Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
' i~l
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
Inerting method for preventing and extinguishing
fires in enclosed spaces
The present invention relates to an inerting method for
reducing the risk of and for extinguishing fires in enclosed
spaces, and to a device for carrying out this method.
In view of enclosed spaces, into which human beings or animals
enter only occasionally, and the installations in which react
sensibly to water impacts, it is known to anticipate the risk
of fires by reducing the oxygen concentration in the area in
question to an average value of about 12 0. Given this oxygen
concentration, most combustible materials can no longer burn.
The areas concerned are mainly data processing areas, electric
switch and distribution rooms, enclosed installations and
storing areas containing high-grade economic goods. The
extinguishing effect resulting from this method is based on
the principle of oxygen expulsion. It is known that the normal
ambient air consists of 21 % oxygen, 78 o nitrogen and 1 s of
other gases. For extinction the nitrogen concentration in the
space concerned is further increased by introducing pure
nitrogen so as to reduce the oxygen portion. It is known that
an extinguishing effect commences once the oxygen content
falls under 15 o by volume. In dependence on the combustible
materials in the space concerned it may be required to further
reduce the oxygen content to the mentioned 12 o by volume.
With said "inert gas extinguishing technique", as the flooding
of a fire hazardous or burning space with oxygen-expulsion
gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen, rare gases and
mixtures thereof is called, the oxygen-expulsion gases are
usually stored in a compressed manner in steel cylinders in
specific side rooms. In the case of need, the gas is then
conducted into the space in question by means of piping
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
2
systems and corresponding exit nozzles. Extinction by means of
the inert gas technique, however, encounters certain problems
and shows clear limits in view of the size of the space. Large
spaces having, for instance, a basic area of 20 x 50 m and a
6.5 m height result in a capacity of 6,500 mj. In accordance
with the standards, the steel cylinders used are those having
a volumetric capacity of 80 1. Inert gas extinction facilities
are filled with a pressure of 200 bar, which is presently the
upper standard parameter due to the ultimate loading capacity
of the available armatures. With a cylinder pressure of 200
bar, 80 l, for example, hold 18.3 kg nitrogen resulting in 16
m3 nitrogen in the relaxed state at 1 bar ambient pressure. In
order to flood the aforementioned space having a capacity of
6.500 m3 with inert gas, the contents of about 300 steel
cylinders would be required. In a filled state such a cylinder
has a weight of about 100 kg, which, given 300 cylinders,
would result in a weight of 30 tons. In addition there would
be the weight of the pipes and armatures, so that very high
demands would have to be made on the load ability of the store
rooms. Moreover, a large floor space would be required for
such a number of cylinders. Thus, it is evident that the inert
gas extinction technique in connection with larger spaces
encounters problems in view of the storability and the
carrying capacity of the store rooms. To store the cylinders
in a cellar is not a satisfying solution either, although the
carrying capacity there is not of importance. Long conduits
would have to be laid from the cellar to the upper floors
involving an additional construction labor, which frequently
cannot be coped with later, and moreover prolonging the flow-
in time of the inert gas in an inappropriate manner.
It is an object of the present invention to provide an
inerting method for reducing the risk of fires and for
extinguishing fires in enclosed spaces, allowing an effective
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
3
extinction of a fire whilst keeping the storing capacity for
the inert gas cylinders at a minimum.
Said object is provided by means of an inerting method of the
above-mentioned kind comprising the following process steps:
At first, the oxygen content in the enclosed space is reduced
to a set base inerting level of, for example, 16 ~, and in the
event of a fire the oxygen content is further reduced to a set
complete inerting level of, for example, 12 o by volume or
less. A base inerting level of an oxygen concentration of 16 $
by volume does not entail any risk for persons or animals, so
that they can still enter the space without any problems. The
complete inerting level can either be adjusted at night, when
no persons or animals enter the space in question, or directly
in response to a detected fire. With an oxygen concentration
of 12 ~ by volume the flammability of most materials has
already been sufficiently reduced so that they can no longer
start to burn.
The advantages of the inventive method particularly consist in
that the number of containers for oxygen-expulsion inert gases
required in the event of a fire is clearly reduced. Thus, the
total costs for fire prevention and the fire extinction system
are considerably reduced. Furthermore, under the
constructional aspect, a smaller pressure relief facility is
required, as in the event of a fire only a smaller gas volume
has to flow in during the short time being available, for
which a constructional relief has to be provided.
Moreover, the aforementioned object is provided by means of a
device for carrying out said method, comprising the following
components: an oxygen measuring device in the space being
monitored; a first system for producing the oxygen-expulsion
gas or for extracting oxygen from the space being monitored; a
second system for rapidly feeding an oxygen-expulsion gas into
CA 02301628 2005-02-24
4
CWCAS-123
the space being monitored; and a fire detection device for
detecting a fire characteristic in the air of the enclosed
space. For providing a solution to the set object a control
unit is provided, which sends a base inerting signal to the
first system for producing the oxygen-expulsion gas or for
extracting the oxygen in accordance with the oxygen content of
the air in the enclosed space being monitored, and which sends
a complete inerting signal to the second system in accordance
with a detection signal from the fire detection device.
Said inventive device realizes in an ideal manner the
connection of the inventive method with a fire detection
device. The control unit according to the invention for
sending the base inerting signal and the complete inerting
signal thereby takes into account the particular conditions of
the space being monitored, the base inerting level of which
was previously calculated on the basis of size and type of the
space.
The inerting method advantageously comprises the following
additional two process steps, which are carried out before the
first process step, namely the reduction of the oxygen content
to a set base inerting level: In accordance with said
embodiment, the oxygen content in the space being monitored is
first measured, whereupon the reduction to the base inerting
level is carried out in a second process step in response to
the measured value of the oxygen. Thus, the inerting method
adjusts to certain leakages in the space by means of a
classical regulation of the oxygen content in the space being
monitored.
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
A detector for fire characteristics is advantageously
integrated into the method, which sends a complete inerting
signal in the event of a fire.
Representative air samples are, for instance, constantly
extracted from the air in the space being monitored prior to
the reduction to a set complete inerting level, which samples
are fed to a detector for fire characteristics, which sends a
complete inerting signal in the event of a fire. Said
embodiment is the process-technical conversion of the
connection of a known aspirative fire detection device with
the inert gas extinction technique. An aspirative fire
detection device hereby refers to a fire detection device
actively drawing in a representative portion of the air in the
space at a plurality of locations via a piping or channel
system and feeding said portion to a measuring chamber
comprising a detector for detecting a fire characteristic.
The term "fire characteristic" refers to physical parameters
being subject to measurable changes in the environment of an
originating fire, for example, the ambient temperature, the
solid or liquid or gas contents in the ambient air (formation
of smoke in the form of particles or aerosols or vapor) or the
ambient radiation.
The method can be carried out in a particularly advantageous
manner, if the base inerting level is implemented by means of
mechanical production and subsequent introduction of oxygen-
expulsion gases, or by means of mechanical oxygen extraction.
This is feasible in so far as more time is available for the
reduction to the base inerting level, so that a gradual
reduction of the oxygen content in the corresponding space by
means of a machine is sufficient. In contrast thereto, an
introduction of oxygen-expulsion gases into the enclosed space
is preferably provided for rapidly obtaining the complete
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
G
inerting level, wherein basically all inert gases may be used.
Said inert gases may advantageously be provided in gas
cylinders, since even with larger spaces the volume to be
filled between the base inerting level and the complete
inerting level no longer causes problems. Moreover, a
mechanical production of oxygen-expulsion gases, for instance
by means of a nitrogen machine, is a great advantage, since
also gas cylinders being responsible for the complete inerting
can thus be refilled upon the use thereof.
It has finally been provided as an advantage that the
introduction of the oxygen-expulsion gases is carried out in
accordance with the oxygen content measured in the enclosed
space, whereby it is achieved that only the amount of gas
being required for the complete inerting is fed at all times.
It has already been mentioned that it is one of the advantages
of the inventive method that it can be combined with the known
fire detection devices. In so-called aspirative fire detection
devices it is necessary to constantly control the flow rate of
the drawn in representative air portions. According to an
embodiment of the inventive device it is provided that the
oxygen measuring device for carrying out the method is
integrated in the detector housing of the fire detection
device; where also the air flow monitoring device is disposed.
The production of the oxygen-expulsion gases for obtaining the
base inerting level is advantageously implemented mechanically
by means of a nitrogen machine or the like. It had already
been mentioned that also the gas cylinders responsible for the
complete inerting can thereby be refilled in an advantageous
manner, once they have been emptied.
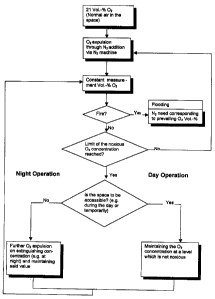
In the following the inventive method is explained in more
detail by means of a flow chart.
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
7
An enclosed space containing normal air with the common oxygen
content of 2I % by volume is to be monitored. In order to
reduce the risk of a fire, the oxygen content in the enclosed
space is reduced to a set base inerting level by means of
introducing nitrogen from a nitrogen machine. The oxygen
content in the space being monitored is constantly measured
before and simultaneously with the reduction to the base
inerting level. The target value was previously calculated on
the basis of the properties of the space and the equipment
thereof with data processing apparatus and the like. An
aspirative fire detection device being provided with a
detector for fire characteristics constantly draws in
representative portions of the air in the space via a piping
or channel system and feeds said portions to the detector for
the fire characteristics. If a fire characteristic is detected
and, with the usual safety loops, recognized as a fire, the
space is rapidly flooded with nitrogen from steel cylinders
until a desired oxygen concentration is obtained. Said
concentration was previously determined on the basis of the
combustible materials in the space.
As long as there is no fire, it is constantly checked by means
of the oxygen measuring device, whether a lower threshold
value of a noxious oxygen concentration is reached. If this is
still not the case, the nitrogen machine still receives the
base inerting signal and continues to flood the space with
nitrogen. If the noxious threshold value is reached, the
target value is inquired as to whether the conditions for a
night operation or the conditions for a day operation are to
be established. If the space is no longer to be entered by
persons or animals, the complete inerting signal is send to
the nitrogen machine, whereupon another oxygen expulsion takes
place in accordance with the measured oxygen content, until
the extinguishing concentration predetermined for the space
and the materials contained therein is reached. If the space,
CA 02301628 2000-02-24
8
however, is still to be entered, the oxygen concentration is
maintained at a non-noxious value of about 16 ~ by means of
the oxygen measuring device.