Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
1
MACHINE AND METHOD FOR FASTENING A LOAD
Field of the invention:
The present invention relates to a machine and a
method for fastening a load. More particularly, the present
invention relates to the fastening of the load by means of a
rope made from a roll of flexible material such as for
example plastic film.
Background of the invention:
The load can be for example a metal coil on a pallet.
According to the prior art, such a metal coil is strapped
down on the pallet by means of steel straps. Then,
sometimes, the metal coil is further wrapped by means of a
stretched film to protect it during transportation or in the
case where it is stored outside. The strapping of the metal
coil on the pallet by means of steel straps is done manually
or automatically.
Known in the art, there is the U.S. patent no.
4,271,657 granted on June 9, 1981 to Patrick R.
LANCASTER, III. This patent describes an apparatus and
process for automatically making a spiral wrapped unitary
package having a ring type or tied closure. In the
apparatus, a series of loads, each containing a plurality of
units are fed one load at a time onto a turntable adjacent a
material dispenser with the leading edge of the material
from the dispenser being formed into a rope-like
configuration by a roper mechanism and held by a clamp
mechanism mounted on the turntable. The material is open to
its full web width, stretched and is spirally wrapped around
the load at which time it is again formed into another rope-
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
=~ '
2
like configuration by the roper mechanism, and is positioned
adjacent the leading edge where it is mechanically joined to
the leading edge of the material by a ring type or tied
closure. The roped material is then released from the clamp
mechanism mounted on the turntable and the material is
allowed to return to its memory position. The clamp
mechanism again clamps the leading edge for the next load
and the material is severed from the wrapped load.
Also known in the art, there is the U.S. patent no.
5,107,657 granted on April 28, 1992 to Werner K. DIEHL et
al. This patent describes an apparatus for wrapping a pallet
load with a wrapping film applied selectively as a film rope
or as a film sheet. The load is supported in an elevated
position. A rotary arm supported above the load is arranged
to be rotatably driven. An upright member depending from the
rotary arm is spaced outwardly from the load in any rotary
arm position. A carriage is arranged to be upwardly and
downwardly driven along such member. A dispenser on the
carriage dispenses the wrapper as a rope or as a sheet. A
guide, which comprises a lever and a hook on the lever, is
moveable among extended, partly retracted, and fully
retracted positions. In the extended position, the guide
guides the rope across the respective corners of the load.
In the partly retracted position, the guide does not
interfere with driving the carriage along the upright
member.
Also known in the art, there is the U.S. patent no.
4,631,898 granted on December 30, 1986 to Dario BRAMBILLA.
This patent describes a process and an apparatus for
continuously wrapping a palletized load, a self-propelling
apparatus is provided, said apparatus being fitted with
CA 02287675 2006-09-25
3
means for electric traction fed by batteries, said machine
moving at a distance around the outer perimeter of a load.
Also known in the art, there are the following U.S.
patents which describe different methods and apparatuses for
wrapping a load: 4,299,076; 4,432,185; 4,691,497; 4,831,812;
5,005,335; 5,054,263; 5,168,691; 5,301,493; 5,408,808;
5,423,163; 5,450,709; 5,606,849; 5,623,808; 5,628,167;
5,701,722; 5,794,418; 5,787,691; 5,802,810; and 5,836,140.
None of the above-mentioned patents provides the
necessary means for fastening loads having a large range of
sizes, rapidly and efficiently.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a
method and a machine for fastening loads having range of
sizes larger than those of the prior art, in a rapid and
efficient manner.
Summary of the invention:
According to the present invention, there is provided
a machine for fastening a load having a given size,
comprising:
a machine frame positioned around a central axis
intersecting a point where, in operation, the load is
brought;
a delivering carriage onto which a roll of flexible
material is rotatively mountable, including an output
delivering means for delivering the flexible material as a
rope, the delivery carriage comprising first and second
parts connected by means of a pivot axis, the first part
being connected to a movable support, the output delivering
means being mounted on the second part;
CA 02287675 2006-09-25
4
first controllable moving means for producing a
relative radial movement of the output delivering means with
respect to the central axis, the first controllable moving
means comprising a controllable cylinder having two
extremities connected respectively to the first and second
parts of the delivering carriage for pivoting the second
part with respect to the first part by means of the pivot
axis to produce the relative radial movement of the output
delivering means with respect to the central axis relative
rotating movement of the rope with respect to the central
axis;
a second controllable moving means for producing a
relative rotating movement of the rope with respect to the
central axis, the second controllable moving means
comprising a motor, a ring gear connected to the motor and
mounted within a gearbox, a rotary arm connected to the ring
gear, and a boom onto which the delivering carriage is
mounted so that the relative rotating movement of the rope
with respect to the central axis is produced by rotating the
delivering carriage by means of the motor;
a third controllable moving means for producing a
relative axial movement of rope in a direction parallel to
the central axis; and
controlling means for controlling:
the relative radial movement by means of the first
controllable moving means in view of the size of the load;
and
the relative rotating and axial movements by means of
the second and third controllable moving means to fasten the
load with the rope once the radial movement has been
produced.
CA 02287675 2006-09-25
Brief description of the drawings:
Figure 1 is a top view of a machine for fastening a
load according to the present invention, wherein there are
5 also shown the load to be wrapped and a conveyor to bring
the load in position to be wrapped.
Figure 2 is a side elevational view of the machine
shown in figure 1.
Figure 3 is a rear elevational view of the machine
shown in figure 1.
Figure 4 is an enlarged view of a part of the machine
shown in figure 2.
Figure 5 is an enlarged view of a part of the machine
shown in figure 3.
Figure 6 is a front view of the part shown in figure
5.
Figure 7 is an enlarged view of a part of the machine
shown in figure 3, in a first operating position.
Figure 8 is a view of the part shown in figure 7, in a
second operating position.
Figure 9 is a view of the part shown in figure 7, in a
third operating position.
Figure 10 is an enlarged view of a part of the machine
shown in figure 1, in a first operating position.
Figure 11 is a view of the part shown in figure 10, in
a second operating position.
Figure 12 is a schematic top view of a machine
according to the present invention, in relation to a large
load.
Figure 13 is a schematic top view of a machine
according to the present invention, in relation to a small
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
6
-load.
Figure 14 is a side elevational view of a part of the
machine shown in figure 2, in a first operating position.
Figure 15 is a rear elevational view of the part shown
in figure 14.
Figure 16 is a side elevational view of the part shown
in figures 14 and 15, in a second operating position.
Figure 17 is a rear elevational view of the part shown
in figure 16.
Figure 18 is a top view of a load.
Figure 19 is a front elevational view of the load
during the fastening thereof.
Figure 20 is a side elevational view of the load
during the fastening thereof.
Figure 21 is a perspective view of the load from above
during the fastening thereof.
Figure 22 is a schematic block diagram of the
controller of the machine shown in figures 1 to 3.
The objects, advantages and other features of the
present invention will become more apparent upon reading of
the following non-restrictive description of a preferred
embodiment thereof, given for the purpose of exemplification
only with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Detailed description of the drawings:
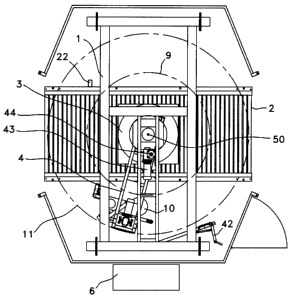
Referring now to figures 1 to 3, there is shown a
machine for fastening a load 3 according to the present
invention. This machine can also be used to wrap the load 3.
More specifically, the machine shown in these figures is an
automatic stretch wrapping machine where a delivering
carriage 5 revolves around the load 3 to fasten it. In the
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
7
present case, the delivering carriage 5 revolves around the
load 3 but, in an alternative embodiment, the load 3 can be
rotated with respect to the machine.
The machine comprises a frame 1 positioned around a
central axis 50 intersecting the point where, in operation,
the load 3 is brought by means of a conveyor 2. The
delivering carriage 5 includes a flexible material
delivering system. The flexible material can be for example
plastic film. A roll 10 of plastic film is rotatively
3.0 mounted on the carriage 5. The carriage 5 includes an output
delivering device for delivering the film as a rope. The
delivering carriage 5 and the output delivering device will
be described with more details in reference to figures 4 to
9.
The machine also comprises a first controllable moving
device for producing a relative radial movement of the
output delivering device with respect to the central axis
50. This first controllable moving device will be described
with more details in reference to figures 10 to 13.
The machine also comprises a second controllable
moving device for producing a relative rotating movement of
the rope with respect to the central axis 50. The second
controllable moving device comprises a motor 43, a ring gear
7 connected to the motor 43 and mounted within a gear box
44, a rotary arm 4 connected to the ring gear 7 and a boom 8
onto which the delivering carriage 5 is mounted. In
operation, the relative rotating movement of the rope with
respect to the central axis 50 is produced by rotating the
delivering carriage 5 by means of the motor 43.
The machine also comprises a third controllable moving
device for producing a relative axial movement of the rope
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
8
in a direction parallel to the central axis 50. This third
controllable moving device will be described with more
details in reference to figures 8 and 9.
The machine also comprises a controller for
controlling the relative radial movement by means of the
first controllable moving device in view of the size of the
load, and the relative rotating and axial movements by means
of the second and third controllable moving devices to
fasten the load with the rope once the radial movement has
been produced. This controller will be described with more
details in reference to figure 22. The controller is located
in the control panel 6.
As can be seen more specifically in figure 1, the
maximum wrapping diameter is indicated by reference numeral
9. The outside diameter which is indicated by reference
numeral 11 is the periphery of the rotating movement of the
delivering carriage 5.
The machine further comprises a photocell 22 mounted
on the conveyor 2 in a position nearby the point where the
load 3 is located. The photocell 22 is for producing an
output signal in relation to the size of the load 3. The
photocell 22 has an output connected to the controller for
sending its output signal thereto.
Referring now more specifically to figures 2 and 3,
there is shown the clamp unit 25 which will be described
with more details in reference to figures 14 and 17.
Referring now more specifically to figure 1, there is also
shown a cut and wipe unit 42 which is a standard device for
an automatic stretch wrapping machine. The function of this
cut and wipe unit 42 is to cut and wipe the film at the end
of a fastening or wrapping sequence. As this cut and wipe
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
9
unit 42 is not part of the present invention, it will not be
described with more details.
Referring now to figures 4 to 9, there is as shown
with more details the delivering carriage 5 shown in figures
1 to 3. The delivering carriage includes the output
delivering device which is provided with a guiding
cylindrical roller 18 for guiding the film 39 from the roll
along a plan toward a predetermined direction. The output
delivering device also comprises two elements 15 and 16.
10 These two elements 15 and 16 are movable along parallel axis
within the plan, transversally to the predetermined
direction. Each of the elements 15 and 16 being provided
with a contact device which is a roping wheel for contacting
lateral opposite edges of the film. The elements 15 and 16
are movable between a first operating position shown in
figure 7 where the elements 15 and 16 are distant from each
other to deliver the film 39 as a web 37, and a second
operating position as shown in figures 8 and 9 where the
elements 15 and 16 are close to each other to deliver the
film 39 as a rope 31.
Controllable moving cylinders 19 and 20 are provided
for moving the elements 15 and 16 between first and second
operating positions as shown in figures 7, 8 and 9. The
controller shown in figure 22 is connected to cylinders 19
and 20 for controlling their movement.
The controllable moving cylinders 19 and 20 are also
used to embody the third controllable moving device by
moving the elements 15 and 16 together along their axis when
they are in their second operating position to produce the
relative axial movement of the rope as shown in figures 8
and 9. A sliding bracket 21 as shown in figures 4, 5 and 6
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
is provided for sliding the delivering carriage with.respect
to the boom S.
Referring now to figures 10 to 13, there is shown that
the delivering carriage comprises first and second parts 52
5 and 54 connected by means of a pivot axis 12. The first part
52 is connected to the boom 8 by means of the sliding
bracket 21 shown in figures 4, 5 and 6. The output
delivering device is mounted on the second part 54. A
controllable cylinder 13 is provided for pivoting the second
10 part 54 with respect to the first part 52. The two
extremities of the cylinder 13 are connected respectively to
the first and second parts 52 and 54 of the delivering
carriage. The relative radial movement of the output
delivering means with respect to the central axis 50 is
produced by means of the controllable cylinder 13 as shown
more specifically in figures 12 and 13. A motor 17 is
provided on the boom 8 for moving the delivering carriage up
and down the boom 8.
Referring now more specifically to figures 12 and 13,
there are shown two operating positions of the output
delivering device for fastening respectively a large load
and a small load. In each case, the load comprises an object
resting on a pallet 28. In figure 12, there is shown the
maximum fastening diameter 9 that is allowed by the machine,
25 and in figure 13 there is shown the minimum fastening
diameter 26 allowed by the machine. It can be seen that the
presence of the controllable cylinder 13 for producing the
relative radial movement of the output delivering device
allows the fastening of loads with a large range of sizes.
30 Referring now to figures 14 to 17, we will now
describe with more details the clamp unit 25 shown in
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
11
figures 2 and 3. In the prior art, a wrapping sequence
begins and ends by clamping the film by means of the
clamping unit which includes a clamp and a guiding bar.
Normally, the clamp and the guiding bar are at fixed
posi-tions and this is not a problem because there is no
radial movement of the output delivering device. But,
according to the present invention, since the delivering
carriage is movable along the radial direction with respect
to the central axis, the jaws 35 of the clamp and the
guiding bar 32 have to be removed from the way during a
fastening sequence.
The jaws 35 and the guiding bar 32 are only needed at
the beginning and at the end of a fastening cycle. During
the fastening cycle, these elements are in a standby mode.
However, they are right on the path of the output delivering
device when the radial movement thereof is performed.
In order to overcome this drawback, controllable
cylinders 34 and 36 are provided for moving the jaws 35 and
the bar 32 out of the way during the fastening cycle so that
the radial movement of the output delivering device is
unobstructed. The jaws 35 and the guiding bar 32 are both
mounted between a home position of the output delivering
device and the central axis 50 shown in figure 1, for
clamping the film at the beginning and end of the fastening
cycle of the delivering carriage.
The controllable cylinder 36 is provided for moving
the jaws 35 between a first position where, during the
fastening cycle, the relative radial movement of the output
delivering device with respect to the central axis is
unobstructed, and a second position where the jaws 35 are in
position to clamp the film at the beginning and end of the
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
12
fastening cycle. The controllable cylinder 34 is provided
for moving the guiding bar 32 between a first position
where, during the fastening cycle, the relative radial
movement of the output delivering device with respect to the
central axis is unobstructed, and a second position where
the guiding bar 32 guides the flexible material extending
from the output delivering device in position so that a
portion of the flexible material can be clamped by the jaws
35. The controller shown in figure 22 controls the operating
positions of the jaws 35 and the guiding bar 32 by means of
the controllable cylinders 34 and 36.
In the first operating position of the clamp, the jaws
35 are 1800 apart from each other as shown in figure 14. In
the second operating position of the clamp, the two movable
jaws 35 are adjacent to each other as shown in figure 16.
The guiding bar 32 has a horizontal upper central
portion terminated by diverging lower extremities. The
horizontal central portion moves between a lower position
bar as shown in figures 14 and 15, and an upper position as
shown in figures 16 and 17. The controllable cylinder 34 is
connected to one of the extremities of the guiding bar 32 to
move the central portion thereof between its lower and upper
positions.
According to the present invention, there is also
provided a method for fastening a load. To describe this
raethod, we will now refer to figures 1, 8, 9, 13 and 18 to
21. In figure 18, there is shown a top view of the load
which comprises an object 30 resting on a pallet 28.
The method comprises the steps of (a) bringing the
load to a point intersected by a central axis 50 as shown in
figure 1; (b) after step (a), producing a relative radial
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
13
movement of the output delivering device with respect to the
central axis 50 in view of the size of the load as shown for
example in figure 13; (c) delivering the film 39 as a rope
31 by means of the output delivering device as shown for
example in figure 8; (d) after steps (b) and (c), producing
a relative rotating movement of the rope with respect to the
central axis; and (e) during step (d) producing a relative
axial movement of the rope 31 in a direction parallel to the
central axis as shown for example in figures 8 and 9 to
fasten the load with the rope 31 by means of the relative
rotating and axial movement thereof as shown in figures 19,
and 21.
In these figures 19, 20 and 21, we can see that the
pallet 28 has four corners and a top board on which the
15 object 30 is resting. Preferably, for each corner of the
pallet 28, the relative axial movement of step (d) includes
a downward movement to pass the rope 31 underneath the top
board of the pallet 28 at said corner, followed by an upward
movement of the rope above the pallet 28 for at least one
20 full turn thereof around the object, as seen more
specifically in figure 21.
Preferably, the method further comprises, after step
(b) and before step (c), steps of (i) delivering the film as
a web by means of the output delivering device as shown in
figure 7; (ii) after step (i) producing a relative rotating
movement of the web with respect to the central axis; and
(iii) during step (ii), producing a relative axial movement
of the web in a direction parallel to the central axis to
wrap the load with at least one layer of the web by means of
the relative rotating and axial movements thereof. In some
cases, the fact that the load is wrapped before the
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
14
fastening provides some advantages.
Preferably, the method further comprises, after step
(e) , step of (iv) delivering the film as a web by means of
the output delivering device as shown in figure 7; (v) after
stex) (iv), producing a relative rotating movement of the web
with respect to the central axis; and (vi) during step (v),
producing a relative axial movement of the web in a
direction parallel to the central axis to wrap the load with
at least one layer of the web by means of the relative
rotating and axial movements thereof. In some cases, the
fact that the load is wrapped after the fastening thereof
provides several advantages.
We will now describe a preferable embodiment of the
method with more details, with reference to figures 1, 2, 3,
10 and 11. In the present case, the load 3 is made of a
metal coil resting on a pallet. The load is brought with a
conveyor 2. While the load is entering the wrapping area, it
is detected and measured by means of a photo eye 22. This
measurement is used to stop the load in alignment with the
central axis 50 of the machine. According to the same
measurement, the machine decides whether the size of the
load is such that the output delivering device of the
carriage 5 has to be repositioned in relation to the central
axis 50. If the output delivering device has to be
repositioned, it will be moved by means of the servo-drive
ball screw cylinder 13. This cylinder 13 can stop at
different positions between its retracted and completely
extended positions.
At the beginning of a cycle, the film end is secured
between the jaws of the clamping unit 25. The cycle begins
with a wrapping sequence to wrap the load 3. The wrapping of
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
the load is preferable to make sure that the rope will stay
in position after the fastening sequence.
After the wrapping sequence, the film has to be
delivered as a rope. Referring now to figures 8 and 9, we
5 will describe how the film is delivered as a rope, and how
the rope is moved up and down. During the wrapping sequence,
the cylinders 19 and 20 are positioned as shown in figure 7.
It is possible to deliver the film as a rope by bringing up
cylinder 19 close to cylinder 20 as shown in figure B. In a
10 similar manner, it is also possible to deliver the film 39
as a rope 31 by bringing down cylinder 20 close to cylinder
19 as shown in figure 9. By using both cylinders 19 and 20
simultaneously, it is possible to move the rope 31 up and
down without any movement of the delivering carriage.
15 Referring to figures 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 19, 20 and 21,
at the end of wrapping sequence, the delivering carriage
returns at its lowest position on the boom 8 to start a
fastening sequence. Then, the cylinders 19 and 20 are moved
to deliver the film 39 as a rope 31. Then, by controlling
the rotative movement of the delivering carriage 5 around
the load 3 and by controlling the movement of the cylinders
19 and 20, it is possible, for each corner of the pallet 28,
to pass the rope 31 underneath it and then make at least one
full turn of the rope 31 around the load 3. This operation
is repeated for each corner of the pallet 28. The user can
select the number of turns around the load for each corner
of the pallet.
When the rope sequence is done, both cylinders 19 and
20 are brought to their home position so that the film 39 is
now delivered as a web 37 as shown in figure 7. Then several
revolutions of the full web is done to cover the rope 31
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
16
with at least one layer of web 37. After this final wrapping
sequence, the delivering carriage 5 is brought back to its
home position where the film 39 is clamped by the clamp unit
25 and cut and wipe by means of the cut and wipe unit 42 to
free the load 3. The load 3 is removed from the fastening
area and a next one can be brought in.
Referring now to figure 22, there is shown a block
diagram of the controller. The controller comprises a
central module 45 and a peripheral module 46 which is only
3_0 concerned with the control of the radial movement of the
output delivering device of the delivering carriage. The
input 65 of the module 45 is for receiving a signal from the
photo eye 22 shown in figure 1. Output 48 of module 45 is
for controlling the rotation of the delivering carriage
around the load by means of the motor 43 shown in figure 1.
The outputs 49 and 50 are for controlling the up and down
movement of the delivering carriage by means of the motor 17
shown in figure 10. The outputs 51, 52, 53 and 54 of module
45 are for controlling the cylinders 19 and 20 shown in
figures 7, 8 and 9 to deliver the film as a web or a rope
and to further move the rope up and down.
Output signals 55, 56, 57 and 58 of the module 45 are
sent to inputs of module 46 which provides by means of its
outputs 59 to 64 control signals for controlling radial
movement of the output delivering device of the delivering
carriage by means of controllable cylinder 13 shown in
figures 10 and 11. Each of the outputs 59 to 64 corresponds
to a different radial position of the output delivering
device with respect central axis.
Although a preferred embodiment of the invention has
been described in detail herein and illustrated in the
CA 02287675 1999-10-27
.=
17
accompanying drawings, it is to be understood that the
invention is not limited to this precise embodiment and that
various changes and modifications may be effected therein
without departing from scope or spirit of the invention.