Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
CRUTCH DEVICE
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is concerned with a crutch-like device designed to
facilitate the ambulation of persons havirig non-weight-bearing lower leg
injuries.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Crutches have long been used as ctevices to assist those suffering from
an injury to the lower extremities to walk. Traditional crutches extend from
the
shoulder/underarm to the ground to bear the weight of the injured person. Such
crutches are usually fabricated from wood or light weight metal and comprise
two upright shafts culminating at one enci in a foot and being attached at the
other end to a crossbar which is accommodated under the arm. A second
crossbar at approximately the mid-point acts as a handle. 'There are several
problems associated with these types of crutches including shoulder fatigue
and
the fact that it is necessary to use the muscles of the upper leg and lower
back
to support the lower leg in a slightly rearwardly upward manner to maintain
sufficient clearance from the walking surface. This physical stature can
result in
painful muscle induced scoliosis. In addition, the hand or hands supporting
the
crutch(es) are not available for other acti'vities. The center of gravity is
also
raised, thereby affecting balance.
The prior art has attempted to address the problems associated with
crutches. U.S. Patent No. 5,575,299, for example, discloses a walking device
having a body member which can be attached to the lower leg. However, this
device does not provide means for secure attachment to the upper limb and
there may therefore be some rotation about the knee which gives a user a
feeling of instability. U.S. Patent No.5,300,016 discloses a foldable
prosthetic
device which includes a shelf for supporting the lower leg. This device is
complex to manufacture and has a plurality of components transferring weight
along parallel axes. Both U.S. Patent No. 5,575,299 and 5,300,016 result in
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
strain being applied to an already injured limb and neither provide the degree
of
stability required for a user to comfortably maintain their balance.
Applicant's co-pending application PCT/CA99/00279 discloses a hands-
free crutch having a support platform for the injured lower extremity affixed
to
an upright support leg such that the weight of the person is transferred
through
the hip, upper leg and knee rather than the shoulder as is the case with
traditional crutches and this therefore affords a more natural distribution as
the
center of gravity is lowered. The device can be attached to the upper leg and
thigh to allow for single hand or hands free operation. The present invention
is
an improvement on the basic concept of 1:he device of co-pending
PCT/CA99/00279 in terms of durability, adjustability and comfort. The present
invention has surprising advantages over the prior art which are made possible
by virtue of the synthetic materials used i.n its construction and the type of
adjusting mechanisms used.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A crutch, for non-weight-bearing lower leg and foot injuries or for
amputees, adapted for hands-free operatiion is provided. The upper leg or
portion thereof is supported on a platform. The forces applied to the platform
are transmitted downwardly along a ground engaging upright leg support. The
device is attached to the upper and lower leg by way of a series of straps.
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, there is provided a light-
weight adjustable prosthetic device of synthetic material comprising:
i) an elongate, essentially vertical leg member comprising a shaft
and a foot member, said leg member having a webbed core;
ii) an essentially horizontal support platform mounted on the leg
member for supporting a user's weight normally supported by an uninjured leg
iii) stabilizing means mounted on the leg member to hold a user's
upper leg in position;
iv) attachment means associated with the stabilizing means and the
support platform to secure the device to a user's leg,
-2.-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
v) clamping means to maintain said stabilizing means and said
support platform in a vertical position;
vi) locking means associated with said support platform to lock said
support platform in position;
wherein the vertical position of each of the support platform and the
stabilizing means is adjustable without the need for any tools.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Several aspects of'the invention ai-e illustrated in the accompanying
drawings, in which like numerals denote like parts throughout the several
views, and in which: Figure 1 is a perspective view of a preferred embodiment;
Figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of the leg member of Figure 1;
Figure 3 illustrates a preferred embodiment of a latch;
Figure 4 illustrates a clamping mechanism;
Figure 5 illustrates a preferred embodiment of the locking means
associated with the support platform;
Figures 6 A, B, and C illustrate various aspects of a support platform;
Figures 7A-D are, respectively, bottom, side, cross-sectional and
schematic representations of a preferred foot pad
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Crutches have traditionally been used to help those suffering from lower
leg injuries to get around. However, crutches limit the use of the hands for
other
activities and are generally described as clumsy, tiring and uncomfortable.
The present invention is particularly applicable to otherwise healthy
individuals who suffer a lower limb injuiy. The device is ideally suited to
the
recovery of injured workers, outdoor enthusiasts and athletes but is also
applicable to patients with diabetes and other afflictions which affect
circulation in the leg as well as for post-operative patients. The device also
has
special application for war victims such as land-mine survivors.
-3-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
Unlike an artificial limb or custom-made prosthetic device, the present
invention is a hands-free crutch or walking aid which can be easily adjusted,
without tools for immediate use. The device supports the knee and upper leg
using a universal and simple fastening system designed to be user friendly. It
provides for virtually unlimited height ar.td limb size adjustments and
represents
a significant improvement in comfort. The device can be adapted for use by
patients of all sizes including children.
Thus, the present invention provides a prosthetic device, or walking aid,
for those suffering from various types of lower leg, ankle and foot injuries
such
as, for example, any surgical procedures below the knee including achilles
tendon, open reduction, internal fixation of the ankle, post surgical
procedures
to the foot such as bunion surgery and of' course, fractures. The device
affords a
platform on which, preferably, the lower part of the leg below the knee is
supported and an upright vertical suppori:. The device takes advantage of the
natural pivoting action provided in the hip and provides walking assistance by
essentially rigidly extending the upper leg to a walking surface. The
individual's weight is transmitted downwardly through the upper leg to the
knee and along the device to the ground.
This device provides an attractive., more versatile alternative to
traditional crutches. Because the device is manufactured from synthetic
materials, it is light and comfortable and can be mass produced at reasonable
costs. The device may replace the crutches currently provided by hospitals to
patients and thus should be able to withst:and extended use by several
different
users. It should also be easily adjustable for users of varying heights and
proportions. The device must also be sturdy enough to support people of
varying weights yet maintain a degree of' flex along the leg member. It is by
virtue of using a synthetic material that the desired properties can be
achieved.
Materials which have inherent characteristics of strength and flexibility are
chosen so as to simulate as much as possible the normal bouncing steps
associated with a natural walking action. With regard to these
characteristics,
synthetic materials have several advantages over wood or metal. For example,
-4-
CA 02284952 2007-03-27
when using a synthetic material, additives such as polymeric or organic fibres
can be added to affect factors such as strength and flexibility. The amount of
potential rotation about a vertical axis can also be controlled. Preferably,
the
device of the present invention does not conduct electricity and it has a
compact
design and low unit cost. The short learning curve associated with the device
and its ease of use to promote the resumption of a normal lifestyle in a very
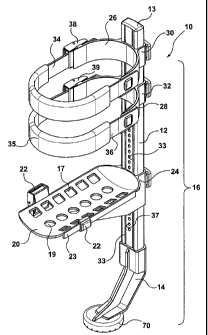
short time. A preferred embodiment is illustrated in Figure 1. The device 10
comprises a shaft 12 and foot member 14 which together form a functionally
unitary leg member =16. Thermoplastic polymer resins are used in the
manufacture of the shaft 12 and foot member 14 as well as the various other
components of the dlevice 10. Although the foot member 14 and the shaft 12 are
extruded or injection molded as separate components they are then bonded to
each other to function as a unitary leg member 16. The shaft may be hinged to
fold as long as in the use position the leg member functions in the same
manner
as if it were a unitary continuous leg. They may be thermally bonded or bonded
with a high strength adhesive. The shape and positioning of the foot memberl4
is designed to allow, as closely as possible, the sensation of normal walking.
The degree by whicli the ground engaging surface of the foot member is offset
relative to the princi,pal vertical axis of the leg member is selected to
align the
hip, the upper leg and the foot member to facilitate a more natural rolling
gait.
A skid resistant foot pad 70 is provided on the foot member 14.
A horizontal support platform 20 is vertically adjustably affixed to the
leg member 16. The user's body weight is transferred from the upper limb to
this platform 20 which may also function to cradle and support an injured
lower
limb. It should be understood that the device 10 may also be used where there
has been an amputation and in this case, the stump of the remaining limb is
supported on the platform 20. In a preferred embodiment the support platform
20 is equipped with attachment means 21 such as a strap (not shown in Figure
-5-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
1, see Figure 5), to hold the lower limb in place and provide additional
stability.
The length of the strap is adjustable and is held in place by a latch members
22.
The position of the attachment means can be adjusted along the length of the
support platform to accommodate lower limbs of varying lengths and shapes as
well as a long or short amputation comfortably. In a preferred embodiment, the
latch members 22 slide along a ridge 23 on each side of the platform 20.
Alternatively, there can be strap mount(s) at fixed locations along the length
of
the support platform. The support platfonn 20 is slidably attached to the leg
member 16 and held in vertical position by way of a toolless clamping member
24. The platform may have perforations 17 to enhance the light weight
characteristic of the device and to provide ventilation to prevent moisture
buildup. Apertures 19 may also be provicled to receive and locate nubs on a
cushion member. The pei-forations and apertures may take on various shapes
and sizes.
The present device also comprises at least one stabilizing member to
align the leg within the device and to pre'vent side to side movement of the
leg.
In a preferred embodiment, upper 26 and lower 28 stabilizing devices are
adjustably affixed to the shaft 12. The upper 26 and lower 28 stabilizing
devices are each slidably attached to the ~shaft 12 and held in vertical
position
by clamping members 30 and 32, respectively which wrap around the shaft and,
when in a closed position, grip the shaft and prevent the stabilizing devices
from sliding along the shaft. A similar sl:iding clamp mechanism 24 is
associated with the support platfol-m 20. This type of clamping member has the
advantage that by virtue of clamping about the shaft it resists the torque
associated with downward pressure on ttie stabilizing devices and support
platform. Also, the shape of the clamp prevents it from rotating around the
shaft. In addition, because the clamping imember is a sliding grip clamp the
degree of adjustment is virtually infinite. Each of the stabilizing means 26,
28 is
provided with attachment means 34, 36, respectively to secure the device to
the
leg. In a preferred embodiment a strap is used as the attachment means 34 and
36. The length of the strap is adjusted by sliding the strap through a latch
38,
-6-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
39, respectively. The strap may be provided with padding 35 for additional
comfort.
In a preferred embodiment, the shaft comprises a webbed core as shown
in Figure 2 in which indexing holes 37 are incrementally spaced along a
section of the shaft. These holes can be used in conjunction with a support
platform locking mechanism which is described further with respect to Figure 5
to lock the support platform in position. P'arallel channels 33 are integrally
formed along the length of the shaft. These channels help to align and hold
the
clamping member in place when it is beirig slid up or down the shaft as
discussed further with respect to Figure 4.
The resins used in the manufacture of the device are selected to be
resistant to ultraviolet radiation and to assure a long life under the
expected
wide range of environments where the device may be used. The resins are also
selected and structurally analyzed to have desired properties in terms of
flexibility, strength, longevity, temperature tolerance and performance
characteristics. Some exemplary types of'resins that can be used are
polycarbonate ABS, nylons and engineered resins.
In a preferred embodiment, the shaft 12 comprises an extruded webbed
core 40 as illustrated in Figure 2. The web is relied on to provide a
controlled
degree of flex along its length and at the same time provide structural
support
for the indexing holes 37 which occur along a section of the shaft. These
holes
may be machine tooled into the shaft. The channels 33 which interact with the
clamping members 24, 30 and 32 are integrally formed in the web. This core
provides additional strength while maintaining the light weight of the device
and is made possible by virtue of the synthetic material used.
In a preferred embodiment as illustrated in Figure 3, the latch 38
comprises a rocker clip which has precise tooth indexing 42. This allows for
very precise adjustment of the strap customized to the user. The strap is
preferably a plastic strap which is stronger and lasts longer than a fabric
strap,
although any kind of attachment means could be used. The strap may be
provided with pads for additional comfort as illustrated in Figure 1. In a
-7-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
preferred embodiment, the latch 38 is easy to use and is all plastic so that
there
are no metal pins or springs. This embodiment is particularly useful in
situations such as around land mines where it is undesirable to have metal
components which can detonate mines. C)f course, it is clearly apparent that,
in
other situations, metal springs and pins or other latching means may be used.
As stated above, the horizontal support platform 20 and the upper 26 and
lower 28 stabilizing devices can be individually vertically adjusted. This is
achieved by loosening the clamping member 24, 30, or 32, respectively and
sliding the support platform 20 or stabilizing devices 26, 28 vertically. Once
they have been adjusted to the desired position, they are again locked in
place.
In a preferred embodiment the clamping member 24, 30 or 32 comprises a
sliding clamp.
An exemplary clamping mechanism 30 for the adjustment of the upper
stabilizing device 26 is illustrated in Figures 4A and 4B and can also be seen
at
30 in Figure 1. Similar clamping mechanisms are associated with the lower
stabilizing device and the support platfolrn. The clamping member has a right
rib 46 and a left rib 48 which are resiliently biased apart and define a
channel
47 adapted to receive the shaft. This channel can therefore slide along the
shaft.
The ends of the two ribs 46, 48 terminate to form a slit 49 between them. In
the
open position shown in Figure 4A, the frictional grip onto the shaft is
released
and the stabilizing means can slide up and down the shaft. The width of the
slit
is selected to allow enough space for the ribs to come together enough to
firmly
grip the shaft. However, the slit is preferably not so wide as to allow the
clamping members to so freely slide along the shaft that they fall to the
bottom
when the clamp is in the open position. Preferably the vertical position of
the
clamping member can be adjusted and then the clamp is closed to securely hold
the position. A lever type member 50 is pivotally associated with one end 52
of
a link arm 54 and the other end 56 is attached to a pivot axis 58. In the open
position, shown in dotted lines on Figure 4B, the lever 50 is lifted thereby
causing the slit 49 to enlarge sufficiently so that the clamp member is no
longer
tightly wrapped around the shaft and the clamp member (with its associated
-8-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
stabilizing means or support platform) can be slid up or down the shaft. The
clamping member may also comprise protrusions 59 which are adapted to fit
within and slide along the parallel channels 33 in the shaft. To close the
clamp,
the lever is pushed in and this provokes the ends 52, 56 of the clamp to move
towards each other thereby causing the clamp to grip the shaft in a tight
frictional hold which maintains the stabilizing means and/or support platform
in
a fixed position. By using a locking mechanism which depends upon frictional
contact with the shaft member, the degree of adjustability is virtually
limitless
in that the sliding clamp can be positioned anywhere along the shaft, not just
at
specific increments. The ability to adjusl: the stabilizing in this manner
allows
for easy and rapid customization of the device for individuals of varying
height
and proportions. A second incremental locking system is associated with
support platform as discussed below with regard to Figure 5. Because of the
inherent properties of the synthetic material used, a further degree of
customization can be easily achieved by removing the cap 13 (shown in Figure
1), cutting the length of the shaft and replacing the cap.
Because of the weight and associated vertical pressure being applied to
the horizontal support platform 20, a locking system 50 is provided in
addition
to the clamping member to ensure that the platform 20 does not creep along the
shaft 12. As illustrated in Figure 5, in a preferred embodiment, the
additional
locking system 80 comprises at least one spring loaded pin 82 associated with
the base 84 of the support platform 20. As discussed above, the shaft 12 is
provided with a webbed core 40 in which there are holes 37. These holes are
adapted to receive the prongs 86 of the pin 82 . The pin is provided with a
springs 83 which urge the prongs 86 into a forward position and hold them in
place in the holes 37. Thus, this locking system 80 which comprises at least
one
spring loaded pin 82 and slots 37 for receiving the prongs 86 of the pin 52 in
the shaft 12, holds the support platform 20 firmly in position. When it is
desirable to adjust the position of the support platform, the user simply
pulls on
the U portion of the pin. The springs 83 are compressed and the prongs 86 are
pulled out of the holes 37. The support platform is then moved to a new
-9-
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
position and the spring is released to allow the prongs to advance into a
different set of holes. For additional security, the base 84 of the support
platform 20 comprises a downwardly prcjecting face 85 which is provided with
alignment holes 68 which can be aligned with the holes 37 in the shaft and
through which the prongs of the pin project and enhance the stability of the
locking mechanism (see also Figure 6C). The downwardly projecting face 85
adds even further stability in that it resists the torsional movement of the
support platform relative to the shaft generated by the downward pressure
which is applied as a result of the platform supporting a user's weight.
The sliding clamp mechanism 24 and the locking mechanism 50
function in concert to provide a very secure means of holding the support
platform in position. Both the sliding clamp and the locking mechanism which
is associated with the base of the platforrn are designed to resist the
torsional
pressure applied to the support platform when it is supporting a user's
weight.
In addition, by using two different lockirig mechanisms in conjunction with
each other the security of the support platform positioning is greatly
enhanced.
It is clearly apparent to one skilled in the art that other types of locking
mechanisms such as an indexed tooth system or various other systems could
also be employed in this invention to lock the support platform in position.
An advantage of the present inverition is that the various components
can be adjusted without using any specialized tools or any tools at all. Thus,
there are no tools to lose and the device can be adjusted by anyone to provide
maximum efficiency of use and comfort, As opposed to custom prosthetic
devices or even crutches which have to be available in a multitude of sizes,
the
present device is virtually universal and can be used
Referring to Figures 6A-C, in a preferred embodiment the support
platform 20 may be curved to cradle the limb. As well as enhancing stability,
this design provides added comfort. A cushion member 60, such as a multi-
density foam pad, is fitted into the platform 20 for additional comfort. In a
preferred embodiment, the cushion member is a foam pad comprising high
density 64 and low density 66 foam. The; cushion member may also optionally
-10-
____
CA 02284952 1999-10-04
comprise nubs 67 adapted to fit into the apertures 19 on the support platform.
This arrangement holds the cushion member in place and prevents movement
on the support platform when the device is in use. The cushion may be
removable from the support platform for cleaning, sterilization or
replacement.
Alternatively, the cushion member may be adhered to the support member with
an adhesive.
Figures 7A-D illustrate a preferred embodiment of the skid resistant foot
pad 70. The foot pad 70 incorporates a number of indentations 72 which
enhance the skid resistant properties of the rubberlike material 74. In a
preferred embodiment, the foot member has a self cleaning tread and has a
tapered design. As shown in Figure 7C, the footpad may also include one or
more molded teeth 76 which are adapted to fit into recesses 78 in the bottom
of
the foot member to prevent rotation.
Although preferred embodiments of the invention have been described
herein in detail, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that
variations
may be made thereto without departing from the spirit of the invention or the
scope of the claims.
-11-