Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
SUPPORT BEARING AND PROCESS FOR ITS MANUFACTURE
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to a process for the manufacture of a support bearing
including an
inner ring, which is surrounded by a readily spaced apart outer ring, whereby
the inner
and outer rings are connected by an intermediate ring of elastic rubber
material
positioned in the gap formed by the mutual spacing of the rings.
Background of the Invention
Such a support bearing is known, for example, from DE 20 61 625 B2
This bearing is used as intermediate support for the articulated drive shaft
of motor
vehicles, whereby the intermediate ring is formed by several circumferential
by evenly
spaced web members of elastic rubber material. The web members extend between
the
inner and the outer ring and in radial direction both in longitudinal section
as well as in
cross section, whereby between radially spaced apart adjacent web members a
stop
buffer is positioned which i.s axed to the outer support ring, extends in the
radial
direction inwardly and in the vibration free condition is positioned at a
radial distance
from the inner ring. However, it is to be observed that the use properties of
the
aforementioned support are not satisfactory over a long period of use.
Subsequent to the
manufacturing process and during the intended use of the support tensile
stress occurs
within the intermediate ring which consists of web members which reduce the
period of
use and can lead to premature failure of the support.
Summary of the Invention
It is the object of the invention to further develop a support ring of the
above described
type and a process for its manufacture so that the intermediate ring is free
of tensile
1
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
r . ... '
stress due to the manufacturing process and even without calibration of the
inner and/or
the outer ring.
The object is achieved with a support bearing and a process for its
manufacture in
accordance with the invention.
wherein during manufacture of the support bearing the inner and the outer ring
are
positioned in a vulcanisation tool with a relative axial displacement which
corresponds
to the shrinkage upon manufacture, the intermediate ring is vulcanised onto
the inner
and outer ring and inclined along an imaginary radial plane corresponding to
the axial
misalignment, and the vulcanised support bearing is removed from the
vulcanisation
tool, and the axial misalignment between the inner and outer rings because of
the
inclined intermediate ring during manufacture is completely compensated during
cooling
and solidification because of shrinkage. The intermediate ring which is
manufactured by
way of the process in accordance with the invention is free of radial tension
stress and
therefore provides consistently good operating properties over a long period
of use. A
manufacture related shrinkage of the intermediate ring subsequent to the
removal of the
support bearing from the vulcanisation tool does not result in tension stress
contrary to a
support bearing in accordance with the art, wherein the vulcanised
intermediate ring is
not inclined in axial direction and the inner and outer rings are positioned
without
mutual axial displacement. The axial misalignment of the inner ring relative
to the outer
ring is automatically and completely compensated by the shrinkage of the
intermediate
ring.
If the support bearing is used, for example, as support for a cardanic shaft
in motor
vehicles, the inner and outer ring can be positioned in a vulcanization tool
with an axial
displacement of 0.1 to 0.5 mm. This displacement is completely compensated by
the
shrinkage of the intermediate ring subsequent to its vulcanisation, so that
the
intermediate ring extends radially between the inner and outer ring when
viewed in axial
cross-section of the support bearing. A calibration of the inner and/or outer
ring
2
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
r ~ ,
subsequent to vulcanisation. is obviated in that the intermediate ring is not
subject to
tension stress reducing the period of use which tension stress is generated
during
manufacture.
The amount of shrinkage is essentially dependent from the material
respectively used
and the thickness of the material of the intermediate ring.
The invention further relates to a support bearing manufactured according to
the
aforedescribed process, including an inner ring which is surrounded by a
radially spaced
apart outer ring, whereby the inner and outer rings are connected by an
intermediate
ring of elastic rubber material positioned in the gap formed by the radial
spacin of the
rings.
For the achievement of this object, it is provided that the intermediate ring -
when
viewed in axial cross-section - during manufacture has a greater length then
in the
condition ready for use. During manufacture, which means immediately after the
removal of the support bearing from the vulcanization tool and prior to the
cooling and
solidification of the intermediate ring, the inner and outer ring are mutually
displaced in
axial direction and the intermediate ring is inclined by the axial
misalignment from an
imaginary radial plane between the inner and outer ring. During the cooling
and
solidification of the intermediate ring, the length of the intermediate ring
decreases
because of the shrinkage until the intermediate ring in the condition ready
for use, which
means in the completely cooled and solidified condition of the intermediate
ring, extends
only in radial direction and is positioned in a singler radial plane together
with the inner
ring and the outer ring. .
It has proven advantageous for most applications when the ratio of the length
during
manufacture to the length in the condition ready for use is 1.05 to 1.15.
Depending on
the material used and the material thickness it is thereby insured that the
intermediate
ring is free of radial tensile stress in the condition ready for use.
3
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
i _ _ ~~ -
The intermediate ring can be formed by at least two circumferentially
distributed web
members which are separated by a circumferential spacing, whereby the web
members
are defined in circumferential direction by end surfaces which extend parallel
to the end
surface of an adjacent web body, whereby all end surfaces are essentially
planar and
inclined in the same direction of rotation and whereby the angle of
inclination of the end
surfaces, relative to the circumferential direction is consistently 15 to 75
degrees,
preferably 30 to 60 degrees. Tensile stress caused during manufacture which
reduces the
period of use of on elastic :rubber materials is reliably prevented with this
construction.
A shrinkage during manufacture of the web members during vulcanisation no
longer
causes tension stress but oily a rotation of the inner ring relative to the
outer ring.
With a view to easy production and installation of the support bearing, it has
proven
advantageous when adjacent web members merge into one another and are evenly
distributed in circumferential direction. The outer ring can include at least
one opening
which is penetrated by the material of the intermediate ring, whereby the
material of the
intermediate ring is continued on the side of the opening opposite of the web
members.
It is hereby an advantage that a secure mechanical fastening of the
intermediate ring on
the outer ring is achieved which remains unchanged even over long periods of
use.
In order to achieve a construction which requires few parts and is
advantageous with
respect to manufacture and economics, the web members in radial direction can
include
inner and outer fastening surfaces, whereby the inner fastening surfaces are
adhesively
connected with the mantle surface of the inner ring and the outer fastening
surfaces with
the inner circumferential surface of the outer ring. The use of additional
support or
stiffening rings is thereby obviated.
In order to avoid a mechanical overload of the web members, stop burls can be
provided
on the respectively opposite end surfaces and in direction of the opposing end
surface.
Large radial and circumferential relative displacements of the inner ring
relative to the
outer ring can be limited by the stop burls positioned on the end surfaces,
whereby the
4
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
t , a
stop burls preferable have .a semi-spherical profile on the side opposite the
opposing
impact surface so that an end position damping commences~upon contact of the
stop
burls with the opposing impact surface.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The support bearing in accordance with the invention as well as the process
for its
manufacture are further described in the following by way of the attached
drawings.
They show preferred embodiments of the support bearing in schematical
illustration.
Figure 1 shows a front elevation of a first embodiment of the support bearing
in
accordance with the invention;
Figure 2 shows the embodiment of Figure 1 in cross section taken along a line
A - A
and in a portion in the condition during manufacture;
Figure 3 shows the embodiment of Figure 2 in the condition ready for use after
complete cooling and solidification of the intermediate ring; and
Figure 4 shows a second embodiment of the support bearing with accordance with
the
invention and similar to the embodiment shown in Figure 1.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiment
The two embodiments of the support are used, for example, as intermediate
shaft
supports for cardanic shafts of motar vehicles. The supports have a
construction with
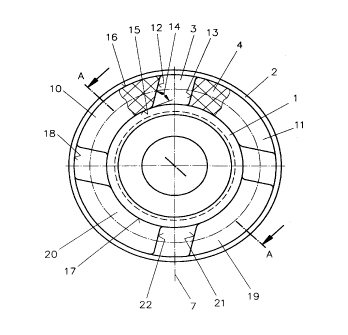
especially few parts, whereby the webbed bodies 10, 11, 19, 20 are directly
vulcanised
with their inner and outer fastening surfaces 15, 16 directly onto the
adjacent surfaces of
the inner ring 1 and the outer ring 2. The inner ring 1 in xhis embodiment is
the~outer
bearing race of a roller bearing, while the outer ring 2 is constructed as a
support ring
S
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
t .. _r
and can be pressed in the first embodiment into a bearing base.
In the second embodiment., the outer ring 2 is enclosed on its outer
circumference by a
rubber track 23 which is itself surrounded, for example, by a bearing mount
and under
elastic pretension.
Figure 1 shows an intermediate ring 4 which is positioned with its inner
fastening
surfaces 15 onto the mantle surface 17 of the inner ring 1 and with its outer
fastening
surfaces 16 onto the inner circumferential surface 18 of the outer ring 2, and
in this
embodiment includes four circumferentially evenly spaced web members 10, 11,
19, 20
which respectively define a gap with their circumferentially opposite end
surfaces 12,
13, 21, 22. The web members 10, 11, 19, 20 are provided with essentially
planar end
surfaces 12, 13, 21, 22 which are all inclined in the same direction of
rotation whereby
the angle of inclination 14, relative to the circumferential direction is
consistently 45
degrees in this embodiment. To limit the relative rotation of the inner and
outer rings 1,
2 relative to one another, the end surfaces 12, 13, 21, 22 can be provided
with stop
burls which are here not illustrated and which are positioned essentially
perpendicularly
to the respectively adjacent end surfaces.
Figures 2 and 3 respectively show an axial cross-section through a support
bearing in
accordance with the invention, whereby the support bearing in Figure 2 is
shown in the
condition during manufacture and in Figure 3 is shown in the condition ready
for use.
As is apparent from Figure 2, the inner ring 1 and the outer ring 2 are
positioned with a
relative axial misalignment 5 relative to one another. The axial misalignment
5
corresponds to the shrinkage during manufacture of the intermediate ring 4
subsequent
to its vulcanisation. The intermediate ring in Figure 2 is inclined by the
axial
misalignment 5 to an imaginary radial plane 7, whereby the axial misalignment
5 as well
as the inclination are exagerated for a better understanding of the invention.
During the
cooling and solidification of the intermediate ring 4 subsequent to the
removal of the
6
CA 02282074 1999-10-28
..
support bearing from the vulcanisation tool, the intermediate ring 4 shrinks,
whereby
the length 8 during manufacture is reduced to the length 9 in the condition
ready for
use. By positioning the web members 10, 11, 19, 20 in circumferential
direction at the
angle of inclination l4 and because of the intermediate ring 4 being free of
radial
tensions, the intermediate ring 4 is in all directions free of tension stress
which would
reduce the period of use and has consistently good operating properties during
a long
period of use.
7