Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -1- PATENT APPLICATION
ARC DISCHARGE LAMP CONTAINING BARIUM
HAVING IMPROVED ARC TUBE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
This invention relates to arc discharge lamps,
and is directed more particularly to a mercury-free
fluorescent lamp.
2. Description of the Prior Art
Arc discharge lamps, such as fluorescent lamps,
are well known in the art and customarily include an
arc tube filled with a rare gas and mercury. While
such lamps are extensively used and in general perform
quite well, the presence of mercury in the lamp may
generate environmental and safety problems. Mercury
is a toxic heavy metal and lamp disposal may be
hazardous. The cost of safe disposal adds to the cost
of the lamp. Accordingly, it is deemed advantageous
to the environment, to safety in manufacture of such
devices, and to reduction of costs, to provide an arc
discharge lamp which includes no mercury but which
performs at least as well as the traditional mercury
lamp.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is, therefore, an object of the invention to
provide an arc discharge lamp in which the contents of
the arc tube are substantially devoid of mercury.
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -2- PATENT APPLICATION
With the above and other objects in view, as will
hereinafter appear, a feature of the invention is the
provision of an arc discharge lamp comprising an arc
tube of a material selected from a group of materials
consisting of yttria, gadolinium oxide, and terbium
oxide, the arc tube containing a fill comprising a
rare gas, and containing metallic barium. An arc tube
mount supports the arc tube at either end of the arc
tube. The arc tube and the arc tube mount are
disposed in an outer glass jacket, and a base member
closes the outer glass jacket.
The above and other features of the invention,
including various novel details of construction and
combinations of parts, will now be more particularly
described with reference to the accompanying drawings
and pointed out in the claims. It will be understood
that the particular device embodying the invention is
shown by way of illustration only and not as a
limitation of the invention. The principles and
features of this invention may be employed in various
and numerous embodiments without departing from the
scope of the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Reference is made to the accompanying drawings in
which is shown an illustrative embodiment of the
invention, from which its novel features and
advantages will be apparent.
In the drawings:
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -3- PATENT APPLICATION
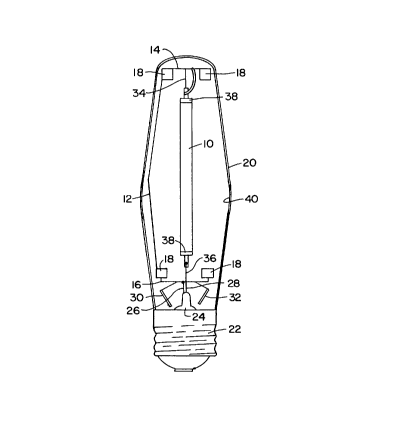
FIG. 1 is a diagrammatic elevational view of one
form of an arc discharge lamp illustrative of an
embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 2 is a schematic representation of a lamp
driving electrical circuit; and
FIG. 3 is a graph illustrating the intensity of
barium emission at various wavelengths in a barium
discharge lamp.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Referring to the drawings, it will ~be seen that
an illustrative lamp includes an arc tube 10 for
containing a fill gas. The arc tube 10 preferably is
of yttria (Y203), but may, alternatively, be of
gadolinium oxide or terbium oxide, all of which have
proven resistant to reaction with barium. The former
is described in U.S. Patent No. 4,166,831, issued
September 4, 1979 to William H. Rhodes, et al. Doping
of the arc tube materials, for example with alumina or
lanthana, improves the sinterability. During
processing, the arc tubes may be brought to high
density (about 95% or greater of theoretical density)
and high translucency (at least 85% total
transmission) by sintering at around 2100°C in an
atmosphere of low oxygen partial pressure. Typical
total transmission values for the arc tubes are around
95%. While sizes and shapes of such tubes may conform
to the desired use, a particular configuration found
acceptable is of a cylindrical shape and about 51.9 mm
in length, end-to-end, and about 6.4 mm in diameter.
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -4- PATENT APPLICATION
The arc tube 10 contains a fill gas which
includes a rare gas, and also contains 5 to 20
milligrams of metallic barium. The rare gas may be
neon or xenon, or the like and may be in the pressure
range of 1-100 Torr. The arc tube 10 may further
include additions, such as metallic sodium and/or
calcium and/or strontium, to balance color. The
barium has been found to radiate in such a manner as
to produce white light, discussed further hereinbelow.
An electrically conductive arc tube mount 12
supports the arc tube 10 in known fashion. The arc
tube mount 12 is of a rigid material, such as
stainless steel, nickel, molybdenum, or the like. The
arc tube mount 12 includes an upper crossbar 14 and a
lower crossbar 16. A plurality of spring-like members
18 are affixed to the arc tube mount 12 for contact
with a glass jacket 20.
The glass jacket 20 is fixed to a base member 22,
typically a screw-type base member of nickel plated
brass, for insertion into a threaded electrical
receptacle (not shown). A glass stem member 24 is
sealed to the jacket 20 and projects thereinto.
Electrical connectors 26, 28 are sealed into, and pass
through the stem member 24, to provide electrical
connections from the exterior to the interior of the
glass jacket 20.
The arc tube mount 12 is affixed to one of the
electrical connectors 26. A pair of getters 30, 32
are attached to the arc tube mount 12 and serve to
insure the integrity of the evacuated jacket 20 by
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -5- PATENT APPLICATION
absorbing from the interior of the jacket any oxygen
present.
The arc tube 10 includes an electrode 34, 36 at
either end thereof. One electrode 34 is affixed to
and is supported by the crossbar 14 of arc tube mount
12, while the other electrode 36 is insulatedly
supported by the other crossbar 16, but is
electrically connected to the electrical connector 28
passing through the stem member 24. The electrodes
34, 36 preferably are of tungsten coated with an
emitter compound for reducing the electrode operating.
temperature. In one embodiment, the emitter is a
barium-calcium-tungsten composition of the type used
in high pressure sodium lamps.
Heat conserving end seals, or bands, 38
preferably are wrapped around the arc tube 10 at each
end thereof proximate the electrodes 34, 36, in order
to reduce heat differential between the ends of the
arc tube 10 and the center of the arc tube l0. The
bands 38 may be of an axial length (i.e., width of
band) of about 6.0 mm.
The glass jacket 20 is evacuated and may be
provided with a interior coating 40 of phosphor.
In operation, a voltage is applied across the
electrical connectors 26, 28, and thence to either end
of the arc tube 10 by the electrode 36 and the arc
tube mount 12 and electrode 34, ionizing the rare gas
in the arc tube 10, which quickly heats the arc tube
10. The lamp's color is initially dominated by rare
gas spectral emission, but as the tube heats, the
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -6- PATENT APPLICATION
barium begins to radiate. The lamp assumes its' white
color from barium atomic and ionic spectral emission
at 455, 493, 553, 614, 650 nanometers. A typical
spectrum for a lamp made with an alumina doped yttria
arc tube filled with 10 milligrams of barium and 33
Torr Xenon at a current of 2.5 amps and arc tube
center temperature of 900°C is shown in FIG. 3. In an
alternative embodiment, it appears that the near
ultraviolet emissions from the neutral barium atom
could excite the phosphor layer 40 on the inside
surface of the outer jacket, which would improve the
color of the lamp emission.
Inasmuch as there is a saturated vapor in the arc
tube 10, the lamp must be operated on alternating
current to avoid cataphoresis, that is, migration of
all active ions to one end or the other of the arc
tube. An alternating voltage source and ballast
impedance assembly is required. Referring to FIG. 2,
it will be seen that a switched direct current may be
used to drive the lamp. An output of a current
limited D.C. supply 50 is routed to an "H-Bridge"
switching circuit 52 via a ballast impedance 54. The
switching circuit 52 includes a switcher 56, the
switching frequency being driven by a clock 58. The
small voltage maintained across the impedance 54
protects the switching circuitry from transients.
It is to be understood that the present invention
is by no means limited to the particular construction
herein disclosed and/or shown in the drawings, but
also comprises any modifications or equivalents within
CA 02274199 1999-06-09
98-1-334 -7- PATENT APPLICATION
the scope of the claims. For example, while a screw
type base member has been shown and described, it will
be apparent to those skilled in the art that other
types of base members are in use and readily can be
used in the instant lamp.