Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
1
DESCRIPTION
MOUNTING AN ARTICLE UPON A SUPPORT
FIELD OF THE INVBNTION
This iztvention relates to mountings for articles upon supports.
BACKGROUND ART
Mountings for articles upon supports are commonplace and diverse in design.
However, mountizags having certain specific requirements need to be of
specific designs
to satisfy those requirements. For instance, some mountings are required to
withstand,
in use, tlxe application of forces applied either to an article or to a
support without there
being any change in relative orientation of the azticle to the support such as
may be
caused by loosening of the mountings or by reason of movement of one part of a
mounting upon another. Pardcular instances of interest are where mountings are
subjected to sudden violent and strong forces placed eitlm upon the article or
upon the
suppor#, such forces being, for instance, either in the form o:Fimpact forces
or vibrational
forces. Such forces are applied in the use of weaponry.
Weapons which depend upon being mounted upon weapon carriers or other
supports sbould have reliable mountings for this purpose, for any change in
condition
of these motuxtings or in relative orientation of their parts, as may be
brought about by
such forces as referred to above, may have disastrous results for the weapon
user.
Similar concerns also apply to parts of weapons which are assembled together
and
which may be caused to loosen or come apart due to the application of sudden
violent
aud/or vibrational forces. By way of example, grenade launching m,achine guns
which
fire relatively slow, heavy rounds necessarily require elevation of their
barrels by a
relatively large angle, perhaps at least 30 dcgrees above the sight line of
the target. In
order to elevate a barrel to the correct angle of elevation and also to enable
it to move
in azitnuth to be able to f;re accurately at a target, an aiming system is
required.
In modem weapons, aiming systems include sight uw'tts coupled by computer to
a visual display unit. There are two critical gun settings. In one setting,
the aiming
system needs to be calibrated. In the other setting, the aiming system needs
to be
"boxesighted" with the gun bore for accurate alignment of the bore with the
sight unit.
Maiutenance of calibration is primarily of importance during use of the
weapon. In
other words, a mounting holding the sight unit onto another part of the
weapon, e.g.
another pmt of the aiming system, rrzust withstand sudden and extreme forces
applied
to it r~vhen the weapon recoils after firing, without any change in mounting
condition
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
2
resulting in shifting the position of the sight unit. It is also necessary to
mai,ntaixx the
critical settings upon reinstallation of the sight unit after removal of the
sight unit from
the gun for transportation purposes.
Hence, a great deal of reliance Ytzust be placed upon a mounting for
connecting
the sight unit. It is known, however, that in existing mountings for this type
of purpose,
loosen.ing of the mounting parts may result durizf,g fuing. Also, after
removal of a sight
unit, it is possible for foreign matter such as dust particles to be present
between mating
parts of the mou,nting which, upon reassembly, prevent intimate mating of
mounting
parts, thereby resulting in inaccuracy in repositioning of the sight unit.
Inaccurate firing
of the weapon will then result,
Mountings which may be subjected to sudden forces, such as forces that may
occur during movement of an assembly of other articles upon supports are also
known.
Such articles include video cameras and theodoiates which are continually
moved, laid
to rest in awkward positions, or transported about, wheteby their mountings
may suffer
indetenninate forces from diverse directions.
SUMIVXATtY OF TIiE INVENTION
The invention seeks to provide a mnounting for mounting an article upot a
support
so that positional orientation of the article remains sabstaztially unchanged
when the
assembly of article and support is subjected to forces in use and also
positional
orientation of the article upon its support is replicated when the article is
remounted
thereon after its removal.
Accordingly, the present invention provides a rn,ounting for mounting an
article
upon a support comprising first and second mounting members which are
relatively
movable into assembled relationship in which the second mounting member is
held in
a seating position by the first mouYiting member, each mounting member having
a
seating means, the seating means of the two mounting members lying in abutting
relationship with the second mounting naember immovably registered in a first
plane
relative to the fhst rnounting member when the second mounting member is in
the
seating position, the mountang also comprising three spaced mounting member
registration projections which are located to provide, in th.e seating
position, contact
between the mounting members in a three spaced position and staggered
relationship
froru side to side of the second mounting member to register the second
mounting
member in a second plane relative to the first mounting member, the
registration
projections providing wiping action between the mounting members during their
movement into assembled relationship; and means for locking the mounting
mernbers
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
3
together with the second mouttting member reenaining in the seating position,
wherein
the looldng means comprises a plurality of locking anr,ns carried by one of
the mounting
members, each azm being spring-ucged to move it into a position of locking
engagement
with the other mounting member when the second mount.ing member is in its
seating
position, and wherein there are two locking arsns carried by the first
mounting member
and pivotable about pivot axes, respectively, to engage opposing sides of the
second
mountixtg member when the second mouttting member is in its seating position.
For "ample, the mounting may be a mounting for mounting a gun upon a
support.
In a preferred arrangement of the invention, the first mounting member has a
receiving channel for receiving the secon,d mounting member during assembly of
the
mounting members. This receiving charuiel has edges defming a first pair of
guide
surfaces. A second pair of guide surfaces orl the opposite sides of the second
mounting
member confxont the first pair of guide surfaces during assembly. Each
projection is
provided as part of a respective one of the guide surfaces. Hence, the
regislration
projections may be provided on both of the guide surfaces of one or the other
pair of
guide surfa.4es. Alternatively one projection may be provided upon one
mounting
member and the other two projections upon the other mounting member.
It is envisaged that the three registration projections may simply register
the
second member in its second plane according to the invention. Idowever, in a
preferred
arrangement, the registration projections serve also to immovably register the
second
mounting member in the first plane relative to the Erst mounting member. Itt
this
preferred arrangement, the guide surfaces of the first pair are inclined, in a
lateral
direction, towards the seating means of the first mounCing member and these
guide
surfaces are convergent along thear length. The second pair of guide surfaces
are
correspondingly inclined and convergent. Hence, during assembly of the two
mounting
members, the guide surfaces of one pair move longitudinally and, because of
the
convergence, also laterally of the guide surfaces of the othex pair. This
movement
brings the second mounting member into the seating position in which each
projection
of a guide surface abuts against an opposing guide surface. This action forces
the
seating means against one another to provide the immovable registration
discussed
above_
The locking means is preferably designed for quick release so as to enable
rapid
disconnection of the two mounting members and thus of the article from the
support on
which it is cazTied. For this purpose the locking means preferably comprises a
plurality
of locking arms, nemely two, carried by one of the mounting members, each arm
being
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
4
spriug-urged about a pivot to move it into a position of locking engagement
with the
other mounting member when the two mounting members are in assembled
relationship.
In order to overcome the possibility of repeated operation of sudden
accelerations
i-aadvertently causing disengagement of one or other ofthe locking arms from
its loclcing
position, each arm is balanced about its pivotal axis so that the mass of the
arm on one
side of the pivotal axis is substantially equal to the mass on the other side.
Preferably, each of the artns has a detent surface to engage said other of the
mounting members and the geometry of the detent surface, arm and its pivots
preferably
are determined so that forces acting to separate the two mounting members are
less than
friction forces between the detent surface and said other of the mounting
members.
Another aspect ofthe invention provides a mownting for mounting an article
upon
a support compxising first and second mounting mernbers which are relatively
rnovable
into assembled relationship in which the second mounting member is held in a
seating
position by the first mounting member, each mountiug member having a seating
means,
the seating means of the two mounting members lying in abutting relationship
with the
second mounting member immovably registered in a first plane relative to the
first
mounting member wheu the second mounting member is in the seating position,
the
mounting also comprAsing three spaced mounting member registration proj
ections which
are located to provide, in the seating position, contact betvveen the mounting
members
in a three spaced position and staggered relationship ftom side to side of the
second
mounting member to register the second mounting member m a second plane
relative
to the fixst mounting member, the registration projections providing wiping
action
between the mounting members during their rtiovement into assembled
relationship; and
means for locking the mounting members together with the second mounting
member
remaining in the seating position, wherein the loeldng xnean,s comprises two
locking
arms carried by the first rnouziting member and pivotable aboutpivot 2-xes,
respectively,
each locking arm being spring-urged into a position of locking engagement with
the
second mounting member when the second mounting member is in its seating
positiost,
each loclring arm being engagable in a respective slot defined in the second
mounting
member to engage a side of the slot and bold the second mounting member in its
seating
position, each locking arm has a latcli end portior, fnr_enaaSing c:id-o-ida
aftho eAvL- an,d---- ------
the configuration and dimensioning of each latch end portion and its
associated slot, and
the position of the pivot axis, are such that, in use, any component of force
teinding to
move the locking arm outwards from its locking position resulting from a force
acting 35 parallel to a directiom of said movement into assembled relationship
is less than the
- ',
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
~
effect of friction between the latch end portion and the associated slot side
and the action
of the spring.
Another aspect ofthe invention provides a mounting for nnountitng an article
upon
a support compzising first and second mounting members which are relatively
movable
into assembled relationship in which the second mou.nting member is held in a
seating
position by the first mounting member, each mounting member having a seating
means,
the seating means of the two mouzlting members lying in abutting relationship
with the
second mounting member imntovably registered in a firet plane relative to the
first
mounting member when the second mountaing member is iu the seating position,
the
xnounting also cornaprisin.g three spaced mounting
mevnberregistrationprojections which
are located to pxovide, in the seating positioia, contact between the
Ynounting members
in a three spaced position and staggered relationship from side to side of the
second
mounting member to register the second mounting member in a second plane
relative
to the first mounting meznber, the registration projections providing wiping
action
between the mounting members during theirmovement into
assenxbledrelatioztship; and
means for locking tha mounting members together with the secon,d mountin,g
member
remaining in the seating position, wherein the loclsiwg means comprises a
plurality of
locking arms carried by one of the mounting members, each arni being spring-
urged to
move it into a position of locking engagement with the other monnting member
when
the second mounting member is in its seating position, rxrherein each locldng
arrn is
pivotable about a pivot axis for movement into said position of looldng
engagement and
has its mass balanced about said pivot axis.
Another aspect of the invention provides a mounting for mounting an article
upon
a support comprising irat and second mounting members which are relatively
movable into
assembled relationship in which the second mounting member is held in a
seating position
by the first mounting menxxber, each mounting member having a seating means,
the seating
means ofthe two mounting members lying in abnttingrelationship with the
secondmounting
member immovably registered in a fizst plane relative to the first mounting
member when
the second mounting member is in the seating position, the mounting also
comprising tluee
spacedmountixtg member registration projections which are located to provide,
in the seating
position, corntact betwecu the mounting members in a three spaced position and
staggered
relationship from side to side of the second mounting member to register the
second
mounting member in a second plane relative to the first mounting member, the
registration
projectionsprornidingwipingactionbetweenthemountingmembersduringthexrmovement
into asse7nbled relationship; and means for locking the mounting members
together with the
, .',
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
6
second mounting member remaining in the seating position, wherein the first
mounting
member has a base and two side flanges extending in opposition to each other
from the base
to define with the base a receiving channel for the second mounting member,
the base having
a seating surface of the seating means facing into the channel, and the
flanges having
inwardly tuirn.ed ffree ends wb,ich provide a first pair of guide surfaces
which converge in a
direction away from an entrance to the channel for receiving the second
mounting member,
the surfaces ofthe fixst pair being incliued, in a lateral direction, towards
the seating surface
of the first mounting member, the second mounting member having a seating
surface of tJle
seating means for abutting contact with the seating surface of the first
mounting when the
second mounting member is in the seating position, the second mounting
merxtber having a
second pair of guide surfaces which converge and are inclined correspondingly
to the first
guide surfaces and each registration projection being provided as part of a
respective guide
surface whereby during movement of the two mounting members into assembled
relationship, each guide swface of one pair moves longitudinally nd laterally
of a
corresponding guide surface of the other pair until, with the second mounting
member in its
seating position, each of the registration projections on its respective guide
surface engages
a corresponding guide surface with the inclination ofthe guide surfaces retai
ny;n ; the abutting
contact of the seating means to immovably register the seoond mounting member
in the first
plane, and further connprising a pair of locldng anns each pivotally mounted
upon a
respective flange of the first mounting member, tbLe locking arms being spring
urged to move
tbrough a slot in a respective flange and into another slot provided in the
second mounting
mernber so as to hold the second mounting member in its seating position.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, a mounting for
mounting
an article upon a support comprising a first mounting member amd a second
mounting
member, one of the first mounting member and the second mounting member for
attachment to the article and the other of said first mounting member and the
second
mounting member for attachment to the support, the mounting ;tnembers being
relatively
movable into assembled relationship in which the second mounting member is
held i.,x
a seating position by the first mounting member, the mounting also including
means for
urging the second mounting member into its seating positioti, the urging means
comprising a plurality of locking arms which are pivotally connected about
pivotal axes
to the first mounting xxzember, each locldng arm being resiliently moved
towards a
locking position in locking engagement with opposite sides of the second
rnounting
member, each locking anm having its mass balanced about its pivotal axis.
Accord.ing to yet another aspect of the invention, a mounting for mounting an
article upon a support comprises first and second mounting members which are
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
7
relatively movable into assembled relationship in which the second mounting
member
is held in a seating position by the first mounting member, each mounting
member
having a seating means with the seating means of the two mounting members
lying in
abutting relationship with the second mounting member immovably registered in
a first
plane relative to the first mounting member when the second mounting member is
in the
seating position, whereiia the first mounting member has a receiving channel
for
receiving the second rnounting member during assembly of the mounting members,
the
receiving channel having edges defined by a first pair of guide surfaces, a
second pair
of guide surfaces being provided on opposite sides of the second n4ounting
member to
conf'iront and move along the first pair of guide suxfaces during assembly,
and each
registration projection is provided as part of a respective one of the guide
suxfaces; and
means for locking the mounting members together with the second mounting
member
in the seated position.
BRIEF DESCRIP'TION OF'Y"HE DRAWINGS
One embodiment of the invention will now be described, by way of example,
with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:-
Figure 1 is a front perspective view of a grenade machine gun according to the
embddimextt;
Figure 2 is a schematic view of the rear of the machine gun; '=
Figure 3 is a rear perspective view of an aiming system of the rrAachin.e gun;
Figare 4 is a rear elevational view of part of the aiming system and showing a
mounting included in the aimiug system;
Figure 5 is a top asometric view of the mounting of Figure 4 in assembled
position;
Figure 6 is aperspective view of the underside of an upper mountiuxg member of
the mounting;
Figure 7 is an underside plan view of the upper mounting member:
Figure 8 is an end view of the upper mounting member in the direction of arrow
VIIY in Figure 5;
Figure 9 is an isonaetric view of the underside of a lower mounting member of
the mounting;
Figure 10 is an end view of the lower mounting mexnber in the direction of
arrow
X in Figure 9;
Figures 11 and 12 are underside isometric views of the mounting members and
showing different positions of the members during assembly;
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
8
Figure 13 is a cross-sectional view of a partial. assembly of the mounting
members taken along line XIII-XIII in Figure 12;
p'igwre 14 is a view of the finished assembly of the mounting in the direction
of
mow VIIT in Figure 5;
Figure 15 is a scrap view, partly in cToss-section and to a much larger scale
showing a]oclang arm in a locking position to hold the mounting members
together;
Figure 16 is a view similar to Figure 9 of a modification to the embodiment;
and
Figure 17 is a view similar to Figure 14 of the modification_
DESCRIPTION OF THE BMBODIMBNT
With reference to Figures 1, 2 and 3, a weapozi embodying the invention,
specifically a grenade machine gun, comprises a weapon body 10 having a barrel
12
mounted in a cradle mount 14, with an aiming system 16 mounted to one side of
the
cradle mount 14. The cradle mount 14 has upstanding arms 18 and 20 extending
one
from each side of the weapon body 10. Joucn-als 22 and 24 (see Figure 2)
project from
opposite sides of the weapon body 10 and into bearings 26 and 28 in arms 18
and 20,
respectively, permitting the weapon to pivot in elevation relative to the
cradle mount 14.
A tapered pintle 30 fixedly secured in a central base unit 36 of a tripod 38
projects upwards through a bearing 32 in a bight portion 34 of oradXe mount
14. Hence,
the cradle mount 24 can rotate in azirnuth relative to the tripod 38.
FTaridles 40 at the
rear end of the weapon body 10 allow the user to pivot the barrel in
elevation, and
azimuth. Three control buttons 42,44 and 46, are disposed adjacent the handles
40 so
that they can be operated by the user. A trigger 48 is positioned between the
two
handles 40.
The aiming system 16 comprises a coupling unit 52 and a sight unit 54 which is
supported upon the coupling unit 52 by a mounting 56 which is to be described
in, detail
below_ A display unit 58 is mounted upon the sight unit 54 by means of a
rearwardly
extending support arm 60 (not shown in Figure 1 - see Figures 2 and 3) so that
the
display unit 58 is immediately above the rear portion of the weapon body 10.
The
support arm 60 may also carry electrical connections (not shown). A support
shaft 62
extends through bearings 64 and 66 in opposite side walls 68 and 70,
respectively, of a
housing 72 of the coupling unit 52. The end portion of shaft 62 supported by
the bearing
64 has a tapered hole 74 to driveably receive a mating tapered end portion 76
ofjournal
24 which projects beyond bearing 28 and cradle mount 14. The shaft 62 thus
constitutes
a first part of the coupling unit that is connected to the weapon for movement
in
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
9
elevation with the barrel 12. For more details, the reader is directed to
Canadian patent
No. 2,245,406.
For purposes of the present invention, further details of this embodiment of
the
machine gun construction, apart from anything relevant to the mounting 56,
need be
mentioned only briefly.
Hence, briefly, a clutch unit 78 acts between coupling unit 52 and cradle
mount
14. Actuation of clutch unit 781ocks the coupling unit 52 and hence the sight
unit 54
to the cradle mount 14.
A second clutch unit 80, inside coupling unit 52, acts upon actuation to lock
the
coupling unit 52 and the sight unit 54 to the shaft 62 and hence to the weapon
body 10.
The clutch units 78 and 80 are operable alternatively of one another, by the
push
button 42 which is a changeover switch. Engagement of clutch unit 80Iocks the
housing
72 to the weapon body 10 and so it can pivot in elevation relative to the
cradle mount
14, the elevation axAgle being measured by an angle decoder, i.e. a resolver
84, mounted
around bearing 66 to measure angula,r displacement between the housing 72 aiad
the
shaft 62. Engagem,ent of clutch unit 78 locks the housing 72 to the cradle mou-
nt 14
while the housing 72 is released from the shaft 62. Consequently the weapon
body 10
and batxe112 can pivot in elevation independently of the aiming system 16 and
the sight
unit 54.
At all times, however, the aiming system 16 will rotate with the weapon body
10
in azimuth as cradle mount 14 rotates about bearing 32. The azimuthal rotation
is
measured by a second resolver 86 mounted around the bearing 32, for providing
a signal
}
repFesenting rotation of cradle mount 14 about pintle 30 which is fixed to the
tripod 3$.
It is essential to ettable consistent and accurate firing of the gun at a
target. Thus,
it is necessary to accurately position various essential parts of the machine
gun and to
ensure that they cooperate correctly. For this purpose, the sight unit 54 is
coupled by
control computer 88 (Figure 2) to the display unit 58. The air-Aing system is
calibrated
in the factory and is instalied onto the weapon aftex-wards, usually "in the
ffield". Once
the sight unit 54 has been installed onto the weapon by engaging the tapered
portion 76
of the journal 24 in the hole 74 in the shaft 62, it must be "boresighted". A
boresighting
device displaying an aiming point marker (not shown) is placed into the barrel
12 and
the position of an aiming reticle (not shown) generated by the control
computer 88 and
displayed by display 58, represents, as is conventional, is adjusted to set a
zero-range
aiming peint or zero-range ballistic solution. Subsequently, the position of
the aiming
reticle will be adjusted by the control computer 88 to give the required
offset for
superelevation and other factors in the ballistic solution. It should be noted
that a
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
rangefinder reticle (not shown) will not be coincident with the aiming reticle
in the
displayed image, reflecting the fact that the sight line of the rangefinder is
offset relative
to the sight line of an imaging device 92.
After the above procedure, it becomes eritxcal to ensure that boresighting and
5 calibration remain unchanged to enable the gun to fire accurately at
targets. 'I'he gun is
constructed, with the intention of enabling removal of the sight unit 54 and
the display
unit 58 as a single entity for transporkation purposes, this single unit then
being again
reassembled onto the gun before use. It is essential that, when the sight unit
and display
unit 58 are returned onto the gun, they returu accurately to their positions
occupied
10 before removal so as to ensure accuracy in returning to the previously set
boresighting
and calibration of the aiming system 16. It is also essential that sudden
impact loadings
placed upon the gxm, which may be repetitive for machine gun operation, should
not
alter the set calibration or boresightitig. In addition, any vibrational
loadings should also
have no effect The mounting 56, now to be described, advantageously ensures
accuracy
in xelocation of the sight unit 54 and the display unit 58 and also prevents
movement of
these units upon the coupling unit 52 in use.
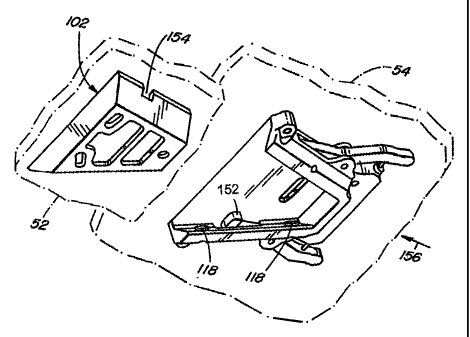
As shown by Figures 4 onwards, the mounting 56 comprises two mounting
members, namely upper mounting member 100 which is fixedly secured underneath
tlxe
base of the sight unit 54, and a lower mounting mezxiber 102 which is fixedly
secured
to the upper surface of the coupling unit 52.
As shown by Figures 5, 6, 7 and 8, in particular, the upper mounting m.ember
100
comprises a planar base 104, by which it is secured to the sight unit 54, and
two flanges
106 depending downwardly from side edges of the base 104. The flanges 106
converge
towards each other so that the base in pIart view has a fiusto-pyramidal
appearance. An
under planar surface 108 of the base 104 is a seating surface which provides
seating
means of the upper mounting meniber which, in conjunction with seating means
of the
lower mounting member (as will be described) relatively locates the mounting
members
together in a horizontal plane. As shown particularly by Figure 8, the flanges
106 turn
inwardly towards each other at their free ends to provide oppositely inclined
guide
surfaces I 10 for guarding reception of the lower mounting member 102. These
guide
surfaces 110 are thus inclined laterally towards the seating surface 108 and
are separated
therefrom by short vertical surfaces 112. The guide surfaces 110, surfaces 112
and the
seating surface 108 define a receiving channel 114. This is for receiving the
lower
mounting merziber. Tlae flanges 106 and thus the guide surfaces 110 converge
away
from an entea-nce 116 for receiving the lowcr mounting member and which is
defined
at the widest part of tho chamber 114.
7
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
11
The upper mounting member 100 also includes tbree mounting meYnber
registration projections 118 which are located to provide, in a seating
position of the
lower mounting meaaber within the upper mounting member, discrete contact in
three
spaced positions lying in staggered relationship from side to side of the
lower mounting
member. As shown in Figu7res 6, 7 and 8, these three projeotions 118 are
provided upon
the two guide surfaces 110. One of the guide surfaces 110 is formed with two
of the
projections 118, one projectiou lying towards the entrance 116 and the
oth.erprojection
lying tovrards a closed end 119 of the receiving channel 114. The other
projection 118
is formed as part of the other guide surface 110 in a position sttbstantially
midway
between the other two projections 118 from the entrance 116 to the channel.
Hence, as
already stated, the projections are staggered down the length of the channel,
from side
to side of the channel.
As shown by Figures 9 and 10, the lower mounting member 102 has a base 120
by which it is secured to the coupling unit 52. Upwardly extending flanges 122
flare
outwardly $om the base 120. These flanges have outer guide surfaces 124 which
are
inclined outwardly complementary in angle to the lateral inclixtation of the
two guide
surfaces 110 of the upper mounting member. The flanges 122 also converge from
an
end wall 128 at a wide end of the mounting member with the angle of
convergence
corresponding to the convergence angle of the guide surfaoes 110. As may be
seen from
Figures 9 and 10, the lower mounting member 102 is basically dish-shaped and
also has
an end wall 130 at its natrower end. The lower mounting member is conveniently
formed by casting or machining from a single piece.
The lower mounting member also has seating means which comprises coplanar
end seating surfaces 132 of the flanges 122 and of the end walls 128,130.
These seating
surfaces are for abutting engagement with the seating surface 108 upon
assembly of the
rnounting members as will be described,
The mduuiing also comprxses means for urging the two motuxting members into
and to remain in assembled relationship with the lower mounting mem,ber 102 in
a
seating position. This urging means comprises two loclcing arms 134 (Figures
5, 7 and
8) located one at each side of the upper mounting member 100 in identical
positions
symrnetrically one on each side of a centre line 136 of the upper mounting
member.
Each loclcing arm is pivoted at a position intermediate its ends by a pivot
pin 137
received through mounting ltigs 138 extending outwards froxn a:
sw,so3iate&flaxrgc=1"~S. -
A projecting end region 140 of each loelcing arm 134 is biased outwardly from
the upper
mounting membez= 100 by a hollow piston 142 which is housed within a cylinder
144 and
urged outwards by a compression spring 145 within the piston 142. A short
operating
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
12
rod 146 having one end secured to the end region 140 of the locking arm 134
extends
to contact at its other end the head of piston 142. Outward movement o~the end
region
140 of the locking arm causes movement of the other end region 148 of the
aocking arm
on the other side of the pivot pizt 137 inwardly into the receiving
channe1114. The other
end region 148 of each arm extends through a receiving slot 150 (Figures 5, 7,
11 and
12) of the upper mounting member 100 with a latch end 152 of the loclCang arm
extending into the receiving chamber. In the position shown in Figures 5, 6,
7, 11 and
12, each locking arm is held in a locking position in which the latch end 152
engages
within an associated slot 154 (Figures 9, 11 and 12) formed in one of the
flanges 122 of
the lower motmtxng member 102, when the two mounting members are in their
assembled positions. For reasons of clarity of the description, Figures 11 and
12
represent the mounting parts from beneath to more cleatly indicate their
relationship.
To assemble the sight unit 54 onto the coupling unit 52, the sight un.it is
manually
positioned over the coupling unit with the mounting members aligned (Figure
11). The
upper mounting member is slid laterally (in a right to left direction in
Figures 2 and 3)
over the lower mounting member so that the narrow end ofthe lower mounting
member
is received into the entrance 116 to the receiving channel 114. Continued
movement in
the direction of arrow 156 in Figures 11 and 12 is accompanied by sliding
contact
movement between the seating surface 108 of the upper mountiug member and the
seating surface provided by the flanges 122 as shown in Figure 13. As the two
members
are slid together, the force acting between the inclined guide surfaces 110
brings the
seating surfaces into engagement.
It will be noticed from Figure 12 and especially from Figure 13, that as the
mounting members 100 and 102 move towards their assembled positions, the guide
surfaces 110 of the upper mounting rnember are spaced away from the guide
surfaces
124 of the lower mounting member because of the convergence of the surfaces of
each
pair. However, as movement towards assembly of the members proceeds, each
surface
110 moves longitudinally and laterally of a respective surface 124. Towards
the end of
the movement, each surface 110 directly faces its respective surface 124 and
the
projections 118 on the surfaces 11.0 engage the surfaces 124. This engagement
takes
place directly before the lower mounting member 102 is in its seating position
effects
a wiping action of the projections ] X$ upon tiae surfaces 124. The wiping
action
displaces any particles of dust or other foreign matter from these surfaces
and also from
the projections themselves. As a result, clean parts of the surfaces 124 are
engaged in
the assernbledposition by clean parts of the projections 118. In addition,
towards the
end ofmovement ofthe mounting members together, the engagement ofthe
projections
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
13
118 upon the surfaces 124 applies an upward force to the lower mounting member
102
which results in engagement between the seating surface 108 of the upper
mounting
member and the seating surfaces 132 of the lower mounting member. Figures 5
and 14
show the mounting member 102 in its seating positioxt.
During assembly of the two mounting members, initially the locking arms 134
are in their locking positions as shown in Figures 6, 7, 11 and 12. However,
as the lower
mounting member 102 moves progressively into the receiving channel, the
flanges 124
engage the latch ends 152 of the locld ,g arms. The divergence of the surfaces
124
towards the trailing end of the lower mounting member then forces the latching
ends 152
of the locldng arms apart. Fi ally, when the upper mounting member has moved
to
bring the lower mounting merrtber into its seating position in the receiving
ehanuel, the
latch ends 152 of the loclsing arms 134 become aligned with the slots 154 in
the flanges
122 and the compression springs 142 acting upon the locking axxns force them
to return
to their lockiug positions. This results in entry of the latch ends 152 into
the slots 154,
as is shown particularly by Figure 15. In this position of each latch end, the
compression
springs continue to urge the two locking members together so as to retain the
lower
member in its seating position.
Tte configuration and dimensioning ofeach latch end 152 and its associated
slot,
and the position of the pivot axis, ensure that, when the gun is in use, any
component of
recoil force which could tend to drive the locldng arnas outwards from their
locking
positions, is less than the effect of to friction between, for example, the
latch end 152
and the associated slot, and, of course, the action of the spring 145, which
tend to resist
outward movement of the locking arm ax1d keep it in the locked position_ A
slight gap
160 must exist between the arm end region 148 and the outer face of the
corresponding
flange 122 to ensure that the contact between locking arm and the flange 122
exists
solely between tlxe surfaces 156 and 158. Latch forces are thus applied
between the
locking arms and the inner nnounting member only in a direction to hold the
mounti;ag
members in assembled positiou. Also, the angle of the face 158 of the latch
end is
important. In the specific embodinaent descrxbed herein, the face 158 was
almost, but
not quite, perpendicular to a line joining the pivot 137 and the outer corner
of the surface
156 of the slot, i.e. where the latch end contacts the s1ot. It was found
that, for a friction
coefficient of 0.15, the angle between the face 158 and the line joiuing the
pivot 137 to
the corner could be up to about 99 degrees without recoil forces causing the
arnxs to
disengage. Lower angles would increase the friction force but make
manuf.acturing
tolerances tighter. It is envisaged that an angle of about 97.5 degrees will
give the best
performance.
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
14
In addition to this, each of the locking arms 134 is balanced on each side of
its
pivot pin 137. This provision in which the mass of the arm on one side of the
pivot axis
substantially equals the mass of the arm on the other side, overcomes any
problem
which could exist when recoil forces in use of the gun act upon each arrrx
about its pivot
position, with any possible tendency to dislodge it from its locking positio-n-
It follows that when the sight unit 54 has been assembled onto the coupling
unit
52 as described above, the projections 1. 18 acting atthe angles of
inclination ofthe guide
surfaces 110, perform two functions. In one of these functions the projections
118 urge
the seating surfaces 108 and 132 together as discussed above so as to hold the
lowez
mounting member 102 in a specific horizontal plane relative to the upper
mounting
member 100. Further to this, the projections 118 acting on opposite sides of
the lower
mounting member and upon the guide surfaces 124 locate and hold the mounting
members together with the lower mounting member in a specific vertical plane
relative
to the upper mounting member. As a result, and with the loclcing arms 134
holding the
mounting mezttbers in assembled relationship, as described above, relative
m.ovement
of the two members is impossible even during repeated firing and the
application of
recoil forces to the mounting. Hence, the calibration of the aiming system
remains as
previously set and no vaxiatian in the boresighting can occur.
As may be seen from the Figures, the end regions 140 of the locking arms 134
project outwards so as to be readily accessible for manual operation. This is
also shown,
for instance, by Figure 3 in which it can be seen that the ends 140 may be
gripped and
moved towards each other against spring action in order to remove the locking
arms
from their locking positions. This action, provides a quick release of the
sight unit 54
and accompanying visual display after a single cable 162 (Figure 3) has been
quickly
disconnected from between the sight unit and the mount. This provides partial
dismantling of the weapon system for transporting or for storage purposes.
The design of the mounting 56 is suc'h that should it be required to
reassemble
the sight unit 54 and display unit 58 onto the coupling unit 52, the mounting
assures that
the sight unit will occupy substantially the same position which it occupied
before
removal. This is partly because the seating surfaces 108 and 132 locate the
sight unit
in exactly the same horizontal plane as it occupied before removal. In
addition, any
foreign matter such as dust or other particles which are present upon the
surfaces 124,
and which could interfere with correct seating against the projections 1 18,
temds to be
wiped away from the sur&ces 124 as the projections raove across the surfaces
124
towards the end of the assembly movecnent. The lower mounting-znember is thus
also
CA 02281754 2007-10-19
disposed in exactly the same vertical pla7ne reIative to the upper mounting
member
which it occupied before removal.
The mounting of the embodiment thus ensures that the sight unit and
accompanying display unit may be removed from the gun and replaced as required
5 without any problem arising concerning boresighting and calibration
settings.
In a modification of the embodiment described above, and as shown in Figures
16 and 17, the seating surfaces 132 of lower mounting member 102 are each
formed
with a seating projection 164 for engagement with the seatiztg surface 108 of
the upper
mounting member. These projections 164 are adjacenC the end wall 128. A third
10 projection 164 is provided upon the free edge of end wall 130, at its
middle (see Figure
17). During movement ofthe two mounting members into assembled relationship,
these
seating projections 164 slide in contact with the seating surface 108 to
perform a
cleaning action upon the seating surface 108 and xemove dust particles or
other foreign
matter. In the assembled position (Figure 17) of the two mounting members
there is
15 thus a six point bearing contact between the mounting members, At three of
these
points, the registration projections 118 bear upwardly against the lower
mounting
member to locate the lower mounting member in its vertical plane. The proj
ections 118
also urge the three seating projeetions 164 at the other three points into
compressive
engagement against the seating surface 108 for Iocating the lower mounting
mem,ber in
the fixed horizontal plane relative to the upper mounting member. Providing
there is not
excessive dirt on the surfaces, the wiping actiou of projections 118 and 164
during the
first few firings of the gun helps to ensure that the mounting members are
always
reassembled in exactly their same relative positions atter they have been
disassembled.
It is envisaged that the comer of slot 154 between the surface 156 and the
outer
surface of momber 102 could be chamfered at about the same angle as face 158,
i.e. so
that the chamfer is substantially parallel to face 158, so as to disttibute
the forces at that
poiut.
',~