Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98I03200
METHOD AND DEVICE FOR FORMING ARTICLES FROM PULP SLURRY
This invention relates to forming machines more particularly for
producing components from a paper pulp or slurry. Egg separators and . egg
boxes are typical examples of components of this kind. although the same
forming process or a similar one is, or may be, used to form containers and
other articles for a variety of purposes.
A known forming machine for making such components requires a
relatively massive surrounding frame to withstand the pressures applied during
a press operation at a press station of the machine. The force required to
press
the paper pulp or slurry into the required shape at the press station may be
in
the order of 20 tons or so and is usually provided by hydraulics.
Consequently, the frame needs to be extremely strong to continually withstand
the very considerable forces involved and the cost of the massive frame tends
to add very considerably to the overall costs. The cost of the frame will
depend upon the size of the machine itself but, typically, may be in the order
of ~ 135,000 or so. There may be other disadvantages of the machine related
to providing the required pressing force; such disadvantages may relate e.g.
to the additional bulk of the machine (i.e. hydraulic ram) and/or to
additional
noise or inconvenience of operation or even undue inefficiency. Furthermore,
the press station is normally pre-set to press the article being formed under
a
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PC'TIGB98/03200
2
particular pressure to a particular thickness. Thus, it tends to be
disadvantageous that, since the machine has been preset to operate at a
particular pressure to press a particular article to a certain thickness,
there is
little control to vary the applied pressure and/or thickness of the article
(without resetting press dies) more particularly in a controlled way to vary
the
,quality and/or characteristics of the article in an accurately predictable
manner.
Additionally, it may be that the temperature required for drying the pressed
article is higher than need be the case andlor the drying time may be longer
than need be the case. At least in some instances, known press stations may
not be able to produce the required shape of an article accurately enough
(e.g.
a 1 ° or 2° angle on a product 100 millimetres deep).
Furthermore, the actual
finish on every surface of the article may not be suitably consistent (e.g.
the
inside surface of an egg box formed from paper pulp is usually irregular and
not as aesthetically pleasing as the exterior).
It is believed that known forming production methods for articles made
from paper or fibre may not provide an article which is of a similar quality
to
that which can be produced from plastics or polystyrene (at least in some
respects) and this tends to adversely affect the marketability of articles
formed
from paper/fibre.
t
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99!22069 PCT/GB98/03200
3
An object of the invention is to at least alleviate one of the
aforementioned, or other) disadvantages associated with forming machines or
press stations and/or to provide a forming machine (or press station) which is
improved in at least some respect.
According to the invention there is provided a forming machine for
forming articles from pulp or slurry, comprising a press station having upper
and lower perforate dies mounted, in use, for relative reciprocatory movement
towards and away from one another and each said die being housed, in use, in
an associated one of a two part chamber, said chamber parts being arranged
to seal together when moved towards one another, and means for evacuating
the sealed chamber whereby a final part of relative movement of the dies
towards one another is caused by the evacuation.
Further according to invention there is provided a press station for a
forming machine for forming articles from a paper or fibre slurry, the press
station including a chamber housing, in use, die means for forming an article
and means to evacuate the chamber in order to press the article in the die
means.
Further according to the invention there is provided a forming machine
including at least one press station in accordance with the immediately
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
4
preceding paragraph.
Still further according to the invention there is provided the
combination of a forming machine in accordance with the immediately
preceding paragraph and a relatively lightweight support frame (weight less
than 7 tons and possibly not more than 2 tons and preferably 3 tons or less or
6 tons or less).
Still further according to the invention there is provided a method of
forming an article by pressing the article in die means, said method
comprising
evacuating a chamber surrounding the die means to provide sufficient pressure
to press the article.
Still further according to the invention there is provided an article when
made by the method according to the immediately preceding paragraph.
According to the applicant, advantageously, the required press loading
force may be attained relatively easily in accordance with embodiments of the
invention, thus substantially obviating the need for a hydraulic pressure ram,
and most significantly, enabling a relatively lightweight and much less costly
frame to be used instead of a massive framework. In embodiments of the
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200 .
present invention the cost of the framework could be reduced by, for example,
40% or so. The saving in weight may be greater than 70% and preferably is
greater than 40% or 50%.
In the press station, the die means may comprise an upper perforate die
or die set co-operable with a lower perforate die or die set in order to press
form an article from paper pulp when said dies/die sets are brought together.
The dies/die sets will usually be relatively reciprocable towards and away
from
one another. It is possible that only the upper die/die set is movable.
The chamber evacuation means preferably comprises a vacuum pump
and the degree of vacuum control applied is preferably variable, for example,
by means of a vacuum valve (variable orifice valve). Additionally or
alternatively, a vent valve may be provided to ambient (atmospheric)
conditions surrounding the chamber.
The chamber is, preferably, in two main parts or halves that can seal
together in use and, preferably) one or each main part/half has a slidably
mounted external skirt (preferably a flanged skirt) and of said skirts may be
provided with a seal co-operable with the opposing skirt to form a sealing
effect when the chamber parts/halves are closed together. Stops may be
provided to limit the retraction and/or extension movement of the skirt
relative
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99122069 PCT/GB98103200
6
to the associated chamber part/half. Alternatively, one chamber part/half may
be slightly larger than the other and be slidably and sealably engageable with
the other. Preferably, at least one of said main parts or halves of the
chamber
is float mounted on a member for moving said chamber partlhalf towards and
away from the opposing chamber part/half.
The forming machine may include a forming station associated with or
serving a plurality of press stations.
Still further according to the invention there is provided an article (e.g.
an eggbox) press formed from a paper or fibre slurry said article being smooth
on all surfaces.
Still further according to the present invention there is provided a press
station for a forming machine for forming articles from a paper or fibre
slurry,
the press station comprising one or more of the following features:-
a) evacuation means to evacuate a chamber surrounding press dies
in order to provide a pressing force;
b) a press die mounted on a floating head;
c) two chamber parts or halves, one or each having a slidably
mounted skirt;
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
7
d) evacuation means as in a), said means being variable to vary the
degree of vacuum in the chamber;
e) means for pressing an article with smooth surfaces in a
controlled way.
Many advantageous features of the invention will be apparent from the
following description and drawings.
Embodiments of the invention will now be described, by way of
example only, with reference to the accompanying simplified diagrammatic
drawings in which:-
FIGURE 1 shows a known forming machine;
FIGURE 2 shows a sectional view of a first embodiment of a press
station of a forming machine in accordance with the invention, with dies
separated;
FIGURE 3 shows substantially the same view as FIGURE 2 with the
dies closed together;
' FIGURE 4 shows an enlarged elevational view of two chamber parts
of the press, and
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
8
FIGURE 5 shows a view of a further embodiment of a press station.
FIGURE I shows schematically a prior art forming machine supported
by a relatively massive frame and aspects of the machine salient to .the
invention are now discussed.
In FIGURE l, the known forming machine comprises a relatively
massive surrounding frame only diagrammatically shown as including uprights
10,12 and cross-members 14. In use, the uprights 10) I 2 are fixed to the
ground.
The forming machine has a first station generally indicated by the
reference (Forming), a second station (Press) and a third station (Conveyor)
which is the loading end of a conveyor indicated by the reference numeral 16.
In the forming station a tank 20 contains paper slurry. A first platen
22 carries a moulding tool 24 which may be a male die and this is arranged
with a motorised drive 18 for lowering the whole platen and tool into the tank
20. The drive 18 may be a hydraulic or pneumatic ram, or an electric motor,
for example driving a rack and pinion or a toothed belt drive system for
lowering the platen 22 and tool 24 into the tank 20 and subsequent raising out
of the tank. The platen 22 is associated with vacuum means (for removal of
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
9
steam or water vapour or the like and/or for adhering pulp to the platen by
"suction" or releasing the pulp from the platen by blowing) and the tools are
suitably perforate, so that water may be drawn through the tool 24, depositing
pulp on its surface. Water continues to be drawn from the pulp when, the
platen 22 has been elevated out of the tank 20.
In vertical alignment with the platen 22 and tool 24 is a second platen
26 and tool 28 which may be a female die. It will be appreciated that the dies
24, 28 are matched, usually so as to produce a component (moulding) of
substantially constant thickness at alI points between the dies. Platen 26 and
tool 28 are mounted on a lifting and lowering mechanism here illustrated as
hydraulic ram 30. The hydraulic ram 30 could be replaced by pneumatic
means.
As will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, the platens 22, 26
may carry a plurality of tool sets for use in manufacturing a plurality of
identical (or different) articles in a single operation.
At a stage after the Iower platen 22 and tool 24 have been elevated, the
upper platen 26 and tool 28 are lowered into contact with the wet pulp formed
on the lower tool. At this stage, the pulp is very fragile and its thickness
is
greater than the desired finished thickness of the article.
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PC'T/GB98/03200
The vacuum on the lower platen 22 is released and a slight positive
pressure is applied via the perforations (not shown). Simultaneously, light
vacuum is applied via the perforations (not shown) in the upper platen 26.
This causes the fragile moulding to separate from the lower platen 22 , and
temporarily adhere to the upper platen 26, which platen 26 is then raised
clear
of the tool 24 on the lower platen. The lower platen 22 and tool 24 are then
lowered into the tank 20 to begin a subsequent forming operation.
The upper platen 26 and tool 28 complete with the fragile moulding
(not shown) are then transferred on to the press station and the moulding is
lowered into contact with the die or tool 32 (generally similar to tool 24)
carried on the lower platen 34 in the press station. The fragile moulding is
then transferred from the upper tool 28 to the lower tool 32 e.g. by positive
pressure applied to the upper die and negative pressure applied to the lower
die
and the tool 28 is then returned to the forming station to repeat the cycle
for
the next fragile moulding (not shown).
In the press station, when the tool 28 is removed, a second similar
upper tool 36, carried by platen 38 of an upper press head is lowered into
contact with the fragile moulding supported on lower tool 32. The tools 36,32
may be closed together more closely than tools 24,28 so as to squeeze the
fragile moulding to a reduced thickness and initiate removal of further water.
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99!22069 PCT/GB98/03200
11
Each of the tool systems 32,36 on the respective platens 34, 38 may be
associated with corresponding vacuum systems and additionally both are
provided with heating means (usually electrical); as is the platen 26, which
causes the production of steam which is also withdrawn through the vacuum
systems. The removal of steam dries the pulp and hardens the moulding, and
the dried and finished moulding may be carried by the tool 36 and deposited
on the conveyor 16. This latter transfer of the moulding is effected by
releasing the moulding from the lower tool 32 by air pressure and retaining
the
moulding on the upper tool 36 by vacuum.
The press operation requires a very considerable force, depending upon
the required degree of compression of the pulp and upon the total area of the
respective platens and the number of components (mouldings) which are being
manufactured. A force equivalent to a number of tons (e.g. over 20 tons) may
be required and this necessitates a substantial and relatively massive frame
to
withstand pressure applied by hydraulic ram 40 carrying the upper press head
of tool 36 and platen 38, and in particular to repeatedly withstand or absorb
the reaction force during the pressing step.
The complete assembly of hydraulic cylinders 30, 40 (cylinder 30 may
be pneumatic) with the two upper platens 26, and tools is reciprocated
generally in the directions of the letter A in transferring mouldings from one
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99122069 PCTlGB98J03200
12
station to the next and to the conveyor, possibly on a beam carried by the
structural framework. The pressure to be exerted at the forming station on the
paper slurry in forming the article is not high in relation to the 20 tons
pressure required at the press station and thus the massive framework 10,12,14
is not necessitated by the forming station.
The invention is concerned with a modification to the press station of
the aforedescribed known type of forming machine, which modification may
alleviate the need for the hydraulic ram of the press station or at least the
high
specification of same and/or alleviate the need for a relatively massive
framework 10,12.
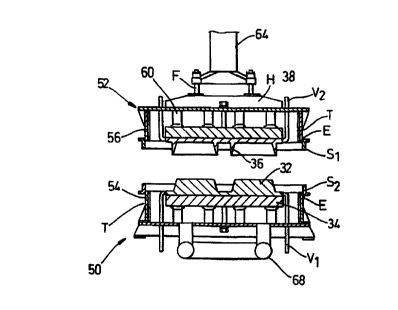
In the illustrated embodiment of the invention shown in FIGURES 2
to 4, a press station has a chamber comprising a lower part or half 50 and an
upper part or half 52. The chamber 50,52 is provided as part of the press
station (not shown in full in FIGURES 2 to 4) of the forming machine. Each
half 50, 52 may be, for example, substantially rectangular with a peripheral
wall 54,56 and the upper half may be dimensioned so as to be a free sliding
fit in the lower half when the two move together more particularly as shown
in our prior patent specification No.9722547.8 forming the priority document
for this application and as shown in FIGURE 5. The word "half' is used in
a merely indicative sense; the two halves could be of widely different volume,
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99122069 PCT/GB98103200
13
although in the embodiment shown in FIGURES 2, 3 and 4 the two "halves"
are very similar in shape and size. As shown in patent specification
No.9722547.8 and as shown in the embodiment of FIGURE 5, sealing may be
effected by an O-ring or the like 58 extending around the periphery of the
external face of the smaller of the two halves 50, 52 so as to seal on the
inner
face of the skirt of the larger of the halves. Alternatively, a highly
resilient
face seal could be used between the two halves. As shown in FIGURES 2 and
3 of this specification a preferred modification has been made to the chamber
halves 50, 52 which includes a spring loaded sliding flanged skirt 51, 52
being
provided on the external wall 54, 56 of each chamber half respectively. A
sliding seal E is provided on each chamber half 50, 52 which allows vertical
reciprocation of the skirt 51, 52 relative to the external wall 54, 56 within
fixed limits. A stop T is provided in the form of a projecting annular edge on
each external wall 54, 56 to limit the retraction movement of each skirt 5 I ,
52
relative to the external walls 54, 56 in a manner which should be evident from
FIGURE 2. If desired, in an alternative embodiment only one skirt (e.g. upper
skirt 51 ) is slidable, the other skirt (e.g. 52) being fixed.
Each of the chamber halves S0, 52 in FIGURE 2 carries a platen and
dies which are generally the same as those shown in the press station in
FIGURE 1 and thus bear the same reference numbers 32, 34, 36, 38.
However, instead of mounting the upper platen 38 on the ram of a hydraulic
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
14
cylinder for pressurisation, which is the arrangement in FIGURE l, in FIGURE
2 and FIGURE 3 the upper platen 38 is carried on stand-off pins 60. It will
be appreciated that the perforate dies 32, 36 communicate with passages which
in this case may extend through the platen 34, 38 to the interior of the half
chamber 50, 52 as well as being ducted away by a secondary vacuum system
V,, V2. The secondary vacuum system V1, V~ is for transfer of the moulded
article and steam extraction which is the case in the arrangement shown in
FIGURE 1.
The upper chamber 52 half is shown float mounted on a member 64
extending vertically, which member may be reciprocated by an electric motor,
for example, so as to carry it between a remote position and a position in
which the chamber halves 50, 52 are engaged sufficiently for the sliding
skirts
S,, SZ to engage with the seal mounted in the upper annular edge of skirt S,
engaging the lower annular edge of skirt S~. Instead of providing a hydraulic
ram to complete the stroke and apply the required pressure, a vacuum pump
is connected through manifold 68 and main vacuum valve 70 (see FIGURE 4)
to the interior of the chamber so that once the seal is engaged, the chamber
S0,
52 can be evacuated. Evacuation of the chamber 50, 52 not only draws water
from the formed moulding but also draws the chamber halves together to close
the dies 32, 36 about the moulding finally, preferably, to a point at which
peripheral abutment faces on the dies come into contact so as to prevent
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
further movement.
Lowering the pressure within the enclosure (chamber 50, 52)
surrounding the press-heads (platens and dies 32, 34, 36, 38) also reduces
,the
temperature at which water in the pulp evaporates, thereby requiring lower
temperatures of the heated platens and/or reduced times for the drying
operation.
One or other or both of the platens 34,38 will be heated in a similar
fashion as in the FIGURE 1 arrangement.
According to a further feature of the invention, a single forming station
generally as shown in FIGURE 1 may be associated with a plurality of press
stations as shown in FIGURE 2 and FIGURE 3. The significance of this
further feature is that the required water extraction and drying operation
requires a substantially longer time than the forming operation carned out in
the first stage as in the FIGURE 1 apparatus, and for increased speed of
production the press operation can be carned out in two or more stages.
Hence, each horizontal reciprocation in the direction of the arrow A will
transfer during a first half of the reciprocation (to the right in FIGURE 1 )
a
' formed wet moulding from the farming station to a first press operation
stage,
and transfer a pressed and part dried moulding from the first press stage onto
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99122069 PCTlGB98/03200
16
a second press stage and so on according to the number of press stations
provided, whilst the second half of each reciprocation (movement to the left
in FIGURE 1 ) returns the tools 28, 3b to the initial position so that a
further
cycle can commence.
It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that in the formation
and handling of components made from wet paper slurry the mouldings are of
varying degrees of fragility at ail times during the process. The strength of
the
mouldings increases as the compression and drying continue from stage to
stage but the pressures applied, particularly when a positive air pressure is
provided to blow a moulding off one die on to another, must be controlled
within fine limits. According to the applicant, the atmospheric pressure which
is possible upon a relatively large area chamber when the vacuum is applied
may be excessive and could possibly lead to an undesirably high pressure
being applied to the mouldings unless limited by abutments on the dies.
Therefore, according to a feature of the invention, means is provided for
limiting the degree of vacuum in the sealed chamber or chambers (where more
than one press station is provided) and possibly for continuously admitting
ambient air under volumelpressure control (and this may sweep the chambers
to evacuate all steam and water when both air is applied and vacuum applied
at one and the same time). This feature may accelerate the operation in each
press stage leading to a higher throughput from any one machine. To this end
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99122069 PCTlGB98103200
17
FIGURE 4) showing an enlarged view of the chamber 50, 52 shown in
FIGURE 2, includes a variable orifice vacuum control valve 100 extending
from the upper half 52 to limit the degree of vacuum in the sealed chamber.
Additionally, an atmospheric vent valve 101 is shown in order to
continuously admit ambient air when required.
A further very important feature of the invention is the provision of the
guided, resilient floating mounting F of the head or unit H in carrying the
upper platen 38, die 36 and chamber half 52.
It is to be understood that the scope of the invention is not to be unduly
limited by the particular choice of terminology and that a specific term may
be replaced by any equivalent or generic term. For example, the term
"machine" could be replaced by "apparatus" or "article" could be replaced by
"product".
Further it is to be understood that individual features, method or
functions relating to the forming machine or press station or evacuation
arrangement might be individually patentable. In particular, any disclosure in
this specification of a range for a variable or parameter shall be taken to
include a disclosure of any selectable or derivable sub-range within that
range
CA 02276106 1999-06-24
WO 99/22069 PCT/GB98/03200
18
and shall be taken to include a disclosure of any value for the variable or
parameter arranged within or at an end of the range. The singular may include
the plural or vice versa.