In use the release liner would be removed,
the device wrapped around the pipe and slid carefully into the
hole and, when properly located, the adhesive on the heat-
sealed strip 7 would be pressed either against the exterior of
the pipe or the interior of the hole, as required. It will be
realised that this embodiment does not provide the flag to
- 12 -
CA 02271229 1999-05-07
indicate installation of the device. Also, as in this
embodiment the adhesive is exposed before the device is
located, care must be exercised in sliding the device along the
pipe to the required location.
In yet another variant, inside the flexible container
and partially surrounding the intumescent material is a member
of, for example, thick foil or thin metal that directs
expansion and flow of expanding material in a particular
direction.
- 13 -