Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99105822 PCT/SE98/01369
Method and Device in a Telecommunications System
Technical Field
The present invention relates to methods for the remote control of
telecommunica-
S tions units in a telecommunications system. The invention also relates to
appara-
tuses for carrying out the methods.
Description of Related Art
Operation and maintenance of telecommunications units are frequently performed
actions in a telecommunications system. US Patent 5,297,193 shows how mainte-
nance of a mobile telecommunications network is carried out by means of a cen-
trally located operation and maintenance (O&M) centre. The disadvantage of
this
solution is that the O&M centre only has the capacity to handle operations of
a gen-
eral character while there is often a need to carry out more specific O&M
actions
1 S intended for a particular telecommunications unit in the system, for
example at start-
up of the telecommunications unit.
US Patent US 5,448,616 describes a method and an apparatus in a mobile telecom-
munications system for automatically measuring the Bit Error Rate (BER) of a
par-
ticular telecommunications unit. This is done by a built-in BER test device in
the
telecommunications system. The apparatus in incorporated in an analogue
channel
unit in the base station to be tested. According to this US Patent the
incorporated
BER test device enables BER tests and the remote control of BER tests from an
O&M centre. A disadvantage of the solution according to US 5,448,616 is that
each
2S test object has to be provided with extra equipment, which implies an
additional
cost. The extra equipment is often installed at an initial stage, which causes
another
disadvantage, in that only the tests for which the equipment was intended at
the ini-
tial stage can be carried out. This reduces the flexibility of O&M. A solution
to this
problem is to go out to each telecommunications unit and carry out tests by
means
of a physical link between the telecommunications unit and a test instrument.
This
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/OS822 PCT/SE98/01369
2
may, however, cause problems if the telecommunications unit is found in a
place
which it is difficult to get to. Normally, costly equipment has to be
transported to
the place in which the telecommunications unit is found, and connected. As a
result
of this, in addition to expensive maintenance, the periods between maintenance
tend
to be long. Another solution would be to connect the O&M terminal to a radio
unit,
or alternatively to an IR unit, and transfer service commands to the
telecommunica-
tions unit by means of radii signals or IR signals. This solution would,
however, re-
quire functions for establishing connections in each test object, which would
incur
to great additional costs.
Summary of the Invention
The present invention deals with the problem of performing high quality
flexible
special service of telecommunications units at a low cost, especially when the
units
are found in places to which it is hard to get.
In accordance with this, a problem that is dealt with is the problem of
establishing,
without the requirement of a physical connection, a connection for special
tests be-
tween an O&M terminal and a selected telecommunications unit, a so called,
test
object, without the need of going to the location of the test object.
According to the invention this problem is solved by providing a service port
in the
telecommunications system, that is able to establish a connection to the
selected test
object as well as the O&M terminal, irrespective of the location of the test
object
and the O&M terminal, respectively, in the telecommunications system.
According to the invention this is achieved by establishing a connection
between the
O&M terminal and the service port. The connection is established in accordance
with a so called first signalling protocol intended for the signalling between
the
O&M terminal and the service port. The service port then establishes a
connection
to the selected test object. The connection is established in accordance with
a so
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
3
called second signalling protocol intended for the signalling between the O&M
ter-
minal and the test object. The service port, according to the invention,
converts
service commands from the O&M terminal to the telecommunications unit and the
other way around. The conversion is made from the first signalling protocol to
the
second signalling protocol and the other way around.
A purpose of the present invention is to transport service commands and other
data
from the O&M terminal to a selected test object and vice versa without
establishing
a physical connection between the O&M terminal and the test object.
Another purpose of the invention is to offer flexible special service of high
quality
to a test object without the need to install test equipment in the test
object.
Yet another purpose of the invention is to let a connection centre common to
the test
objects handle the establishment of connections between the O&M terminal and a
selected test object.
An advantage of the invention is that the high quality flexible special
service of a
test object in a telecommunications system can be offered at a low cost.
Another advantage of the invention is that service may be performed for
several dif
ferent test objects without the need to provide each test object with extra
equipment.
The invention will now be described in more detail by way of preferred embodi-
ments and with reference to the enclosed drawings.
Brief Description of the Drawings
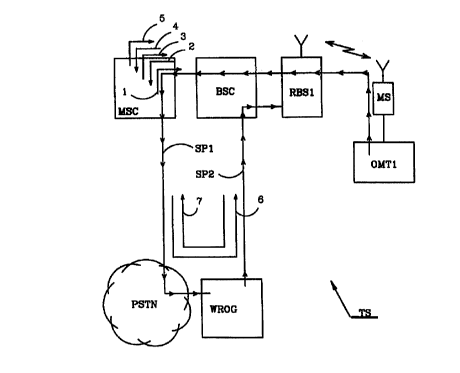
Figure 1 is a block diagram of a telecommunications system in which an
external
service port has been provided.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT1SE98/01369
4
Figure 2 is a flow chart of an inventive method. The method is carried out by
means
of the configuration shown in Figure 1.
Figure 3 is a block diagram of a telecommunications system comprising an
internal
service port.
Figure 4 is a flow chart of an inventive method. The method is carried out by
means
of the configuration shown in Figure 3.
Figure 5 is a block diagram of an inventive apparatus.
Preferred Embodiments
An embodiment of the inventive method for the remote maintenance of a Radio
Base Station (RBS) RBS 1 will now be described. In Figure 1 a
telecommunications
system TS is shown. The telecommunications system comprises a mobile switching
centre MSC connected to a terrestrial public services telephone network PSTN.
A
base station controller BSC is connected to the MSC and the RBS RBS1 is con-
nected to the base station controller BSC. The mobile switching centre MSC,
the
base station controller BSC and the radio base station RBS are all in this
embodi-
ment part of a GSM system. A service port WROG is, in this embodiment, con-
nected between the terrestrial network PSTN and the base station controller
BSC.
The service port communicates through the PSTN network with a so called first
sig-
nalling protocol SPl, which is a standardized GSM protocol that is well
defined in
the ETSI GSM Technical Specification. The GSM protocol has a transmission rate
of 9.6 kbit/s. The service port also communicates with the base station
controller
BSC by means of a so called second signalling protocol SP2, which is a
standard-
ized transmission protocol that is well defined in ANSI T 1.403 and ITU-T
recom-
mendations 6.703. The transmission protocol has a transmission rate of either
1544
kbit/s (I.SMbit) or 2048 kbit/s (2Mbit) divided into time slots of 64 kbit/s.
In the 1.5
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
Mbit case there are 24 time slots and in the 2 Mbit case there are 32 time
slots of 64
kbit/s. The service port WROG can convert incoming signals to the service port
from the PSTN network in accordance with the first 9.6 kbit/s signalling
protocol
SP1 to signals intended for the second 64 kbit/s signalling protocol SP2.
Commands
and other data are then translated from 9.6 kbit/s format to 64 kbit/s format.
Com-
mands are transmitted after conversion from the service port WROG to the base
station controller BSC. The service port WROG also converts signals in the
oppo-
site direction, that is, incoming signals from the base station controller are
converted
to signals having a suitable format for the PSTN network. This bi-directional
con-
version technique is known in the art. According to the inventive method the
service
port WROG also carries out a security check. This security check will be
described
in more detail below. Figure 1 shows an o&M terminal OMT1. The O&M terminal
in this embodiment is a portable personal computer. The O&M terminal is
normally
used for operation and maintenance of the radio base station RBS 1. This has
been
achieved according to prior art by connecting the O&M terminal to the base
station
by means of a physical connection. The O&M terminal OMT1, however, according
to the embodiment is connected to a mobile telephone MS and the mobile
telephone
is arranged to communicate with the radio base station ltBS 1 by means of
radio sig-
nals. These radio signals in Figure 1 are shown as a flash shaped symbol
between
the radio base station and the antenna of the mobile telephone.
In the following the inventive method will be described in more detail. The
method
is a method of performing operation and maintenance of the radio base station
RBS 1, and more specifically a method of reading error statistics. As a first
step in
the method according to this embodiment the above mentioned service port WROG
has been connected between the PSTN network and the base station controller.
Also, the O&M terminal OMT1 has been connected to the mobile telephone MS.
The method after this comprises the following additional steps:
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
6
- A user of the O&M terminal OMT1 decides to perform operation or maintenance
of one or more telecommunications units in the telecommunications system.
- A connection SP 1 is established, at the request of the user, between the
O&M
terminal OMT 1 and the service port WROG. The connection is established by the
user stating the connection number of the service port by means of the
keyboard
of the O&M terminal. On the established connection SP i messages are trans-
ported according to the above mentioned standardized GSM protocol with a
transmission rate of 9.6 kbit/s.
- An authorization request 1 is transmitted on the established connection from
the
service port WROG through the PSTN network, the mobile switching centre
MSC, the base station controller BSC, the radio base station RBS 1 and the
radio
interface, to the O&M terminal OMT 1. In the authorization request 1 user spe-
cific parameters are requested. The parameters are needed for the
authorization of
the user.
- The requested parameters, for example, a password, are given by the user and
transmitted in a parameter message 2 to the service port WROG. The parameters
for authorization are analyzed in the service port WROG. This authorization
can
include additional parameter requests and answers. The authorization is well
known in the art and will not be described in more detail.
- After the authorization has been successfully completed an acceptance
message 3
is transmitted from the service port WROG back to the O&M terminal OMT1.
- The acceptance message 3 is received in the O&M terminal OMT1 and the mes-
sage that the authority has been allowed is presented to the user.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
7
- The user selects the radio base station RBS1 as the object to be handled.
The user
defines the base station RBS 1 by pressing keys on the keyboard of the O&M
terminal.
S - A connection command 4 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT 1 to the
service port WROG. The connection command comprises information about to
which one of the telecommunications units in the telecommunications systems a
connection is requested, that is, in this case, the base station RBS 1.
- The service port WROG receives a request for a connection to the base
station
RBS l and a connection SP2 is established between the service port WROG and
the base station RBS 1. The established connection is of the standardized
trans-
mission protocol mentioned above, with a transmission rate of 64 kbit/s.
- When the connection has been established a connection message S is
transmitted
from the service port WROG to the O&M terminal OMT 1. The message is pre-
sented to the user in the O&M terminal OMT 1.
- The user decides to read error statistics for the base station RBS 1
specified
above. The user of the O&M terminal specifies this wish by pressing keys.
- A service command 6 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT1 to the serv-
ice port WROG.
- The service command 6 is converted from the transmission rate 9.6 kbit/s to
a
transmission rate of 64 kbit/s.
- The service command is forwarded from the service port WROG through the
base station controller to the base station RBS 1.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
~ °°~ 4 IIDPa~~ S }~ nSi~I I~ ~ T-1f 1~1T ~Pt~~ fn~~02 /s~ ~
Zv~~ ::~ ~~ rl V~~f'1&Gs~k~ Nii~s~"~»
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
9
have been explained above. The method is carried out in accordance with Figure
2
and in accordance with the brief explanation of the Figure given below.
- The service port WROG is connected between the PSTN network and the base
station controller BSC and is connected to the O&M terminal OMT1 to the mo-
bile telephone MS 1, according to a block 101.
- The connection SP 1 is established on request of the user between the O&M
ter-
urinal OMT1 and the service part WROG, according to a block 102.
- An authorization request 1 is transmitted on the established connection from
the
service port WROG to the O&M terminal OMT1, according to a block 103.
- The requested parameters are entered by the user and transmitted in the
parameter
message 2 to the service port WROG, according to a block 104.
- When the authorization has been successfully completed the acceptance
message
3 is transmitted from the service port WROG back to the O&M terminal OMT1,
according to a block 105.
- The user selects the base station RBS i as the object to be handled,
according to a
block 106.
- The connection command 4 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT 1 to the
service port WROG, according to a block 107.
- The connection SP2 is established between the service port WROG and the base
station RBS1, according to a block 108.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
- The user decides to read the error statistics for the base station RBS 1
specified
above, and the service command 6 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT1
to the service port WROG, according to a block 109.
5 - The service command 6 is converted from the transmission rate 9.6 kbit/s
to a
transmission rate of 64 kbit/s, according to a block, and the service command
is
forwarded from the service port WROG through the base station controller BSC
to the base station RBS 1, according to a block 110.
10 - The requested error statistics 7 is read from the base station RBS 1 to
the service
port WROG, according to a block 111.
- The error statistics 7 is converted from the transmission rate 64 kbit/s to
the
transmission rate 9.6 kbit/s, according to a block 112.
- The error statistics is presented to the user in the O&M terminal OMT1,
accord-
ing to a block 113.
Figure 3 shows an alternative to the embodiment shown above in connection with
Figure 1. The purpose of the embodiment shown in Figure 3 is, among other
things,
to show that the inventive idea can be kept even if the telecommunications
system is
modified. Figure 3 shows parts of the telecommunications system shown above.
The
telecommunications system comprises the mobile switching centre, connected to
the
terrestrial telephone network PSTN. The base station controller, as before, is
con-
nected to the mobile switching centre MSC. A service port iWROG is in this em-
bodiment found in the mobile switching centre MSC. The internal service port,
indi-
cated in Figure 3 as a dotted line, is implemented in software in the mobile
switch-
ing centre MSC. The service port 1WROG communicates, as before, through the
PSTN network, with the first signalling protocol SP 1 having a transmission
rate of
9.6 kbit/s. The service port also communicates with the base station
controller BSC
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
W O 99/05822 PCT/SE98/01369
11
by means of the second signalling protocol SP2 having a transmission rate of
64
kbit/s. The internal service port IWROG has the same function as described
above,
that is, the service port converts incoming signals to the service port from
an o&M
terminal OMT2, through the PSTN network in accordance with the first
signalling
protocol, to signals intended for the second signalling protocol SP2. The
service port
IWROG also converts signals in the opposite direction, that is, signals from
the base
station controller BSC to the O&M terminal OMT2. The O&M terminal OMT2,
which is in this embodiment intended for the setting of parameters in the base
sta-
tion controller BSC, has been connected by a modem (not shown in Figure 3) to
the
PSTN network.
In the immediately following the inventive method according to the alternative
em-
bodiment will be described. The method is a method of performing operation and
maintenance of the base station controller BSC, and more specifically a method
of
1 S setting parameters in the base station controller. The method comprises
the follow-
ing steps:
- A user of the O&M terminal OMT2 decides to perform operation or maintenance
of telecommunications units in the telecommunications system.
- A connection SP 1 is established, at the request of the user, between the
O&M
terminal OMT2 and the service port IWROG. The connection is established by
the user stating the connection number of the service port by means of the key-
board of the O&M terminal. The established connection has a transmission rate
of 9.6 kbit/s.
- The user selects the base station controller BSC as the object to be
handled.
- A connection command 11 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT2 to the
service port IWROG. The connection command comprises information about to
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCTISE98101369
12
which one of the telecommunications units in the telecommunications systems
connection is requested, that is, in this case, the base station controller
BSC.
- The service port IWROG receives a request fox a connection to the base
station
controller BSC and a connection SP2 is established between the service port
IWROG and the base station controller BSC. The established connection is the
standardized transmission protocol mentioned above, with a transmission rate
of
64 kbit/s.
- When the connection SP2 has been established a connection message 12 is
transmitted from the service port IWROG to the O&M terminal OMT2. The mes-
sage is presented to the user.
- The user decides to set parameters for the base station controller BSC. The
user
of the O&M terminal OMT2 specifies, by pressing keys, the parameters to be set
and the new values for these parameters in a monitor in the O&M terminal
OMT2.
- A modify command 13 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT2 to the
service port IWROG.
- The modify command 13 comprising the desired parameters is converted from
the transmission rate 9.6 kbit/s to a transmission rate of 64 kbit/s.
- The service command is forwarded from the service port IWROG to the base sta-
tion controller BSC.
- The parameters defined in the modify command are modified in the base
station
controller according to the specified request.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99105822 PCTISE98/01369
13
- A result message 14 is transmitted from the base station controller through
the
internal service port IWROG and the PSTN network to the O&M terminal
OMT2. Conversion is made in the service port IWROG from the transmission
rate 64 kbit/s to a transmission rate of 9.6 kbit/s.
- The resulting parameter setting is presented to the user.
Figure 4 is a flow chart of the described method. The most important steps to
the in-
vention are shown in the Figure. Abbreviations used in the Figure are
considered to
have been explained above. The method is carried out in accordance with Figure
4
and in accordance with the brief explanation of the Figure given below.
- The user of the O&M terminal OMT2 decides to perform operation or mainte-
nance of telecommunications units in the telecommunications system, according
to a block 201.
- The connection SP 1 is established on request of the user between the O&M
ter-
urinal OMT2 and the service port IWROG in the mobile switching centre MSC,
according to a block 202.
- The user selects to handle the base station controller BSC, according to a
block
203.
- The connection command 11 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT2 to the
service port IWROG, according to a block 204.
- The connection SP2 is established between the service port IWROG and the
base
station controller BSC, according to a block 205.
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99105822 PCTISE98/01369
14
- The connect message 12 is transmitted from the service port IWROG to the
O&M terminal OMT2 and is presented to the user, according to a block 206.
- The user of the O&M terminal OMT2 defines, by pressing keys, the parameters
to be set and their new values, according to a block 207.
- The modify command 13 is transmitted from the O&M terminal OMT2 to the
service port IWROG, according to a block 208.
- The modify command 13 is converted from the transmission rate 9.6 kbit/s to
a
transmission rate of 64 kbit/s, according to a block 209.
- The parameters defined in the modify command are modified in the base
station
controller BSC, according to a block 210.
- The result message 14 is transmitted from the base station controller
through the
internal service port IWROG and the terrestrial network PSTN to the O&M ter-
minal OMT2, according to a block 211. Conversion is made in the service port
IWROG from 64 kbit/s to 9.6 kbit/s.
- The resulting parameter setting is presented to the user, according to a
block 212.
Figure 5 shows, yet another embodiment of an inventive apparatus for carrying
out
the inventive methods shown above. The apparatus comprises an O&M terminal 40
comprising a modem 41. The modem 41 is connected through a first telecommuni-
cations connection 70 to a modem S 1 in a service port 50. The service port 50
also
comprises yet another modem 52 which is connected to a test object 60 through
a
second telecommunications connection 80. The modem 41, the first telecommuni-
cations connection 70 and the modem 51 all constitute means for establishing a
connection between the O&M terminal and the service port in accordance with
the
CA 02297050 2000-O1-19
WO 99/05822 PCTISE98/01369
above mentioned first signalling protocol SP 1 specified above, between the
terminal
40 and the port 50. The modem 52 and the second telecommunications connection
80 constitute means for establishing a connection between the service port 50
and
the test object 60 in accordance with the above mentioned second signalling
proto-
5 col SP2, specified above. The service port 50 also comprises means 55 for
selecting
a test object specified by the user, in this case the test object 60. The
service port
also comprises means 56 for exchanging service parameters between the O&M ter-
minal 40 and the selected test object 60 and means 57 for converting signals
be-
tween the two signalling protocols SP1, SP2.
In the embodiments described in this document two different signalling
protocols
SP 1 and SP2 have been specified. Other protocols than these two could also be
used. The above mentioned 9.6 kbit/s standardized GSM protocol could be
replaced,
for example, by the GSM standard General Packet Radio Service (GPRS). Alterna-
1 S tively the GSM protocol could be exchanged for the High Speed Circuit
Switched
Data (HSCSD) protocol for several data channels. It is also possible to let
the stan-
dardized 64 kbit/s transmission protocol be shared with other units in the
telecom-
munications network, for example, for signalling in another form to and from
base
stations, to and from base station controllers, so that instead of the above
mentioned
transmission rate of 64 kbit/s a transmission rate of 32 kbit/s is achieved.
In the embodiments a GSM system has been used as a part of the telecommunica-
tions system, but here as well other telecommunications systems could be used
without affecting the inventive idea. It should also be noted that the mutual
order of
the method steps shown above could be changed within the scope of the
invention.
Thus, the invention is not limited to the embodiments described above and
shown in
the drawings, but can be modified within the scope of the appended claims.