Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CLAIMS.
What is claimed is:
1. A method and system for encoding a video session wherein the encoding
process results in the generation of an Encoded Video Session (EVS), and where
the EVS comprises:
a) Un-coded Broadcast Video Data (UBVD); and
b) Video Object Information (VOI) data.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein a UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast Video
Data) session comprises a succession of video frame images, or the UBVD video
session can be divided into a succession of video frame images.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein a minimum of one video image object
contained within a minimum of one video frame image of the UBVD, is
designated as being user selectable.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the Video Object Information (VOI) for
each user selectable object comprises:
a) Product Caption Data (PCD); and
b) Object Location Data (OLD).
5. The method of claim 1 and claim 4, wherein a plurality of objects can be
designated as being user selectable, and wherein each User Selectable Object
(USO) can be assigned a unique Object Identification Code (OIC).
6. The method of claim 1, claim 4 and claim 5, wherein the PCD (Product
Caption Data) for each USO (User Selectable Object) may/will comprise:
a) product identification code;
b) product description data;
c) product price data;
d) product manufacturer data; and
e) an Internet Access Information (IAI) hyperlink.
7. The method of claim 2, wherein a UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast Video
Data) session comprises a succession of video frame images, or the UBVD video
session can be divided into a succession of video frame images, and further
wherein each video frame image can be assigned a Video Session Frame
Identification Code (VSFIC).
8. The method of claim 4, wherein the USO (User Selectable Object) Object
Location Data (OLD) comprises a plurality of Object Frame Location (OFL)
elements, and wherein an Object Frame Location (OFL) data further comprises:
a) the VSFIC (Video Session Frame Identification Code)
corresponding to the video frame image in which the USO (User
Selectable Object) appears;
b) OIC (Object Identification Code) for each USO contained within
the video frame image; and
c) the USO's X and Y co-ordinates as determined by the objects
position within the video frame image, and wherein the OFL
data is represented in an EVS standard format.
9. The method of claim 4, claim 4, claim 5, claim 6, claim 7 and claim 8,
wherein
the said VOI (Video Object Information) is represented by a hierarchy
comprising:
a) Object Caption Structure (OCS); and
b) Object Frame Structure (OFS).
10. The method of claim 9, wherein the OCS (Object Caption Structure)
further comprises an array of elements, and wherein each element will/may
comprise:
a) OIC (Object Identification Code);
b) product identification code;
c) product description data;
d) product price data;
e) product's manufacturer data; and
f) an Internet Access Information (IAI) hyperlink
11. The method of claim 9, wherein the OFS (Object Frame Structure) further
comprises a double dimensional array of elements, which array of elements is
indexed by an OIC (Object Identification Code) and the VSFIC (Video Session
Frame Identification Code), and wherein each element (being an Object Frame
Location (OFL) element), will/may comprise:
a) OIC (Object Identification Code);
b) VSFIC (Video Session Frame Identification Code); and
c) the object's X and Y co-ordinates as determined by the objects
position within the video frame image and represented in a EVS
standard format.
12. A method and apparatus providing an Operator User Interface (OUI) which
allows an operator to interface with a Video Session Encoder (VSE), and
wherein
the OUI comprises a means of:
a) defining those object's contained within the video frame image
that are to be user selectable;
b) assigning each USO an Object Identification Code (OIC); and
c) inputting OCD (Object Caption Data) for each USO (User
Selectable Object).
13. The method and apparatus of claim 12, wherein the VSE (Video Session
Encoder) and the OUI (Object User Interface) allow a method of generating the
OFS (Object Frame Structure) data for each USO (User Selectable Object), and
wherein the object's X and Y coordinates are generated by means of operator
input, and the method and apparatus further comprises:
a) a UBVD(Un-coded Broadcast Video Data) displayed
continuously on a Video Display Facility(VDF);
b) a position sensor integrated with the VDF (Video Display
Facility);
which is controlled by operator input and which is capable of
outputting Position Sensor Data (PSD);
c) a method of formatting position sensor data into EVS standard
format; and
d) a method of associating a USO's (User Selectable Object) X
and Y coordinates to a VSFIC (Video Session Frame
Identification Code);
14. A method in accordance with claim 12 and claim 13, wherein the USO
(User Selectable Object's) OCD (Object Caption Data) may be inputted either
prior to/or following the inputting of the OFS (Object Frame Structure) data.
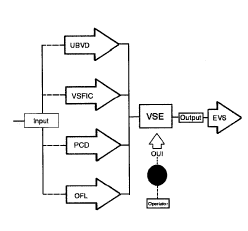
15. The apparatus of claim 12, being a VSE (Video Session Encoder) capable
of generating VOI (Video Object Information) data, as well as an EVS (Encoded
Video Session), and wherein the VSE apparatus further comprises:
a) a Video Display Facility (VDF) (Eg.: video monitor);
b) a means and apparatus capable of generating PSD (Position
Sensor Data) via operator input,
c) a means of processing UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast Video
Data);
d) a means of generating PCD (Product Caption Data), wherein
the PCD is determined and generated by operator input;
e) a means of storing the EVS (Encoded Video Session) output
data;
f) a random access storage memory capable of storing UBVD
(Uncoded Broadcast Video Data); and
g) a processor integrated with the VSE (Video Session Encoder)
wherein the processor is programmed with, and capable of:
i.) a means of displaying the UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast
Vide Data) on the VDF (Video Display Facility);
ii.) a means of dividing the UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast
Video Data) into a succession of video frame images,
and assigning each video frame image a unique Video
Session Frame Identification Code (VSFIC).
iii.) a means of receiving and processing PSD (Position
Sensor Data) generated via operator input, wherein
the processed PSD is formatted in accordance with
EVS format storage standards;
iv.) an OUI (Operator User Interface) capable of a means
of generating PCD (Product Caption Data); and
v.) an Operator User Interface (GUI) providing an
operator the means to specify options and means for
storing EVS (Encoded Video Session) data generated
during an encoding session.
16. The method of claim 15, wherein the PSD (Position Sensor Data) is
generated via an OUI (Operator User Interface), and the OUI comprises a pen
sensitive screen interface.
17. The method of claim 15, wherein the PSD (Position Sensor Data) is
generated via an OUI (Operator User Interface), and the OUI comprises a touch
sensitive screen interface.
18. The method of claim 15, wherein the PSD (Position Sensor Data) is
generated via an OUI (Operator User Interface), and the OUI comprises a cursor
sensitive screen interface.
19. The method of claim 15, wherein the PSD (Position Sensor Data) is
generated via an OUI (Operator User Interface), and the OUI comprises a method
and apparatus different from the OUI identified in claim 15, claim 17, and
claim
18.
20. The method of claim 11 and claim 15, wherein VOI (Video Object
Information) for a plurality of USO (User Selectable Object's) may be
generated
by repeating the method of claim 1 for each USO.
21. The method of claim 11 and claim 15, wherein VOI (Video Object
Information) for a plurality of USO (User Selectable Objects) can be generated
simultaneously by allowing for concurrent multiple operator input.
22. The method of claim 11 and claim 15, wherein the VSE (Video Session
Encoder) is also an encoding editor, and wherein the VSE further comprises:
a) a means of accessing video frame images in a random (as
opposed to sequential) manner;
b) a means of replaying the EVS (Encoded Video Session) for
verification purposes wherein the USO (User Selectable
Object) and their location within the video frame image are
displayed in a hi-lighted manner;
c) a means of editing a particular video frame image whereby
allowing repositioning and/or re-identification of the USO
(User Selectable Object);
d) a means of re-commencing a paused video session at a
particular video frame image, wherein allowing for further
operator input of OFS (Object Frame Structure); and
e) a means of allowing for editing of OCD (Object Caption
Data).
23. The method of claim 15, wherein the VSE (Video Session Encoder)
provides a means of storage of the EVS (Encoded Video Session ) data, which
EVS data comprises
a) UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast Video Data); and
b) VOI (Video Object Information) data.
24. The method of claim 15 and claim 23, wherein the VOI (Video Object
Information) and UBVD (Unedited Broadcast Video Data) are stored on the same
storage medium (e.g.: disk file, video tape, etc.) as show on diagram 1.
25. The method of claim 15 and claim 23, wherein the VOI (Video Object
Information) data is stored on a separate storage location. And an IAI
(Internet
Access Information) hyperlink to the storage location containing the USO (User
Selectable Object) VOI data is recorded together along with the UBVD(Un-coded
Broadcast Video Data).(see Diagram 2)
26. The method of claim 15 and claim 23, wherein:
a) the EVS (Encoded Video Session) is assigned a unique
identification code;
b) the UBVD (Un-coded Broadcast Video Data) is stored on a
separate location from the VOI (Video Object Information); and
c) both the VOI and UBVD are encoded with the said EVS
identification code.
(see Diagram 3)
27. The method of claim 15 and claim 23 wherein the VOI (Video Object
Information) may be divided into a set of logically independent components and
stored and processed on a separate location and/or medium.