Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/LTS97/20588
-1
Electric Circuit Actuating Mechanism
BACKGROUND
This invention relates generally to a safety device
for power tools and more specifically to an electric
s circuit actuating mechanism which when appropriately
mounted on a power tool stand, allows the operator to turn
on the tool's drive motor by a conscious depression of a
relatively small sized actuator, but permits the motor to
be turned off by depression of a relatively broad surface
1o by a body part and especially by a body part other than
the hands of the operator whereby there is no need for
the operator to take his eyes or hands off the work and
the cutting or abrading tool.
U.S. Patent Nos. 3,312,799; 4,166,202; and 4,389,550
1s each describe various forms of switch actuating mechanisms
including a broad surface panel member of one type or
another pivotally mounted in proximity to the operator's
station and this member is mechanically linked to the
on/off lever of the toggle switch. Once the motor of the
2o tool is turned on, it may be turned off by bumping the
broad surface panel member with one or more parts of the
operator's anatomy other than his hands and this operation
may be accomplished without having to glance away from the
working surface of the tool being used. This, of course,
25 leads to greater safety by preventing accidental or
inadvertent movement of the workpiece or hands into a
position where they may be injured by the tool.
However, it can be appreciated that due to the hinged
mounting of the broad surface in U.S. Patent Nos.
30 3,312,799; 4,166,202; and 4,389,550, bumping the broad
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97120588
-2-
1 surface member along the edge adjacent and parallel to
the pivot axis as well as adjacent to the pivot axis may
not cause the broad surface member to pivot and cause
actuation of the switch or result in turning off the motor
s of the tool. Although other manners of mounting the broad
surface members are known such as shown in U.S. Patent
No. 3,233,071, while reducing the possibility that
pushing the broad surface member would not cause actuation
of the switch, such arrangements did not eliminate the
1o possibility.
U.S. Patent No. 5,510,587 describes a form of switch
actuating mechanism including a broad surface panel
member which overcomes deficiencies of the prior art by
enabling any point of the broad surface to move in an
15 actuation direction to de-energize the electric circuit.
Specifically, the construction of U.S. Patent No.
5,510,587 utilizes a multiplicity of de-energizing
momentary switches which operate a control relay. It
can then be appreciated that the control relay and the
2o electric circuit associated therewith as well as the
costs of the momentary switches themselves increase the
price of the electric circuit actuating mechanism to
limit its marketability to industrial and similar
commercial applications.
2s Further, the fabrication of prior actuating mechanisms
tended to be overly costly to manufacture because of the
number of parts involved and the difficulty of assembly,
making it somewhat difficult to market at a price
commensurate with the cost of the tool on which the safety
3o mechanism was adapted to be used.
The present invention according to the preferred
teachings provides an electric circuit actuating mechanism
of the general type described but is designed to be
substantially less complicated in terms of the number and
35 cost of parts and their assembly into a completed article.
This has been done while increasing the element of safety
for which the earlier devices were designed.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-3-
1 Specifically, the present invention solves problems
encountered by prior mechanisms in the field of electric
circuit actuation and other needs in the field by
providing, in the most preferred form, a front wall
movably mounted relative to a housing enabling any point
of the front wall to move in an actuation direction and
an actuation member movable from a rest position towards a
de-energizing position when any point of the broad surface
moves in the actuation direction from its normal position
io to its actuation position, with the actuation member being
in operative relation to de-energize the electric circuit
when the actuation member is moved from the rest position
to the de-energizing position, with the electric circuit
not being energized by movement of the front wall.
1s In other aspects of the present invention, the
slideable actuator of an electric circuit actuating
mechanism includes an actuator aperture extending in a
nonparallel manner to the slide or actuation direction and
which is aligned with an aperture formed in the housing
2o when the actuator is in the non-actuated position for
receiving a lock for preventing the actuator from moving
from the non-actuated position, with the actuator being
free to move when the lock is removed from the actuator
and housing apertures.
25 In further aspects of the present invention, the
housing of an electric circuit actuating mechanism is
formed by a mount having its lower end removably slideably
interconnected to the end wall of a channel and by a lid
having its lower end removably slideably interconnected
3o to the lower end of the mount, with a front wall being
movably mounted to the mount and slideably received in
the collar of the lid, with the channel, mount, and lid
being secured together at a position spaced from the lower
ends and the channel end wall.
35 It is accordingly the principal object of the present
invention to provide a new and improved safety device for
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-4-
1 use in conjunction with electrical motor-driven power
tools or the like.
Another object of the invention is to provide an
electric circuit actuating mechanism for use with
s electrically powered tools and disposed such that the
power may be turned on by the depression of a relatively
small surface of an actuator and turned off through the
application of a force against a broad surface.
Yet another object of the invention is to provide an
1o improved safety device for the control of power-driven
tools, the safety device including a broad surface movably
mounted to a housing which, in turn, is arranged to be
connected at a desired location on a power tool stand
whereby the operator's knee, thigh, hip or other part of
15 his anatomy other than his hands may be used to disconnect
the power tool from its power supply.
Still another object of the invention is to provide
an electric circuit actuating mechanism formed from
components which are snapped and/or slid in place and
2o secured together with minimal number of screw, threaded,
or similar type and forms of fasteners.
Still a further object of the invention is to provide
an electric circuit actuating mechanism which can be
locked in its non-actuated position by sliding the clasp
2s of a padlock through aligned apertures formed in the
slideable actuator and the housing.
These and further objects and advantages of the
present invention will become clearer in light of the
following detailed description of illustrative embodiments
30 of this invention described in connection with the
drawings.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The illustrative embodiments may best be described by
reference to the accompanying drawings where:
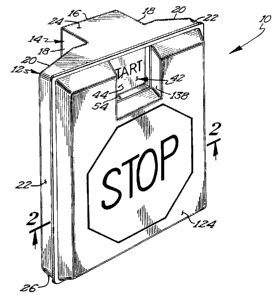
35 Figure 1 shows a perspective view of an electric
circuit actuating mechanism according to the preferred
teachings of the present invention.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-5-
i Figure 2 shows a cross-sectional view of the electric
circuit actuating mechanism of Figure 1 according to
section line 2-2 of Figure 1, with portions broken away
and shown in phantom to show constructional features.
s Figure 3 shows a cross-sectional view of the electric
circuit actuating mechanism of Figure 1 according to
section line 3-3 of Figure 2, with portions broken away
and shown in phantom to show constructional features.
Figure 4 shows a partial, cross-sectional view of the
to electric circuit actuating mechanism of Figure 1 according
to section line 4-4 of Figure 2.
Figure 5 shows a partial, perspective view of the
electric circuit actuating mechanism of Figure 1, with
portions shown in phantom to show constructional features.
15 Figure 6 shows a perspective view of an alternate form
of an electric circuit actuating mechanism according to
the preferred teachings of the present invention.
Figure 7 shows an exploded, perspective view of the
electric circuit actuating mechanism of Figure 6.
2o All figures are drawn for ease of explanation of
the basic teachings of the present invention only; the
extensions of the figures with respect to number, position,
relationship, and dimensions of the parts to form the
preferred embodiment will be explained or will be within
25 the skill of the art after the following description of
the preferred embodiment has been read and understood.
Further, the exact dimensions and dimensional proportions
to conform to specific force, weight, strength, and
similar requirements will likewise be within the skill of
3o the art after the following description of the preferred
embodiment has been read and understood.
Where used in the various figures of the drawings,
the same numerals designate the same or similar parts.
Furthermore, when the terms "top", "bottom", "first",
3s "second", "inside", "outside", "front", "back", "outer",
"inner", "upper", "lower", "height", "width", "length",
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-6-
1 "end", "side", "horizontal", "vertical", "rear", and
similar terms are used herein, it should be understood
that these terms have reference only to the structure
shown in the drawings as it would appear to a person
viewing the drawings and are utilized only to facilitate
describing the preferred embodiment.
DESCRIPTION
An electric circuit actuating mechanism according to
the preferred teachings of the present invention is shown
to in the drawings and generally designated 10. Mechanism 10
generally includes a housing 12. In the preferred form,
housing 12 includes a channel 14 including a planar
bottom 16 and first and second planar sides 18 extending
generally perpendicularly from the opposite side edges of
bottom 16. Housing 12 further includes first and second
extensions 20 extending from and outwardly of sides 18.
Extensions 20 terminate in first and second planar side
walls 22 extending generally parallel to sides 18. An
upper end wall 24 extends generally perpendicular between
2o bottom 16, sides 18, extensions 20, and side walls 22.
A lower end wall 26 extends generally perpendicular
between extensions 20 and side walls 22, with the lower
end of channel 14 being open.
Housing 12 further includes an L-shaped divider 28
having a first plate 30 and a second plate 32 extending
generally perpendicular to first plate 30. Plate 30 has
a width for slideable receipt between sides 18 and a
height generally equal to sides 18. Plate 32 has a width
of a size for abutting with the top edges of sides 18 and
3o a length extending from plate 30 to upper end wall 24
parallel to bottom 16 of channel 14. Suitable slides 34
can be formed on sides 18 and bottom 16 for slideable
receipt of plate 30. A toggle switch 36 is mounted to
plate 30 having a toggle 38 extending from plate 30 in the
same direction as plate 32 and a body 40 located on the
opposite side of plate 30 than plate 32. Toggle 38 is
movable between an on position and an off position, with
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-7-
1 switch 36 in the on position maintaining the electric
circuit and in the off position breaking the electric
circuit.
Mechanism l0 further includes a generally U-shaped
actuator 42 having a planar front 44 and first and second
legs 46 extending in a spaced parallel relation from the
back surface of front 44. Actuator 42 is slideably
mounted to plate 32 such as by legs 46 extending through
parallel first slots 48 extending from the free edge of
plate 32 towards plate 30. In the preferred form,
parallel second slots 50 extend from the free edge of
plate 32 towards plate 30 parallel to and intermediate
slots 48. An ear 52 extends into each of slots 48
adjacent the free edge of plate 32 and extending in a
1s direction opposite to slots 50. Ears 52 abut with the
top edge of a slot formed in the upper edges of legs 46.
It can then be appreciated that the material of plate 32
between slots 48 and 50 can be flexed sufficiently to
allow insertion of legs 46 in slots 48 past ears 52 but
2o will return so that ears 52 capture legs 46 in slots 48
after insertion. A U-shaped actuator guide 54 integrally
extends from plate 32 adjacent its free edge and in a
direction opposite to plate 30. Guide 54 has a size and
shape for slideably receiving front 44 of actuator 42.
2s First and second parallel ears 56 integrally extend
from plate 32 opposite to guide 54 and on opposite sides
of slots 48. A U-shaped bracket 58 is pivotally mounted
to ears 56. Bracket 58 is pivotable between a locked or
interfering position extending from ears 56 generally
3o parallel to the slideable movement of actuator 42 and an
unlocked or non-interfering position. Bracket 58 includes
an L-shaped cam leg 60 integrally extending therefrom.
A lock 62 of a commercial variety is mounted to one of
sides 18 and includes a latch 64 extending in a non-
parallel angle to the rotation axis of lock 62 and located
intermediate cam leg 60 and bracket 58. Thus, rotation
of lock 62 causes latch 64 to rotate bracket 58 between
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-g-
i the locked and unlocked positions. In the locked position
as best seen in Figure 5, the free ends of legs 46 of
actuator 42 in its outer, non-actuated position terminate
in channel 14 and abut with bracket 58 to prevent actuator
42 from being slid inward from its non-actuated position.
In its unlocked position, bracket 58 is in a non-
interfering position with actuator 42 and actuator 42
is free to slide relative to plate 32 to its actuated
position. For ease of assembly, a detent can be formed
1o in one of ears 56 or bracket 58 for slideable receipt in
an indent formed in the other of ears 56 or bracket 58 to
hold bracket 58 in its locked position during assembly of
mechanism 10.
Third and fourth elongated parallel ears 68 integrally
is extend from plate 32 opposite to guide 54 and intermediate
ears 56 and plate 30. A switch lever 70 is pivotally
mounted between ears 68 intermediate its upper and lower
ends. Switch lever 70 is suitably connected to actuator
42 so that slideable movement of actuator 42 causes
2o pivotal movement of switch lever 70. In the preferred
form, slots 72 are formed in the lower edges of legs 46
of actuator 42 for slideably and pivotably receiving the
upper end of switch lever 70. The lower end of switch
lever 70 is suitably connected to switch 36 or similar
2s electric control so that pivotal movement of switch lever
70 causes switch 36 to move between its actuated and non-
actuated position. Lever 70 is in a suitable operative
relation to switch 36 and in the preferred form, a fork
74 is formed on the lower end of switch lever 70 for
3o slideably and pivotably receiving the free end of toggle
38 of switch 36. With actuator 42 in its outer, non-
actuated position as shown in Figures 3 and 5, switch
lever 70 holds toggle 38 of switch 36 in its non-actuated
position. Plate 32 includes an opening 76 formed
35 intermediate guide 54 and plate 30 and generally aligned
with switch lever 70.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/fJS97/20588
_g_
i Housing 12 further includes a planar divider 78 having
a width for slideable receipt between sides 18 and a
height generally equal to sides 18. Suitable slides 80
can be formed on sides 18 and bottom 16 for slideable
s receipt of divider 78. A female electrical outlet 82 is
mounted to divider 78. Also an electrical cord 84
including a suitable strain relief extends through divider
78. Suitable electrical connection is made between switch
36, outlet 82, and electrical cord 84 inside of channel
14 intermediate plate 30 and divider 78. A suitable dust
cover 86 is provided to close the top opening of channel
14 intermediate plate 30 and divider 78. A suitable cord
clamp 88 is provided in channel 14 on the opposite side of
divider 78 than divider 28. Specifically, an electrical
cord as shown in phantom in Figure 3 and having a male
electrical outlet for connection to outlet 82 can be
removably secured by clamp 88 to prevent unintentional
removal from mechanism 10.
Mechanism 10 further includes a mount 90 having a
2o generally U-shape and generally including a generally
planar top plate 92 and first and second side plates 94
extending generally perpendicular from the opposite side
edges of plate 92. Plate 92 has a width generally equal
to and for abutting with the top edges of sides 18 and has
2s a length extending from lower end wall 26 to plate 30.
Side plates 94 are slideably received on the outside
surfaces of sides 18 and have lower edges which abut with
the upper surfaces of extensions 20. Ears 96 are
integrally formed on side plates 94. Suitable provisions
3o are made to removably secure ears 96 to extensions 20 such
as bolts secured to ears 96 and extending through suitable
apertures formed in extensions 20, with nuts threadably
received on the bolts and abutting with the opposite sides
of extensions 20 than ears 96. It should be noted that
35 dividers 28 and 78 and cover 86 are snapped or slid in
place without other forms of securement for ease of
assembly, with the securement of mount 90 abutting with
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-10
1 and preventing disassembly of dividers 28 and 78 and cover
86 as they are sandwiched between mount 90 and bottom 16
of channel 14.
First and second parallel ears 98 extend from the
s upper surface of mount 90 opposite sides 18 and
intermediate plate 30 and divider 78. An actuation
lever 100 is movably mounted relative to housing 12
and specifically is pivotally mounted between ears 98
intermediate its upper and lower ends for movement
to between a normal or rest position and an actuation or
de-energizing position. Lever 100 is biased from the
actuation position to the normal position such as by a
spring 102 located between lever 100 and mount 90 and
located intermediate the upper end of lever 100 and ears
is 98. An actuation finger 104 integrally extends from
adjacent the upper end of lever 100 and through opening
76 for engaging with toggle 38 and/or switch lever 70
adjacent fork 74. Finger 104 engages lever 70 when switch
36 is in its actuated position and lever 100 is in its
2o normal position. Thus, finger 104 operatively relates
lever 100 and switch 36 to de-energize the electric
circuit when lever 100 is moved from the normal position
to the actuation position.
Upper and lower, spaced protuberances 106 are
2s integrally secured to each side plate 94 and to ears 96
also integrally secured thereto. In the most preferred
form, protuberances 106 are in the form of hollow
rectangular parallelepipeds having open bottoms. Each
protuberance 106 includes an aperture 108 and a pivot
3o ear 110 .
Mechanism 10 further includes upper and lower
actuation arms 112 and 114 pivotably mounted to and
between ears 110 about axes which are parallel to but
spaced from the axis of actuation lever 100. Actuation
3s arms 112 and 114 are generally U-shaped and each include
an elongated central portion 116 extending parallel to the
pivot axis of arms 112 and 114 and each further including
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98121732 PCT/US97/20588
-11-
1 first and second legs 118 extending perpendicularly from
central portions 116. Upper actuator arm 112 includes a
tab 120 which abuts with the upper end of lever 100 in its
normal position and with legs 118 extending from portion
116 generally parallel to or at a slight angle upward
from top plate 92. It should be appreciated that if one
or both legs 118 of arm 112 are pushed to pivot actuator
arm 112 so that the free ends of legs 118 move toward
extensions 20, tab 120 pushes the upper end of lever 100
1o towards plate 32 and causes lever 100 to pivot from its
normal position to its actuation position. Similarly,
lower actuator arm 114 includes a tab 122 which abuts with
the lower end of lever 100 in its normal position and with
legs 118 extending from portion 116 generally parallel to
i5 or at a slight angle upward from top plate 92. It should
be appreciated that if one or both legs 118 of arm 114 are
pushed to pivot actuator arm 114 so that the free ends of
legs 118 move toward extensions 20, tab 122 pushes the
lower end of lever 100 away from plate 92 and causes lever
20 100 to pivot from its normal position to its actuation
position. In its most preferred form, arms 112 and 114
are of identical construction to reduce fabrication costs
and specifically include both tabs 120 and 122, only one
of which is utilized depending upon whether utilized as
25 upper or lower arm 112 and 114.
Mechanism 10 according to the teachings of the present
invention further includes a cover 124 movable relative
to housing 12 and having a front wall including a broad
surface. Four pins 126 integrally extend from the rear
3o surface of cover 124 at locations for slideable receipt in
apertures 108 of protuberances 106. In the most preferred
form, pins 126 have heads 128 formed on the free end of
stems 130, with stems 130 having a cross sectional size
equal to and for slideable receipt in apertures 108 while
35 heads 128 have an enlarged cross sectional size larger
than apertures 108. Heads 128 each include a plurality of
axially extending, circumferentially spaced slots 132
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-12-
1 which allow heads 128 to be compressed to a size allowing
passage through apertures 108 but preventing undesired
removal after insertion. Cover 124 is biased away from
mount 90 in the preferred form by coil springs 134
positioned on pins 126 and sandwiched intermediate the
rear surface of cover 124 and the front surface of
protuberances 106. Pins 126 and springs 134 are arranged
in a non-linear manner.
Four tongues 136 integrally extend from the rear
io surface of cover 124 at locations corresponding to and for
abutment with legs 118 spaced from central portions 116.
Thus, actuation arms 112 and 114 are in operative relation
to lever 100 and also to cover 124 for moving lever 100
from its rest position towards its de-energizing position
i5 when any point of the broad surface of cover 124 moves in
the actuation direction from the normal position to the
actuation position.
In the most preferred form, cover 124 includes a
cutout I38 extending from its upper edge for extending
2o around guide 54 of housing 12. In the most preferred
form of the present invention, the back surface of cover
124 includes a network of ribs 140. It can then be
appreciated that ribs 140 increase the strength of cover
124 allowing its formation from reduced thickness
25 materials.
Housing 12 is preferably fabricated from sheet metal
or plastics, as is conventional for electrical switch
boxes, with mechanism 10 generally fabricated from
plastics in the most preferred form.
3o Now that the details of the construction of mechanism
according to the preferred teachings of the present
invention have been set forth, consideration will be given
to its mode of operation and advantages. As has already
been mentioned, the present invention comprises a safety
35 device in the form of electric circuit actuating mechanism
10 for facilitating the control of electrical circuits
such as for drive motors or the like commonly used with
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-13-
i power tools. For example, the present invention may be
used with a wide variety of power tools including table
saws, drill presses, lathes, sanders, joiner/planers and
the like. Mechanism 10 is mounted at a convenient
s location proximate the operator s usual work station and
power is brought into housing 12 through electric cord 84.
The electrical cord for the power tool or the like is
plugged into outlet 82 and secured by clamp 88. Due to
the solid construction of housing 12 and specifically
1o channel 14, dividers 28 and 78 and dust cover 86 thereof,
the interior defined by housing 12 in the most preferred
form encloses the electrical components of switch 36,
outlet 82, and the electric connections therebetween and
with cord 84 and protects them from the environment such
15 as but not limited to sawdust and the like which may be
in the air.
To start the motor, the operator must first unlock
mechanism 10 by rotating the key for lock 62. The
operator may now depress planar front 44 of actuator 42
2o to move switch 36 from its off position to its on position
to maintain a closed circuit between the power supply and
the motor being controlled. It can then be appreciated
that actuation of switch 36 does not occur as the result
of movement of cover 124.
2s All the while, the machine can be running in that
switch 36 effected an energization of the electric
circuit. When the operator desires to again turn off the
motor, he may apply a force either with his hand, but
preferably with another part of his anatomy such as his
3o thigh, knee or hip, against the broad front surface of
cover 124 to thereby overcome the force of one or more of
coil springs 134 and force cover 124 against one or more
of legs 118 of arms 112 and/or 114. Depression of cover
124 against legs 118 then causes one or both of arms i12
35 and 114 to pivot such that switch 36 is moved from its on
position to its off position. With switch 36 in its off
position, the electrical connection to the motor is
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-14-
1 broken, disconnecting the motor from the power supply.
When cover 124 is released, coil springs 134 return it
to its normal position while springs 102 associated with
lever 100 ensure that lever 100 and arms 112 and 114 will
s also be returned to their de-energizing position.
It can then be appreciated that de-energization of the
electric circuit can be accomplished by pushing cover 124
in different manners. Specifically, in the preferred
form, as one or more pins 126 can slide through apertures
to lOg relative to mount 90 against the bias of springs 134,
cover 124 is movably mounted relative to housing 12
enabling any point of the broad surface of cover 124 to
move in an actuation direction from the normal position to
the actuation position, with the front wall being biased
15 from the actuation position to the normal position by
springs 134. Particularly, cover 124 can be pushed to
move cover 124 adjacent to upper end wall 24 towards
housing 12 causing cover 124 to pivot about an axis
parallel and adjacent to lower end wall 26 in a similar
2o manner as in U.S. Patent No. 4,389,550. It can be
appreciated that the portions of cover 124 adjacent to
side walls 22 will move in a non-parallel manner relative
to side walls 22. Such movement of cover 124 will pivot
arm 112 which in turn pushes the upper end of lever 100
2s towards housing 12 to thus de-energize the electric
circuit. However, unlike U.S. Patent No. 4,389,550, cover
124 can be pushed to move cover 124 adjacent to lower end
wall 26 towards housing 12 causing cover 124 to pivot
about an axis parallel and adjacent to upper end wall 24.
3o It can be appreciated that the portions of cover 124
adjacent to side walls 22 will move in a non-parallel
manner relative to side walls 22. Such movement of cover
124 will pivot arm 114 which in turn pushes the lower end
of lever 100 away from housing 12 to thus de-energize the
35 electric circuit. Furthermore, unlike U.S. Patent No.
4,389,550, cover 124 can be pushed to move cover 124
adjacent to one of the first and second side walls 22
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-15-
1 towards housing 12 causing cover 124 to pivot about an
axis parallel to and adjacent the other of the first and
second side walls 22. It can be appreciated that the
portions of cover 124 adjacent to end walls 24 and 26 will
s move in a non-parallel manner relative to end walls 24 and
26. Such movement of cover 124 will simultaneously pivot
arms 112 and 114 which in turn pivot lever 100 so that
its upper end moves towards housing 12 and the lower end
moves away from housing 12 to thus de-energize the
io electric circuit. Further, unlike U.S. Patent No.
4,389,550, cover 124 can be pushed towards housing 12
adjacent to the upper right corner causing cover 124 to
pivot about an axis extending between the left side wall
22 and end wall 26. It can be appreciated that the
is remaining portions of cover 124 will move in a non-
parallel manner from the remaining portions of housing 12.
Such movement of cover 124 will engage the right leg 118
of arm 112 to pivot arm 112 which in turn pivots the upper
end of lever 100 towards housing 12 to thus de-energize
2o the electric circuit. Similarly, cover 124 can be pushed
adjacent its other corners to thereby move switch 36 from
its on position to its off position.
It can then be appreciated that the positioning of
the body part other than the hand such as thigh, knee,
2s or hip on cover 124 is not as accurate as a hand would
be, especially when cover 124 is not being viewed and
even further under emergency situations where fast
actuation is desired. Mechanism 10 then provides a
substantial improvement over mechanisms including
3o actuation surfaces which are pivotally mounted through
the use of a hinged mounting such as in U.S. Patent Nos.
3,312,799; 4,166,202; and 4,389,550 in the ability to
quickly and consistently de-energize the electric circuit.
Furthermore, the present invention provides a substantial
3s improvement over mechanisms including actuating surfaces
which are not mounted through the use of hinge mountings
such as in U.S. Patent No. 3,233,071. Specifically, such
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-16-
i mechanisms were not consistent in causing actuation of
the switch. For example, in some circumstances, the
surface would bottom out by hitting other portions of
the mechanism before actuating the switch. Further,
considerable travel of the surface would be required
especially when pushed at the corner before the switch
was actuated, and similarly considerable force would be
required in these circumstances especially if a typical
start/stop type switch was utilized. Mechanism 10
io according to the teachings of the present invention then
takes a novel and unique design direction from prior
mechanisms such as shown in U.S. Patent No. 3,233,071.
Specifically, lever 100 and arms 112 and 114 are utilized
such that the amount of travel of cover 124 and the amount
of force to push cover 124 required to actuate switch 36
are minimized. But more importantly, the use of lever
100 and arms 112 and 114 allows the use of one start/stop
type switch 36 to be possible and practical. It can then
be appreciated that lever 100 and arms 112 and 114
2o according to the teachings of the present invention allow
different movements of cover 124 to actuate switch 36
especially if movement occurs at the corners of a
generally right parallelepiped-shaped mechanism 10 in the
most preferred form. Thus, mechanism 10 according to the
teachings of the present invention effectively eliminates
the possibility that pushing cover 124 will not cause
actuation of switch 36 causing de-energization of the
electric circuit and overcomes the disadvantages and
limitations of prior mechanisms including but not limited
3o to the types as shown in U.S. Patent Nos. 3,233,071;
3,312,799; 4,166,202; and 4,389,550.
To lock actuating mechanism 10 and to thereby prevent
unauthorized use of the power tool, the operator turns the
key for lock 62 which prevents actuator 42 from sliding
and removes the key.
By making front 44 relatively small and by recessing
front 44 behind the front surface of cover 124, accidental
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/2U588
-17-
1 operation of switch 36 is practically eliminated. It of
course can be appreciated that actuator 42 can be located
at other positions in housing 12 or other manners can be
utilized to energize the electric circuit according to the
s teachings of the present invention as long as movement of
switch 36 from its off position or energization of the
electric circuit does not occur as the result of the
movement of cover 124. Once switch 36 is operated to turn
the machine on, the operator need not search around for
1o an off switch in that application of a force anywhere on
cover 124 functions to turn off the machine.
It can then be appreciated that cover 124 formed by
walls defining a sleeve which telescopes inside of walls
22, 24, and 26 is believed to be advantageous in making
1.s disassembly more difficult. Specifically, if cover 124
were telescoped on the outside of housing 12 such as
disclosed in U.S. Patent 3,233,071, the back edges of
the cover could be easily flexed outwardly to release the
cover from the housing, with such flexing being the result
20 of an object accidentally catching on the back edges or
by simply being gripped by the fingers of a vandal which
can be a significant problem in a school or similar
environment. Due to the construction of mechanism 10
according to the preferred teachings of the present
2s invention, disassembly requires the securement of mount
90 to be removed from extensions 20 allowing access to
heads 128, which is very time consuming and also very
difficult to perform especially when mechanism 10 is
mounted on the work station.
3o An alternate form of electric circuit actuating
mechanism 10 according to the preferred teachings of the
present invention is shown in Figures 6 and 7 and includes
a housing 12'. Housing 12' includes channel 14 having
bottom 16, sides 18 and end walls 24' and 26' integrally
3s extending generally perpendicular between and having
heights equal to sides 18. End wall 26' mounts outlet 82
and the strain relief for cord 84. End wall 26' further
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-18-
1 includes first and second slots 150 formed adjacent its
top edge and spaced from each other. Standoffs 152 are
formed in channel 14 on sides 18 adjacent and parallel to
end wall 24' and spaced from end wall 26' and having a
height less than the heights of sides 18. Divider 28 has
a size for slideable receipt in channel 14, with the
height of plate 30 being generally equal to the height
of standoffs 152 such that when plate 30 is received in
slides 34, plate 32 extends generally parallel to bottom
l0 16. Plate 32 includes apertures 154 generally aligned
with standoffs 152.
Mechanism 10 further includes mount 90' having a
generally planar top plate 92' of a size generally equal
to and for abutting with the top edges of sides 18 and
1s walls 24' and 26' of channel 14. Ears 156 are integrally
formed with the lower surface of top plate 92' for receipt
in slots 150 of channel 14 for removably, slideably inter-
connecting mount 90' to channel 14. Plate 92' further
includes apertures 158 generally aligned with standoffs
20 152 but of a size substantially larger than apertures 154.
Ears 160 are integrally formed with the upper surface of
top plate 92' generally opposite to ear 156. Ears 162 are
integrally formed with the upper surface of top plate 92'
adjacent to but spaced from end wall 26'. Slots 164
25 extend through top plate 92' adjacent to but spaced from
divider 28.
Mount 90' generally includes a frame 166 separately
formed from top plate 92' and including protuberances 106
including apertures 108 for slideably receiving stems 130
30 of cover 124, pivot ears 110 for actuator arms 112 and 114
and pivot ears 98 for actuator lever 100 of the type as
disclosed for mechanism 10 of Figures 1-5. The lower edge
of frame 166 includes a flange 168 which is slideably
received in ears 162. The upper edge of frame 166
35 includes hooks 170 for snap type receipt in slots 164 when
flange 168 is inserted in ears 162. Thus, frame 166 is
removabiy interconnected or secured to plate 92' by a
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCTlUS97/20588
-19-
1 sliding interfit between ears 162, flange 168, slots 164
and hooks 170 and specifically without the use of screw,
threaded, or other types and forms of fasteners. In the
most preferred form, actuator lever 100, actuator arms 112
and 114, springs 102 and 134, and cover 124 are assembled
to frame 166 before its securement to top plate 92' and
before mount 90' is positioned on channel 14. It should
then be appreciated that mount 90' can be removed from
plate 92' by moving hooks 170 from beneath the lower
1o surface of plate 92' so that they pass through slots 164,
with heads 128 being accessible when mount 90' is removed
from top plate 92'.
Housing 12' further includes a lid or cover 172
having an annular collar 1?4 fox abutment with plate 92'
1s opposite to end wall 26' and sides 18 and of a size for
slideable receipt of cover 124 so that cover 124 tele-
scopes within collar 174 in a similar manner as cover 124
telescopes inside of walls 22, 24, and 26 of Figures 1-5.
The lower edge of collar 174 includes slots 176 for
2o slideable receipt of ears 160 of mount 90' for removably,
slideably interconnecting cover 172 to mount 90'. A
U-shaped plate 178 extends from the upper edge of collar
174 for abutment with plate 92' of mount 90'. A U-shaped
actuator guide 54' integrally extends from plate 178
2s adjacent its upper edge in a direction parallel to the
slide or actuation direction of actuator 42 and integrally
extends from collar 174. Guide 54' has a size and shape
for slideably receiving front 44 of actuator 42. In the
most preferred form, the first and second portions of
ao guide 54' on opposite sides of actuator 42 include
apertures 180 which are aligned with apertures 182 formed
in legs 46 of actuator 42 in its off position, with
apertures 180 and 182 extending in a nonparallel manner
and preferably perpendicular to the actuation or slide
35 direction of actuator 42. Thus, the elongated clasp of a
conventional padlock 184 can be inserted through apertures
180 and 182 to prevent actuator 42 from sliding from its
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/LIS97/20588
-20-
1 off position and relative to guide 54' of housing 12'.
Plate 178 includes sockets 186 generally aligned with
standoffs 152 and of a size for slideable receipt within
apertures 158 but larger than apertures 154 so that
sockets 186 abut with plate 32. Screws 188 pass through
sockets 186 and apertures 158 and 154 and are threadably
received within standoffs 152 for securing channel 14,
mount 90' and cover 172 together at a position spaced from
the lower ends of mount 90', cover 172 and channel 14 and
1o from end wall 26'. The heads of screws 188 are located
within sockets 186 and have an extent generally equal to
or slightly recessed below the outer surface of plate 178.
It should then be noted that cover 172 sandwiches plate
92' against the top edges of channel 14, that plate 92'
i5 sandwiches divider 28 in channel 14, and that sockets 186
sandwich plate 32 against standoffs 152. In the most
preferred form, cover 172 includes an integral skirt 190
integrally extending from its outer periphery and
extending over the outer periphery of plate 92' and the
2o top portions of the outer periphery of channel 14.
operation of mechanism 10 of Figures 6 and 7 according
to the teachings of the present invention is substantially
the same as set forth for mechanism 10 of Figures 1-5.
However, actuator 42 is located in its off position and is
25 prevented from sliding to its on position by the clasp of
padlock 184 extending through apertures 180 and 182 and
thereby preventing movement of legs 46 relative to guide
54'. To start the motor, the operator must first remove
the clasp of pladlock 184 from apertures 180 and 182.
3o With padlock 184 removed, the operator may now depress
planar front 44 of actuator 42 to move switch 36 from
its off position to its on position to maintain a closed
circuit between the power supply and the motor being
controlled. It can then be appreciated that actuation of
ss switch 36 and energization of the circuit does not occur
as the result of movement of cover 124.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-21-
1 It should then be appreciated that housing 12'
according to the preferred teachings of the present
invention is particularly advantageous as the various
components are snapped or slid in place and secured
s together with only two screws 188. Specifically, after
the proper positioning of actuator lever 100, actuator
arms 112 and 114, and spring 102 on frame 166 and springs
134 on pins 126 of cover 124, heads 128 can be snapped
through apertures 108 to retain cover 124, lever 100, arms
io 112 and 114, and springs 102 and 134 to frame 166. At
that time, flange 168 can be slid into ears 162 and hooks
170 snapped into slots 164 to secure frame 166 and all the
components retained thereon to plate 92'. At that time
and after divider 28 and all the components retained
is thereon have been positioned in channel 14, ears 156 can
be inserted into slots 150 and plate 92' pivoted about an
axis defined thereby to abut with the top edges of channel
14. At that time, slots 176 can be inserted unto ears 160
and cover 172 pivoted about an axis defined thereby to
2o abut with plate 92' of mount 90'. At that time, screws
188 can be extended through sockets 186 and apertures 158
and 154 and threaded into standoffs 152 which prevent
pivoting of cover 172 about the axis defined by ears 160
and slots 176 and prevent separation of the components of
2s mechanism 10.
It can be appreciated that frame 166 can be secured to
plate 92' of mount 90' in other manners according to the
teachings of the present invention. As an example, frame
166 could be removably secured to plate 92' by sliding on
3o plate 92' in a plane parallel to plate 92' and into ears
arranged in a U-shape and held in position by a detent or
hook member. After frame 166 is slid in place, actuator
lever 100, actuator arms 112 and 114, and spring 102 could
be positioned on frame 166. Cover 124 with springs 134
3s thereon could then be snapped into position on frame 166.
CA 02271415 1999-OS-11
WO 98/21732 PCT/US97/20588
-22-
1 It can be appreciated that after assembly in this manner,
access to heads 128 may not be easily available making
disassembly difficult if not impossible without damage.
Now that the basic teachings of the present invention
s have been explained, many extensions and variations will
be obvious to one having ordinary skill in the art. For
example, although in the most preferred form, a single
switch 36 is utilized to both energize and de-energize the
electric circuit, the electric circuit could be separately
to energized and de-energized. In this regard, a second
switch 142 shown in phantom in Figures 3 and 5 could be
provided to de-energize the electric circuit. In this
regard, switch 142 could be actuated by a protuberance 144
formed on switch lever 70 in the form shown and/or secured
is to actuation finger 104. Likewise, switches 36 and/or 142
could be of the momentary type, with switch 142 shown in
the preferred form of the momentary type.
Likewise, although outlet 82 and cord 84 are shown in
the preferred form mounted to divider 78 or end wall 26',
2o divider 78 and end wall 26' according to the teachings of
the present invention could include knockouts for passage
of electric lines so that switches 142 and/or 36 or other
electric controls provided in mechanism 10 can be directly
wired between the source of power and the power tool or
z5 the like being controlled.
Further, although cover 124 is movably mounted to
housing 12 by a multiplicity of pins 126 sliding through
apertures 108 and positioning springs 134 between cover
124 and housing 12 in the preferred form, other manners of
3o movably mounting cover 124 relative to housing 12 and
which enables any point of the broad surface to move in
the actuation direction can be utilized including but not
limited to springs or other biasing members spaced from
pins 126, the construction shown in U.S. Patent No.
35 5,510,587, or the like.