Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
93
WE CLAIM:
1. A combinatorial library of two or more compounds of the
formula:
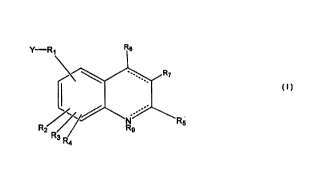
Image
wherein in the above Formula I, the dashed lines (-----) means fully saturated
or fully
unsaturated and further wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkenylene, C2 to C10 substituted alkenylene,
C2 to
C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring,
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl ring, amino, (monosubstituted)amino, a
goup of the formula: -CH2CONH- and a goup of the formula:
-(CH2)p-Ar-(CH2)q
94
wherein p and q are independently selected from a number 0 to 6, wherein both
p
and q are not both 0; and Ar is an aryl group selected from the group
consisting of
phenyl, substituted phenyl, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1 to C10 alkyl, C2 to
C10
alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy,
C1 to
C7 acyloxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted
cycloalkyl, C5
to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic ring,
substituted
heterocyclic ring, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene, cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene,
substituted
cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene, carboxy, protected carboxy, hydroxymethyl,
protected hydroxymethyl, amino, protected amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
protected (monosubstituted)amino, (disubstituted)amino, carboxamide, protected
carboxamide, C1 to C4 alkylthio, C1 to C4 substituted alkylthio, C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 alkylsulfoxide, C1
to C4
substituted alkylsulfoxide, phenylthio, substituted phenylthio,
phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, phenylsulfonyl and substituted phenylsulfonyl;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to
C10
alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7
to C12
substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy, protected carboxy, C1 to C7 aryl, C1 to C7
substituted aryl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl
ring
and substituted heteroaryl ring;
95
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 4, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2
to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5
to C7
cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl,
naphthyl,
substituted naphthyl, C5 to C7 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
C1 to
C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, C1 to C4 alkyl sulfoxide, phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, C1 to C4 alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C10 substituted alkyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted
phenylalkyl,
phenyl, and substituted phenyl;
R9 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C1 to C12
phenylalkyl,
C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, C1 to C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl,
phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4
96
substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1 to C6 substituted
alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted phenylaminocarbonyl,
provided that when the ring is unsaturated, R9 is absent; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of CO2H, OH, SH, NHR12, C(O)NHR12,
CH2OH, CH2NH2, and CH2NHR12, wherein R12 is selected from the group
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
and a
functionalized resin,
or a salt of said compounds.
2. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring,
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl sing, amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
and a
group of the formula: -CH2CONH-;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the goup consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene, and vitro;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to
C10
substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7
cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7
substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted
naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy,
97
protected carboxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, heterocyclic
ring,
substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl
ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of a phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl,
substituted
phenyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, and C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl;
R7 is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
and C1
to C10 substituted alkyl;
R9 is selected from the group consting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1
to C10
substituted alkyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
C1 to C7
acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl,
C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1
to C6 substituted alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted
phenylaminocarbonyl; and
98
Y is selected from the group consisting of CO2H, NHR12, C(O)NHR12, wherein R12
is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1
to C6
substituted alkyl, and a functionalized resin.
3. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of
CH2CONH- and -CH2CH(NHR8)-, wherein R8 is selected from the group
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
C2 to
C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10
substituted
alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C7 to C12
phenylalkyl,
C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, C1 to C6 aryl, C1 to C6 substituted aryl,
aminocarbonyl, protected aminocarbonyl, (monosubstituted)aminocarbonyl,
protected (monosubstitituted)aminocarbonyl, (disubstituted)aminocarbonyl, C1
to
C4 alkylsulfonyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, halo, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7
alkylene, and nitro;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, carboxy, C1 to
C10
alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C1 to C10 alkenyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, phenyl, substituted
phenyl,
naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic
ring,
heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
99
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl, a
group of the
formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl, and
substituted
phenyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and C1 to C10
alkyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
4. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present is selected from the group
consisting of
100
CH2NHCO and CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-
toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-
trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
101
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl,
3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=H-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-(3-oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-
methyldecyl,
2-pentyl, 2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-
(methylenedioxy)-
102
6-nitrophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl, 4-chloro-3-
nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
pyridinyl,
9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and N-methyl-N-
acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
5. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting of acetyl,
.alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-
p-tolnoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl,
cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
103
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenroyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohe:xanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
104
anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-triimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-a-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, 4-chlorobenzoyl; acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl,
.alpha.-methylcinnamoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl,
cyclobutanecarboxyl,
cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexaneburyroyl, cyclohexanecarboxyl,
cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacelyl, cyclopentanecarboxyl,
cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl, 4-cyanobenzoyl,
hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl, isobutyroyl,
isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl, m-anisoyl,
m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, rucotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-anisoyl, o-
toluoyl,
octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl, phenylacetyl,
picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, traps-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl; -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
105
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichdorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chdoronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trirnethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazine;carboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
106
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-(3-oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-
methyldecyl,
2-pentyl, 2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-
(methylenedioxy)-
6-nitrophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl, 3, 5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl,
4-chloro-3-nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-
pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-vitro-2-fwryl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
pyridinyl,
9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and N-methyl-N-
acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
107
6. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is absent or CH2NHCO;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl, 2-(3-oxa-3-
propionoyl)-phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-methyldecyl, 2-pentyl,
2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-
nitrophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl, 4-chloro-3-
nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-vitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
pyridinyl,
9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and N-methyl-N-
acetyl-amino;
108
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
7. The combinatorial library of claim 1, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of
-CH2NHCO- and CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-
p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3- dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
109
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotvioyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl,
3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
110
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, vitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, phenyl,
chloroacetyl,
cyclohexanyl, D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromoacetyl, trimethylacetyl, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl, 2,3-difluorophenyl, 2,4-
dichlorophenyl,
2,5-difluorophenyl, 2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl,
2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl, 2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 2-
ethylbutyryl,
2-fluorophenyl, 2-(2-oxymethylenecarboxy)phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl,
2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-
nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3,5-dichlorophenyl,
3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl, 3-bromophenyl,
3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-formylchromonyl, 3-furyl,
3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-vitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl,
3-phenylbutyryl, 3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl,
4-carboxyphenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl,
6-methyl-2-pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, 2,3-dimethylvaleryl, 2,2-dimethyl-
4-pentenyl,
3-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 2-methylbutyryl,
2-methylvaleryl, 4-chloro-3-vitro-phenyl, 4-trifluromethyl)phenyl,
2-methylundecanyl, and .beta.-phenylcinnaminyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of nalidixoyl, 2-phenyl-4-
quinolinecarboxy,
2-pyrazinecarboxy, niflumoyl, 4-nitrophenylacetyl,
4-(4-nitrophenyl)butyroyl,(3,4-dimetho:xyphenyl)-acetyl,
3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenylacetyl, 4-nitrocinnamoyl,
3,4,-(methylenedioxy)cinnamoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl, benzoyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-nitrobenzoyl, 2-(p-toluoyl)benzoyl, 2,4-
dinitrophenylacetyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-propionyl, 4-biphenylacetyl, 1-napthylacetyl,
(2-napthoxy)acetyl, trans-cinnamoyl, picolinyl, 3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoyl,
111
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-biphenylcarboxy, thiophenoxyacetyl, 1-benzoylpropionyl, phenylacetyl,
hydrocinnamoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionyl,
4-phenylbutyryl, phenoxyacetyl, (+/-)-2-phenoxypropionyl,
2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoyl,
2,4-dihydroxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl,
3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl, 2-benzoylbenzoyl, 1-napthoyl, xanthene-9-carboxy,
4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoyl, 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl,
2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl,
4-nitrobenzoyl, 3-(dimethylamino)benzoyl, p-methylbenzoyl, p-methoxybenzoyl,
trimethylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl, (-)-menthoxyacetyl, cyclohexanecarboxy,
cyclohexylacetyl, dicyclohexylacetyl, 4-cyclohexylbutyroyl,
cycloheptanecarboxy,
13-isopropylpodocarpa-7,13-dien-15-oyl, acetyl, octanoyl, (methylthio)acetyl,
3-nitropropionyl, 4-amino-3 hydroxybenzoyl,
3-(2-methyl-4-vitro-1-imidizoyl)propionyl, 2-furoyl, (s)(-)-2-pyrrolidone-5-
carboxy,
(2-pyrimidylthio)acetyl, 4-methoxy-2-quinolinecarboxy, 1-adamantanecarboxy,
piperonoyl, 5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazole-4-carboxy, rhodanine-3-acetyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, nicotinoyl, 9-oxo-9H-thioxanthene-3-carboxyl-10,10
dioxide,
2-thiophenecarboxy, 5-vitro-2-furanoyl, indole-3-acetyl, isonicotinoyl,
3.alpha.-hydroxy-5.beta.-cholan-24-oyl, (3.alpha.,7.alpha.,12.alpha.)-
trihydroxy-5.beta.-cholan-24-oyl, (3.alpha.,
5.beta.-12.alpha.)-3,12, dihydroxy-5-cholan-24-oyl, (3.alpha., 5.beta.,
6.alpha.)-3,6-dihydroxy-cholan-24-oyl,
L-alaninyl, L-cysteinyl, L-aspartinyl, L-glutaminyl, L-phenylalaninyl,
glycinyl,
L-histidinyl, L-isoleucinyl, L-lyscinyl, L-leucinyl, L-methionylsulfoxide,
L-methionyl, L-asparginyl, L-prolinyl, L-glutaminyl, L-arganinyl, L-serinyl,
L-threoninyl, L-valinyl, L-tryptophanoyl, L-tyrosinyl, D-alaninyl, D-
cysteinyl,
D-aspartinyl, D-glutaminyl, D-phenylalanin,yl, glycinyl, D-histidinyl, D-
isoleucinyl,
D-lyscinyl, D-leucinyl, D-methionylsulfoxide, D-methionyl, D-asparginyl,
D-prolinyl, D-glutaminyl, D-arganinyl, D-serinyl, D-threoninyl, D-valinyl,
D-tryptophanoyl, D-tyrosinyl, 2-aminobutyroyl, 4-aminobutyroyl,
2-aminoisobutyroyl, L-norleucinyl, D-norleucinyl, 6-aminohexanoyl,
7-aminoheptanoyl, thioprolinyl, L-norvalinyl, D-norvalinyl, .alpha.-
ornithinyl, methionyl
112
sulfonyl, L-naphthylalaninyl, D-naphthyllalaninyl, L-phenylglycinyl,
D-phenylglycinyl, .beta.-alaninyl, L-cyclohexylalaninyl, D-
cyclohexylalaninyl,
hydroxyprolinyl, 4-nitrophenylalaninyl, dehydroprolinyl, 3-hydroxy-1-
propanesulfonyl, 1-propanesulfonyl, 1-octanesulfonyl, perfluoro-1-
octanesulfonyl,
(+)-10-camphorsulfonyl, (-)-10-camphorsulfonyl, benzenesulfonyl,
2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl, p-toluenesulfomyl, 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl,
n-acetylsulfanilyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzenesulfonyl, 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl,
2-mesitylenesulfonyl and 2-napthalenesulfonyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
8. The combinatorial library of claim 1, comprising a plurality of
mixtures of the 4-substituted quinoline compounds of claim 1, wherein within
each of
the mixtures all the compounds have at least one substituent in common,
wherein the
substituent is selected from the group consisting of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6,
R7, R8, R9,
R10, R11, R12, n and Y, with the proviso that not all of the substituents are
in common
end that all other noncommon substituents are present as equimolar mixtures.
9. A method for preparing the combinatorial library of claim 1
comprising the following steps:
(a) reacting a resin-bound aniline: with an aldehyde to obtain an imine; and
(b) reacting, in the presence of m acid, the imine of step (a) with a
dienophile to yield a 4-substituted quinoline.
10. A method for preparing the combinatorial library of claim 1,
113
comprising the following steps:
(a) reducing the nitro group of a resin-bound substituted- or
protected-amino-nitroaryl species to produce an aniline;
(b) reacting the resin-bound aniline with an aldehyde to obtain an imine;
and
(c) reacting, in the presence of an acid, the imine of step (b) with a
dienophile to yield a 4-substituted quinoline.
11. The method of claim 9, further comprising the step of cleaving
the 4-substituted quinoline from the resin.
12. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of cleaving
the 4-substituted quinoline from the resin.
13. The method of claim 9, wherein the combinatorial library
contains a plurality of mixtures of the 4-substituted quinoline compounds and
further
where in each mixture all compounds of the mixture have at least one
substituent in
common, wherein the substituent is selected from the group consisting of R1,
R2, R3,
R4, R5, R6, R10, R11 and Y, with the proviso that not all the substituents are
in common
and that all other noncommon substituents are present as equimolar mixtures.
14. The method of claim 10, wherein the combinatorial library
contains a plurality of mixtures of the 4-substituted quinoline compounds and
further
where in each mixture all compounds of the mixture have at least one
substituent in
common, wherein the substituent is selected from the group consisting of R1,
R2, R3,
R4, R5, R6, R10 R11 and Y, with the proviso that not all the substituents are
in common
and that all other noncommon substituents are present as equimolar mixtures.
114
15. The method of claim 9, further comprising the step of
condensing the 4-substituted quinoline resulting from step 9(b) with a reagent
selected
from the groups consisting of carboxylic acid, carboxylic acid anhydride, acid
halide,
alkyl halide and isocyanate.
16. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of
condensing the 4-substituted quinoline resulting from step 10(c) with a
reagent
selected from the group consisting of carboxylic acid, carboxylic acid
anhydride, acid
halide, alkyl halide and isocyanate.
17. The method of claim 9, further comprising the step of oxidizing
the 4-substituted quinoline resulting from step 9(b) with an oxidant selected
from the
group consisting of peracetic acid, metachloroperbenzoic acid and iodine,
provided
that R9 is a hydrogen atom prior to oxidizing and is absent after oxidation.
18. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of
oxidizing the 4-substituted quinoline resulting from step 10(c) an oxidant
selected from
the goup consisting of peracetic acid, metachloroperbenzoic acid and iodine,
provided
that R9 is a hydrogen atom prior to oxidizing and is absent after oxidation.
19. A single compound of the formula:
Image
114/1
wherein in the above Formula I, the dashed lines (-----) means fully saturated
or fully
unsaturated and further wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkenylene, C2 to C10 substituted alkenylene,
C2 to
C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C2 to C10 cycloalkenyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic; ring, substituted heterocyclic
ring,
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl ring, amino, (monosubstituted)amino, a
group of the formula: -CH2CONH- and a group of the formula:
-(CH2)p-Ar-(CH2)q-
wherein p and q are independently selected from a number 0 to 6, wherein both
p
and q are not both 0; and Ar is an aryl group selected from the group
consisting of
phenyl, substituted phenyl, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1 to C10 alkyl, C2 to
C10
alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy,
C1 to
C7 acyloxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted
cycloalkyl, C5
to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic ring,
substituted
heterocyclic ring, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene, cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene,
substituted
cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene, carboxy, protected carboxy, hydroxymethyl,
protected hydroxymethyl, amino, protected amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
protected (monosubstituted)amino, (disubstituted)amino, carboxamide, protected
114/2
carboxamide, C1 to C4 alkylthio, C1 to C4 substituted alkylthio, C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 alkylsulfoxide, C1
to C4
substituted alkylsulfoxide, phenylthio, substituted phenylthio,
phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, phenylsulfonyl and substituted phenylsulfonyl;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to
C10
alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C1
to C12
substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy, protected carboxy, C1 to C7 aryl, C1 to C7
substituted acyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl
ring
and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 4, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2
to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5
to C7
114/3
cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl,
naphthyl,
substituted naphthyl, C1 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted
phenylalkyl, C1 to
C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, C1 to C4 alkyl sulfoxide, phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, C1 to C4 alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R7 is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C12 phenylalkyl, C1 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, phenyl, and substituted
phenyl;
R9 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup consiting
of a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C1 to C12
phenylalkyl,
C1 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, C1 to C7 aryl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl,
phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4
substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1 to C6 substituted
alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted phenylaminocarbonyl,
provided that when the ring is unsaturated, R9 is absent; and
Y is selected from the goup consisting of CO2H, OH, SH, NHR12, C(O)NHR12,
CH2OH, CH2NH2, and CH2NHR12, wherein R12 is selected from the goup
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
and a
functionalized resin,
or a salt thereof.
20. The single compound of claim 19, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl,C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C1 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring,
114/4
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl ring, amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
and a
group of the formula: -CH2CONH-;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7
alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C1 alkylene, and nitro;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to
C10
substituted alkyl C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7
cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7
substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted
naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy,
protected carboxy, C1 to C1 acyl, C1 to C1 substituted acyl, heterocyclic
ring,
substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl
ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of a phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl,
substituted
114/5
phenyl, C1 to C12 phenylalkyl, and C1 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and C1 to C10
alkyl;
R9 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to C10
substituted alkyl, C1 to C12 phenylalkyl, C1 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
C1 to C7
acyl, C1 to C1 substituted acyl, phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl,
C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1
to C6 substituted alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted
phenylauninocarbonyl; and
Y is selected from the goup consisting of CO2H, NHR12, C(O)NHR12, wherein R12
is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1 to
C6
substituted alkyl, and a functionalized resin.
21. The single compound. of claim 19, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup
consisting of
-CH2CONH- and -CH2CH(NHR8)-, wherein R8 is selected from the goup
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
C2 to
C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10
substituted
alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C1 to C12
phenylalkyl,
C1 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, C1 to C6 acyl, C1 to C6 substituted aryl,
aminocarbonyl, protected aminocarbonyl, (monosubstituted)aminocarbonyl,
protected (monosubstitituted)aminocarbonyl, (disubstituted)aminocarbonyl, C1
to
C4 alkylsulfonyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the goup consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, halo, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1 to C1 alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7
alkylene, and nitro;
114/6
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, carboxy, C1 to
C10
alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C1 to C10 alkenyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, phenyl, substituted
phenyl,
naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic
ring,
heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl, a
group of the
formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl, and
substituted
phenyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and C1 to C10
alkyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the goup consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
114/7
functionalized resin.
22. The single compound of claim 19, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present is selected from the group
consisting of
CH2NHCO and CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-
p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
mehylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
114/8
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,5-dimethyl-p-anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl,
4'-ethyl-4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-
biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the goup consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the goup consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
114/9
2,3- difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-
difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-(3-oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-
methyldecyl,
2-pentyl, 2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl,
3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl,
4-chloro-3-nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-
pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl,
6-methyl-2-pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl,
cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl,
and N-methyl-N-acetyl-amino;
R' is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
23. The single compound of claim 19, wherein:
114/10
R1 is CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting of acetyl,
.alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-
p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl,
cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl,
4-fluoro-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl,
tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl,
1-phenyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-
dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
114/11
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacf;tyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohe;xanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3, 5, S-trimethylhexanoyl, 3, 5-
bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,5-dimethyl-p-anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-metlhoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-metlzylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-a-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-tluopheneacetyl,
4'-ethyl-4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-
biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacxtyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, 4-chlorobenzoyl; acetyl, a-cyclohexylphenylacetyl,
.alpha.-methylcinnamoyl, .alpha., .alpha., .alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha., .alpha., .alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl,
.alpha., .alpha., .alpha.-trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl,
cyclobutanecarboxyl,
cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl, cyclohexanecarboxyl,
cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl, cyclopentanecarboxyl,
cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl, 4-cyanobenzoyl,
hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl, isobutyroyl,
isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl, m-anisoyl,
m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-anisoyl, o-
toluoyl,
octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl, phenylacetyl,
picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl,
4-fluoro-a-methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tent-
butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl. tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
114/12
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl,
3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl, 3-iodo-4-
114/13
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-
isoquinolinecarboxyl,lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl,
4'-ethyl-4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-
biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-(3-oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-
methyldecyl,
2-pentyl, 2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-
(methylenedioxy)-6-nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl,
4-chloro-3-nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-
pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl,
6-methyl-2-pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl,
cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and
N-methyl-N-acetyl-amino;
114/14
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
24. The single compound of claim 19, wherein:
R1 is absent or CH2NHCO;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-oxa-3-propionoyl)-phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-methyldecyl, 2-
pentyl,
2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-
nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl,
4-chloro-3-nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-
pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl,
6-methyl-2-pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl,
cyclohexanyl,
114/15
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and
N-methyl-N-acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
25. The single compound of claim 19, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present. is selected from the group
consisting
of -CH2NHCO- and CH2CH(NHR~), wherein R~ is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.,-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-
trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl,
4-fluoro-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl,
tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
114/16
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl,
1-phenyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-
dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4, 5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,
3,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,5-dimethyl-p-anisoyl,3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
114/17
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,3-
phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,4-
chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, vitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, phenyl,
chloroacetyl,
cyclohexanyl, D,L- 1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromoacetyl, trimethylacetyl, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl, 2,3,4-
trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl, 2,3-difluorophenyl, 2,4-
dichlorophenyl,
2,5-difluorophenyl,2,5-dimethylphenyl,2,6-difluorophenyl,2-bromophenyl,2-
chloro-5-nitrophenyl,2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl,2-cyanophenyl,2-ethylbutyryl,2-
fluorophenyl,2-(2-oxymethylenecarboxy)phenyl,2-methoxy-1-naphthyl,2-nitro-
5-chlorophenyl,2-nitrophenyl,2-pyridinyl,3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl,3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,3,5-dichlorophenyl,3-(3,4-
dichlorophenoxy)phenyl,3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,3-bromophenyl,3-
carboxyphenyl,3-cyanophenyl,3-fluorophenyl,3-formylchromonyl,3-furyl,3-
hydroxyphenyl,3-vitro-4-chlorophenyl,3-nitrophenyl,3-phenoxyphenyl,3-
phenylbutyryl,3-pyridinyl,4-bromo-2-thiophenyl,4-bromophenyl,4-
carboxyphenyl,4-cyanophenyl,4-fluorophenyl,4-nitrophenyl,4-pyridinyl,4-
quinolinyl,5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl, ;5-vitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-
methyl-2-pyridinyl,9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl,2,3-dimethylvaleryl,2,2-dimethyl-4-
pentenyl,3-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl,3-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl,2-methylbutyryl,
2-methylvaleryl,4-chloro-3-vitro-phenyl,4-trifluromethyl)phenyl,2-
methylundecanyl, and .beta.-phenylcinnaminyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of nalidixoyl,2-phenyl-4-
quinolinecarboxy,
114/18
2-pyrazinecarboxy, niflumoyl, 4-nitrophenylacetyl,
4-(4-nitrophenyl)butyroyl,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-acetyl,
3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenylacetyl, 4-nitrocinnamoyl,
3,4,-(methylenedioxy)cinnamoyl,3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,benzoyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl,2-nitrobenzoyl,2-(p-toluoyl)benzoyl,2,4-dinitrophenylacetyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-propionyl,4-biphenylacetyl,1-napthylacetyl,
(2-napthoxy)acetyl,trans-cinnamoyl,picolinyl,3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl,2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,3,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-biphenylcarboxy,thiophenoxyacetyl,1-benzoylpropionyl,phenylacetyl,
hydrocinnamoyl,3,3-diphenylpropionyl,3,3,3-triphenylpropionyl,
4-phenylbutyryl,phenoxyacetyl,(+/-)-2-phenoxypropionyl,
2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,3,4-dihydroxybenzoyl,
2,4-dihydroxybenzoyl,3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl,3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl,3,4,5-
trihydroxybenzoyl,2-benzoylbenzoyl,1-napthoyl,xanthene-9-carboxy,
4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoyl,2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoyl,4-chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl,
2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoyl,4-dimethylaminobenzoyl,4-(diethylamino)benzoyl,
4-nitrobenioyl,3-(dimethylamino)benzoyl,p-methylbenzoyl,p-methoxybenzoyl,
trimethylacetyl,tert-butylacetyl,(-)-menthoxyacetyl,cyclohexanecarboxy,
cyclohexylacetyl,dicyclohexylacetyl,4-cyclohexylbutyroyl,cycloheptanecarboxy,
13-isopropylpodocarpa-7,13-dien-15-oyl,acetyl,octanoyl,(methylthio)acetyl,
3-nitropropionyl,4-amino-3 hydroxybenzoyl,3-
(2-methyl-4-nitro-1-imidizoyl)propionyl,2-furoyl,(s)(-)-2-pyrrolidone-5-
carboxy,
(2-pyrimidylthio)acetyl,4-methoxy-2-duinolinecarboxy,1-adamantanecarboxy,
piperonoyl,5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazole-4-carboxy,rhodanine-3-acetyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl,nicotinoyl,9-oxo-9H-thioxanthene-3-carboxyl-10,10 dioxide,
2-thiophenecarboxy,5-nitro-2-furanoyl,indole-3-acetyl,isonicotinoyl,3.alpha.-
hydroxy-5.beta.-cholan-24-oyl,(3.alpha.,7.alpha.,12.alpha.)-trihydroxy-5.beta.-
cholan-24-oyl,(3.alpha.,5.beta.-
12.alpha.)-3,12,dihydroxy-5-cholan-24-oyl,(3.alpha.,5.beta.,6.alpha.)-3,6-
dihydroxy-cholan-24-oyl,
L-alaninyl,L-cysteinyl,L-aspartinyl,L-glutaminyl,L-phenylalaninyl,glycinyl,
L-histidinyl,L-isoleucinyl,L-lyscinyl,L-leucinyl,L-methionylsulfoxide,L-
methionyl,L-asparginyl,L-prolinyl,L-glutaminyl,L-arganinyl,L-serinyl,
114/19
L-threoninyl,L-valinyl,L-tryptophanoyl,L-tyrosinyl,D-alaninyl,D-cysteinyl,D-
aspartinyl,D-glutaminyl,D-phenylalaninyl,glycinyl,D-histidinyl,D-isoleucinyl,
D-lyscinyl,D-leucinyl,D-methionylsulfoxide,D-methionyl,D-asparginyl,D-
prolinyl,D-glutaminyl,D-arganinyl,D-serinyl,D-threoninyl,D-valinyl,D-
tryptophanoyl,D-tyrosinyl,2-aminobutyroyl,4-aminobutyroyl,
2-aminoisobutyroyl,L-norleucinyl,D-norleucinyl,6-aminohexanoyl,
7-aminoheptanoyl,thioprolinyl,L-norvalinyl,D-norvalinyl,.alpha.-ornithinyl,
methionyl
sulfonyl,L-naphthylalaninyl,D-naphthylalaninyl,L-phenylglycinyl,
D-phenylglycinyl,.beta.-alaninyl,L-cyclohexylalaninyl,D-
cyclohexylalaninyl,
hydroxyprolinyl,4-nitrophenylalaninyl,dehydroprolinyl,3-hydroxy-1-
propanesulfonyl,1-propanesulfonyl,1-octanesulfonyl,perfluoro-1-octanesulfonyl,
(+)-10-camphorsulfonyl,(-)-10-camphorsulfonyl,benzenesulfonyl,
2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl,p-toluenesulfonyl,4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl,
n-acetylsulfanilyl,2,5-dichlorobenzenesulfonyl,2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl,
2-mesitylenesulfonyl and 2-napthalenescafonyl;
R7 is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
26. A single compound of the formula:
114/20
Image
wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkenylene, C2 to C10 substituted alkenylene,
C2 to
C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring,
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl ring, amino, (monosubstituted)amino, a
group of the formula: -CH2CONH- and a group of the formula:
-(CH2)p-Ar-(CH2)q-
wherein p and q are independently selected from a number 0 to 6, wherein both
p
and q are not both 0; and Ar is an aryl group selected from the group
consisting of
phenyl, substituted phenyl, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1 to C10 alkyl, C2 to
C10
114/21
alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy,
C1 to
C7 acyloxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted
cycloalkyl, C5
to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic ring,
substituted
heterocyclic ring, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene, cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene,
substituted
cyclic C2 to C7 heteroalkylene, carboxy, protected carboxy, hydroxymethyl,
protected hydroxymethyl, amino, protected amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
protected (monosubstituted)amino, (disubstituted)amino, carboxamide, protected
carboxamide, C1 to C4 alkylthio, C1 to C4 substituted alkylthio, C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 alkylsulfoxide, C1
to C4
substituted alkylsulfoxide, phenylthio, substituted phenylthio,
phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, phenylsulfonyl and substituted phenylsulfonyl;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to
C10
alkynyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7
substituted
cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl,
substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7
to C12
substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy, protected carboxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C1 to C7
substituted aryl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl
ring
and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
114/22
wherein n is from 1 to 4, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2
to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5
to C7
cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7 substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl,
naphthyl,
substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted
phenylalkyl, C1 to
C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, C1 to C4 alkyl sulfoxide, phenylsulfoxide,
substituted phenylsulfoxide, C1 to C4 alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to
C10 substituted alkyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted
phenylalkyl,
phenyl, and substituted phenyl;
R9 is selected from the group consiting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
C1 to C10
substituted alkyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
C1 to C7
acyl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl,
C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1
to C6 substituted alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted
phenylaminocarbonyl, provided that when the ring is unsaturated, R9 is absent;
and
Y is selected from the group consisting of CO2H, OH, SH, NHR12, C(O)NHR12,
CH2OH, CH2NH2, and CH2NHR12, wherein R12 is selected from the group
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
and a
functionalized resin,
114/23
or a salt of the 4-substituted quinoline.
27. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of C1
to C10 alkylene, C1 to C10 substituted alkylene, C2 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10
substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl,
phenylene,
substituted phenylene, naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl,
C7 to
C12 substituted phenylalkyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic ring,
heteroaryl ring, substituted heteroaryl ring, amino, (monosubstituted)amino,
and a
group of the formula: -CH2CONH-;
R2, R3, and R4 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen
atom, halo, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, C1 to C7 substituted alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene,
substituted cyclic C2 to C7 alkylene, and nitro;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to
C10
substituted alkyl, C3 to C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C3 to C7
cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C5 to C7 cycloalkenyl, C5 to C7
substituted cycloalkenyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl, naphthyl, substituted
naphthyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, carboxy,
protected carboxy, C1 to C7 acyl, C1 to C7 substituted aryl, heterocyclic
ring,
substituted heterocyclic ring, heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl
ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of a phenyl, substituted phenyl,
napthyl,
substituted naphphyl, a group of the formula:
Image
114/24
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the goup consisting of a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl,
substituted
phenyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, and C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl;
R7 is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl,
and C1
to C10 substituted alkyl;
R9 is selected from the goup consting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1
to C10
substituted alkyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkyl, C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl,
C1 to C7
aryl, C1 to C7 substituted acyl, phenylsulfonyl, substituted phenylsulfonyl,
C1 to C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C4 substituted alkylsulfonyl, C1 to C6
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1
to C6 substituted alkylaminocarbonyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, and substituted
phenylaminocarbonyl; and
Y is selected from the goup consisting of CO2H, NHR12 , C(O)NHR12, wherein R12
is selected from the goup consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1 to
C6
substituted alkyl, and a functionalized resin.
28. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is absent or present and, when present, is selected from the goup
consisting of
-CH2CONH- and -CH2CH(NHR8)-, wherein R8 is selected from the goup
consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl,
C2 to
C10 alkenyl, C2 to C10 substituted alkenyl, C2 to C10 alkynyl, C2 to C10
substituted
alkynyl, C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, C7 to C12
phenylalkyl,
114/25
C7 to C12 substituted phenylalkyl, C1 to C6 acyl, C1 to C6 substituted acyl,
aminocarbonyl, protected aminocarbonyl, (monosubstituted)aminocarbonyl,
protected (monosubstitituted)aminocarbonyl, (disubstituted)aminocarbonyl, C1
to
C4 alkylsulfonyl, C7 to C12 phenylalkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
substituted
phenylsulfonyl;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, halo, C1 to C6 alkyl, C1 to C7 alkoxy, cyclic C2 to C7
alkylene, and nitro;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, carboxy, C1 to
C10
alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, C1 to C10 alkenyl, C1 to C10 substituted
alkenyl,
C3 to C7 cycloalkyl, C3 to C7 substituted cycloalkyl, phenyl, substituted
phenyl,
naphthyl, substituted naphthyl, heterocyclic ring, substituted heterocyclic
ring,
heteroaryl ring and substituted heteroaryl ring;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, substituted phenyl, a
group of the
formula:
Image
wherein n is from 1 to 2, and a group of the formula:
Image
119/26
wherein R10 and R11 are, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, C1 to C10 alkyl, C1 to C10 substituted alkyl, phenyl, and
substituted
phenyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and C1 to C10
alkyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
29. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present is selected from the group
consisting of
CH2NHCO and CH2CH(NHR), wherein R' is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, a-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, a-:methylcinnamoyl, a, a, a-trifluoro-m
-toluoyl, a, a, a-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, a, a,.a-trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl,
butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chdorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl,
4-fluoro-a-methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-
butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-a-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl, (2,
5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (a,a,a-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl, (methylthio)acetyl,
114/27
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-.1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl,
1-phenyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2, 3-
dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2, 5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2, 5-
dimethylbenzoyl, 2,
6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4, 5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl,
(+/-)-2-ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-
carboxyl,
(+/-)-2-methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-
napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentamoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-tripherrylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl, 3,
5-dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,:5-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,5-dimethyl-p-anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4, 5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-a-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl,
4'-ethyl-4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-
biphenylacetyl,
114/28
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-
dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl, 2,3-
difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl, 2,5-
dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl, 2-
chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl, 2-(3-(3-
oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-methyldecyl, 2-
pentyl, 2-vitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-
(methylenedioxy)-
6-nitrophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3,5-
dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl, 3-
bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl, 3-
furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl, 3-
nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl, 3-
pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl, 4-chloro-3-
nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl, 4-
quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl, D,L-1,2-
(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-
dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and N-methyl-N
acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
114/29
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
30. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting of acetyl,
.alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-
p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl,
cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,-1-
adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
114/30
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,2-
bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4, 5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,2-
chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl, (+/-)-2-
ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxyl, (+/-)-
2-
methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-napthoyl, 2-
norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl, 2-
thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl, 3,4,5-
triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4, 5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4, 5-trimethoxycinnamoyl, 3,4-
dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-
imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-
dimethylbenzoyl, 3, 5, 5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl, 5-
bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl, 3,5-
dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl, 3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3-(3,4, 5-
trimethoxyphenyl,propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl, 3-(3,4-
dimethoxyphenyl,propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,3-
chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl, 3-
dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl, 3-
fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl, 3-iodo-4-
methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl, lauryl, 3-
methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl, 3-
phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl, 4-
chloro-o-anisoyl, 4-chlorobenzoyl; acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl,
.alpha.-
methylcinnamoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-
trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl, crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl,
cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl, cyclohexanecarboxyl,
cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl, cyclopentanecarboxyl,
cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl, 4-cyanobenzoyl,
114/31
hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl, isobutyroyl,
isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl, m-anisoyl, m-
toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-anisoyl, o-
toluoyl,
octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl, phenylacetyl,
picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butyla cetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-
3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl, 4-
isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl, (2, 5-
dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (4-
pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl, -1-
adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,4-
difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-
dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-
dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl, 2,6-
dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl, 2-
bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl, 2-
chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl, (+/-)-2-
ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxyl, (+/-)-
2-
methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-napthoyl, 2-
norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl, 2-
thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl, 3,4,5-
triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl, 3,4-
dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-
imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-
dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl,3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,5-
bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl,3,5-
dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3,5-dimethoxybenzoyl,3,5-dimethyl-p-
114/22
anisoyl, 3, 5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl,
4'-ethyl-4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-
biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom;
R5 is selected from the goup consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-(3-oxapropanoic acid))phenyl, 2-methoxy--1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-
methyldecyl,
2-pentyl, 2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-
(methylenedioxy)-
6-nitrophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl,
3,5-dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl, 4-chloro-3-
nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
114/33
pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl, D,L-1,2-
(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and
N-methyl-N-acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
31. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is absent or CH2NHCO;
R2 R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl,
2,3-difluorophenyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl,
2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl,
2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 3-pentyl, 2-fluorophenyl,
2-(3-oxa-3-propionoyl)-phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl, 2-butyl, 1-methyldecyl, 2-
pentyl,
2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-
nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3,5-
114/34
dichlorophenyl, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl,
3-bromophenyl, 3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-chromonyl,
3-furyl, 3-hydroxy-4-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl,
3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 2-phenylpropyl,
3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-carboxyphenyl, 4-chloro-3-
nitro-phenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromosalicyl, 5-nitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl, 6-methyl-2-
pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, phenyl, chloromethyl, cyclohexanyl,
D,L-1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, hydrogen atom, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromomethyl, trifluoro-p-tolulyl, and 2-methyl-2-propyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-ethoxyphenyl,
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 2,4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl, N-pyrrolidonyl, and
N-methyl-N-acetyl-amino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.
32. The single compound of claim 26, wherein:
R1 is absent or present, and, when present, is selected from the group
consisting of
-CH2NHCO- and CH2CH(NHR8), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting
of acetyl, .alpha.-cyclohexylphenylacetyl, .alpha.-methylcinnamoyl, .alpha.,
.alpha., .alpha.-trifluoro-m-toluoyl,
.alpha., .alpha., .alpha.-trifluoro-o-toluoyl, .alpha., .alpha., .alpha.-
trifluoro-p-toluoyl, benzoyl, butyroyl,
crotonoyl, cyclobutanecarboxyl, cycloheptanecarboxyl, cyclohexanebutyroyl,
cyclohexanecarboxyl, cyclohexanepropionoyl, cyclohexylacetyl,
114/35
cyclopentanecarboxyl, cyclopentylacetyl, ethoxyacetyl, 4-chlorocinnamoyl,
4-cyanobenzoyl, hydrocinnamoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-ethoxybenzoyl,
isobutyroyl, isonicotinoyl, 4-ethoxyphenylacetyl, isovaleroyl, 4-ethylbenzoyl,
m-anisoyl, m-toluoyl, m-tolylacetyl, methoxyacetyl, nicotinoyl, niflumoyl, o-
anisoyl,
o-toluoyl, octanoyl, p-anisoyl, p-toluoyl, p-tolylacetyl, phenoxyacetyl,
phenylacetyl, picolinoyl, piperonoyl, propionoyl, pyrrole-2-carboxyl, 4-fluoro-
.alpha.-
methylphenylacetyl, -4-fluorobenzoyl, 4-fluorophenylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl,
tetrahydro-2-furoyl, tetrahydro-3-furoyl, tigloyl, trans-3-(3-pyridyl)acroyl,
trans-3-hexenoyl, trans-cinnamoyl, trans-styrylacetyl, trimethylacetyl,
triphenylacetyl,
4-isobutyl-.alpha.-methylphenylacetyl, -vinylacetyl, xanthene-9-carboxyl,
(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl, (2-naphthoxy)acetyl, (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, (.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-m-tolyl)acetyl,
(methylthio)acetyl,
(phenylthio)acetyl, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentanecarboxyl,
-1-adamantaneacetyl, 1-naphthylacetyl, 1-napthoyl, 1-phenyl-1-
cyclopropanecarboxyl, 4-iodobenzoyl, 4-isopropoxybenzoyl, 2,3-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-methoxyphenylacetyl, 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
2,4-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
2,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 2,4-hexadienoyl, 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,5-
dimethylbenzoyl,
2,6-dichlorobenzoyl, 2,6-difluorobenzoyl, 4-methylcyclohexaneacetyl,
2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl, 2-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamoyl, 4-methylvaleroyl,
2-bromobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4,5-difluorobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-fluorophenylacetyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-ethoxybenzoyl, 2-ethyl-2-hexenoyl, 2-ethylbutyroyl, (+/-)-2-
ethylhexanoyl, 2-fluorobenzoyl, 2-furyl, 4-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxyl, (+/-)-
2-
methylbutyroyl, 2-methylcyclopropanecarboxyl, 2-naphthylacetyl, 2-napthoyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, 2-phenylbutyroyl, 2-propylpentanoyl, 2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
2-thiopheneacetyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionoyl,
3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl,
3,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorophenylacetyl, 3,4-difluorobenzoyl,
4-imidazolecarboxyl, 4-tert-butyl-cyclohexanecarboxyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl,
3,4-dimethylbenzoyl, 3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl,
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoyl, 5-bromonicotinoyl, 5-phenylvaleroyl, 3, 5-
114-36
dichlorobenzoyl, 6-chloronicotinoyl, 3, 5-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3, 5-dimethyl-p-
anisoyl,
3,5-dimethylbenzoyl, 3-(2-methoxyphenyl)propionoyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetyl,
3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propionoyl, heptanoyl, 3-benzoylpropionoyl, 3-
bromobenzoyl,
3-bromophenylacetyl, chromone-2-carboxyl, 5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxyl,
3-chlorobenzoyl, 3-cyanobenzoyl, 3-cyclopentylpropionoyl,
3-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 3-fluoro-4-methylbenzoyl, 3-fluorobenzoyl,
3-fluorophenylacetyl, 6-methoxy-.alpha.-methyl-2-napthaleneacetyl,
3-iodo-4-methylbenzoyl, formyl, 6-methylnicotinoyl, 1-isoquinolinecarboxyl,
lauryl,
3-methoxyphenylacetyl, 3-methyl-2-thiophenecarboxyl, 3-methylvaleroyl,
3-phenoxybenzoyl, 3-phenylbutyroyl, 3-thiopheneacetyl, 4'-ethyl-4-
biphenylcarboxyl,
4-(diethylamino)benzoyl, 4-benzoylbenzoyl, 4-biphenylacetyl,
4-biphenylcarboxyl, 4-bromobenzoyl, 4-bromophenylacetyl, 4-butylbenzoyl,
4-chloro-o-anisoyl, and 4-chlorobenzoyl;
R2, R3, and R4 are each, independently, selected from the group consisting of
a
hydrogen atom, hydroxy, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, methyl, methoxy, nitro
and
-CH=CH-CH=CH- fused to adjacent positions;
R5 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, phenyl,
chloroacetyl,
cyclohexanyl, D,L- 1,2-(dihydroxy)ethyl, carboxy, acetyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl,
tribromoacetyl, trimethylacetyl, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolyl, 1-napthyl,
2,3,4-trifluorophenyl, 2,3,5-trichlorophenyl, 2,3-difluorophenyl, 2,4-
dichlorophenyl,
2,5-difluorophenyl, 2,5-dimethylphenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 2-bromophenyl,
2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl, 2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl, 2-cyanophenyl, 2-
ethylbutyryl,
2-fluorophenyl, 2-(2-oxymethylenecarboxy)phenyl, 2-methoxy-1-naphthyl,
2-nitro-5-chlorophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 2-pyridinyl, 3,4-(methylenedioxy)-6-
nitrophenyl,
3,4-difluorophenyl, 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3,5-dichlorophenyl,
3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl, 3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl, 3-bromophenyl,
3-carboxyphenyl, 3-cyanophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3-formylchromonyl, 3-furyl,
3-hydroxyphenyl, 3-nitro-4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, 3-
114/37
phenylbutyryl, 3-pyridinyl, 4-bromo-2-thiophenyl, 4-bromophenyl,
4-carboxyphenyl, 4-cyanophenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-pyridinyl,
4-quinolinyl, 5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl, 5-vitro-2-furyl, 5-norbornene-2-yl,
6-methyl-2-pyridinyl, 9-ethyl-3-carbazolyl, 2,3-dimethylvaleryl, 2,2-dimethyl-
4-pentenyl,
3-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl, 3-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl, 2-methylbutyryl,
2-methylvaleryl, 4-chloro-3-nitro-phenyl, 4-trifluromethyl)phenyl,
2-methylundecanyl, and .beta.-phenylcinnaminyl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of nalidixoyl, 2-phenyl-4-
quinolinecarboxy,
2-pyrazinecarboxy, niflumoyl, 4-nitrophenylacetyl,
4-(4-nitrophenyl)butyroyl,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-acetyl,
3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenylacetyl, 4-nitrocinnamoyl,
3,4,-(methylenedioxy)cinnamoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl, benzoyl,
2-chlorobenzoyl, 2-nitrobenzoyl, 2-(p-toluoyl)benzoyl, 2,4-
dinitrophenylacetyl,
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-propionyl, 4-biphenylacetyl, 1-napthylacetyl,
(2-napthoxy)acetyl, trans-cinnamoyl, picolinyl, 3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoyl,
(4-pyridylthio)acetyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl, 3,4-dichlorobenzoyl,
4-biphenylcarboxy, thiophenoxyacetyl, 1-benzoylpropionyl, phenylacetyl,
hydrocinnamoyl, 3,3-diphenylpropionyl, 3,3,3-triphenylpropionyl,
4-phenylbutyryl, phenoxyacetyl, (+/-)-2-phenoxypropionyl,
2,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoyl,
2,4-dihydroxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl, 3,4,5-triethoxybenzoyl,
3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl, 2-benzoylbenzoyl, 1-napthoyl, xanthene-9-carboxy,
4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoyl, 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoyl, 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl,
2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoyl, 4-dimethylaminobenzoyl, 4-(diethylamino)benzoyl,
4-nitrobenzoyl, 3-(dimethylamino)benzoyl, p-methylbenzoyl, p-methoxybenzoyl,
trimethylacetyl, tert-butylacetyl, (-)-menthoxyacetyl, cyclohexanecarboxy,
cyclohexylacetyl, dicyclohexylacetyl, 4-cyclohexylbutyroyl,
cycloheptanecarboxy,
13-isopropylpodocarpa-7,13-dien-15-oyl, acetyl, octanoyl, (methylthio)acetyl,
3-nitropropionyl, 4-amino-3 hydroxybenzoyl,
3-(2-methyl-4-nitro-1-imidizoyl)propionyl, 2-furoyl, (s)(-)-2-pyrrolidone-5-
carboxy,
114/38
(2-pyrimidylthio)acetyl, 4-methoxy-2-quinolinecarboxy, 1-adamantanecarboxy,
piperonoyl, 5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazole-4-carboxy, rhodanine-3-acetyl,
2-norbornaneacetyl, nicotinoyl, 9-oxo-9H-thioxanthene-3-carboxyl-10,10
dioxide,
2-thiophenecarboxy, 5-nitro-2-furanoyl, indole-3-acetyl, isonicotinoyl,
3.alpha.-hydroxy-5 .beta.-cholan-24-oyl, (3 .alpha., 7.alpha.,12.alpha.)-
trihydroxy-5.beta.-cholan-24-oyl,
(3.alpha., 5.beta.-12.alpha.)-3,12, dihydroxy-5-cholan-24-oyl, (3.alpha.,
5.beta., 6.alpha.)-3,6-dihydroxy-cholan-24-oyl,
L-alaninyl, L-cysteinyl, L-aspartinyl, L-glutaminyl, L-phenylalaninyl,
glycinyl,
L-histidinyl, L-isoleucinyl, L-lyscinyl, L-leucinyl, L-methionylsulfoxide,
L-methionyl, L-asparginyl, L-prolinyl, L-glutaminyl, L-arganinyl, L-serinyl,
L-threoninyl, L-valinyl, L-tryptophanoyl, L-tyrosinyl, D-alaninyl, D-
cysteinyl,
D-aspartinyl, D-glutaminyl, D-phenylalaninyl, glycinyl, D-histidinyl, D-
isoleucinyl,
D-lyscinyl, D-leucinyl, D-methionylsulfoxide, D-methionyl, D-asparginyl,
D-prolinyl, D-glutaminyl, D-arganinyl, D-serinyl, D-threoninyl, D-valinyl,
D-tryptophanoyl, D-tyrosinyl, 2-aminobutyroyl, 4-aminobutyroyl,
2-aminoisobutyroyl, L-norleucinyl, D-norleucinyl, 6-aminohexanoyl,
7-aminoheptanoyl, thioprolinyl, L-norvalinyl, D-norvalinyl, .alpha.-
ornithinyl, methionyl
sulfonyl, L-naphthylalaninyl, D-naphthylalaninyl, L-phenylglycinyl,
D-phenylglycinyl, .beta.-alaninyl, L-cyclohexylalaninyl, D-
cyclohexylalaninyl,
hydroxyprolinyl, 4-nitrophenylalaninyl, dehydroprolinyl, 3-hydroxy-1-
propanesulfonyl,
1-propanesulfonyl, 1-octanesulfonyl, perfluoro-1-octanesulfonyl,
(+)-10-camphorsulfonyl, (-)-10-camphorsulfonyl, benzenesulfonyl,
2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl, p-toluenesulfonyl, 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl,
n-acetylsulfanilyl, 2, 5-dichlorobenzenesulfonyl, 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl,
2-mesitylenesulfonyl and 2-napthalenesulfonyl;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom and methyl;
R9 is a hydrogen atom; and
Y is selected from the group consisting of C(O)NH2 and C(O)NH bound to a
functionalized resin.