Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
1
A drying device
The invention relates to a drying device, particulary for drying wood and
semi-products of wood like veneer or sawn wood as well as other products.
A groving tree as a woody perennial plant contains relatively huge amounts of
moisture content warying from one kind to another which stays in the tree
after being cut down. As it is known wood contains capillaries in cells that
contain free liquid and absorbed moleculas of water called moisture content
which must be lowered to a certain level to satisfy needs of industrial use.
For
that reason, wood has to be properly treated, namely dried to a certain value
of
acceptable end moisture distribution content in a way to prevent occuring of
all kinds of drying defects. The drying process is a mayor factor in economic
terms.
Wood could be dried under natural circumstances in the open - air drying if
wood climate relation conditions are good enough and consequently
generating acceptable quality of dried sawn wood. It has to be considered that
air drying of wood is a long term process which could extend into years.
When finally wood is dried it needs proper storage conditions that include
natural circuiation of dry warm air and other terms of planning. It has to be
considered that absorbed water in the wood can emerge and evapoprate with
the help of sourrounding air flow only in case if the surface is not covered
by
rain fall water, snow or other substances. Influencing on air drying tehnology
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
2
by restacking with ventilation abilities do help in minor values with the
constant risk of wood being attacked by mould, microoorganismus, fungi,
insects including uneven drying that can worsen quality of wood expresed
with other terms concerning its quality. There is always a potential problem
of
shape deformations that can emerge because of natural air - drying
unpredictable situations that cannot be prevented by any preventive process
control tehnology or monitoring of any kind. Moisture distribution content in
wood is by using technology of drying by air after a certain period of time
depending on climate conditions what means that time variation is present in
planning emerging other problems usually leading to higher costs, too much
rejections of quality assurance and alike. On the other hand there are also
some other efects of such a technology like low energy consumption, huge
drying areas, storage departments, safety procotions. There were some
expriments executed to shorten air - drying process by engaging axial fans,
but there are too many other parametres like relative humidity and others on
which axial fans cannot influence.
With the intention to reduce drying time in the aspect of cost, quality and
time
were developed drying devices of different kinds, which can be distinguished
by a technological approach in a following manner: The first type is a
compartment type and tunnel kiln type. Both known types of drying devices
can be characterized as stationary types. By the first type of drying devices
the
wood is placed in avaliable compartment which has the ability of generating
different physical conditions like: temperature, humidity, air flow capacity
and
alike, with the intention of proceeding of the drying process. By the second
type of drying devices the wood is transported with the help of horizontal
transport unit through the drying device where it is sequently processed under
different physical conditions, mainly for the purposes of gradualy executing
the drying process. Compartment type drying devices are cheaper, but with
lower production rate in comparison with the tunnel kiln type drying devices,
where investment costs are relatively high.
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
3
The already known types of drying devices have certain disadvantages which
will be explained in details as follows including the decisions of great
investment cost and setting up difficulties in aspect of economy factors.
The technology processes used nowadays by drying the wood are performed
either by low temperatures between 15 and 45 C or by medium temperatures
between 45 and 90 C or also by high temperatures between 90 and 130 C
with the posibility of achieving above specified temperatures e.g. by means
dielectrical, convectional, conduction or radiation principles.
By certain types of drying devices the wood is put into compartment by means
of suitable transport carriages. With the ventilators placed on the ceiling or
rarely on other locations an air flow is created which is in some cases blown
transversely, yet by others the air flow is lead horizontaly and transversely
and
still in other versions the air is lead longitudinaly.
By all these known drying devices the transport units are constructed in a
manner and with such dimensions that enable loading as great quantities of
wood as possible in the kiln volume. The wood is stacked by along ventilation
in a way that air flow is possible at least in one horizontal plane. A certain
compromise has to be achieved with the consideration of dimensions of the air
gap that is neccessary for air flow and the amount of wood in the kiln. The
hot
air is then blown through the air gaps in order to fasten up the intensity of
drying. When the hot air gets in contact with the wood containing high
moisture level it absorbs it to its highest possible value, what causes
enabling
of absorption of moisture, that is still present deeper in the pile.
Consequently
that means that ventilators create enough strong air flow yet with the highest
moisture level possible what means only a lot of waste of energy. Because of
high moisture level in the air it is very likely that it condenses on cooler
places
such as walls and other equipment causing damage. The condensed liquid that
stays in the kiln volume efects harmfull on it as well as to the drying
process.
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
4
As noted in the patent aplication EP 0 170 648 Al which is intended to
execute one of the latest drying technologies the compartment has warm-
insulated walls. The sawn wood is being stacked by longitudinaly ventilation
in the kiln volume. In the drying device there is installed a ventilator which
enables air flow passing through a heating register then continuing on trough
stacked wood to the cooling register where the air flow is led in a way of
repeating the same loop. In the area of heating register the air is warmed up
then as passing trough the stacked wood it picks up moisture which is then
released by passing trough the colling register to the warming register. Such
a
combination is likely to create condensate if fresh sawn wood is processed
but is quite suitable for wood with low moisture volume - the final touch -
before being used up by industry.
If desired that by means of satured air generated by drying process of stacked
wood as highest as possible quantity of moisture should be departed from
compartment, the air must be heated. The disposal of great amounts of
saturated air is combined with great looses of heat used before as heating
air.
Energy yield by using this technology of drying wood is low.
Except of the above mentioned drying technologies also a vacuum drying
technology is described in the PCT/DK87/00012 and WO 87/04779, where
e.g. intensivity of drying process could be monitored in order to avoid drying
defects. The devices with applied vacuum technology are very sensitive in
mantaining proper vacuum conditions and are more suitable for drying
processes for wood containing lower values of moisture what means that other
drying technology for eliminating the majority of moisture has to be used
therebefore.
By all these known solutions it can be summarized that all of them have
certain imperfections, e.g. relatively low energy yield being unacceptable for
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
global economy, or high requirements in respect of the space consumption,
highly dependance on power sources, a high probability of drying defects,
very small or no adaptable abilities and are moreover built as a stationary
type
with drying capacities that dictate the amounts of drying wood and
technology.
According to the invention, the drying unit is provided by an aerated housing,
the inner area of which is connected by the circumferential area by means of
exhausting conduits and aerating conduits. Thus, in accordance with the
principals of the invention, the new drying device is created on the basis of
many ventilation air systems containing different type of airflow intake as
well
as disposal air possibilities that are fixed to the drying device. Such a
device is
equipped by a heat condensation device containing a heating unit, a
condensation unit and a ventilator. The drying device has a drying kiln in
which with the help of transporting carriage is placed wood intended to be
dried. The drying process is executed in the drying kiln by enforced
circulating air. At least one wall of the kiln compartment is equipped by
suitable air shafts for aerating or exhausting functions as an integrated unit
of
the drying device including the system vent which has the function of air pre-
orientation in any time required during the drying process in coinsistence
with
air deflector placed above the loading volume integrated in the kiln
compartment by the heat condensation unit, which extends from the opposite
side of the drying compartment and ends at the bottom of the kiln cmpartment.
The air deflector by the heat condensation device has mounted at least one
vent, which could be self-adjustable and an integrated unit consisting of a
partition wall and the top of kiln volume, which in combination with the top
of the kiln compartment presents a tunnel-shaped air shaft in which the
ventilation system is placed. The whole above mentioned section is called an
air deflector. The already mentioned air shafts start on the micro climate
vent
mounted on the top of the kiln compartment, then they are lead mainly along
the side wall and are ended within the space of the kiln volume.
_.., __ _.. ._ _ _ __..._....~~,.,.,......~..., ~d ..,.._ . _ _... __. _
_......_._....~. . . . _ _ ._._.
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
6
In the kiln volume there is arranged at least one ventilation unit with the
ability of angular adjustment with the posibility of positioning it either in
the
on- or in the off-state function. With the microclimate went in closed
position
connected with the air shafts, ranging from the top of the kiln compartment
ending in the kiln volume are generated conditions for creating an internal
air
circulation, but in open position the internal circulation gets in contact
again
with the help of the shafts with external athmosphere with paralell air flow
of
mostured air blown out of the kiln volume in the athmosphere and sucked in
fresh dry air in the tunnel shaped air shaft due to the pressure difference.
In
the tunnel-shaped air shaft is recommended an instalation of heating elements.
In accordance with the invention is the unit for stacking wood or other
products intended for drying also equiped with accessories that enable
vertical
and horizontal stacking and longitudinal ventilation. The accessories also
enable vertical positioning of dominant surfaces of the drying wood. The
distance holders that enable stacking of wood are placed vertically in
relationship to each another and are shorter than the vertical supports of the
unit. The said units can be mounted one on each other. The botton carriage
can be equiped by transport wheels. In accordance with the present solution in
the kiln compartment space close to the micro climate vent is placed an UV-
emittor meant for emitting ultra-violet rays to the moisture contained in the
air
with the intention of eliminating the posibility of development culters like
mould, fungi and other microorganismus.
In accordance with the principals of the invention is the new drying device
equiped with magnets assembled in the kiln compartment in bipolar
arrangement what means that magnetization treatment influences on all the
processes - chemical, phyisical and biological.
According to the invention, the drying device also comprises a heating
condensation device with a ventilator assembled in the opening of partition
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
7
wall. The heating condensation device is designed in a way of iregular
medium flow linking to increase condensation efect as well as heating
emission.
Now, the invention will be described in more detail on the basis of an
embodiment as shown in the accompanied drawings, where
Fig. 1 is a longitudinal cross-section of the drying device in a vertical
plane;
Fig. 2 is a transversal cross-section of the device in the vertical plane;
Fig. 3 is a longitudinal cross-section of the device in a horizontal plane;
Fig. 4 is a longitudinal cross-section of the device in the vertical plane,
however during its operation mode comprising combination of
dehumidification drying and convection drying with the wood stacked
to enable ventilation in the longitudinal direction;
Fig. 5 is a transversal cross-sestion of the device according to Fig. 5 in its
vertical plane;
Fig. 6 is a longitudinal cross-section of the device according to Fig. 1- 3,
however during its further operation mode suitable for accelerated
process of natural air drying, again with the stacked wood;
Fig. 7 is a transversal cross-section of the drying device according to Fig.
5;
Fig. 8 shows a condesation unit of the device according to the invention; and
Fig. 9 shows a unit for stacking wood also comprised by the device according
to the invention.
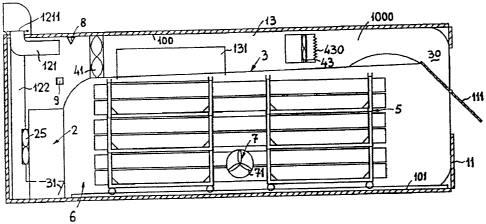
A drying device shown in Fig. 1 - 3 is in generally designed for drying wood
and other materials with the kiln compartment 1 constructed as to fulfill
standards and other requirements known in the field of transport where
standard containers are used for all known transport posibilities. The
proportions of the kiln compartment 1 have certain advatages comparing with
all till now known drying devices as well as certain limitations, which may be
however overcome by the solution according to the invention. In such a
CA 02308245 2008-09-30
8
manner it is possible to exploit the drying device by the user either e.g. as
a
stationary or a mobile device with extremely quick and simple installation to
appropriate location.
At least one of the side walls 11, 12, 13, 14 of the kiln compartment 1,
namely
in this case the longitudinal wall 13, is equiped by a suitable door 131,
allowing e.g. to enter the kiln compartment I and being e.g. intended for
personal access. On the other hand, by the shown embodiment the wall 11 is
equipped by a lifting loading door, in which is in this case fixed at least
one
system vent 111, which is otherwise arranged in the area of the said wall 11.
In accordance with the general idea of the invention will the role of the
system
vent 11 I be explained in more detail as follows.
On the opposite side of the kiln compartment 1, namely on the top of the wall
12, there are fixed suitable integrated micro climate vents 1211 equiped with
appropriate exaust funnels 1210, 1220 of the aerating respectively exhausting
air shafts 121, 122 as a way by which the interior of the kiln compartment is
connected with the extemal athmosphere. With the help of the micro climate
vent 1211 the air shaft 121 connects or disconnects the exterior athmosphere
and the interior area 10' near the top 100 of the kiln compartment 1;
analogous
the air shaft 122 is connected in the same way with the help of appropriate
micro climate vent 1221 to external atmosphere and the interior space 10" near
the bottom 101 of the kiln compartment I in a certain distance with respect to
the back wall 12, where is also placed a heat condensation device 2. By using
the micro climate vent 1211 great advantages are obtained in cases when
performing the drying program is in automatic mode.
The heating condensation device 2 is schematically shown in FIG. 8 and
consists of the following parts: a housing 20 equipped with an outlet 201
for condensate, a condensation unit 21, a heating unit 22, a compressor 23
and a tlu=ottling valve 24, which are mutually connected in appropriate
circuit 26 together with
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
9
condensation unit 21 and heating unit 22 and a ventilator 25 which enables an
air flow from condensation unit 21 to heating unit 22 continuing on in the
same direction towards other interior areas of the kiln compartment 1. Such a
heating condensation device 2 enables that warm moistured air with the help
of condensation unit 21 reduces the amount of moisture in it formed as
condensate flowing out trough a escape - pipe 201. The air is warmed up in
the heating unit 22 for approximately 2 C with respect to temperature of the
air entering the kiln volume from its circumferential area.
In the kiln compartment 1 is asembled the top of the kiln volume, partition
wall with an air deflector 3 close to the heat condensation unit 2 in a
certain
distance from the side wall 12 which is connected with the bottom area 101 of
the kiln compartment 1. The air shafts 121, 122, and heat condensation device
2 are placed between the side wall 12 and the top area 100 with the air
deflector 3 placed under the top area 100 of the kiln compartment 1 in a
certain distance from the top area 100 extending to the door 11 with the
system shaft 111 of the kiln compartment 1. The top area 100 with air
deflector 3 is positioned in relationship to top 100 and door 11 with the
system
shaft l 11 of kiln compartment I in a way to close the passage 30 between the
top 100, side wall 112 and the top with air deflector 3. The system shaft 111
can be led in automatic mode.
The shape and the position of the air deflector 3 placed under the top area
100
enable forming a tunnel shaped air shaft 1000, in which is placed the
ventilation unit 40 comprising two properly spaced ventilators 41, 42
installed
near the air shafts 121, 122 with the possibility of two more ventilators 43,
44
placed in the middle part of the kiln compartment 1 equiped also with heating
elements 430, 440.
Under the top and air deflector 3 is in the space between the bottom 101 and
system vent 111 and the wall respectively the loading doors 11 and the rest of
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
the kiln volume 6 do offer enough large kiln volume that loading of at least
one ore more carriages with stacking units 5 is possible on which is stacked
wood or other materials intended to be dryied. In accordance with the
principle of the invention will all details considering position 5 be
explained
as following.
In the drying device there is also installed at least one ventilaton unit 7
consisting of at least one ventilator 71 with the ability of angular disperson
72
of the current air flow. In position when ventilator is arranged parallel to
adjacent side wall of the kiln compartment 1 is in inactive state and - vice
versa - when being swung in another position it is in the active state.
Ventilator has to be swung in its inactive state e.g. when the carriages 5 are
moved along the kiln volume 6 for whatever the reason. Two ventilators 71',
and 71" as shown in the Fig. 3 are separately arranged on appropriate supports
72', 72" each at the one side of the longitudinal side walls 13, 14 of the
kiln
compartment 1.
The carriage stacking unit 5 for wood as shown on Fig. 9 is equiped by wheels
and foreseen for placing into the kiln volume 6. The carriage stacking unit 5
is
in accordance to the invention constructed in such a way that it enables
stacking the wood in a vertical position with the help of vertical distant
elements 51 that also enable vertical stacking 52 with ensuring stacking
through the width in specific degree. At least one stacking unit 5 is equiped
by
wheels 50 on Fig. 4 with the recommendation of having more stacking units.
In this way it is possible to mount one on each other separate stacking units
5
equipped by wheels 50 to the required height. In this way as shematically
shown on Fig. 5 and 7 is achieved stacking in vertical and horizontal
direction
in the required value through out the kiln volume 6 what consequently ensures
good air permeability.
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
11
According to the invention it is most suitable to choose stacking of wood in
the kiln volume 6 on the stacking units 5 in a way to achieve that dominant
surfaces of wood are in arranged in a vertical plane. Parts of wood of smaller
width needs to be stacked in the stacking unit 5 by being put one on each
other
in a vertical position with ensured air gap distance between the wood by
means of appropriate distance element 51'.
In accordance with the invention is moreover in the kiln compartment 1, more
exactly in the area 10', a UV-radiation device 8 is mounted, which is
preferably an emitor of ultra-violet and is foreseen for emitting of UV-rays
to
the moisture contained in the air with the intention of eliminating the
posibility of development cultures like mould, fungi and other microorganism.
In the kiln compartment I in the area 10' there are furthermore available at
least two magnets 9 in bipolar arrangement where magnetization treatment
influences on all processe - chemical, phyisical and biological and on
properties of all moisture that is present in the kiln volume 1.
In accordance with the invention the drying device on Fig. 4 and 5 enables an
integrated drying process of dehumidification by condensation-convection
method in a way as explained before. The wood intended to be dryied is put
into kiln volume 6 by opening loading lifting dooors 11 on staking units 5 on
which is properly staked wood with accessories 51, if needed also with
vertical distance elements 51' and horizontal distance elements 52. A thin
layer of wet substance sticked to rough surface of sawn wood is present on
wood in this phase preventing further lossing of moisture content from wood.
After the wood is put in the kiln volume 6 and the doors 11 closed the proces
of drying is started by activation of ventilators 41, 42, 43, 44, ventilation
unit
40, ventilator 25 attached to the heat condensation unit and activated
ventilators 71. The system vent 111 assembled in the wall respectively the
door 11 is closed. The heat condensation unit 2 is activated and appropriate
air
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
12
circulation is generated on a preset temperature value achieved by activating
heating elements 430, 440 of the ventilation unit 40. When the conditions
correspond to those as required, the heating elements 430, 440 are
disactivated
and the required heat may be supplied only with activated heat condensation
device 2. With the intention of acceleration of the drying process appropriate
circulation of suitable warmed up air has to be established. When moisture
present on/in the wood is absorbed by the air it is lead through the heat
condensation device 2 where it is eliminated with the help of condensation
unit 21 as shown in the Fig. 8 and thereafter led out of the device by means
of
the escape pipe 201. In this phase can the kiln compartment 1 be connected
with external air by means of air shafts 121 and 122. When passing trough the
heat condensation device 2 the air is warmed up to a certain degree and
sucked by ventilators 25 and 41, 42, 43, 44 in a circulating movement trough
the tunnel shaped air shaft 1000 where it is heated up if necessary by means
of
appropriate heating elements 430 and 440 threafter it passes trough the
passage 30 and by the system vent 111 and air deflector 3 entering in the kiln
volume 6 where it is lead by ventilators 17 depending on the configuration of
the wood that is stacked on carriage stacking units 50.
The drying conditions enable an intensive transfer of moisture from wood to
the circulating air. Through the air shaft 122 the air emerges from the kiln
volume 6 and the kiln compartment I outwards to the external atmosphere. As
it is known from the science, the coller air enriched with moisture has
downstream tendency, in this case therefore towards the bottom 101 of the
kiln compartment 1. However, due the pressure difference is simultaneously
the emerged air through the air shaft with the help of micro climate vent 1211
replaced by fresh air containing less moisture through the air shaft 121.
The rest of the air available in the kiln volume 6 passes trough the heat
condensation unit 2 where moisture from the air is released by the -help of
condesing unit 21 and partially dried and heated up by means of the heating
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
13
unit 22 to the desired degree emerges entering the tunnel air shaft 1000 with
the help of all ventilators starts a new circulating cycle by entering into
the
kiln volume 6. The drying mode as described enables especially at the
beginning when a lot of free water is present on the wood and in it an
eficient
way to dry wood without heating it up to high temperature causing possible
drying defects known by drying in the past.
In order to achieve pre-defined and controlled value of air moisture with the
above described drying technology in the kiln compartment 1 and the kiln
volume 6, now the drying conditions have to be changed. As it is known, the
wood contains capillars in cells that contain free liquid and absorbed
molecules of water called moisture content which by being lowered if
applying the right drying technology must be executed in the proper climate
conditions depending mainly on the kind of wood and varying essentially from
kind to kind, where circulating air should always be capapble of reducing
moisture content, constantly emerging from the drying wood.
In the above mentioned way it is possible to execute drying in a simple and
surprisingly short time by the new developed drying device in kiln volume 6
without engaging acsessories of any kind and restaking processes of wood and
without additional heating of air. The air passes through the passage 30 near
the air deflector 3 and the system vent 111 is opened as shown on Fig. 6 and
7 in consideration that in most cases adittional heating of air is not needed,
even functional exterminated the implementation of the new developed drying
process can be executed. The micro climate vent 1211 and the air shafts 121
and 122 are by implementation of new developed drying manner in their
closed position.
Therefore, according to the invention, the difference comparing to known
solutions of drying processes is physical prevention of repeted circulation
and
mixing of dry and saturated air what would cause low efficiency. The
CA 02308245 2000-04-17
WO 99/23430 PCT/S198/00008
14
activated ventilators 41, 42, 43, 44 of the venting unit 40, ventilator 25 of
the
heat condensation device 2, and ventilators 71 generate appropriate air
circulation. The external air led into the kiln compartment 1 and consequently
into the kiln volume 6 passes through the system vent 111, which is opened,
and is thereafter led through the kiln volume 6 and through a self-adjustable
vent 31 and after that through the heat condensation device 2 containing
heating unit 22 is mostly or even permanently functionally exterminated but
with the help of ventilator 25 is led through the tunnel-shaped air shaft 1000
to the air passage 30. When the system vent 111 is in the opened position the
air emerging from the air passage 30 cannot reenter the kiln volume 6 but is
exhausted from the kiln compartment 1 to the external athmosphere. In this
way it is achieved that only a dry fresh air has the ability to get in contact
with
the drying wood. Those skilled in the art should understand that the intaken
fresh air would have to be treated in certain ways in cases of extreme climate
conditions what can be done with the help for this meant accessories what
does not influence on the principle of the invention.