Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
78034-53
CA 02299810 2000-OS-17
CEILING FAN HAVING SIDE MOUNTED BLADE IRONS
CROSS REFERENCES
This application is a continuation-in-part of U. S.
Design Patent Application Serial No. 29/101,390 entitled
"Ceiling Fan and Light Fixture" filed March 3, 1999, which is
expressly incorporated by reference herein in its entirety,
and is also a continuation-in-part of U. S. Design Application
Serial No. 29/101,400 entitled "Ceiling Fan and Light Fixture",
filed March 3, 1999, which is expressly incorporated by refer-
ence herein in its entirety.
BACKGROUND
1.0 Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to ceiling
fans and, more particularly, to ceiling fans having the blade
irons which support the fan blades mounted to a rotatable fan
housing.
2.0 Related Art
Ceiling fans include a plurality of fan blades which
are rotated by an electric motor to provide a supplementary
means of conditioning air within both commercial and
residential buildings. Ceiling fans typically include a
stationary fan housing, which may include an ornamental
exterior design and may assume a wide variety of shapes,
disposed in surrounding relationship with the electric motor.
Fan housings are sometimes referred to in the art as motor
housings. However, it is understood in the art that the
primary purpose of fan housings is to obscure the electric
motor from view to provide a more aesthetically pleasing
appearance to the ceiling fan and it is further understood that
the fan housing is not part of the electric motor but instead
is a separate component of the ceiling fan. The stationary fan
housing is supported by the stationary structure used to
suspend the ceiling fan. For instance, with ceiling fans
utilizing a downrod and ball arrangement in conjunction with a
ceiling mounted canopy to suspend the fan, the stationary fan
housing may be attached to an adaptor which is secured to the
lower end of the downrod.
1
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
The electric motors used in ceiling fans comprise either "standard
configuration"
or ''inside-out" electric motors. lVith "standard conliguration" motors the
rotor, which
comprises a rotating portion of the motor, is disposed radially inwardly of
the stator or
stationary portion of the motor which includes the electric windings of the
motor. The
opposite configuration exists in "inside-out" motors, i.e., the rotor is
disposed radially
outwardly of the stator. Regardless of the type of electric motor used, it may
be
appreciated that the fan blades must be connected to and rotatably driven by a
rotating
portion of the motor to provide the desired rotation of the blades. The
rotating portion of
an "inside-out" electric motor may include upper and lower end caps or end
bells in
addition to the rotor.
Various means may be used to mount the fan blades to the rotating portion of
an
"inside-out" electric motor of a ceiling fan, with one commonly employed
mounting
arrangement being disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,462,412. As best seen in rig.
2, each
fan blade 20 is fastened to a distal end 66 of a blade iron 62, with the
proximal end 64 of
each blade iron 62 being fastened to a lower surface 72 of motor 16 via screw
70.
Another commonly employed ceiling fan blade mounting arrangement is
disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,222,864. As shown in Figs. 2 and 3, the
radially inner end
of each fan blade 20 is mounted to a wedge shaped member 84 disposed on an
upper
surface 22 of motor 16 via screws 88. It is noted that the fan housings
disclosed in each
of the foregoing patents (denoted by reference no. I 8 in both patents)
comprise stationary
housings.
U.S. Patent No. x,94-4,487 discloses yet anotl~cr ceiling I;In bla~lc
attaclunent
Systelll. As shown in Pig. 1, the disclosed system includes a blade mounting
ring 21
which is disposed below and fixedly attached to a motor mounting face S of a
rotatable,
lower motor casing portion 13 of inside-out motor 1 via bolts 17. The blade
mounting
ring 21 includes a plurality of fan blade mounting brackets 31 which extend
outwardly
from a substantially cylindrical portion 29 of ring 21. Each of tire disclosed
fan blades 35
is affixed to the underside of one of the brackets 31 with screws or bolts.
U.S. Design Patent D.361,377 discloses Uvo embodiments of a ceiling fan and
light fixture which include a fan housing having stationary upper and lower
portions and
a rotatable center portion disposed therebetween, with each fare blade passing
through
5:\II\IIuW e~ Ivan ?001\Illv I'alrnl ?Ia00Li0 I'a1c111~:\rlllrallun lilr
21J()U-1)?i0 I-I?-:(N)4 I)I)13.d'x
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
sluts formed in tl~e center portion of the fan housin3 at a location near tl~e
inner end of tile
blade. Although not shown in the design patent, it is known in the art that
the rotatable
center portion oCthe fan housing is mounted to a rotatable lower portion of
the included
electric motor. As further known in the art, the radially inner end of each
fan blade is
S attached to a radially outer portion of a blade iron which is attached, at a
radially inner
end thereof, to the rotatable lower portion of the electric motor.
Known ceiling fans also include those having a rotatable fan housing with a
lower
portion of the fan housing secured to the lower, rotatable end cap of the
electric motor,
with these fans filrther including blade irons attached to a bottom,
downwardly facing
surface of the lower portion of the fan housing.
With regard to "standard configuration" electric motors, the fan blades may be
attached to blade irons which are in turn are attached to a rotating flywheel
which is
secured to a rotor shaft of the electric motor.
Although each of the foregoing fan blade mounting arrangements have enjoyed
widespread use, ceiling fan designers continue to search for alternative fan
blade
mounting arrangements which provide a different "look" to the ceiling fan and
which
may provide various advantages associated with the manufacture, shipment,
assembly
and operation of the ceiling fan.
SUn~IMARY
In view of the foregoing needs, the present invention is directed to a ceiling
fan
having a different look which is aesthetically pleasing, and several
functional advantages,
due to the incorporation of side mounted Made irons. More particularly, the
ceiling fan
of the present invention includes blade irons which are mounted to a radially
outwardly
facing surface of a rotatable fan housing, with each fan blade being attached
to one of the
blade irons. In a preferred embodiment, this surface is an outer surface of a
substantially
cylindrical sidewall of the housing. Since the blade irons are mounted
directly to a side
surface of the rotatable motor housing, the blade irons may lie smaller than
those often
used \VI111 COIlvelltlOllal ceiling fans which are mounted to a bottom portion
of the motor
and are "looped" to obtain tile desired vertical position of the blade iron.
Accordingly,
the blade irons incorporated by the ceiling fans of the present invention may
be cheaper,
IigIUer and have a longer service life due to reduced chance of fatigue, as
compared to
3
S:\I I\I punier Ivan 200(H)\l ll~ I'atrnt 21 J00\?i01'anntG~pplicatiun liar ?
I JOt)-tl?51) I _ 12_W(N) I11)13 ,luc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
blade irons typically used with conventional ceiling fans. Further, the
mounting position
of the blade irons will result in less imbalance and therefore reduced
"wobble" during
operation of the ceiling fan due to a reduction in manufacturing variations in
radial
location of the bolt holes used to attach the fan blades to the blade irons.
The expected
reduction in operational ceiling fan wobble is also clue to a variety of
additional factors
including the following. 1n the first instance, it is believed that the
geometry of the blade
irons, which extend radially outwardly from the base attached to the
substantially
' cylindrical sidewall of the rotatable housing, will permit less variation in
blade center of
gravity and blade pitch angle as compared to ceiling fans incorporating blade
irons
'having more complex geometries, such as the aforementioned "loop" due to
attachment
to the bottom portion of the motor. As known in the art, variations in blade
pitch angle
contribute to ceiling fan wobble. Furthermore, the simplified geometry of the
blade irons
results in substantially raclially directed forces, as compared to the complex
force vector
of conventional blade irons having more complex geometry, which enhances the
chance
for improved fan balancing and therefore reduces operational wobble. Yet
another
advantage associated with the ceiling fan of the present invention is
associated with the
shipment of the fan from the manufacturer's facility. The attachment of the
rotatable
motor housing to the rotor, via multiple circumferentially spaced fasteners,
provides a
more rigid structure than that associated with many conventional ceiling fans
employing
a stationary motor housing attached to a centrally disposed adaptor connected
to the
statot shaft of the motor. Accordingly, the package used to ship the ceiling
fan of the
present invention may be simplified relative to that employed with many
conventional
ceiling fans. The blade mounting arrangement included in the ceiling fan
according to
the present invention also provides a simple installation of the blade irons,
used to
support the fan blades, for the end consumer which is considered to be easier
than that
associated with typical fan blade mounting arrangements of conventional
ceiling fans.
For instance, with conventional ceiling fans, it is often necessary for the
consumer to
remove at least a top cover of the ceiling fan switch housing to gain access
to the motor
surface to which the blade irons are attached.
According to one prefewed embodiment the present invention is directed to a
ceiling fan comprising a means for suspending the ceiling fan from the ceiling
of a
S:\II\Ilunter Ivan 20000\Ilf Patent 21100\2>01'atcnt4lpPlicatiun pin 21x00-
0?SO I-12-2(NN) 13f)n.Joc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
structure and an ~lcctric motor having a rotating portion and a stator. TI>e
rotating
portion of the electric motor includes a rotor, an upper end cap and a lower
end cap, with
the upper and lower end caps being attached to the rotor. The stator includes
a stator
shaft connected to the means for suspending flue ceiling fan. The means for
suspending
the ceiling fan may include a hollow canopy which includes a seat and may be
mounted
to the ceiling of the stmcture via a bracket, a downrod, an adaptor secured to
a lower end
of the downrod, and a ball secured to an upper end of the downrod and disposed
within
the seat of the canopy. The adaptor may include a radially extending flange
portion anti
upper and lower substantially cylindrical portions, with the upper
substantially cylindrical
portion being secured to the downrod and the lower substantially cylindrical
portion of
the adaptor being secured to the stator shaft.
The electric motor may comprise an inside-out electric motor wherein the rotor
of
rotating portion of the motor is disposed radially outwardly of the stator.
However, in
other embodiments, the motor may comprise a standard configuration electric
motor, i.e.,
1 S one in which the rotor is disposed radially inwardly of the stator.
The ceiling fan further comprises a rotatable fan housing disposed in
surrounding
relationship with the electric motor, with the rotatable fan housing being
attached to the
rotating portion of the electric motor. In one preferred embodiment, the
rotatable Can
housing is attached to a bottom surface of the lower end cap of the rotating
portion of the
motor. The ceiling fan may include a plurality of resilient grommets, each
having an
upper portion disposed between the electric motor and the rotatable fan
housing, which
act as vibration isolators or ~iamh~ners. 'fhe rotatable Ian housing includes
a radially
outwardly facing surface which may Dave a substantially cylindrical shape.
The ceiling fan further includes a plurality of blade irons, and a like number
of fan
blades, with each of the blade irons being mounted to and protruding outwardly
from the
radially ouhvardly facing surface of the rotatable fan housing. Each of the
fan blades
includes a radially outer and a radially inner end, with the radially inner
end being
supported by one of the blade irons. each of tl~e blade irons include a
circumferentially
extending base, which is mounted to the radially outwardly facing surface of
the rotatable
fan housing, amp a raclially outwardly extending blade supporting portion.
(;ach blade
iron may also include a connecting portion interconnecting the base and blade
supporting
S'\II\Ilnnler Fan 20000\I IF Patent 21.J00\?>0 Patrnt\Aphlicatinn liar 21.lIN)-
0210 1-12-2000 nflfi.duc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
portion. Tl~e base, blade supl)ortin3 portion and connecting portion arc
preferably made
as an ilegral casting. The blade supporting portion may include a plurality of
internally
threaded bosses for the purpose of fastening the raciially inner ends of the
blades to the
blade supporting portions of the blade irons.
The ceiling fan may further include a stationary fan housing which is attached
to
the means for suspending the ceiling fan. In one embodiment, the stationary
Can housing
is attached to the radially extending flange portion of the adaptor included
in the means
for suspending the ceiling fan.
BRIEh' DESCRIPTION OF TILE DRA~'VINGS
These and other features, aspects, and advantages of the present invention
will
become better understood with regard to the following description, appended
claims and
accompanying drawings, wherein:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view illustrating a ceiling fan according to the
present
invention;
1 S Fig. 2 is an elevational view of the ceiling fan shown in Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is an enlarged, perspective view of the ceiling fan shown in Fig. 1,
with the
included Can blades being shown in fragmentary view;
Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view further illustrating the ceiling Fan shown in
Figs.
1-3.
Fig. 4A is an enlarged, fragmentary, cross-sectional view corresponding to a
portion of the cross-sectional view shown in Fig. 4;
Fig. 5 is an enlarged perspective view of one of the blade irons included in
the
ceiling fan according to the present invention;
Fig. 6 is a top plan view of the blade iron shown in Fig. 5;
2~ Fig. 7 is a bottom plan view of the blade iron shown in Figs. S and 6;
Fig. 8 is an end view of the blade iron shown in Figs. S-7; and
Fig. 9 is a cross-sectional view of the blade iron shown in Figs. 5-8.
C
S:\II\Ilnnter Ivan 200t)n\III~ Patent 2140050 PatentV\pplicati~m pin ZI~IIN)-
0?5() 1-12-211(lO 131)l3.iluc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
DI:'1':111.1?1) 1)I:SCRII''fION
Referring now to the drawings, wherein like reference numerals have been used
for similar elements throughout, rig. 1 is a perspective view illustrating a
ceiling fan 10
according to the present invention, and rigs. 2-4 are elevational, enlarged
perspective and
cross-sectional views, respectively, of ceiling fan 10. Ceiling fan 10
includes a means,
indicated generally at 12, for suspending the fan 10 from the ceiling (not
shown) of a
residential or commercial structure, an electric motor 14 which is connected
to and
supported by the means 12 for suspending the fan 10, and a plurality of fan
blades 16
which are rotatably driven by the electric motor 14 to provide a supplemental
means of
conditioning the air within the residential or commercial structure. In the
illustrative
embodiment, the means 12 for suspending the ceiling fan 10 includes a bracket
18 which
may be attached directly to the ceiling of the structure via fasteners in a
manner which is
known in the art and a hollow canopy 20 which is attached to the bracket 18
via fasteners
22. As shown in Fig. 4, the canopy 20 includes a seat 24 formed in a lower end
thereof.
The means 12 for suspending the ceiling fan 10 further includes a downrod 26,
a ball 28
and an adaptor 30 which are interconnected as subsequently described.
The electric motor 14 includes a rotating portion comprising a rotor 32, an
upper
end cap or end bell 34, and a lower end cap or end bell 3G. Each of the end
caps 34 and
3G are attached to the rotor 32, by a plurality of fasteners (not shown) as
known in the art.
The electric motor 14 further includes a stationary stator 38 which includes
electrical
stator windings 40 and a stator shaft 42. In the illustrative embodiment,
electric motor 14
comprises an inside-out electric motor since the rotor 32 is disposed radially
ouhvardly of
the stator 38. However, it should be understood that the ceiling fan 10 of the
present
invention may lie used in conjunction with standard conCguration electric
motors, i.e.,
those in which the stator is disposed radially outwardly of the rotor, as
subsequently
discussed in greater detail.
As shown in Fig. 4, the ball 28 is secured to an upper end of the downrod 2G
via a
pin 44 and is disposed within the seat 24 of canopy 20. The pin 44 engages a
shoulder 46
formed in the interior of ball 28 when fan 10 is in an installed position due
to the vertical
loads exerted on the downrod 2G when fan l0 is attached. An outer surface of
the ball 28
and an inner surface of the seat 2=1 of canopy 20 Dave mating slryes to permit
the ceiling
7
1:111\Ilunlcr Ivan 2(ll)OIHIII~ I'alrnl ~I~IIIII~SI)
I':I1VII1\t~171111OL111111 I'ur 21.JIH1-II?SQ I-12-21NH1 lil)IS.iluc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
fan 10 to pivot about tall 28 and seat 2:1 to aCCOllllllodate a Vaulted or
sloped ceiling. For
instance, as known in tile art, the ball 2S may have a hemispherical outer
surface and the
inner surface of canopy seat 24 may be shaped to match.
As shown in Fig. 4, the adaptor 30 includes a radially extending flange
portion 48
and upper SO and lower 52 substantially cylindrical portions, each having
internal
threads. The lower end of the downrod 2G is secured to the upper,
substantially
cylindrical portion 50 of the adaptor 30, by threading the lower end of the
downrod 26
into the substantially cylindrical portion 50, and may be further secured by
one or more
set screws 54 which pass through the substantially cylindrical portion 50 and
press
against the lower end of the downrod 2G. The upper end of the stator shaft 42
of the
electric motor 14 is secured to the lower, substantially cylindrical portion
52 of adaptor
30 by threading the upper end of the stator shaft 42 into the substantially
cylindrical
portion 52. The upper end of the stator shaft 42 may be further secured to
portion 52 by
one or more set screws (not shown) passing through portion 52 into contacting
1 S engagement wish the upper end of the stator shaft 42. In the foregoing
manner, the means
12 for suspending the ceiling fan 10 provides support to the electric motor 14
and the
remainder of the ceiling fan 10.
Ceiling fan 10 further includes a stationary fan housing SG having an upper
flange
portion 58 which is attached to the flange portion 4S of the adaptor 30 by a
plurality of
fasteners (not shown), thereby securing the stationary fan housing SG to the
adaptor 30.
The fan housing SG may comprise a variety of shapes and the outer surface of
the fan
housing SG may include an ornamental design. The stationary fan housing SG
further
includes a plurality of apertures GO formed therethrough for the purpose of
dissipating
heat created by motor 14 during the operation of the ceiling fan 10. In the
illustrative
embodiment, the apertures GO comprise circular holes which are arranged in a
plurality of
circumferentially spaced CO11111111S. 1-lowever, in other embodiments, the
apertures GO may
have a variety of otllcr shapes and be arranged in a different manner. The
shape and
awangement of apertures GO may add to the ornamental design of the stationary
fan
housing SG.
Ceiling fan 10 further includes a hollow, rotatable fan housing G2 which is
disposed in surrounding relationship with the electric motor 14 and is
connected to a
S:\II\Ilunter ran N)V00\Ilf f'atcnt 21a00~'~0 I'atcnt\Alplicutiun li>r 21-
JIIfI-0250 I-12-2(NlO 131)n.rluc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
rotating portion of tl3e motor 14, for rotation therewith. More particularly,
in the
illustrative en3bocliment, the rolatable fan housing G2 includes a lower
flange portion G4
which is attached to the lower end cap 3G of the electric motor 14 via a
plurality of
conventional fasteners, such as screws GG. In a preferred embodiment, a
grommet G7 is
used in conjunction with each screw GG. Grommets G7 are made of a resilient
material
such as rubber, and act as vibration isolators or dampeners. In the
illustrative
embodiment, the rotatable fan housing G2 is directly connected to the rotating
portion of
motor 14 due to the attachment, or fastening, of flange portion G4 to the
lower end cap
36. However, in other embodiments, when the electric motor of fan 10 comprises
a
standard configuration electric motor, i.e., one in which the stator is
disposed radially
outwardly of the rotor, the included rotatable fan housing may be attached to
a rotatable
flywheel which is connected to a rotating shaft of the motor, thereby
providing indirect
connection of the rotatable fan housing to the electric motor.
As best seen in the enlarged view shown in Fig. 4A, each grommet 67 includes
an
1 S upper portion 69 disposed between the lower end cap 3G and the rotatable
fan housing G2,
thereby dampening the vibrations transmitted from motor 14 to housing G2 and
blades 1G.
Each grommet 67 passes through a hole in fan housing G2, includes an annular
notch to
accept fan housing G2, and filrther includes a centrally disposed opening
passing
therethrough to receive one of the screws GG. 1n the illustrative embodiment,
fan 10
includes four of the screws GG and vibration isolation grommets G7, although
other
quantities may be used, which results in a reduction of parts relative to
conventional
ceiling fans which often incoporate vibration isolators in conjunction with
each fastener
used to attach the fan blades to the blade irons. For instance, if three
fasteners and
vibration isolators are used to mount each blade, and the fan includes three
blades, a total
of nine vibration isolators would be required compared to the four grommets 67
of fan
10.
The fan housing G2 further includes a substantially cylindrical sidewall G8
which
is radially spaced from the electric motor 14 and includes an inner surface 70
and an
outer surface 72, each having a substantially cylindrical shape, with surface
72
comprising a radially outwardly facing surface.
9
S:\II\Ilnnter Ian 2()000\III~ Patent 21.300\?50 Patent\Application fur ?I.Jt>n-
(1250 I-12-?000 13n13.doc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
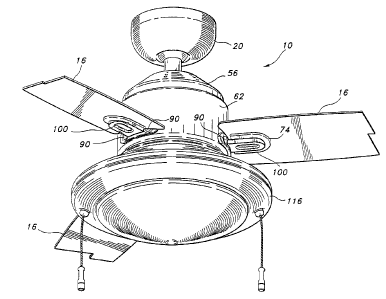
Ceilin 3 fan 10 further includes a plurality of blade irons 74, with each
being
mounted to and protruding outwardly from the radially outwardly facing surface
72 of the
rotatable fan housing 62. In the illustrative embodiment, ceiling fan 10
includes three
blade irons 74 and three fan blades 16. However, in other embodiments, ceiling
fan 10
may incoporate a different number of blade irons 74 and fan blades 16,
provided a like
number of blade irons 74 and fan blades 16 are provided. As best seen in Figs.
5-9,
which illustrate a single blade iron 74, each of the blade irons 74 includes a
circumferentially extending base 76, a radially outwardly extending blade
supporting
portion 78 and a connecting portion 80 which extends between and interconnects
the base
76 and blade supporting portion 78. In a preferred embodiment, base 76, blade
supporting portion 78 and connecting portion 80 are made as a one piece,
integral casting.
In other embodiments, the connecting portion 80 may be eliminated, such that
the blade
supporting portion abuts the base and protrudes radially outwardly therefrom.
The circumferentially extending base 76 has an elongated shape and is hollow
for
1 S weight savings purposes. Base 76 includes inner 82 and outer 84 surfaces
and a plurality
of bosses 86 extending inwardly from the inner surface 82. 1n the illustrative
embodiment, blade iron 74 includes two of the bosses 86, although three or
more may be
used within the scope of the present invention. Each boss 86 defines a
clearance hole 88
which is effective for receiving a fastener, such as one of the bolts 90 shown
in Fig. 3, for
the purpose of fastening the base 76 to the sidewall 68 of the rotatable fan
housing 62,
such that base 76 is mounted to the radially outwardly facing surface 72 of
sidewall 68.
'flte outer surface 84 of base 76 includes a lair of countersinks 92 which are
effective for
receiving the head of bolts 90 so that they may be substantially plush with
the outer
surface 84 when installed. Each of the bolts 90 may he secured by a
conventional
2~ fastener, such as a nut 9=l disposed on tl~e inner surface 70 of the
sidewall 68 of the
rotatable fan housing 62, as shown in Fig. 4.
The blade supporting portion 78 of blade iron 74 includes upper 96 and lower
98
surfaces, and has a distinctive spade-like shale as best seen in Figs. 5-7.
The lower
surface 98 includes a centrally disposed, oval-shaped depression 100 which
contributes to
the unique design and aesthetically pleasing appearance of glade irons 74. 1n
other
embodiments, the blade supporting portion 78 of blade iron 74 may have a wide
variety
S:\II\Ilunler Ivan 21H)00\Illv I'atcnt 21~J111)1?>0 I'atrnl41pllicalion liar
211011.11250 I-12-2111H) I)I)Il.duc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
of other sllapcs and configurations, as well as ornamental designs, consistent
with the
overall design of the particular ceiling fan.
As best seen in Fig. 5, the upper surface 9G of the blade supporting portion
78 has
a "dished-out", concave shape. The blade supporting portion 78 includes a
plurality of
bosses 102 which are integral with and extend upwardly from the upper surface
96 of the
blade supporting portion 78. Each of the bosses 102 include internal threads
104 which
are effective for receiving a fastener used to attach one of the blades 1 G to
the blade
supporting portion 78 of the corresponding blade iron 74. Each of the blades 1
G includes
a radially inner end l OG and a radially outer end 108 with the radially inner
end l OG being
supported by and attached to the blade supporting portion 78 of one of the
blade irons 74.
More particularly, the radially inner end I OG of each blade 16 is fastened to
the blade
supporting portion 78 of one of the blade irons 74 by a plurality of
conventional
fasteners, such as screws 110 (one shown in Fig. 4) which pass through
apertures formed
in the inner end l OG of each blade 1 G and are threaded into one of the
bosses 102 of the
blade supporting portion 78 of one of the blade irons 74, thereby securing
each fan blade
1 G to one of the blade irons 74 so that the fan blades 1 G and blade irons 74
rotate with the
rotatable fan housing 62.
Ceiling fan 10 further includes a switch housing 112 which is attached to a
lower
end of the stator shaft 42 and contains electrical wires 114 which are
connected at an
upper end to the source of electrical power in the structure in which fan 10
is suspended,
and are routed downward through the hollow canopy 20, the hollow downrod 26
and the
hollow stator shaft 42 to motor 14. fVires I 14 are then routed downward
through the
lower end of the stator shaft 42 to the interior of switch housing 112. Wires
114 may
then be connected to various switches, as subsequently discussed for
controlling the
operation of fan 10.
1n the illustrative embodiment, ceiling fan 10 includes a light fixture 11G
which is
disposed below the rotatable fan housing G2 and is secured to switch housing 1
12.
However, it should be understood that the use of the light fixture 11G is
optional and that
in other embodiments the ceiling fan according to the present invention may
not include a
light fixture. Additionally, a wide variety of liglU fixtures may lie used
which have
shapes and ornamental features different from those of fixture 1 1 G. Light
fixture 11 G
s:\I1111untcr Ivan 200(H)1111 I'atcnt 21-10()1?s0 I'alrnt4lpplic~tiun rm
21~J1H1-(1?51) I-12-Z(H)0 IlDl3.drx
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
includes a somcwllat bell-shaped shade 1 I S hamn3 an upper portion 119 and a
lower
portion 120 which are attached to one another by a plurality of conventional
fasteners
such as bolts 121 (one shown). The lower portion 120 of shade 118 is attached
to switch
housing 1 12 by a plurality of fasteners such as screws 113 (one shown). The
light fixture
S 116 also includes a base 122 which is attached to the lower portion 120 of
shade 118 by a
plurality of conventional fasteners such as screws 123 and the associated
threaded inserts.
Light fixture 116 further includes a light emitting globe 124 which is
removably secured
to and retained in position by the base 122. Globe 124 may be secured to base
122 in a
conventional manner, for instance with a helical thread formed on globe 124
and a
retention feature on base 122 which engages the helical thread. The particular
means for
securing globe 124 to base 122 do not form a part of the present invention.
The liglri
fixture I 16 further includes a light bulb 126, which comprises a halogen bulb
in the
illustrative embodiment, which is secured to a bracket 128 mounted to the base
122. As
shown in Fig. 4, the ceiling fan 10 includes switches 130 and 132, which are
electrically
1 S coupled to selected ones of the wires 114 in a manner not shown and are
used to control
power to the light bulb 126 and the rotational speed of motor 14 respectively.
The ceiling
fan 10 may further include an additional switch (not shown) to control the
rotational
direction of motor 14.
In operation, electrical power is provided from the structure in which ceiling
fan
10 is suspended to motor 14 via wires I 14, causing the rotating portion of
motor 14 to
rotate in the desired direction at the desired speed. The rotatable fan
housing 62, which is
attached to the lower end cap 36 rotates with the rotating portion of the
motor. Blade
irons 74 and lan blades 16 also rotate with the rotating portion of the motor
since the
blade irons 74 are attached to the rotatable fan housing 62, thereby providing
a
supplemental means of conditioning the air within the structure from which
ceiling fan 10
is suspended.
The configuration of the ceiling Can of the present invention provides several
advantages relative to conventional ceiling fans. More particularly, since the
included
blade irons 7-1 are fastened to the substantially cylindrical sidewall 68 of
the rotatable fan
housing, various advantages arc; achieved which are associated with the
manufacture,
shipment, assembly and operation of the ceiling fan 10. Since the blade irons
74 are
12
S:\ll\Iluntcr Ivn ?00(>n\Ilf I'annt ZIaIHI\~1U I':lIO111\A1111I11':1111111
Ibr?I.IUO-11?i0 I-12-2txN1 n1~13.Juc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
mounted directly to a side surlac~ of the rotatablc fan housing 62, the blade
irons 7=l may
lie smaller than those often used with conventional ceiling fans which are
mounted to a
bottom portion of the motor and arc "looped" in an upward arc to achieve the
desired
position of the blade iron. Accordingly, blade irons 74 may be cheaper,
lighter and have
a longer service life due to reduced chance of fatigue, as compared to blade
irons which
are often used with conventional ceiling fans. Additionally, it is believed
that the
simplified geometry and mounting location of blade irons 74 will result in
reduced
chance of ceiling fan wobble during operation of fan 10. As may be appreciated
by a
review of the various figures included herein, an end consumer has an
unobstructed
access to the sidewall 68 of the rotatable fan housing 62 which simplifies the
installation
of blade irons 74 as compared to those used on many existing fans where the
blade irons
are mounted to a bottom portion of the electric motor for instance. The
assembly
required by the end consumer is further simplified, and the overall quantity
of parts is
reduced, by the use of vibration isolation grommets 67 which are disposed
between motor
1 S 14 and rotatable fan housing 62 and are installed by the manufacturer, as
compared to the
use of vibration isolators in conventional ceiling fans in conjunction with
the fasteners
used to attach the blades to the blade irons, which are typically installed by
the end
consumer. Furthermore, the mounting arrangement permits the particular design
of the
illustrative ceiling fan 10, which could not lie achieved with blade irons
mounted to a
bottom portion of the motor 14. Additionally, the attachment of the rotatable
fan housing
62 to the electric motor 14 via a plurality of circumferentially spaced
fasteners 66
provides a more rigid structure as compared to conventional ceiling fans
employing only
a stationary fan housing secured to the means for suspending the ceiling fan.
This in turn
allows a simplification of the package used to ship the fan in a disassembled
condition.
For instance, with conventional fans it 1S COlllllloll to include rubber
stabilizers under the
relatively heavy motor to prevent damage during shipment, which is not
required with the
fan of the present invention.
While the foregoing description has set forth the preferred embodiments of the
present invention in particular detail, it must be understood that numerous
modifications,
substitutions and changes can be undertaken without departing from the true
spirit arid
scope of the present invention as defined by the ensuing claims. Tlre
invention is
13
S:\II\Ilnnter fan ?IH>OOpll I'atcnt 21~OO~j01'atrnt~Applicatiun put 21-llNl-
f)?50 1-12-2(X10 111113 ~luc
CA 02299810 2000-02-23
therefore not limited to specific preferred embodiments as described, but is
only limited
as defined by the following claims.
14
S:\II\Ilumer Fan 20000\IIF Patent 21~100~~0 PatentNPPlicatiun lim 2141)0-0250
I-12-2000 l3Dfl.doc