Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
POLYURETHANE FOAM SEATING COMPONENTS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The invention relates to a seating component incorporating a cushion comprised
of a cushioning material surrounding a cavity disposed within the cushioning
material,
wherein the cavity is bounded by an air impermeable elastomeric filin bonded
to the
cushioning material.
2. Description of the Prior Art
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have steadily increased their
automotive seating performance requirements with regards to comfort, e.g., wet
compression set, ball rebound, hysteriesis, etc. The approach taken by many
molders has
been to use newly developed polyol(s) or isocyanate(s) in creating improved
polyurethane foam formulations to produce more comfortable seats and seating
components. Unfortunately, such efforts merely push the limits of what
polyurethane
foam cushions are capable of providing in terms of improved comfort
performance.
Numerous objections have been raised with respect to such conventional foam-
only cushions, as well as seats and seating components that use more
conventional
cushioning material. The polyurethane foams used in most current seats and
seating
components are typically encased in a covering made of vinyl, cloth or
leather. While
these materials provide a certain level of comfort to the rider, they are
merely window
dressing in terms of the overall cushioning effect of the seat. It is the
polyurethane foam
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
itself that absorbs the weight of the load placed on the cushion. The
polyurethane foam
forms itself to the contours of the load (e.g., a seated passenger) by
releasing air trapped
in the cells of the foam upon compression. When the load is removed, air is
brought back
into the cells of the foam. The repetition of this process over a period of
time gradually
causes the cushion to become less compressible and, thus, less resilient. The
results can
vary from separation of the foam from the seat cover to an overall decrease in
rider
comfort as the rider contacts the seat or seating components less on foam and
more on the
rigid base to which the foam is attached. This decrease in foam resiliency and
comfort is
the inevitable result of such foam-only cushion configurations. Desirably, a
configuration would exist that would provide a constant level of support and
comfort to
the rider while being freely adjustable to the contours of multiple possible
riders/loads.
Numerous prior art references describe the use of bladders or air pockets to
provide adjustable cushioning configurations. Many such configurations, such
as U.S.
Patent No. 5,711,575, provide for adjustable lumbar supports. Lumbar support
is not
integral to most seat designs, but comprises an additional separate device
attached to the
seat to provide seat comfort. It is always maintained above one (1) atmosphere
(atm)
pressure and is not subjected to the pressure load, which is normally exerted
on a seat. In
addition, most prior art lumbar supports merely provide a bladder with a
covering. The
lack of a cushioning material makes such supports uncomfortable over extended
use
periods. Desirably, a cushion/seat having both improved comfort and
adjustability would
be provided.
Similarly, the use of an airtight bladder in a seat configuration is not new
in the
design of various cushioning configurations. U.S. Patent No. 5,711,573, for
example,
2
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
teaches the use of an airtight bladder as an airtight casing around the foam
cushion.
While this design overcomes the air leakage problem of many prior art designs,
it
sacrifices adjustability in that the casing, from fully accommodating the
contours of any
possible rider, constricts the foam. Further, since the casing is exposed to
weathering
under the porous covering, it will become brittle and less airtight over time.
Finally, WO 9717001 discloses a cushioning device which incorporates a bladder
composed of two films which are welded together to form a sealed compartment
that is
further sealed with spot welds to create multiple sub-compartments. This
disclosure
overcomes many of the deficiencies of the prior art, but only at the cost of
creating new
deficiencies. Specifically, the use of dual sheets rather than a continuous
film to create
the internal bladder introduces the increased incidence of leakage of the
bladder. The
dual sheet configuration will introduce increased wear at the welds,
especially in those
situations where multiple subcompartments press against the spot welds and one
another.
The 9717001 disclosure further introduces the feature of a loose film forming
one side of
the bladder. While this configuration offsets pressure problems, it
drastically increases
the likelihood of leakage. Finally, in terms of overall comfort, no cushioning
material
beyond the bladder itself is disclosed. As discussed above, this reduces the
overall
comfort of the rider and increases damage caused by wear. Another type of
configuration
uses a bladder, which is covered by a foam cushioning material. While this
improves on
the design exemplified by the 9717001 disclosure, it still suffers from many
of the same
disadvantages including friction wear between the cushioning material and the
bladder or
between the bladder and the seat support.
3
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides a seating component comprising a base, a
cushion
disposed on the base and a covering disposed over the seating component to
enclose the
cushion and defining the exterior surface of the seating component. The
cushion of the
seat comprises a resilient cushioning material capable of holding a
pressurizing material
within the material structure, with an air impermeable bladder disposed within
the
cushioning material. The seating component may further comprise a valve
extending
from the bladder and through the cushioning material and in sealed
relationship with the
bladder, the valve including a valve operator disposed external to the
covering for
opening and closing communication between the bladder and the external
environment
around the seat.
The encased bladder cushion design may be incorporated into an adjustable
seating component where the seating component is a seat, a lumbar support,
armrest,
headrest, console or other seating component.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
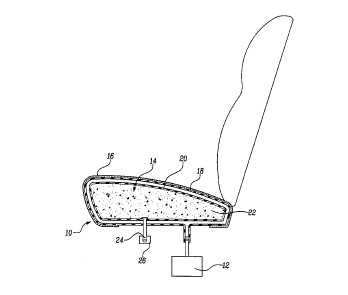
Figure 1 is a cross-section view of a seat configuration of the invention.
Figure 2 is a cross-section view of a headrest configuration of the invention.
Figure 3 is a cross-section view of a lumbar configuration of the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The invention preferably uses a continuous thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
film as a barner layer for the elastomeric bladder. The TPU film is preferably
bonded to
a surrounding polyurethane foam layer, creating a pocket within the foam. The
4
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
polyurethane foam may be formed through any of the several conventional
methods well
known in the art. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, an adjustable
one-way
valve is incorporated into the elastomeric bladder structure. In an
alternative embodiment,
the valve may accommodate a charge or pump to maintain air pressure within the
bladder. The bladder may either be wholly contained within the cushioning
material of
the seat, or may extend through the cushioning material to rest flush with the
seat
covering. The resulting seat configuration provides improved compression set,
comfort
and weight reduction of the polyurethane foam setting.
The air pressure in the pocket is preferably maintained at one (1) atmosphere
(atm) using a one-way valve. By using the one-way valve, the deficiencies of
some prior
art adjustable bladders, such as those utilized in lumbar supports, is
avoided.
Specifically, there is no worry about long-term pressure leak with the bladder
of the
instant invention. Such leaks often result in long term failure of the
aforementioned
lumbar supports. Preferably, the walls of the bladder will have a thickness of
from about
0.01 to about 1.0 inch.
The air pressure within the impermeable elastomeric bladder is preferably
maintained between 0.5 to S.0 atmospheres (atm) by using mechanical or non-
mechanical
pressurizing devices such as an aerosol charge, a mechanical pump or a manual
pump,
wherein the pressurizing device is removably attached to the valve operator.
The
mechanical pump may be distinguished from the manual pump as having a sensing
apparatus attached to it and in communication with the valve operator which
senses
decreases in pressure within the bladder and automatically compensates by
pumping air
or any other pressurizing material into the bladder. The manual pump will
comprise a
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
hand pump that may be used by the rider whenever seat discomfort indicates a
need for
increased pressure within the bladder. The bladders of the invention are
designed to
retain pressure over a period of time and re-pressurizing should only be
necessary on a
monthly or less frequent basis, depending on use. Preferably, the bladder will
contain a
one-way valve to maintain the air pressure at 1 atm when under load and
breathe back
after the load is removed.
In an alternative embodiment, a two-way valve may be incorporated in place of
the one-way valve. This configuration offers improved adjustability in
situations where
multiple users comprising varying loads may adjust the pressure in the bladder
to
individual comfort levels. The overall bladder-encased design would continue
to provide
increased comfort while substantially reducing leakage of any pressurizing
material.
The size and shape of the bladder depends on the design of the surrounding
polyurethane foam. The bladder can be either completely concealed or be
partially
visible on the surface by being positioned flush with the seat covering. In an
alternative
embodiment, the bladder can be attached to a device that will increase its air
pressure
either manually or mechanically. The bladder is incorporated into, preferably,
a
polyurethane foam cushioning material by suspending the bladder in the
polyurethane
mold and then pouring the foam around it.
The preferred TPU materials or elastomers should have good adhesion
characteristics with polyurethane foams. Preferably, the bladder is
constructed of
composite TPU laminates, TPU + EVOH and similar materials.
6
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
The seating component of the invention can be used for automotive seating,
wheelchair seats, household and office seats, mattresses, bicycle seats,
stadium seats,
saddles, and cushioning pads for hospital beds, etc.
Preferably, the bladder will be air filled. Other higher molecular weight
gases or
gels can be used in place of air in the sealed bladders to maintain the
pressure for a longer
period of time. Such compounds include inert gas, liquids, gels, oils,
microspheres
coated with lubricant or elastic particles in a thermoplastic bonding agent.
TPU or TPU laminated bladders can be produced from sheet laminates in a heat
seal process or blow-molding processes. Preferred bladder materials include
polyurethane/stretch-knit polyamide laminates, polyurethane vinyl, PVC, latex,
rubber,
synthetic rubber, thermoplastic elastomers or EVAs. TPU or TPU laminated
bladders can
also have different designs to enhance their load bearing characteristics,
such as
contacting half sphere bladders on either side of the seat or shape variations
including
squares, convex saucers, circles, triangles and the like.
Preferably, the cushioning material of the seat comprises a polyurethane foam.
Alternatively, the material may include any natural or synthetic fibers, felt,
animal hair
and the like. Natural fibers useful as a cushioning material include cotton,
jute, coconut,
hemp, silk, ramie, and any natural fiber known in the art. Synthetic fibers
that may be
utilized as a cushioning material include polyethylene glycol terephthalates
or other
polyester resins, spandex, polyolefins, such as polyethylene, polypropylene
and the like,
as well as nitrite polymer fibers, such as vinyl cyanide or acrylonitrile,
acrylic acid and
acrylic ester polymers, vinyl polymers, such as vinyl chloride, vinyl acetate,
and
vinylidene chloride, and fibers formed from modified natural materials, such
as
7
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
nitrocellulose, rayon and casein, any combination thereof, graft polymers
thereof and
mixtures thereof. In particular, the polyester fiber cushioning material may
be an
important alternative in applications where a high degree of recyclability is
desirable.
The seating component of the invention may further include a liner material
surrounding the cushioning material and protecting it from friction and other
external
sources of wear which may be exerted directly on the seat covering. Such
liners may
comprise any type of thermoplastic or thermoset material suitable for such
application,
including liners that incorporate seat heaters.
The seating component covering may comprise leather, vinyl, cloth or similar
materials as are normally used for such applications. The design of the
invention allows
for the use of any covering material without restriction.
Finally, the base of the seating component may be either a flat plane upon
which
the remainder of the seating component rests, or it may incorporate one or
more springs
to provide additional comfort and protection from vibration. The base itself
may be
constructed of any material suitable for a rigid flat piece, including
thermoplastics and
metals.
The bladder design of the invention may be incorporated into any number of
seating components, including consoles, head rests, lumbar supports and
armrests.
Where the bladder is used as part of a seat back lumbar support, the lumbar
support will
preferably be disposed or flush with the surface of a seat back. When used as
part of a
headrest, the bladder will preferably include a pressure-sensitive valve that
will release air
to absorb the weight of a contacting head, providing superior cushioning
performance.
8
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
Regardless of the type of seating component chosen, the features described
above with
respect to the seat design may be applied to other seating components as well.
Example 1
Figure 1 shows a seat 10 comprising a base 12, a cushion 14 disposed on the
base
12, and a covering 16 disposed over the seat 10 to enclose the cushion 14. The
cushion
14 comprises a resilient cushioning material 18 surrounding an air impermeable
bladder
20. The bladder 20 contains a pressurizing material 22. The seat further
comprises a
valve 24 extending from the bladder 20 and through the cushioning material 18
and in
sealed relationship with the bladder 20. The valve 24 includes a valve
operator 26
disposed external to the covering 16.
Example 2
Figure 2 shows a headrest 30 comprising a base 32, a cushion 34 disposed on
the
base 32, and a covering 36 disposed over the headrest 30 to enclose the
cushion 34. The
cushion 34 comprises a resilient cushioning material 38 surrounding an air
impermeable
bladder 40. The bladder 40 contains a pressurizing material 32. The headrest
further
comprises a valve 44 extending from the bladder 40 and through the cushioning
material
38 and in sealed relationship with the bladder 40. The valve 44 includes a
valve operator
46 disposed external to the covering 36.
Example 3
Figure 3 shows a lumbar support 50 comprising a base 52, a cushion 54 disposed
on the base 52, and a covering 56 disposed over the lumbar support SO to
enclose the
cushion 54. The cushion 54 comprises a resilient cushioning material 58
surrounding an
air impermeable bladder 60. The bladder 60 contains a pressurizing material
52. The
9
CA 02285813 1999-10-12
lumbar support further comprises a valve 64 extending from the bladder 60 and
through
the cushioning material 58 and in sealed relationship with the bladder 60. The
valve 64
includes a valve operator 66 disposed external to the covering 56.