Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98101170 -
5-AMINOALKOXY-1,4-DIHYDROQUINOXALINE-2,3-DIONES BEING DOPAMINE AGONISTS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
s This invention relates to N-substituted 5-aminoethoxy-1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-
2,3-
diones which are dopamine D2 agonists and therefore useful as antipsychotic
agents and
anti-parkinson agents.
BACKGROUND OF INVENTION
Io
Efforts to induce antipsychotic activity with dopamine autoreceptor agonists
have
been successful (Dorsini et al. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol., 16 , 645-648,
1977;
Tamminga et al., Science , 200, 567-568, 1975; and Ta~mminga et al..,
Psychiatry, 398-
402, 1986). A method for determining intrinsic activity at the dopamine DZ
receptor was
Is recently reported (Lahti et al.., Mol. Pharm., 42, 432-438, 1993) Intrinsic
activity is
predicted using the ratio of the "low-affinity agonist" (LowAg) state of the
receptor and the
"high-affinity agonist" (HighAg) state of the receptor, i.e. LowAg/HighAg.
These ratios
correlate with the agonist, partial agonist, and antagonist activities of a
given compound,
which activities characterize a compounds ability to elicit an antipsychotic
effect. The
2o compounds of this invention are dopamine agorusts various degrees of
intrinsic activity
some of which are selective autoreceptor agonists, and therefore partial
agonist (i.e. activate
only autoreceptors versus postsynaptic D2 dopamine receptors). As such, they
provide
functional modulation of the dopamine systems of the brain without the
excessive blockade
of the postsynaptic dopamine receptors which have been observed to be
responsible for the
2s serious side effects frequently exhibited by agents found otherwise
clinically effective for
the treatment of schizophrenia. Activation of the dopamine autoreceptors
results in reduced
neuronal firing a well as inhibition of dopamine synthesis and release and
therefore provide
a means of controlling hyperactivity of the dopaminergic systems. The
compounds of this
invention were also found to have high intrinsic activity and therefore they
can behave as
3o the natural neurotransmitter i.e. as full agonists. As such, they are
useful in the treatment
of diseases having abnormal concentrations of dopamine could be used as
dopamine
surrogates possibly in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The compounds of
this
invention are essentially free of extrapyramidal side effects.
3s
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
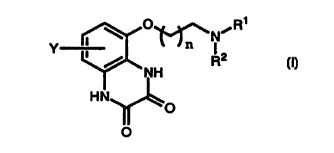
The compounds of this invention are represented by the following Formula I:
-1-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
O~~NiR~
Y I l_Jn
NH
HN
,O
O
I
wherein:
s R' and RZ are independently selected from hydrogen, straight-chain and
branched alkyl group having up to 10 carbon atoms or -(CHz)mAr
where Ar is phenyl, naphthyl or thienyl, each optionally
substituted by one or two substituents selected independently from
C,~6 alkyl, halogen) C,--C6 alkoxide and trifluoromethyl;
to or NR'RZ is 1) 2, 3, 4-tetrahydroquinolin-1-yl or 1, 2, 3, 4-
tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl;
m is 1-5;
n is 1 or 2;
Y is halogen, C,-C6 alkyl, and Cl-C6 alkoxy;
t s and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are prepared by methods well known to the
art
and are formed with both inorganic or organic acids including but not limited
to fumaric,
malefic, benzoic, ascorbic, pamoic, succinic, bismethylenesalicylic,
methanesulfonic,
ethanedisulfonic, acetic, oxalic, propionic, tartaric, salicyclic, citric,
gluconic, lactic, malic,
2o mandelic, cinnamic, citraconic, aspartic, stearic, palmitic, itaconic,
glycolic, p-
aminobenzoic, glutamic, benzene-sulfonic, hydrochloric hydrobromic, sulfuric,
cyclohexylsulfamic, phosphoric and nitric acids.
-2-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The compounds of Formula I can be prepared by the overall sequence as follows:
s
Scheme I
R1
I
H CI~ O~CI O~'N~R2
/ NH2 (")n CI / NH2 H2---.~ / NH2
K2C03 ~ I7M
N02 MEK ~ NO2 SO ~ NO2
1 ~ _
~N
O CF3 O CF3 O Nv
(CF3C0)20 O~N~ R2 H2NNH2 ~nN' R2 O N~N
---~
CH2CI2 / NH2 ethanol / NH2 THF
Pd/C
N02 NH2
_4
O CF3
H
O ~'nNw R2 O~nNw R2
1. K2C03 H
N O methanol / N O
-'~' I ~ HCl
N O 2. HCI ~ N O
H H
-3-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
The compounds of Formula I, where R1 and R2 form a ring, are prepared by the
overall sequence as follows:
Scheme II
I
O~N / O~N /
/ NH2 H2NNH2 NH
/ 2
ethanol
N02 Pd/C ~ NH2
2c
N
N O N I
~O O ' l'l n /
H
/ N O
~ HCl
2. HCl ~ H O
Specific exemplification of the production of representative compounds of this
io invention is given in the following procedures. These syntheses are
preformed using
reagents and intermediates that are either commercially available or prepared
according to
standard literature procedures. These examples are included to illustrated the
methods of
this invention and are not to be construed as limiting in any way to this
disclosure.
is
Intermediate 1
2-(2-Chloro-ethoxy)-6-nitro-phenylamine
2o A slurry containing 2-amino-3-nitrophenol (32.0 g, 0.208 mol), I,2-
dichloroethane
(260.0 g, 2.65mo1), potassium carbonate (35.0 g, 0.252 mol) and 2-butanone
(750 mL)
was refluxed for 24 hr. The mixture was cooled, filtered and the solids were
washed with
ethyl acetate. The filtrate was concentrated to an oily residue that was
dissolved in ethyl
-4-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
acetate (500 mL). The organic layer was washed with 1 N sodium hydroxide (250
mL),
water (500 mL), and brine (2X 500 mL), dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate.
Concentration of the filtered solution and trituation of the residue with
hexane afforded
37.8 g (84.6%) of product as an orange solid, mp 71-73° C; MS (+)PBEI
mle 216/218
s (M+).
Elemental analysis for C8H9C1N203:
Calc'd: C, 44.36; H, 4.19; N, 12.93
Found: C, 44.45; H, 4.02; N, 12.97
to
Intermediate 2a
(2-(2-Benzylamino-ethoxy)-6-nitro-phenyl)-amine
A mixture of 2-(2-chloroethoxy)-6-nitro-phenylamine (3.0 g, 13.8 mmol) and
benzylamine (9.0 g, 84.0 mmol) was heated at 100-110° C for 6 hr. The
excess
benzylamine was removed by distillation under vacuum (70 - 75° C / 0.1
mm) . The residue
was poured into 1 N sodium hydroxide (300 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate
(2X, 300
2o mL). The combined organic layer was washed with water (2X, 300 mL) and
brine (300
mL). The ethyl acetate layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered, and the
solvent removed under vacuum to give 5.1 g of crude red oil. Purification by
chromatography (500 g silica gel, ethyl acetate : 2 M NH3 in methanol, 20 : I
) afforded
3.54 g (89.3%) of a red semi-solid, mp 33-60°C; MS EI mle 287 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C15H17N303:
Calc'd: C, 62.71; H, 5.96; N, 14.62
Found: C, 62.64; H, 6.04; N, 14.23
3 o Following this general procedure utilizing 4-chloro-benzylamine and 1, 2,
3 , 4-
tetrahydro-isoquinoline afforded respectively:
2b 2-[2-(4-Chloro-benzylamino)-ethoxy]-6-nitro-phenylamine quarter hydrate
as an orange solid (87.8 %): mp 61-62 °C; MS (+)CI mle 322/324 (M+H)+.
Elemental analysis for C16H19N3~3 ' 0.25 H20:
Calc'd: C, 55.22; H, 5.10; N, 12.88
Found: C, 55.27; H, 4.96; N, 12.88
-S-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
2c 2-[2-(3,4-Dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-6-vitro-phenylamine as a
yellow solid (87.1 %), mp 95-96 °C; MS EI mle 313 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C17H19N3p3;
s Calc'd: C, 65.16; H, 6.11; N, 13.41
Found: C, 64.87; H, 6.11; N, 13.40
Intermediate 3a
to
N-[Z-(2-Amino-3-vitro-phenyoxy)-ethyl]-N-benzyl-2,2,2-trifluoro
acetamide
To a solution containing 2-(2-benzylamino-ethoxy)-6-vitro-phenylamine (3a,
0.50
1 s g, 1.74 mmol), triethylamine (0.50 mL) and methylene chloride ( 10 mL) was
slowly added
trifluoroacetic acid anhydride (0.32 mL, 2.26 mmol). After 2 hr, the reaction
mixture was
poured into 1 N sodium hydroxide (SO mL) and extracted with methylene
chloride. The
organic layer was washed with water (2X, 50 mL) and brine (50 mL), dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent removed under vacuum to
give a
2o crude yellow residue. Crystallization of this material from ethyl acetate-
hexane afforded
0.55 g (81.7 %) of a yellow solid, mp 134-135 °C; MS EI mle 383 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C17H16F3N304:
Calc'd: C, 53.27; H, 4.21; N, 10.96
2s Found: C, 53.09; H, 4.35; N, 10.93
Following this general procedure and utilizing 2-[2-(4-chloro-benzylamino)-
ethoxy]-6-nitro-phenylamine afforded:
so 3b N-[2-(2-Amino-3-vitro-phenoxy)-ethyl]-N-(4-chloro-benzyl)-2,2,2-
trifluoro-acetamide as a yellow solid (84.0 %), mp 138-139 °~ MS (+)FAB
mle 418/420
(M+H)+.
Elemental analysis for C17H15C1F3N304:
3s Calc'd: C, 48.88; H, 3.62; N, 10.06
Found: C, 48.66; H, 3.47; N, 9.82
-6-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
Intermediate 4a
N-Benzyl-N-[2-(2,3-diamino-phenoxy)-ethyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
s To a mixture containing N-[2-(2-amino-3-nitro-phenyoxy)-ethyl]-N-benzyl-
2,2,2-
trifluoro-acetamide (3a, 0.4 g, 1.04 mmol), 10% palladium on carbon (0.1 g) in
ethanol
(30 mL) was slowly added a solution of hydrazine hydrate (0.6 mL) in ethanol
(10.0 mL).
The mixture was heated to 55-60 aC and stirred at that temperature for 1 hr.
The mixture
was cooled to 25 °C, filtered and the catalyst was washed with ethanol.
The filtrate was
1 o concentrated under vacuum and the residue was diluted with ethyl acetate (
100 mL). The
organic layer was washed with water (2X, 100 mL) and brine ( 100 mL), dried
over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent removed under vacuum to
give
0.32 g (87.5% crude yield) of product as a brown viscous oil; MS (+)FAB mle
354
(M+H)'.
is
Following this general procedure and utilizing N-[2-(2-amino-3-vitro-phenoxy)-
ethyl)-N-(4-chloro-benzyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide afforded:
4b N-(4-Chloro-benzyl)-N-[2-(2,3-diamino-phenoxy)-ethyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-
2o acetamideas a brown oil (80.9 %); MS EI mle 387/389 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C17H17C1F3N302:
Calc'd: C, 52.65; H, 4.42; N, 10.84
Found: C, 52.47; H, 4.51; N, 10.60
2s
Intermediate Sa .
N-Benzyl-N-[2-(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinoxalin-5-yloxy)-ethyl)-
30 2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
A mixture of N-benzyl-N-[2-(2,3-diamino-phenoxy)-ethyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-
acetamide (0.49 g, 1.40 mmol) and oxalyl diimidazole (0.44 g, 2.09 mmol) in
anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) was refluxed for 2 hr. The reaction was poured into
water and
3s extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 150 mL). The organic layer was dried over
anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered) and the solvent removed under vacuum.
Purification by
chromatography (70 g silica gel, ethyl acetate) afforded 0.25 g (43.8 %) of
solid.
_7-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
Crystallization from ethyl acetate/hexane gave a white solid, mp 218-220
°C; MS EI mle
407 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C19H16F3N304:
s Calc'd: C, 55.77; H, 3.90; N) 10.05
Found: C, 56.02; H, 3.96; N, 10.32
Following this general procedure and urilizing N-(4-chloro-benzyl)-N-[2-(2,3-
lo diamino-phenoxy)-ethyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide, N-(4-chloro-benzyl)-N-[2-
(2,3-dioxo-
1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinoxalin-5-yloxy)-ethyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide (Sb)
was obtained
a semi-solid material(47 %).
is Intermediate 6
3-[2-(3,4-Dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-Z-yl)-ethoxy]-benzene-1,2-diamine
The general procedure followed in intermediate 4 using 2-(2-(3,4-dihydro-
20 1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-6-nitro-phenylamine (2c) afforded 3-[2-(3,4--
dihydro-1H-
isoquinolin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-benzene-1,2-diamine as a solid (95 %), mp 76-77
°C. This
material was characterized as the dihydrochloride 0.4 H20 salt; MS EI mle 283
(M+).
Elemental analysis for CI7H2IN30 ~ 2 HCl ~ 0.4 H20:
2s Calc'd: C, 56.17; H, 6.60; N, 11.56
Found: C, 56.15; H) 6.68; N, 11.25
Example I
5-(2-Benzylamino-ethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione
A suspension of potassium carbonate (0.33 g, 2.40 mmol) and N-benzyl-N-[2-
(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinoxalin-5-yloxy)-ethyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-
acetamide
3s (0.21g, 0.52 mmol) in methanol-water (25 mL : 1.5 mL) was heated to reflux
for 2 hr.
The solvent was evaporated and the residue dissolved in ethyl acetate ( 100
mL). The
organic layer was washed with water (80 mL), dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate,
_g_
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
filtered, and the solvent concentrated under vacuum to give the crude base as
a white solid,
mp 242-245 °C. Without further purification, this material was
dissolved in methanol and
treated with an excess amount of 1 N HCl in ether to afford 0.11 g (75.0%) of
the
hydrochloride salt as a white solid) mp >250 °C: MS (+)ESI mle 312
(M+H+).
Elemental analysis for C16I-I17N302 ~ HCI:
Calc'd: C, 60.09; H, 5.67; N, 13.14
Found: C, 59.84; H, 5.59; N, 12.92
to
Example 2
5-[2-(4-Chloro-benzylamino)-ethoxy]-1,4-dihydro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione
is Following the general procedure used in example 1 using N-(4-chloro-benzyl)-
N-
[2-(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinoxalin-5-yloxy)-ethyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-
acetamide
afforded 5-[2-(4-chloro-benzylamino)-ethoxy]-1,4-dihydro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione
~ HCl
0.75 H20 as a beige solid (90.0 %), mp >250 °C; MS (+)FAB mle 346
(M+H+).
2o Elemental analysis for C17H16C1N303:
Calc'd: C, 60.09; H, 5.67; N, 13.14
Found: C, 59.84; H, 5.59; N, 12.92
2s Example 3
5-[2-(3,4-Dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-1,4-dihydro-quinoxaline
2,3-dione
3o The general procedure used in example 1 using 2-[2-(3,4-dihydro-1H-
isoquinolin-
2-yl)-ethoxy]-6-nitro-phenylamine afforded 5-[2-(3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-
yl)-
ethoxy]-1,4-dihydro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione ~ quarter hydrate as a white solid
(66.7 %), mp
>250 °C; MS (+)FAB mle 338 (M+H').
3s Elemental analysis for C19H19N3~3 ~ 0.25 H20:
Calc'd: C, 66.75; H, 5.75; N, 12.29
Found: C, 66.93; H, 5.60; N, 12.25
-9-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
Treatment of the above solid with excess 1 N hydrogen chloride in ether
gave the monohydrate hydrochloride salt of the title compound as a white solid
(90.0 % ),
mp 243-245 °C; MS (+)FAB mle 338 (M+H+).
s
Elemental analysis for C19H19N3~3 ~ HCl ~ H20:
Calc'd: C, 58.24; H, 5.66; N, 10.72
Found: C, 58.20; H, 5.43; N, 10.85
to
The compounds of this invention are dopamine autoreceptor agonists, that is,
they
serve to modulate the synthesis and release of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
They are
thus useful for treatment of disorders of the dopaminergic system, such as
schizophrenia,
Parkinson's disease and Tourette's syndrome. Such agents are partial agonists
at the
i s postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptor and are thereby useful in the treatment
of alcohol and
drug addiction.
Affinity for the dopamine autoreceptor was established by a modification of
the
standard experimental test procedure of Seemen and Schaus, European Journal of
2o Pharmacology 203, 105-109, 1991, wherein homogenized rat striatal brain
tissue is
incubated with 3H-quinpirole (Quin.) and various concentrations of test
compound, filtered
and washed and counted in a Betaplate scintillation counter.
High affinity for the dopamine D-2 receptor was established by the standard
experimental test procedure of Fields, et al., Brain Res., 136, 578 (1977) and
Yamamura
2s et al., eds., Neurotransmitter Receptor Binding) Raven Press, N.Y. ( 1978)
wherein
homogenized limbic brain tissue is incubated with 3H-spiroperidol (Spiper.)
and various
concentrations of test compound, filtered and washed and shaken with
Hydrofluor
scintillation cocktail (National Diagnostics) and counted in a Packard 460 CD
scintillation
counter.
so The results of the tests with compounds representative of this invention
are given in
the immediately following table.
Example IC50 (nM) IC50 (nM) Ratio
No. D2 Quin. D2 Spiper
1 20.8 2187 105.1
2 64.6
3
-10-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
Hence, the compounds of this invention effect the synthesis of the
neurotransmitter
dopamine and thus are useful in the treatment of dopaminergic disorders such
as
schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Tourette's Syndrome, alcohol addiction,
cocaine
addiction, and addiction to analagous drugs.
s
Applicable solid carriers for pharmaceutical compositions containing the
compounds of this invention can include one or more substances which may also
act as
flavoring agents, lubricants, solubilizers, suspending agents, fillers,
glidants, compression
aids, binders or tablet-disintergrating agents or an encapsulating material.
In powders, the
1 o carrier is a finely divided solid which is in admixture with the finely
divided active
ingredient. In tablets, the active ingredient is mixed with a carrier having
the necessary
compression properties in suitable proportions and compacted in the shape and
size
desired. The powders and tablets preferably contain up to 99% of the active
ingredient.
Suitable solid carriers include, for example, calcium phosphate, magnesium
stearate, talc,
15 sugars, lactose) dextrin, starch, gelatin, cellulose, methyl cellulose,
sodium carboxymethyl
cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidine, low melting waxes and ion exchange resins.
Liquid Garners may be used in preparing solutions, suspensions, emulsions,
syrups
and elixirs. The active ingredient of this invention can be dissolved or
suspended in a
2o pharmaceutically acceptable liquid carrier such as water, an organic
solvent, a mixture of
both or pharmaceutically acceptable oils or fat. The liquid carrier can
contain other suitable
pharmaceutical additives such as solubilizers, emulsifiers, buffers,
preservatives,
sweeteners, flavoring agents, suspending agents, thickening agents, colors,
viscosity
regulators, stabilizers or osmo-regulators. Suitable examples of liquid
carriers for oral and
2s parenteral administration include water (particularly containing additives
as above e.g.
cellulose derivatives, preferably sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution),
alcohols
(including monohydric alcohols and polyhydric alcohols e.g. glycols) and their
derivatives,
and oils (e.g. fractionated coconut oil and arachis oil). For parenteral
administration the
carrier can also be an oily ester such as ethyl oleate and isopropyl
myristate. Sterile liquid
3o carriers are used in sterile liquid form compositions for parenteral
administration.
Liquid pharmaceutical compositions which are sterile solutions or suspensions
can
be utilized by, for example, intramuscular, intraperitoneal or subcutaneous
injection.
Sterile solutions can also be administered intravenously. Oral administration
may be either
3s liquid or solid composition form.
-11-
CA 02278757 1999-07-21
WO 98/35948 PCT/US98/01170
Preferably the pharmaceutical composition is in unit dosage form, e.g. as
tablets or
capsules. In such form, the composition is sub-divided in unit dose containing
appropriate
quantities of the active ingredient; the unit dosage forms can be packaged
compositions, for
example packeted powders, vials, ampoules, prefilled syringes or sachets
containing
s liquids. The unit dosage form can be, for example, a capsule or tablet
itself, or it can be the
appropriate number of any such compositions in package form.
The dosage to be used in the treatment of a specific psychosis must be
subjectively
deternlined by the attending physician. The variables involved include the
speck
to psychosis and the size, age and response pattern of the patient.
-12-