Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/OI696 PCT/KR99/00346
3-ALKYLPYRROLOI3,2-C]QUINOLINE DERIVATIVES
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
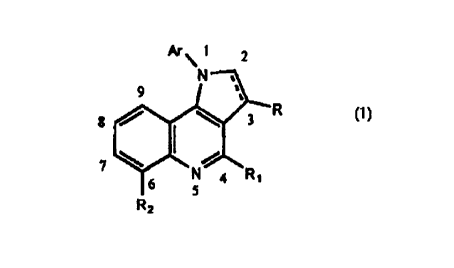
The present invention relates to
3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives represented
by the formula 1, their pharmaceutically acceptable
salts, process for preparation thereof, and
pharmaceutical composition thereof for treating gastric
ulcer.
More particularly, the present invention relates
to 3-alkylpyrrolof3,2-c]quinoline derivatives which
inhibit gastric acid secretion of mammal; their salts;
and process for preparation thereof. The pharmaceutical
composition comprising quinoline derivatives of the
present invention as an active ingredient is effective
for inhibiting gastric acid secretion and treating
gastric ulcer.
FORMUL:: 1
~~ 1 2
N'~:1
8
y y -a- w
N 4 Ra
5
R2 (I)
Wherein,
1
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
R is an alkyl group of C,_4, may be substituted
with hydroxy group, alkoxycarbonyl group of C1_4,
alkylcarbonyl group of C1_y, arylcarbonyl group,
aldehyde, alkoxy group of C1_4, amino group,
aminoalcohol, carboxy group, or halogen;
R; is hydrogen, alkyl of C1_~, phenyl group,
hydroxymethyl group, halogen, alkylthio group of C1_r,
alkoxy group of C1_6, or amino group of C1_substituted
or unsubstituted with hydroxy group;
R- is hydrogen, alkyl group of Cl_~, alkoxy group of
C1_r substituted or unsubstituted with hydro~y group or
fluorine, hydroxy group, hydroxymethyl group, or amino
group of C__; ; and
Ar is a phenyl or benzyl group substituted or
unsubstituted with hydrogen, alkyl group of C1_~
substituted or unsubstituted with halogen, haloalkoxy
group of C__~ substituted or unsubstituted with halogen,
alkylthio group of Cl_6, halogen, cyano group, amino
group, nitro group, hydroxy group, etc.
So far, benzimidazole derivatives containing
pyridine, as represented by the Omeprazole, have been
commonly used as inhibitors of gastric acid secretion.
Benzimidazole derivatives containing pyridine have
displayed a prominent remedial result, but have raised
a problem in long term administration because of their
2
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
irreversible reaction mechanism. That is, there have
been a sustained effect of medicine after stopping
administration or a side effect of stomach wall
thickening by administration, etc.
On the one hand, quinoline derivatives have been
known as an inhibitor for gastric acid secretion of
mammal, and there have been attempts to develop them as
a reversible inhibitor for gastric acid secretion. [EP
Appl. 87-307824.0; USP 5,362,743; PCT/KR 94-29274; EP
Appl. 89-301801.0; EP Appl. 89-301805.1; EP Appl.
89-301802.8; EP Appl. 88-306583.1; PCT/KR 97-00074; KR
Pat. Appl. 96-38314; KR Pat. Appl. 97-30692; KR Pat.
Appl. 97-30693; J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 3413; and J.
Med. Chem., 1995, 38, 2742].
For example, EP Appl. 88-306583.1 describes
pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives of the following
structure.
~o
3
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
Wherein,
A is -CH=CH-, - (CHz) ~- or - (CHZ) ~-;
R1 to R_ are hydrogen, alkyl group of C,_4, alkoxy
group of C__~, phenyl group, alkylthio group of C1_e,
alkanoyl group of C;_4, amino group, alkylamino group of
C1_6, dialkylamino group of Cl_~, halogen,
trifluoromethyl group or nitro group, respectively;
R~, to R~ are hydrogen, alkyl group of C1_~, alkoxy
group of C:_: , alkylthio group of C1_~, halogen, cyano
group, amino group, hydroxy group, carbamoyl group,
carbonyl group, alkanoyl group of C1_~, trifluoromethyl
group or nitro group, respectively; and
Rlo is hydrogen, alkyl group of C1_E, halogen,
hydroxy group, -CH~OH, alkylthio group of C1_~,
Z5 NH(CH.)r,OH (wherein n is 0 to 4) or -NR1;R1~.
The literature mentioned above described that
compounds of the above formula and their salts acted as
an inhibitor for gastric acid secretion by inhibiting
gastric H'/K--ATPase, and are useful for treating ulcers
in mammal, particularly in human.
Also, in J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 1845-1852, it
was described 1-arylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives
as a reversible inhibitor for gastric acid secretion,
particularly on the effect of substituent R,o.
And KR Pat. Appl. 97-38512 describes the use of
haloalkyl groups as R,.
4
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
Despite of a good deal of effect, however, there
has been no report about the introduction of
substituent into 3-position since it is difficult to
synthesize such compounds. -
We, the inventors of the present invention, have
investigated to develop a novel inhibitors for gastric
acid secretion, and synthesized novel
3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives and their
salts by introducing various substituents into
3-position, which display an excellent inhibition of
gastric acid secretion and stability. The synthesis
was based on the application of a new synthetic method
developed recently using palladium catalyst
(Tetrahedron Letter, 1998, 39, 627 and Heterocycles,
1996, 43, 1641) .
SU~~ARY OF TSE INVENTION
It is the object of the present invention to
provide 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives
represented by the formula 1 and their pharnlaceutically
acceptable salts.
It is another objective of the present invention
to provide process for preparing 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-
5
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
c]quinoline derivatives represented by the formula 1.
It is still another objective of the present
invention to provide pharmaceutical composition for
treating gastric ulcer, which comprises 3
alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives represented by
the formula 1 and their pharmaceutically acceptable
salts as an active ingredient.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-
c]quinoline derivatives of formula 1, and their
pharmaceutically acceptable salts:
FORMULA 1
N
8 / , \ 3 R
N 4
S
wherein,
R is an alkyl group of C1_s, may be substituted
with hydroxy group, alkoxycarbonyl group of C1_4,
alkylcarbonyl group of C,_~, arylcarbonyl group,
aldehyde, alkoxy group of C1-4, amino group,
6
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
aminoalcohol, carboxy group, or halogen;
R1 is hydrogen, alkyl of C 1_,; phenyl group,
hydroxymethyl group, halogen, alkylthio group of C1_6,
alkoxy group of Cl_b, or amino group of C,_; substituted
or unsubstituted with hydroxy group;
R~ is hydrogen, alkyl group of Cl_e, alkoxy group of
C-__~ substituted or unsubstituted with hydroxy group or
fluorine, hydroxy group, hydroxymethyl group, or amino
group of C;_~ ; and
Ar is a phenyl or benzyl group substituted or
unsubstituted with hydrogen, alkyl group of Cl_E
substituted or unsubstituted with halogen, haloalkoxy
group of C,_~ substituted or unsubstituted with halogen,
alkylthio group of C1_e, halogen, cyano group, amino
group, nitro group, hydroxy group, etc.
In addition, the present invention provides
process for preparation of 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-
c]quinoline derivatives. The compounds of the present
invention can be prepared by two methods, process I
represented by the following reaction scheme 1, and
process II represented by the following reaction scheme
2.
REACTION SCHEME 1
7
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 ' PCT/KR99/00346
o '
1
AriV~l,(~
AN Rt _
RZ
M.,~R~A
Cit~tl
-
N
REACTION SCHEME 2
C!
I
ArNH 2(1~
R,
R H ~s
(ill)
Ar a
IfA~ aSIC ~ iNlll) detilyrlativn
C~t-Pd
~1
M) fix)
(I)
8
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/Oi696 PCT/KR99/00346
The process for preparation according to the
present invention, by the foregoing reaction scheme 1,
comprises the steps of:
1) chlorinating a compound of formula (III) to
give the quinoline substituted with chlorine, of
formula (IV) (step 1);
2) reacting the quinoline substituted with
chlorine, of formula (IV), with the aryl amine of
formula (V) to give the quinoline of formula (VI) (step
2);
3) reacting the quinoline of formula (VI) with an
allyl halide (AX) in the presence of a base to give the
compound of formula (VII) (step 3); and
4) cyclizing the compound of formula (VII) with
palladium catalyst to give the compound of formula 1
(step 4) .
Also, the process for preparation according to the
present invention, by the foregoing reaction scheme 2,
comprises the steps of:
1) chlorinating a compound of formula (III) to
give the quinoline substituted with chlorine, of
formula (IV) (step 1);
2) reacting the quinoline substituted with
chlorine, of formula (IV), with the aryl amine of
formula (V) to give the quinoline of formula (VI) (step
9
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 a PCT/KR99/00346
2) ;
3) reacting the quinoline of formula (VI) with the
alkynes substituted with alkylsilane, of formula
(VIII), to give the compound of formula (IX) (step 3);
and
4) removing silyl group in the compound of formula
(IX) to give the compound of formula 1 (step 4).
The compound of formula (III) used as a starting
material in the process of the present invention, was
obtained from the compound of the following formula
(II) by the known method [Synthesis, 1977, 865] by
introducing iodine into 3-position of quinolone.
FORMULA 2
Wherein, R1 and R~ are defined as above .
The starting materials used in the present
invention were synthesized according to a known method
[Heterocyclic compounds, Quinolines, Vol. 32, PART 1].
The process of each step according to the present
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
invention will be described below in more detail.
At first, in the process I represented by the
reaction scheme 1:
1) In the said reaction scheme 1, the compound of '
formula (III) is chlorinated with phosphoryl chloride
(POClz), thionyl chloride (SOC1~), phosphorus
pentachloride (PC15), etc. to give the compound of
formula (IV). In this reaction 1-10 equivalent of
chlorinating reagent can be used, the reaction solvent
may be selected from the group consisting of
1,2-dichloroethane, methylene chloride, etc. or the
reaction can be performed without solvent.
2) The compound of formula (IV) and aryl amine (V)
are reacted in 1,4-dioxane or in the absence of
solvent, at 100-150 °C for 1-2 hours to~give the
compound of formula (VI). Here, the number of
equivalents of aryl amine is preferably 1-10.
3) The compound of formula (VI) is reacted with
various allyl halides in the presence of a base at room
temperature for 2-3 hours to give the compound of
formula (VII). Here, a solvent may be selected from the
group consisting of tetrahydrofuran, methylene
chloride, chloroform, diethyl ether, etc.
11
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
4) 3-Alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline of formula 1 is
obtained from the compound of formula (VII) by a
cyclization reaction using palladium catalyst, a new
heterocycle synthetic method [Heterocycles, 1996, 43,
1641]. In this reaction, 1-10 molo of palladium
catalyst, 1-5 equivalents of a base, and an organic or
inorganic chloride salt are used, and the reactants are
reacted in various solvents at 80-150 °C for 3-4 hours
to give cyclized quinoline derivatives. It is
preferable to use palladium acetate [(CH~C00)=Pd],
potassium acetate (CH;,COOK), tetrabutylammonium
chloride [(n-Bu)4NC1] in tetrahydrofuran (THF).
Also, in the process II represented by the
reaction scheme 2:
1) In the said reaction scheme 2, the compound of
formula (III) is chlorinated with phosphoryl chloride
(POC13), thionyl chloride (SOC1-~), phosphorus penta-
chloride (PC1=), etc. to give the compound of formula
(IV). In this reaction 1-10 equivalents of chlorinating
reagent can be used, the reaction solvent may be
selected from the group consisting of
1,2-dichloroethane, methylene chloride, etc. or the
reaction can be performed without solvent.
2) The compound of formula (IV) and aryl amine (V)
12
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
are reacted in 1,4-dioxane or in the absence of
solvent, at 100-150 °C for 1-2 hours to give the
compound of formula (VI). Here, the number of
equivalents of aryl amine is preferably 1-10.
3) The compound of formula (VI) and various
alkynes of formula (VIII) substituted with alkylsilane,
are reacted in various solvents by using a new
heterocycle synthetic method [Tetrahedron Letters,
1998, 39, 627] to give a compound of formula (IX). At
this time, 1-10 mol% of palladium catalyst, 1-5
equivalents of a base, and an organic or inorganic
chloride are used, and the reactants are reacted by
using various solvents at 80-150 °C for 4-8 hours to
give a cyclized compound of formula (IX). The compound
of fornlula (IX) is obtained easily by using preferably,
palladium acetate, potassium acetate, lithium chloride
(LiCl) in dimethy~.formamide (DMF).
4) Silyl group in the compound of formula (IX) is
removed in the presence of acid catalyst in various
solvents, to give the compound of formula 1.
3-Alkyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline,
the compound of formula 1 of which 2- and 3-positioned
carbon are saturated with hydrogen, is prepared by
13
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
selective hydrogenation reaction of
3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline prepared according to
the above processes I and II, with catalyst such as
platinum oxide (PtOz), sodium borohydride (NaBH~),
sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH~CN), etc. [Reaction in
Orgainc Chemistry, 1984, M. Hudlicky, Ellis Horwood
Ltd., pp 55-57].
On the one hand, R1 in the compound of formula 1
can be transformed into various functional groups by
the known method [Heterocyclic Compound, Quinolines,
Vol 32, Part I, II] . That is, in case of R1 being CHz,
nitrogen at 5-position is oxidized with hydrogen
peroxide to give 5-oxide, and the rearrangement in the
presence of acetic anhydride and the hydrolysis
transform the functional group into CHZOH [J. Am. Chem.
Soc. 1954, 76, 1286]. In addition, in case of R-_ being
hydrogen, chlorine is introduced into 4-position by
reacting 5-oxide with phosphoryl chloride, sulfonyl
halide, thionyl chloride, etc., and the compound in
which chlorine is introduced into 4-position is reacted
with various nucleophiles to give compounds wherein
substituted amino, alkylthio or alkoxy is introduced
into R- of the said formula 1 [Chem. Abstr., 1951, 45,
8525; Chem. Abstr., 1957, 51, 8742; Chem. Abstr., 1958,
52, 14605] .
14
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 ~ PCT/KR99/00346
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 3-
alkylpyrrolo(3,2-c]quinoline derivatives prepared
according to the above, can be prepared by using
suitable organic or inorganic acids according to the
general method. At this time, acids can be selected
from the group consisting of hydrochloric acid,
sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, citric acid, malefic
acid, formic acid, etc.
3-Alkylpyrrolo(3,2-c]quinoline derivatives of the
present invention and their pharmaceutically acceptable
salts inhibit reversibly gastric acid secretion,
therefore pharmaceutical composition comprising them as
an active ingredient is useful for inhibiting gastric
acid secretion and treating gastric or duodenal ulcer.
Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of
gastric ulcer, comprising 3-alkylpyrrolo(3,2
c]quinoline derivatives of the present invention and
their salts as an active ingredient, can be prepared
for oral or non-oral administration by mixing with
generally-used nontoxic and pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier and diluent in addition to the compound of the
formula 1.
Pharmaceutical composition of the present
invention can be prepared in type of oral administrable
forms such as pill, troche, water-soluble or
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
oil-soluble suspension, powder, granule, emulsion, hard
or soft capsule, syrup, or elixirs. For preparation of
pill or capsule, binding agent such as lactose,
sucrose, sorbitol, mannitol, starch, amylopectin,
cellulose or gelatin; diluent such as dicalcium
phosphate; dissolute such as corn starch or sweet
potato starch; and lubricant such as magnesium
stearate, calcium stearate, sodium stearyl fumarate or
polyethylene glycol, etc. can be included. In case of
preparation of capsule, liquid carrier like fatty oil
can be included in addition to the above mentioned
substances.
Also, pharmaceutical composition comprising the
compound of the formula 1 as an active ingredient, can
be prepared for injection, and such a preparation is
administered by the method of hypodermic injection,
intravenous injection, intramuscular injection or
intrathoracic injection. To prepare such a preparation,
the compound of the formula 1 and a stabilizer or
damping agent in the water is mixed to make in the form
of an aqueous solution or a suspension, and ampule or
vial for unit dosage is prepared by using them.
3-Alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives of the
present invention and their pharmaceutically acceptable
salts show a prominent inhibition on gastric acid
16
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
secretion, and can solve a problem in long term
administration because of their reversible action
mechanism in inhibiting gastric acid secretion, and
therefore those can be used effectively as a new
treatment for gastric ulcer.
Practically and presently preferred embodiments of
the present invention are illustrative as shown in the
following examples.
However, it will be appreciated that those skilled
in the art, on consideration of this disclosure, may
make modification and improvements within the spirit
and scope of the present invention.
In the following examples, the process I was
applied to examples 1-22, and the process II was
applied to example 23 to prepare the compound of
example 1. The compounds of examples 1-31 can be easily
prepared by the process II described in the example 23.
<Example 1> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolol3,2-clquinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-
8-methoxyquinoline
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoline (41.47 g, 0.13
mol) and 2-methylaniline (41 g, 0.4 mol) were refluxed
17
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
at 125 °C for 4 hours. The reaction mixture was
dissolved in methylene chloride (600 ml) and washed
with sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, the organic
layer was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the
residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (42 g,
83%).
'H NMR(CDC1~) s 2.45(s, 3H), 4.07(s, 3H), 6.08(brs,
1H), 6.51(m, 1H), 6.96-7.30(m, 6H), 9.07(s, 1H).
m/e; 390 (M+) .
m.p. ; 155-156 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c7quinoline
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
methoxyquinoline (2.8 g, 7.1 mmol) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 1 g), and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. Allyl iodide (CH~CHCHZI,
2.8 g, 16 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred
for 5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by adding
saline to the reaction mixture and separating the
organic layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride
[(n-Bu)qNCl, 2.37 g, 6 mmol], sodium formate (0.84 g,
12 mmol), potassium acetate (1.34 g, 12 mmol) and
18
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
palladium acetate (80 mg) and the mixture in
tet rahydrofuran ( 2 0 ml ) was ref luxed at 12 0 °C f or 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
separated. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (1.4 g,
770), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDClz) b 1.91(s, 3H), 2.52(s, 3H), 4.08(s,
3H), 6.66-7.49(m, 8H), 9.21(s, 1H).
m/e; 302 (M+) .
m.p.; 131-133 °C .
<Example 2> Preparation of 3-ethyl-6-methoxy-1-(2-
methylpheayl)-1H-pyrrolol3,2-clquinoliae
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
methoxyquinoline (1.17 g, 3.0 mmol) prepared by the
process of the step 1 of example 1 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.75 g) and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution crotyl
bromide (CH:CHCHCH~Br, 1.02 g, 7.5 mmol) was added, and
the mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the
intermediate obtained by adding saline to the reaction
19
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
mixture and separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.72 g, 3 mmol), sodium
fortnate (0.42 g, 6 mmol), potassium acetate (0.61 g, 5
mmol) and palladium acetate (40 mg) and the mixture in
tetrahydrofuran (15 ml) was refluxed at 120 °C for 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.4 g, 43%).
'H NMR(CDClz) b 1.43 (t, 3H) , 1.92 (s, 3H) , 3 .00 (q,
2H), 6.67-7.49(m, 8H), 9.24(s, 1H).
m/e ; 316 (M+) .
<Example 3> Preparation of 3-isopropyl-6-methoxy-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-clquinoline
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
methoxyquinoline (0.78 g, 2 mmol) prepared by the
process of the step 1 of example 1 dissolved in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium
hydride (NaH, 0.24 g), and the reaction mixture was
stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. To this
solution 4-bromo-2-methyl-1-butene (0.59 g, 4 mmol) was
added, and the mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the
intermediate obtained by adding saline to the reaction
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
mixture and separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.22 g, 1 mmol), sodium
formate (0.14 g, 2 mmol), potassium acetate (0.2 g, 2
mmol) and palladium acetate (20 mg), and the mixture in -
tetrahydrofuran (15 ml) was refluxed at 120 ''C for 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.18 g, 55%).
1H NMR(CDC13) b 1.45 (d, J=6.9Hz, 6H) , 1.89 (s, 3H) ,
3.43(m, 1H), 4.07(s, 3H), 6.67-7.47(m, 8H), 9.29(s,
1H) .
m/e; 330 (M+) .
<Example 4> Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-
6-methoxy-3-methyl-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-clquinoline
( Step 1) Preparation of 4- (4-fluoro-2-
methylpheaylamino)-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoline
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoline 13.83 g, 12
mmol) and 4-fluoro-2-methylaniline (2.3 g, 18 mmol)
were refluxed at 125 °C for 4 hours. The mixture was
dissolved in methylene chloride (70 ml) and washed with
sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, the organic layer
21
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (4.67 g, 95%).
-H NMR(CDC13) b 2.39(s, 3H), 4.05(s, 3H), 5.97(brs,
1H), 6.47-7.20(m, 6H), 9.02(s, 1H).
m/e; 408 (M+) .
m.p. ; 150-151 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-
methoxy-3-methyl-1H-pyrrolol3,2-c]quinoline
4-(4-Fluoro-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-
8-methoxyquinoline (0.5 g, 1.2 mmol) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.2 g), and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
allyl iodide (CH~CHCH1I, 0.55 g, 4 mmol) , and the
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the reaction mixture and
separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.22 g, 1 mmol), sodium
formate (0.14 g, 2 mmol), potassium acetate (0.2 g, 2
mmol) and palladium acetate (40 mg) and the mixture in
tetrahydrofuran (15 ml) was refluxed at 120 ''C for 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
22
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.18 g, 64%), and the compound
was crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDC13) ~ 1.88(s, 3H), 2.49(s, 3H), 4.06(s,
3H), 6.64-7.37(m, 7H), 9.18(s, 1H).
m/e; 320 (M+) .
m.p. ; 156-158 °C.
<Example 5> Preparatioa of 3-ethyl-1-(4-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-1H-pyrroloL3,2-clquinoline
To 4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
methoxyquinoline (0.55 g, 1.36 mmol), prepared by the
process of the step 1 of example 4 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.2 g), and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution an excess
of crotyl bromide (CH,CHCHCH,Br) was added dropwise, and
the mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the
intermediate (0.5 g, 80%) obtained by adding saline to
the reaction mixture and separating the organic layer
were added tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.25 g, 1.08
mmol), sodium formate (0.15 g, 2.16 mmol), potassium
acetate (0.25 g, 2.16 mmol) and palladium acetate (20
mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was
23
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
refluxed at 120 °C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture
was concentrated and extracted with ethyl acetate, and
the organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, '
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (0.2 g,
56%), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDC1:) b 1.42 (t, 3H) , 1.89 (s, 3H) , 2.97 (q,
2H), 4.08(s, 3H), 6.63-7.41(m, 7H), 9.22(s, 1H).
m/e; 334 (M+) .
m.p. ; 174-175 "C.
<Example 6> Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-2-
methylpheayl)-6-methoxy-3-methyl-1H-pyrrolo(3,2-
c~quinoliae
(Step 1) Preparation of 4-(4-beazyloxy-2-
methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoliae -
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoline (5.1 g, 16
mmol) and 4-benzyloxy-2-methylaniline (6.8 g, 32 mmol)
were refluxed at 125 °C for 4 hours. The reaction
mixture was dissolved in methylene chloride (100 ml)
and washed with sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution,
the organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
24
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (6.5 g,
820) .
'H NMR(CDC1,) ~ 2.38(s, 3H), 4.08(s, 3H), 5.06(s, -
2H), 6.10(brs, 1H), 6.61-7.48(m, 11H), 9.02(s, 1H)
m/e; 496 (M*) .
m.p.; 162-163 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 3-methyl-6-methoxy-1-(4-
benzyloxy-2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo(3,2-clquinoline
To 4-(4-benzyloxy-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
methoxyquinoline (1 g, 2 mmol) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20m1) was added 60o-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.5 g), and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
allyl iodide (0.7 g, 4 mmol), and the mixture was
stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by
adding saline to the reaction mixture and separating
the organic layer were added tetrabutylammonium '
chloride (0.47 g, 2 mmol), sodium formate (0.27 g, 4
mmol), potassium acetate (0.4 g, 4 mmol) and palladium
acetate (23 mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (20
ml ) was ref luxed at 120 "C for 2 hours . The reaction
mixture was concentrated and extracted with ethyl
acetate, and the organic layer was separated, dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was purified by
silica gel column chromatography to give the desired
compound (0.56 g, 680), and the compound was
crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
'H NMR(CDC1,) b 1.86 (s, 3H) , 2.50 (s, 3H) , 4.08 (s,
3H), 5.16(s, 2H), 6.72-7.52(m, 12H), 9.18(s, 1H).
m/e; 408 (M+) .
m.p. ; 163-164 °C.
(Step 3) Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-6-
methoxy-3-methyl-lIi-pyrrolo I3, 2-c~ quinoliae
3-Methyl-6-methoxy-1-(4-benzyloxy-2-methylphenyl)-
1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline (0.45 g, 1.1 mmol) in
methanol (20 ml) was stirred in the presence of
5o-palladium catalyst and hydrogen (H,, 40 psi) at room
temperature for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was
filtered and concentrated to give the desired compound
(50 mg, 15%).
1H NMR(CDC1,) b 1.08(s, 3H), 2.49(s, 3H), 4.02(s,
3H), 6.76-7.18(m, 7H), 9.16(s, 1H).
m/e; 318 (M+) .
m.p. ; 270 °C.
<Example 7> Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-2-
methylphenyl)-3-ethyl-6-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
26
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
c]quinoliae
(Step 1) Preparation of 1-(4-beazyloxy-2-methylphenyl)-
3-ethyl-&-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[3~2-clquinoline
To 4-(4-benzyloxy-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
methoxyquinoline (1 g, 2 mmol) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.5 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution crotyl bromide
(CH~CHCHCH~,Br, 0.63 g, 4 mmol) was added, and the
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the reaction mixture and
separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.47 g, 2 mmol), sodium
formate (0.27 g, 4 mmol), potassium acetate (0.4 g, 4
mmol) and palladium acetate (23 mg), and the mixture in
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was refluxed at 120 ''C for 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.25 g, 30%), and the compound
was crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
-H NMR(CDC13) b 1.42 (t, 3H) , 1.87 (s, 3H) , 2 .97 (q,
2H), 4.08(s, 3H), 5.17(s, 2H), 6.75-7.50(m, 12H),
9.18(s, 1H).
27
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
m/e; 422 (M' ) .
m.p.; 55-57 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-3-
ethyl-6-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
1-(4-Benzyloxy-2-methylphenyl)-3-ethyl-6-methoxy-
1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline (0.25 g, 0.59 mmol) prepared
in the step 1 of example 7 in methanol (10 ml) was
stirred in the presence of 5o-palladium catalyst and
hydrogen (H_, 40 psi) at room temperature for 2 hours.
The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated to
give the desired compound (0.12 g, &2%).
1H NMR(DMSO-d6) b 1.45 (t, 3H) , 1.82 (s, 3H) , 2.98 (s,
2H), 4.07(s, 3H), 6.80-7.25(m, 7H), 9.15(s, 1H).
m/e; 332 (M+) .
m.p. ; 247-250 °C.
<Example 8> Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-2-
methylphenyl)-3-isopropyl-6-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c] quinoline
1-(4-Benzyloxy-2-methylphenyl)-3-isopropyl-6-
methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline (448 mg, 1.03 mmol)
prepared by the process of the step 1 of example 7 in
methanol (10 ml) was stirred in the presence of
5o-palladium catalyst and hydrogen (H~, 40 psi) at room
28
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
temperature for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was
filtered and concentrated to give the desired compound
(240 mg, 690) .
'H NMR(DMSO-d6) b 1.45(d, 6H), 1.78(s, 3H), 3.41(m, -
1H), 4.08(s, 3H), 6.76-7.23(m, 7H), 9.23(s, 1H).
m/e; 346 (M+) .
m.p.; 264-266 °C.
<Example 9> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(1-
phenylethyl)-1H-pyrroloL3,2-c]quinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of 3-iodo-8-methoxy-4-(1-
phenylethylamino)quinoline
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxyquinoline (2 g, 6.2 mmol)
and 1-phenyl-1-ethylamine (2 g, 16 mmol) were refluxed
at 125 'C for 4 hours. The reaction mixture was
dissolved in methylene chloride (50 ml) and washed with
sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, the organic layer
was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (1.6 g, 63%).
'H NMR(CDC1~) b 1.64 (d, 3H) , 4.04 (s, 3H) , 4 .70 (brd,
1H), 5.10(m, 1H), 6.97-7.53(m, 8H), 8.87(s, 1H).
m/e; 404 (M') .
m.p.; 166-167 °C.
29
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
(Step 2) Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(1-
phenylethyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c)quinoline
To 3-iodo-8-methoxy-4-(1-phenylethylamino)
quinoline (0.6 g, 4.4 mmol) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.2 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added an
excess of allyl iodide, and the mixture was stirred for
5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by adding saline
to the reaction mixture and separating the organic
layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.39 g,
1.7 mmol), sodium foxmate (0.23 g, 3.4 mmol), potassium
acetate (0.34 g, 3.4 mmol) and palladium acetate (20
mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was
ref luxed at 120 °C for 2 hours . The reaction mixture
was concentrated and extracted with ethyl acetate, and
the organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (0.4 g,
70%), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
'H NMR(CDClz) ~ 1.96(s, 3H), 2.45(s, 3H), 4.05(s,
3H), 6.29(q, 1H), 6.92-7.71(m, 9H), 9.13(s, 1H).
m/e; 316 (M+) .
m.p.; 142-144 °C.
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
<Example 10> Preparation of 3-ethyl-6-methoxy-1-(1-
phenylethyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
The reaction with 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-
ethoxyquinoline in place of 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-
methoxyquinoline as a starting material, was performed
by the same method in the example 9 to give the desired
compound.
-H NMR (CDClz) b 1.42 (t, 3H) , 2 . 04 (d, 3H) , 2 . 96 (q,
2H), 4.07(s, 3H), 6.34(q, 1H), 6.97-7.76(m, 9H),
9.22(s, 1H).
m/e; 330 (M+) .
m.p. ; 89-90 °C.
<Example il> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3,4-dimethyl-1-
(2-methylphenyl)-1X-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of 3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methyl-4-(2-
methylphenylamino)quiaoline
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methylquinoline (33 g, -
0.1 mol) and 2-methylaniline (30 g, 0.27 mol) were
refluxed at 125 °C for 4 hours. The reaction mixture
was dissolved in methylene chloride (400 ml) and washed
with sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, the organic
layer was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the
residue was purified by silica gel column
31
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00101696 PCT/KR99/00346
chromatography to give the desired compound (30 g,
75%) .
'H NMR(CDC1,) ~ 2.45 (s, 3H) , 3.04 (s, 3H) , 4.06 (s,
3H), 6.13(brs, 1H), 6.41(m, 1H), 6.93-7.28(m, 6H).
m/e; 404 (M+) .
(Step 2) Preparation of 6-methoxy-3,4-dimethyl-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
To 3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methyl-4-(2-
methylphenylamino)quinoline (2.8 g, 7.1 mmol) in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added 60%-sodium
hydride (NaH, 1 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added an
excess of allyl iodide, and the mixture was stirred for
5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by adding saline
to the reaction mixture and separating the organic
layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride (2.37 g,
6 mmol), sodium formate (0.84 g, 12 mmol), potassium
acetate (1.34 g, 12 mmol) and palladium acetate (80
mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) were
refluxed at 120 °C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture
was concentrated and extracted with ethyl acetate, and
the organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (1.4 g,
32
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
77%), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDC1,) ~ 1.92 (s, 3H) , 2.61 (s, 3H) , 3.10 (s,
3H), 4.05(s, 3H), 6.60-7.50(m, 8H).
m/e; 316 (M+) .
<Example 12> Preparation of 3-ethyl-6-methoxy-4-methyl-
1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo(3,2-c~quinoline
The reaction with crotyl bromide in place of allyl
halide, was performed by the same process of the
example 11 to give the desired compound.
'H NMR(CDCl~) b 1.40 (t, J=7.3Hz, 3H) , 1. 91 (s, 3H) ,
3.09(q, J=7.3Hz, 2H), 3.10(s, 3H), 4.05(s, 3H), 6.60-
7.52(m, 8H).
m/e; 330 (M') .
<Example 13> Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrolo(3,2-
c]quinoline
( S tep 1) Preparation of 4- (4-fluoro-2-
methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methylquinoline
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methylquinoline (7 g,
20.9 mmol) and 4-fluoro-2-methylaniline (5 g, 40 mmol)
were refluxed at 125 °C for 4 hours. The mixture was
dissolved in methylene chloride (100 ml) and washed
33
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
with sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, the organic
layer was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the
residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (6 g, 680).
iH NMR(CDC1,) b 2.42 (S, 3H) , 3.04 (S, 3H) , 4.05 (S,
3H), 6.04(brs, 1H), 6.37-7.17(m, 6H).
m/e; 422 (M') .
m.p. ; 180-181 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-
methoxy-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
To 4-(4-fluoro-2-methyiphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
methoxy-2-methylquinoline (0.89 g, 1.2 mmol) in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added 60o-sodium
hydride (NaH, 0.3 g), and the mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
an excess of allyl iodide, and the mixture was stirred
for 5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by adding
saline to the reaction mixture and separating the
organic layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride
(0.48 g, 2.1 mmol), sodium formate (0.28 g, 4.2 mmol),
potassium acetate (0.41 g, 4.2 mmol) and palladium
acetate (23 mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (20
ml) was refluxed at 120 °C for 2 hours. The reaction
mixture was concentrated and extracted with ethyl
34
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
acetate, and the organic layer was separated, dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and
concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was purified by
silica gel column chromatography to give the desired
compound (0.33 g, 47s), and the compound was
crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
'H NMR(CDClz) ~ 1.86 (s, 3H) , 2.57 (s, 3H) , 3 .06 (s,
3H), 4.01(s, 3H), 6.55-7.33(m, 7H).
m/e; 334 (M') .
m.p.; 199-200 °C.
<Example 14> Preparation of 3-ethyl-4-methyl-6-methoxy-
1-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
To 4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
methoxy-2-methylquinoline (0.89 g, 1.2 mmol) prepared
by the process of the step 1 of example 13 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.5 g), and the reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
crotyl bromide (CH~CHCHCH~Br, 0.67 g, 5.0 mmol) , and the
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the reaction mixture and
separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.48 g, 2.1 mmol), sodium
fozmate (0.28 g, 4.2 mmol), potassium acetate (0.41 g,
4.2 mmol) and palladium acetate (23 mg), and the
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
mixture in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was refluxed at 120
°C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated
and extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer
was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.37 g, 51%), and the compound
was crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
iH NMR(CDClz) b 1.39(t, 3H), 1.89(s, 3H), 3.09(q,
2H) , 3 .10 (s, 3H) , 4.04 (s, 3H) , 6. 61-7 .39 (m, 7H) .
m/e ; 348 (M+)
m.p. ; 162.5-136.5 °C.
<Example 15> Preparation of 6-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c~quinoline
To 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline (0.86 g, 2.84 mmol) prepared by
the process of step 1 and 2 of example 11 with 3-iodo- _
8-methoxy-4-(2-methylphenylamino)quinoline in place of
3-iodo-8-methoxy-2-methyl-4-(2-methylphenylamino)
quinoline in methylene chloride (20 ml) was added
dropwise slowly boron tribromide (BBr;, 1 g, 3.9 mmol),
and the reaction mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 2 hours. The mixture was washed with
dilute aqueous soda solution, the organic layer was
36
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (0.57 g, 70%).
'H NMR(CDC1,) ~ 1.89 (S, 3H) , 2 .49 (S, 3H) , 6 .49 (dd,
i
1H), 6.89-7.50(m, 7H), 9.00(s, 1H).
m/e ; 228 (M') .
m.p.; 137-139 °C.
<Example 16> Preparation of 6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-
methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrroloL3~2-c]quinoline
6-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-
pyrrolo [ 3 , 2 - c] quinaline ( 0 . 2 9 g, 1 mmol ) prepared by
the process of step 1 and 2 of example 11 with 3-iodo-
8-hydroxy-4-(2-methylphenyl)quinoline in place of 3-
iodo-8-methoxy-2-methyl-4-(2-methylphenylamino)
quinoline, ethylene carbonate (1,3-dioxolan-2-one, 3 g)
and potassium carbonate (KzC03, 0.3 g) were refluxed at
130 °C for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was dissolved
in methylene chloride (20 ml), washed with distilled
water, the organic layer was separated, dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated
in vacuo, and the residue was purified by silica gel
column chromatography to give the desired compound (0.3
g, 90%) .
37
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
'H NMR(CDClz) ~ 1.93 (S, 3H) , 2.54 (S, 3H) , 4.04 (t,
J=4.3Hz,2H), 4.32(t, J=4.3Hz, 2H), 6.72-7.52(m, 8H),
9 . 16 (s, 1H) .
m/e; 332 (M+) .
<Example 17> Preparation of 6-trifluoromethoxy-3-
methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c7quinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of ethyl 4-oxo-8-trifluoromethoxy-
1,4-dihydro-3-quinoliaecarboxylate
The mixture of 2-trifluoromethoxyaniline (17.7 g,
0.1 mol) and diethyl ethoxy methylene malonate(17.7 g,
0.1 mol) was refluxed at 90 °C for 30 minutes. The
intermediate obtained by concentrating the mixture in
vacuo to remove the ethanol produced during reaction,
was dissolved in diphenyl ether (200 ml), and the
mixture was refluxed at 260 °C for 2 hours. The mixture
was allowed to cool to room temperature, petroleum
ether (200 ml) was added, and the mixture was stirred
for 30 minutes. The solid produced was filtered to give
the desired compound (23.1 g, 77%).
'H NMR (DMSO-dd) b 1.30 (t, 3H) , 4.25 (q, 2H) , 7 .50 (t,
1H), 7.82(d, 1H), 8.18(d, 1H), 8.42(d, 1H), 12.38(d,
1H) .
m/e; 301 (M+)
m.p.; 228-230 °C.
38
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 - PCT/KR99/00346
(Step 2) Preparation of 8-trifluoromethoxy-1,4-dihydro-
4-quinolinone
140 ml of 10%-soda aqueous solution was added to
ethyl 4-oxo-8-trifluoromethoxy-1,4-dihydro-3-
quinolinecarboxylate (30.1 g, 0.1 mol), and the
reaction mixture was refluxed for 3 hours. The mixture
was allowed to cool to room temperature, neutralized
(pH= 2) with dilute hydrochloric acid to give a white
solid, and the solid was separated and dried. biphenyl
ether (250 ml) was added to the solid, and the solution
was refluxed at 260 °C for 3 hours. The mixture was
allowed to cool to room temperature, poured into
petroleum ether (250 ml) and stirred for 30 minutes.
The solid produced was filtered to give the desired
compound (22 g, 96%).
'H NMR(DMSO-d~) b 6.15(d, 1H), 7.40-8.10(m, 4H),
11. 85 (brs, 1H) .
m/e; 229 (M+) .
m.p.; 145-146 °C.
(Step 3) Preparation of 3-iodo-8-trifluoromethoxy-1,4-
dihydro-4-quinolinone
8-Trifluoromethoxy-1,4-dihydro-4-quinolinone (22.9
g, 0.1 mol) was dissolved in 10%-soda solution (200
ml>, iodine (36.5 g) was dissolved in 20%-potassium
39
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
iodide aqueous solution, and the latter solution was
added dropwise slowly to the former. The mixture was
stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The solid
produced by adding the excess of acetic acid and -
distilled water (300 ml) to the mixture, was filtered
to give the desired compound (27.6 g, 79%)
1H NMR(DMSO-db) ~ 7.50 (t, 1H) , 7.83 (d, 1H) , 8.18 (d,
1H), 8.43(d, 1H), 12.40(br, 1H).
m/e; 355 (M')
m.p.; 278-279 °C.
(Step 4) Preparation of 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline
The mixture of 3-iodo-8-trifluoromethoxy-1,4-
dihydro-4-quinolinone (33 g) and phosphorus oxychloride
( 80 ml ) was ref luxed at 110 °C far 1 hour, the mixture
was poured slowly into ice water, neutralized with
dilute soda solution to give a solid, and the solid
produced was filtered to give the desired compound -
(33.5 g, 95%).
'H NMR(CDCI;) ~ 7.60-7.75(m, 2H), 8.25(dd, 1H),
9.21(s, 1H).
m/e; 373 (M+)
m.p. ; 95-96 °C.
(Step 5) Preparation of 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
8-trifluoromethoxyquinoline
The mixture of 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (10 g, 26.8 mmol) and 2-
methylaniline (10 g) was refluxed at 125 °C for 4
hours. The mixture was dissolved in methylene chloride
(100 ml), washed with sodium bicarbonate aqueous
solution, the organic layer was separated, dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated
in vacuo, and the residue was purified by silica gel
column chromatography to give the desired compound (9
g, 760) .
iH NMR(CDC1,) b 2 .42 (s, 3H) , 6 .18 (s, 1H) , 6.59 (m,
1H), 7.00-7.56(m, 6H), 9.12(s, 1H).
m/e; 444 (M') .
m.p.; 104-106 °C.
(Step 6) Preparation of 6-trifluoromethoxy-3-methyl-1-
(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrroloL3~2-c)quinoline
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (1.14 g, 2.5 mmol) in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium
hydride (NaH, 0 .3 g) , and the mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
ally iodide (2.8 g, 16 mmol), and the mixture was
stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by
adding saline to the mixture and separating the organic
41
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.45 g,
2 mmol), sodium formate (0.28 g, 4 mmol), potassium
acetate (0.45 g, 4 mmol) and palladium acetate (30 mg),
and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was refluxed
at 120 °C for 2 hours. The mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound ( 0 . 25 g, 28 0 ) , and the compound
was crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
iH NMR(CDC13) b 1.92 (s, 3H) ,. 2.52 (s, 3H) , 6.95
7.50(m, 8H), 9.28(s, 1H).
m/e; 356(M+), 341(15.6), 271(11.8), 257(11.8),
255(19.8), 69(79.2).
m.p. ; 103-105 °C.
<Example 18> Preparation of 3-ethyl-6-trifluoromethoxy-
1- (2-methylphenyl) -1.H-pyrrolo L3, 2-c7 quinoline
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (1.14 g, 2.5 mmol) prepared
by the process of step 1-5 of example 17 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.3 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
crotyl bromide (CH~CHCHCHZBr, 2.8 g, 16 mmol), and the
42
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the mixture and separating
the organic layer were added tetrabutylammonium
chloride (0.45 g, 2 mmol), sodium formate (0.28 g, 4 -
mmol), potassium acetate (0.45 g, 4 mmol) and palladium
acetate (30 mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10
ml) was refluxed at 120 °C for 2 hours. The mixture was
concentrated and extracted with ethyl acetate, and the
organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (0.33 g,
35%) .
~H NMR(CDC13) b 1.42 (t, 3H) , 1.95 (s, 3H) , 2 . 98 (q,
2H), 6.95-7.55(m, 8H), 9.31(s, 1H).
m/e ; 370 (M+) , 355 (100) , 69 (60) .
<Example 19> Preparation of 3-isopropyl-6-
trifluoromethoxy-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolol3,2-
c~ quiaoliae
To 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (1.14 g, 2.5 mmol) prepared
by the process of step 1-5 of example 17 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.3 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added 4-
43
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
bromo-2-methyl-1-butene (2.8 g, 16 mmol), and the
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the reaction mixture and
separating the organic layer were added
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.45 g, 2 mmol), sodium
formate (0.28 g, 4 mmol), potassium acetate (0.45 g, 4
mmol) and palladium acetate (30 mg), and the mixture in
tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was refluxed at 120 "C fox 2
hours. The mixture was concentrated and extracted with
ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was separated,
dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and
concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was purified by
silica gel column chromatography to give the desired
compound (0.23 g, 24%), and the compound was
crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
'H NMR(CDC1~) b 1.45(d, 6H), 1.92(s, 3H), 3.41(m,
1H), 6.94(s, 1H), 7.00-7.55(m, 7H), 9.37(s, 1H).
m/e; 384 (M+) , 370 (24.2) , 369 (100) , 69 (31.5) .
m.p.; 111-112 °C.
<Example 20> Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-6-trifluoromethoxy-3-methyl-iH-
pyrrolo t3, 2-c] quinoliae
(Step 1) Preparation of 4-(4-fluoro-2-
methylphenylamiao)-3-iodo-8-trifluoromethoxyquinoline
44
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
4-Chloro-3-iodo-8-trifluoromethoxyquinoline (4.25
g, 11.3 mmol) and 4-fluoro-2-methylaniline (4.25 g)
were refluxed at 125 °C for 36 hours. The mixture was
dissolved in methylene chloride (100 ml) and washed -
with sodium bicarbonate, the organic layer was
separated , dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound (4.5 g, 86%).
'H NMR (CDClz) b 2 .40 (s, 3H) , 6 .10 (brs, 1H) , 6.55-
7.55(m, 6H), 9.10(s, 1H).
m/e; 462 (M+) .
m.p.; 116-117 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-
trifluoromethoxy-3-methyl-1H-pyrrolol3~2-clquinoline
To 4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (1.14 g, 2.5 mmol) in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium
hydride (NaH, 0.3 g) , and the mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
allyl iodide (2.8 g, 16 mmol), and the mixture was
stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate obtained by
adding saline to the mixture and separating the organic
layer were added tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.45 g,
2 mmol), sodium formate (0.28 g, 4 mmol), potassium
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
acetate (D.45 g, 4 mmol) and palladium acetate (30 mg),
and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was refluxed
at 120 °C for 2 hours. The mixture was concentrated and
extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was -
separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was
purified by silica gel column chromatography to give
the desired compound ( 0 . 25 g, 27 % ) , and the compound
was crystallized with a small amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDClz) ~ 1.90(s, 3H), 2.54(s, 3H), 6.92(s,
1H), 7.00-7.47(m, 6H), 9.26(s, 1H).
m/e; 374 (M+, 100) , 359 (7.4) , 69 (72.4) .
m.p. ; 129-131 °C.
<Example 21> Preparation of 3-ethyl-1-(4-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-6-trifluoromethoxy-iH-pyrroloL3,2-
c1 quiaoline
To 4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenylamino)-3-iodo-8-
trifluoromethoxyquinoline (1.14 g, 2.5 mmol} prepared
by the process of step 1 of example 20 in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) .was added 60%-sodium hydride
(NaH, 0.3 g), and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. To this solution was added
crotyl bromide (CH~CHCHCH~Br, 2.8 g, 16 mmol), and the
mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the intermediate
obtained by adding saline to the mixture and separating
46
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
the organic layer were added tetrabutylammonium
chloride ( 0 . 45 g, 2 mmol ) , sodium formate ( 0 . 2 8 g, 4
mmol), potassium acetate (0.45 g, 4 mmol) and palladium
acetate (30 mg), and the mixture in tetrahydrofuran (10
ml) was refluxed at 120 °C for 2 hours. The mixture was
concentrated and extracted with ethyl acetate, and the
organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
and the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (0.24 g,
25%), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
1H NMR(CDClz) 5 1.42(t, 3H), 1.91(s, 3H), 2.97(q,
2H), 7.02-7.47(m, 6H), 9.30(s, 1H).
m/e; 389 (M++1, 54.7) , 388 (M') , 373 (100) , 358 (5 .7) ,
303(14.5), 287(10), 273(11.4), 69(34.2).
m.p. ; 155-156 °C.
<Example 22> Preparation of 6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)3- -
methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrroloL3,2-c]quinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of ethyl 4-oxo-8-(2,2,2-
trifluoroethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-3-quinoliaecarboxylate
The mixture of 2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)aniline
(19.1 g, 0.1 mol) and diethyl ethoxy methylene malonate
(I7.7 g, 0.1 mol) was refluxed at 90 °C for 30 minutes.
47
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
The intermediate obtained by concentrating the mixture
.in vacuo to remove the ethnaol produced during
reaction, was dissolved in diphenyl ether (200 ml), and
the mixture was refluxed at 260 °C for 2 hours . The
mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature,
petroleum ether (200 ml) was added, and the mixture was
stirred for 30 minutes. The solid produced was filtered
to give the desired compound (25.2 g, 80%).
'H NMR(DMSO-d~) b 1.30(t, 3H), 4.24(q, 2H), 5.05(q,
2H), 7.35-7.85(m, 3H), 8.42(br, 1H), 11.80(brd, 1H).
m/e; 315 (M+) .
m.p. ; 236-238 °C.
(Step 2) Preparation of 8-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-1,4-
dihydro-4-quinolinone
10%-soda aqueous solution (140 ml) was added to
ethyl 4-oxo-8-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-3-
quinolinecarboxylate (31.5 g, 0.1 mol) and the reaction
mixture was refluxed for 3 hours. The mixture was
allowed to cool to room temperature, neutralized to pH
2 with dilute hydrochloric acid to give a white solid,
and the solid was separated and dried. biphenyl ether
(250 ml) was added to the solid, and the solution was
refluxed at 260 °C for 3 hours. The mixture was allowed
to cool to room temperature, poured into petroleum
ether (250 ml) and stirred for 30 minutes. The solid
48
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
produced was filtered to give the desired compound (23
g, 95 0 ) .
'H NMR (DMSO-db) ~ 4 . 98 (q, 2H) , 6 . 07 (d, 1H) , 7 .21-
7.85(m, 4H), 11.25 (brs, 1H).
m/e; 243 (M') .
m.p.; 173-175 °C.
(Step 3> Preparation of 3-iodo-8-(2,2,2-
trifluoroethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-4-quinolinone
8-(2,2,2-Trifluoroethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-4-
quinolinone (24.3 g, 0.1 mol) was dissolved in 10s-soda
solution (200 ml), iodine (36.5 g) was dissolved in
20%-potassium iodide aqueous solution, and the latter
solution was added dropwise slowly to the former. The
reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3
hours. The solid produced by adding the excess of
acetic acid and distilled water (300 ml) to the
mixture, was filtered to give the desired compound
(30.6 g, 83a) -
'H NMR(DMSO-dr) ~ 5.00 (q, 2H) , 7 .29-8 .30 (m, 4H) ,
11. 65 (br, 1H) .
m/e; 369 (M+) .
m.p. ; 187-189 ''C.
(Step 4) Preparation of 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-(2,2,2-
trifluoroethoxy)quiaoline
49
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
The mixture of 3-iodo-8-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-
1,4-dihydro-4-quinolinone (9.2 g, 24.9 mmol) and
phosphorus oxychloride (20 ml) was refluxed at 110 "C.
After the reaction for 1 hour, the mixture was poured
slowly into ice water and neutralized with dilute soda
solution, and the organic layer was extracted with
ethyl acetate and separated. The organic layer was
dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and
concentrate in vacuo, and the residue was purified by
silica gel column chromatography to give the desired
compound (8.0 g, 83%).
'H NMR(CDC13) b 4.47 (q, 2H) , 7.30 (d, 1H) , 7 .56 (t,
1H), 7.99(q, 1H), 9.13(s, 1H).
m/e; 387 (M+) .
m.p.; 135-136 °C.
(Step 5) Preparation of 3-iodo-4-I2-methylphenylamino)-
8-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)quinoline
The mixture of 4-chloro-3-iodo-8-(2,2,2-
trifluoroethoxy)quinoline (6.9 g, 17.8 mmol) and 2-
methylaniline (8.0 g) was refluxed at 125 °C for 4
hours. The mixture was dissolved in methylene chloride
(100 ml) and washed with sodium bicarbonate aqueous
solution, and the organic layer was separated. The
organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (7.0 g,
85%) .
'H NMR(CDC1~) b 2.42 (s, 3H) , 4.72 (q, 2H) , -
6.10(brs, iH), 6.50-7.30(m, 7H), 9.07(s, 1H).
m/e; 458 (M+) .
m.p. ; 115-117 °C.
(Step 6) Preparation of 6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-3-
methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrroloL3,2-c]quinoline
T o 3-iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-(2,2,2-
trifluoroethoxy)quinoline (1.15 g, 2.5 mmol) in
anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) was added 60%-sodium
hydride (NaH, 0.3 g), and the reaction mixture was
stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. To this
solution was added ally iodide (2.8 g, 16 mmol), and
the mixture was stirred for 5 hours. To the
intermediate obtained by adding saline to the mixture
and separating the organic layer were added -
tetrabutylammonium chloride (0.45 g, 2 mmol), sodium
fozmate (0.28 g, 4 mmol), potassium acetate (0.45 g, 4
mmol) and palladium acetate (30 mg), and the mixture in
tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was refluxed at 120 ''C for 2
hours. The mixture was concentrated and extracted with
ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was separated. The
organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium
51
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, and the
residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (0.5 g,
54 0 )
lH NMR(CDClz) b 1.90 (s, 3H) , 2.52 (s, 3H) , 4.78 (q,
2H), 6.80-7.50(m, 8H), 9.22(s, 1H).
m/e; 370 (M') .
The following examples 23-31 relates to the
preparation of 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c)quinoline
derivatives according to the process II.
<Example 23> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c~quinoline
(Step 1) Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-
methyl)-2-trimethylsilyl-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
3-Iodo-4-(2-methylphenylamino)-8-methoxyquinoline
(2 g, 5.3 mmol), trimethylsilyl-1-propyne (1.8 g, 16
mmol), lithium chloride (0.22 g, 5.3 mmol), potassium
acetate (1 g, 10.6 mmol) and palladium acetate (59 mg,
5 mmol%) in dimethylfortnamide (50 ml), were refluxed at
100 °C for 4 hours. The mixture was concentrated in
vacuo and the organic layer was extracted with diethyl
ether. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo,
52
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
the residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (1.51 g,
720), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether. -
'H NMR(CDCl~) b 0.10 (s, 9H) , 1.85 (s, 3H) , 2 .64 (s,
3H), 4.08(s, 3H), 6.45-7.49(m, 7H), 9.20(s, 1H).
m/e; 376 (M+) .
(Step 2) Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-methyd-1-(2-
methylphenyl)-1X-pyrroloL3,2-cJquinoline
6-Methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methyl)-2-trimethylsilyl-
1H-pyrrolo [3 , 2- c] quinoline ( 1. 51 g, 4 mmol ) in
trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, 8 ml) was refluxed for 3
hours. The mixture was concentrated and the organic
layer was separated by extraction with ethyl acetate.
The organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo, the
residue was purified by silica gel column
chromatography to give the desired compound (1.1 g,
92°s), and the compound was crystallized with a small
amount of diethyl ether.
The compounds of examples 24-31 were prepared by
the same process of example 23, with 3-trimethylsilyl-
2-propyn-1-of in place of trimethylsilyl-1-propyne.
53
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
<Example 24> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-hydroxymethyl-
1- (2-methylphenyl) -1H-pyrrolo L3.2-c] quinoline
Yield=82o.
1H NMR(CDCl~) ~ 1.91 (s, 3H) , 2.10 (brs, 1H) , 4.08 (s,
3H), 5.10 (s, 2H), 6.66-7.49(m, 8H), 9.21(s, 1H).
m/e; 318 (M+) .
m.p. ; 96-98 °C.
<Example 25> Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3-hydroxymethyl-1H-pyrroloL3,2
c]quinoline
Yield=80~.
1H NMFt (CDC13) b 1. 88 (s, 3H) , 2 .25 (brs, 1H) , 4 . 06 (s,
3H), 5.10(s, 2H), 6.64-7.37(m, 7H), 9.18(s, 1H).
m/e; 336 (M+) .
m.p. ; 168-170 °C.
<Example 26> Preparation of 1-(4-methoxy-2- -
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3-hydroxymethyl-1H-pyrrolo(3~2-
c]quinoliae
Yield=78o.
'H NMR(CDCla) b 1.80 (s, 3H) , 2.25 (s, 1H) , 4.02 (s,
3H), 5.10(s,2H), 6.76-7.18(m, 7H), 9.16(s, 1H).
m/e; 334 (M') .
m.p.; 198-200 °C.
54
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
<Example 27> Preparation of 6-methoxy-3-(2-
hydroxyethyl)-1-(2-methylphenyl)-iH-pyrrolo(3,2-
c1 quinoline
Yield=75%.
'H NMR(CDC13) b 1.91(5, 3H), 2.10(brs, 1H), 3.20(t,
2H), 4.00(t, 2H), 4.08 (s, 3H), 6.66-7.49(m, 8H),
9.21(5, 1H).
m/e; 332 (M+) .
m.p.; 86-88 °C.
<Example 28> Preparation of 1-(4-fluoro-2-
methylpheayl)-6-methoxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-
pyrrolo(3,2-c~quiaoliae
Yield=79%.
-H NMR (CDC13) b 1. 88 (s, 3H) , 2 .25 (brs, 1H) ,
3.20(t,2H), 4.00(t,2H), 4.06(s, 3H), 6.64-7.37(m, 7H),
9.18(5, 1H).
m/e; 350 (M+) .
m.p.; 150-152 °C.
<Example 29> Preparation of 1-(4-methoxy-2-
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-
pyrrolo(3,2-c]quinoliae
Yield=73%.
-H NMR(CDC1,) b 1.80 (S, 3H) , 2 .25 (S, 1H) , 3.20 (t,
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PGT/KR99/00346
2H), 4.00(t, 2H), 4.02(5, 3H), 6.76-7.18(m, 7H),
9.16(5, 1H).
m/e; 348 (M+) .
m.p.; 170-172 "C.
<Example 30> Preparation of 1-(4-methoxy-2-
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3-methyl-1H-pyrroloL3,2-
c1 quinoline
Yield=74%.
'H NMR(CDC13) b 1.88 (s, 3H) , 2.51 (s, 3H) , 3 .92 (s,
3H), 4.09(5, 3H), 6.73-7.31(m, 7H), 9.19(5, 1H).
m/e; 332 (M+) .
m.p.; 192.5-193.5 °C.
<Example 31> Preparation of 1-(4-methoxy-2-
methylphenyl)-6-methoxy-3-ethyl-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c1 quinoline
Yield=78°s.
1H NMR(CDC1~) ~ 1.39 (t, 3H) , 1.84 (s, 3H, J = 7.5
Hz), 2.95(q, 2H, J - 7.5 Hz), 3.88(5, 3H), 4.05(s,
3H), 6.70-7.30(m, 7H), 9.19(5, 1H).
m/e; 346 (M+) .
m.p. ; 138-140 °C.
3-Alkyipyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives of the
56
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
present invention as well as the compounds of examples
1-31, can be prepared easily by the processes I and II.
The preparation examples of pharmaceutical
composition comprising 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
derivatives of the present invention and their
pharmaceutically acceptable salts as an active
ingredient, are described below.
The following preparation examples are just
representative examples of the present invention, and
never limit the scope of the present invention.
<Preparation 8xample 1> Preparation of syrup comprising
3-alkylpyrrolot3,2-c]quinoline derivatives as an active
ingredient
Syrup comprising 2 % (wt/vol.) of 3-
alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives of the present
invention and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, _
was prepared by the following process.
Acid salt of 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline
derivatives, sugar and saccharin were dissolved in 80
g of warm distilled water, the solution was allowed to
cool, and then the solution consisting of glycerin,
saccharin, sweetener, sorbic acid and distilled water
was added to the above solution. Distilled water was
57
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
added to the solution until the volume of the solution
was 100 ml. The acid part of
3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives can be
substituted with another acid.
The followings are the components of the syrup.
6-Methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c] quinoline HC1 salt . . . . . 2 g
Saccharin . . . . . . . . 0.8 g
Sugar . . . . . . . . 25.4 g
Glycerin . . . . . . . . 8.0 g
Sweetener . . . . . . . . 0.04 g
Ethanol . . . . . . . . 4.0 g
Sorbic acid . . . . . . . 0.4 g
Distilled water . . . . . . q.s.
<Preparation Example 2> Preparation of pill comprising
3-alkylpyrroloL3,2-clquinoline derivatives as an active
ingredient
Pill comprising 15 mg of 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-
c]quinoline derivatives and their pharmaceutically
acceptable salts, was prepared by the following
process.
250 g of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline~HCl salt was mixed with 175.9
58
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
g of lactose, 180 g of corn starch and 32 g of
colloidal silicic acid. 10% Gelatin solution was added
to the mixture, and the mixture was pulverized,
filtered with No. 14 mesh sieve and dried. Hereto was
added 160 g of potato
starch, 50 g of talc
and 5 g of
magnesium stearate to obtain the mixture, and the
mixture was prepared in type of pill. The followings
are the components of
the pill prepared by
the above
process.
6-Methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]quinolineHCl salt . . . . . 250 g
Lactose . . . . . . . . 175.9 g
Corn starch . . . . . . . 180 g
Colloidal silicic acid . . . . . 32 g
Potato starch . . . . . . . 160 g
Talc . . . . . . . . 50 g
Magnesium stearate . . . . . . 5 g
10 o Gelatin solution
<Preparation Example 3> Preparation of ampule
comprising 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-clquinoline
derivatives
as an active ingredient
Ampule comprising 10 mg of 3-alkylpyrrolo (3, 2-
c]quinoline derivatives and their pharmaceutically
59
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
acceptable salts, was prepared by the following
process.
1 g of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H
pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline~HC1 salt, 0.6 g of sodium
chloride and 0.1 g of ascorbic acid were dissolved in
distilled water, to prepare 100 ml of solution. This
solution was put into the bottle, and pasteurized by
heating at 20 ''C for 30 minutes. The followings are the
components of the ampule prepared by the above process.
6-Methoxy-3-methyl-1-(2-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]quinoline~HC1 salt . . . . . 1 g
Sodium chloride . . . . . . 0.6 g
Ascorbic acid . . . . . . . 0.1 g
Distilled water . . . . . . q.s.
Dose of 3-alkylpyrrolo[3,2-c]quinoline derivatives
represented by the formula 1 according to the present _
invention, can be varied in accordance with the age,
weight, gender, type of administration, health of
patient and severity of disease, however, dose per day
is preferably 15-25 mg on the basis of adult male.
To confirm the prominent effect on inhibiting
gastric acid secretion of 3-alkyipyrrolo[3,2-
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
c]quinoline derivatives represented by the formula 1
according to the present invention, in vivo assay of
pharmacological activity was performed.
<Experimeat 1> In vivo assay of pharmacological
activity
In vitro enzyme assay of H+/Ki-ATPase collected
from a pig stomach was carried out, wherein the
negative control was the activity of H+/K'-ATPase
stimulated by Mg'; and the positive control was the
activity of H-/K+-ATPase stimulated by Mg'+ and K+.
Sprague Dawley male rats (150-200 g, 6 weak-old)
were fasted for 24 hours, and the compound of the
present invention suspended in 0.5o CMC, was orally
administered in 30, 100, 300 mg/kg dose. After 1 hour,
1 ml of 97% ethanol was orally administered, and the
mouse was sacrificed an hour later with ether. Stomach
was resected, 13 ml of 1% formalin was inj ected into
stomach, and the stomach was put into 1o formalin
solution and fixed for 1 hour. The stomach was incised
along greater curvature and opened, and the length of
gastric ulcer was measured and compared with that of
the control to which only solvent was administered, to
calculate o protection and to determine the 50%
protection dose.
61
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
The result was shown in the following table 1.
TABLE 1
Inhibition rate of In vitro
Example No.
gastric ulcer enzymatic
of compound
relative to Omeprazole reaction
1 +++ +++
2 ++ +
3 + ++
4 +++ ++
5 +++ +++
7 + +++
8 + +++
+ +++
* Relative
15 in vivo
pharmaceutical
efficacy
to
comparative
compound;
+++(strong),
++(similar),
+(weak)
* Omeprazole;
compound
of EP No.
9105959.0
As a result, it was confirmed that 3
alkylpyrrolo[3,2-cJquinoline derivatives according to
the present invention and their pharmaceutically
acceptable salts inhibit more prominently the gastric
acid secretion than Omeprazole.
<Experimeat 2> Toxicity test
3000 mg/kg of the compound of example 5, which had
been suspended in 5% CMC, was administered to 5 white
62
*rB
CA 02301510 2000-02-23
WO 00/01696 PCT/KR99/00346
mice, the acute toxicity did not appear and any
abnormality was not found for 2 weeks. 300 mg/kg/day of
the compound of example 1 was administered to 5 Sprague
Dawley male rats (150-200 g) for 3 weeks. The rats grew '
without any abnormality, and there was no abnormality
in the rats sectioned after stopping administration.
63