Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
Description
Glass composite element, especially glass sliding roof for motor vehicles
This invention relates to a glass composite element, especially a glass
sliding roof
for motor vehicles, comprising a glass plate, which is injection/foam moulded
at the outer
edge with a plastics material frame, wherein retaining parts are foam moulded
in, as well as
a surrounding groove provided at the outer periphery of the frame for
inserting a seal.
Such glass composite elements, especially glass sliding roofs (often also
called sun
roofs) are increasingly used in motor vehicles as a replacement for metal
sliding roofs,
since they give the vehicle interior additional transparency. The glass plate
is made as large
as possible within the roof opening for this. The plastics material frame
surrounding the
glass plate, of a thermoplastic material or polyurethane foam, should thus be
as narrow as
possible. This plastics material frame of the glass sliding roof also serves
for fixing
is retaining parts, for example tongues, to which the drive mechanism for
opening the glass
sliding roof is connected, especially when the glass sliding roof is also in
the form of a
lifting or rising roof or the glass composite element is used as a side
ventilation window.
The fixing of the plastics material frame to the glass plate together with the
retaining parts assumes substantial importance, since the glass plate of the
glass sliding
2o roof should be flush with the roof surface for aerodynamic reasons. Thus
the plastics
material frame is provided essentially only on the peripheral edge and a
narrow region on
the underside of the glass sliding roof. Moreover the plastics material frame
also has the
function of retaining a surrounding seal, in order to ensure a reliable and
rain-proof seal.
In general a surrounding groove is provided in the plastics material frame for
2s reliable sealing, which ensures secure fixing of the surrounding seal.
Secure retention of
the seal must be ensured in particular to avoid the seal becoming misaligned
or folding
over. A T-shaped formation of the surrounding groove has proved advantageous
for this.
However this groove for insertion of a surrounding seal creates substantial
manufacturing
problems. Thus this formation requires a very expensive foam or injection
moulding tool,
3o since four (or more) sliders have firstly to be extracted separately from
the injection
moulded groove and then swung away at the four surrounding sides of the glass
sliding
roof, in order to make removal of the foam or injection moulded glass sliding
roof.
These four (or more) sliders for formation of the surrounding groove needed
for the
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
-2-
manufacture further interfere with the foam flow of the plastics material
during the
injection or foam moulding operation, so that jointing to the glass plate over
the whole area
frequently cannot be ensured. Since however this contact surface of the
plastics material
frame with the glass plate is essential for the strength of the glass
composite element,
s especially the glass sliding roof, on account of the flush condition at the
upper side
required by the aerodynamics, the contact areas are frequently over-
dimensioned, so that
the frame then has to have a relatively wide design, especially when the glass
sliding roof is
used for high speed motor vehicles, because substantial'forces act on these
contact surfaces
at high speeds.
Furthermore, with the prior manufacturing methods with four (or more) sliders
in
the foam moulding tool, there is the disadvantage of a high cycle time, since
the four
sliders have to be removed from the workpiece, swung up and cleaned, before
removal of
the workpiece. In addition, the measurement accuracy is often inadequate, on
account of
the number of tool parts, especially since twisting and thus a certain
inaccuracy in
z5 measurements can result from the number of sliding surfaces in the tool and
development
of heat during the manufacture. The same applies to the sliding surfaces of
the sliders of
the manufacturing tool, so that flashes can occur at the edges of the plastics
material frame,
which require a lot of finishing work.
Accordingly the invention is based on the object of providing a glass
composite
2o element, especially a glass sliding roof, which avoids the above
disadvantages, especially
the tooling costs, and reduces the cycle time, as well as offering a higher
dimensional
accuracy with reduced finishing work.
This object is met by the glass composite element according to the features of
claim 1.
25 By making the surrounding groove after the injection moulding operation, by
means
of contour milling machining of the plastics material frame, the plastics
material frame can
be produced in the injection/foam moulding in a simple foam moulding tool. In
particular
the expensive sliding and pivoted sliders at the four sides of the tool for
the glass
composite element of glass sliding roof can be dispensed with. Thus the foam
moulding
so tool is constructed essentially of only the tool upper part and the tool
lower part. This
moreover facilities a simpler arrangement of the ejectors and of the sealing
surfaces, so that
a better seal is achieved during manufacture. The expense of the finishing
work is reduced
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
-3-
substantially by this. In addition a very good foam flow is achieved by this,
so that
complete wetting of the glass plate at the lower edge is achieved. The
strength between the
glass plate and the plastics material frame is increased by this, or is
ensured in a
reproducible way, so that the quality of the glass composite element or the
glass sliding
roof is improved overall.
In particular, by contour milling the frame in order to produce the
surrounding,
preferably T-shaped groove, it is also ensured that the outer contours of the
glass sliding
roof are kept to exactly and a more secure seat for the surrounding seal is
ensured as well.
Finishing work on the outer contour can be effected at the same time as the
groove is
to milled, as well as flash removal from the outer edges by means of a
multiple milling tool.
In particular, by centring during the contour milting, preferably at the
retaining parts, an
exact relative disposition between the sealing groove and the retaining parts
is achieved, so
that a uniform application of the seal is obtained when closing or opening the
glass
composite element, especially a sliding roof, and a better sealing of the roof
opening is
15 achieved all in all.
Further advantageous arrangements are the subject matter of the dependent
claims.
In particular it should be noted that, in the preferred use of a CNC milling
machine for the
contour milling of the groove, a simple alteration of the seal dimensions can
be effected.
Thus it is possible to adapt for example the seal width to the new dimensions
in a simple
2o way, instead of the expensive re-tooling of the foam moulding tool for
production changes.
In addition a "mixed" manufacture of the glass composite elements, especially
glass sliding
roofs, is possible, so that different glass sliding roofs can be produced on
one production
line. In particular the two-part foam moulding tool can be used for several
variants.
An embodiment of the invention will now be explained and described in more
2.5 detail with reference to the drawings, in which:
Fig. 1 shows a glass composite element implemented as a sliding roof in the
installed position in a motor vehicle;
Fig. 2 shows the glass sliding roof during production in the foam moulding
tool;
and
3o Fig. 3 is an enlarged view of the outer periphery with a schematically
shown
profile miller for contour milling of a T-shaped groove.
A glass composite element 1 in the form of a glass sliding roof for
installation in a
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
_ø
roof opening 2 of a motor vehicle is shown in Fig. 1. The glass sliding roof
essentially
comprises a glass plate 3, which is surrounded at the outer edge by a plastics
material
frame 4, preferably of PU foam. This frame 4 is injection or foam moulded on
the outer
edge of the glass plate 3 in a foam moulding tool (cf. Fig. 2). Retaining
parts 5, preferably
s angle irons Sa, are moulded in, so that the torsional stiffness of the glass
plate 3 is
increased on the one hand and, on the other, attachment to the drive mechanism
for sliding
or raising the glass sliding roof is facilitated.
A surrounding, preferably T-shaped groove 6 for insertion of a seal 7 is
provided in
the radially outwardly facing edge of the plastics material frame 4, in the
plane of the glass
to plate 3. In contrast to the state of the art, this T-shaped groove 6 is
only made after the
injection moulding operation and thus in the hardened and optionally tempered
state of the
frame 4, by means of contour milling, whereby the advantages recited above
result, such as
reducing the cycle time and the tooling costs, as well as higher measurement
accuracy,
since thermal distortion of the glass plate 3 can also be compensated by this.
15 The foam moulding tool 10 is shown schematically in Fig. 2, consisting of a
tool
upper part 1 l and a tool lower part 12. However, the tool 10 can also be
turning through
180°, so that the glass plate 3 is then positioned concavely. As can be
seen, the moulding
cavity at the outer edge of the glass plate 3 for forming the frame 4 is shown
stippled and is
shaped to favour the flow, so that reliable filling of the mould is obtained.
2o This is particularly essential, since the glass plate 3 and the retaining
parts S are
fixed only by the contact surface with the frame 4. As well as the simplified
structure,
doing away with the four (or more) sliders for the T-shaped groove 6 otherwise
needed, the
moulding cavity shown stippled here for forming the frame 4 can be sealed
especially well,
preferably with a self parting sealing plate 13, which reliably prevents the
plastics material
2s foam entering preferably through a plurality of injection openings 14
getting on to the top
side of the glass plate 3. The upper side of the glass plate 3 is kept clean
by this sealing
plate 13 during the foam moulding operation, so that hardly any final
finishing is needed.
In addition, it is apparent that a reliable seal to ejectors 15 provided
further in is
possible, so that reliable filling of the moulding cavity with injection
around the retaining
3o parts 5 is ensured. Furthermore it is apparent that the tool upper part 11
with the sealing
plate 13 extends substantially continuously outwards, so that different kinds
of tool lower
parts 12 can be used with the same tool upper part 1 I. Thus, on a production
line with the
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
-5-
same stamp-like tool upper part 11, it is possible to manufacture different
variants of the
glass composite element 1, e.g. glass sliding roof, with variously position
retaining parts 5.
In addition, simple raising of the tool upper part 11 or lowering of the tool
lower part 12
suffices for removal of the finished glass sliding roof with the frame 4, so
that the cycle
time is reduced substantially.
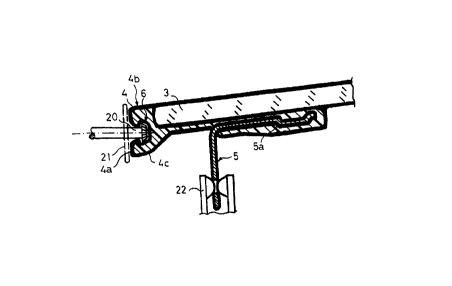
The milling of the surrounding, preferably T-shaped groove 6 in the foam
moulded
frame 4 with small dimensions is shown to a larger scale in Fig. 3. It should
however be
noted that the groove 6 can also be made substantially flat and parallel to
the plane of the
glass plate 3, while a seal with a plurality of flash-shaped detent hooks is
then used. With a
to T-shaped groove 6, a contour milling cutter 20 with a relative small
diameter is used, with
which the connection to the T-shaped groove 6 is first effected by axial
displacement along
its axis of rotation. By traversing the contour milling cutter 20 along the
outline of the
frame 4 (here perpendicular to the drawing plane), the T-shaped groove 6 is
then produced
by means of contour milling. After a complete circulation of the contour
milling cutter 20,
i5 this is withdrawn from the T-shaped groove 6 of the frame 4 at the point of
entry. A disc-
shaped flash removal tool can also be provided for flash removal and finishing
to
dimension of the outer face 4a of the plastics material frame 4, as is
indicated by the disc-
shaped face mill 21. It should be noted however that a milling cutter with
cutters which
hinge out at higher speeds of rotation can be used or a disc milling cutter
with a vertical
2o axis of rotation can be used for a flat slit design of the groove 6, an
entry feed into the
plastics material of the plastics material frame 4 being effected
approximately parallel to
the glass plate 3.
The glass plate 3 and the plastics material frame 4 attached thereto is
preferably
received centred in a vacuum table, not shown (since known per se). In
addition or
25 alternatively, the retention during the contour milling of the glass
sliding roof or its
surrounding plastics material frame 4 can also be effected on the retaining
parts 5. A
retaining clamp 22 is shown for this, engaging for example in a bore or
stamped opening of
the angle iron 5a. As well as the fixing the glass sliding roof is at the same
time indexed
and a relative positioning to the milling tool 20 and optionally also 21 is
thus provided.
3o The contour milling of the groove 6 preferably takes place with a CNC
machine or
a copier milling machine. Possible alterations to the dimensions of the groove
6 for
adapting to a changed geometry of the seal 7 for example can thus be effected
particularly
CA 02281900 1999-08-20
rapidly by simple program changes. As will as the fixing/indexing, the outer
contour of the
glass composite element 1 produced in the tool 10 can also be effected with a
separate
measuring device, not shown. For example measuring sensors can engage for this
on the
retaining parts 5, so that the relative positioning to the profiled milling
cutter 20 moving
s along the outer contour can again be produced. Slight tolerances, for
example from thermal
distortion during the manufacture, can be compensated through this
particularly well, since
the contour milling and the measuring are effected in the cooled state of the
frame 4, so
that all in all a precise positioning between the retaining parts 5 and the
surrounding groove
6 for the seal 7 is achieved. The sealing when installed in the motor vehicle,
for example
1o relative to the roof opening 2, is improved overall substantially by this,
since a uniform
application of the seal is ensured.