Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
wo ~nms4 pc~rrnz9sroos6s
1
WEB FEEDING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR FEEDING A WEB END
The present invention relates to a web feeding
device as defined in the preamble of claim 1 and to a
procedure for web feeding as defined in the preamble of
claim 18
The invention concerns especially chemical
pulp machines and a procedure for feeding the end of a
pulp web from one aggregate to another, e.g. from a
drying chamber to a sheet cutter, in such machines.
However, the invention is not restricted to this
application, but it can also be used e.g. in
conjunction with paper machines or cardboard machines
as well as various machines for further processing of
paper and cardboard
In conjunction with the treatment of light-
weight webs, a commonly known technique to use an air
blowing system for web feeding. However, in the case of
thicker and heavier webs, the air blowing method is not
workable and therefore a manual method is mainly used
for web feeding e.g. in the case of a chemical pulp
web.
Feeding the web end manually from one
aggregate to another is a slow operation which
constitutes a significant safety risk for the operating
personnel. Especially in the case of long distances,
manual web feeding is difficult because especially a
thick high-grammage web generally has to be supported
at intermediate positions instead of merely drawing by
the end. On old, relatively slow machines, manual web
feeding has been feasible, but as the speed is
increasing, which is a natural trend of development
even in chemical pulp machines, the manual web feeding
process is difficult and is continuously becoming more
and more so.
The object of the present invention is to
eliminate the drawbacks mentioned above. A specific
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
wo ~nms4 pc~r~9sroos6s
2
object of the present invention is to disclose a new
type of web feeding device and a corresponding
procedure, which allow web feeding without the web
being touched manually, especially in the case of a
relatively heavy chemical pulp web.
As for the features characteristic of the
invention, reference is made to the claims.
In the text to follow it will mainly be spoken
of a web, and this may refer to the web in its entire
width, but preferably it refers to a narrower leader
which has been cut from one edge of the web and which
is first fed to another aggregate and which can be used
to draw the whole web in its entire width to the other
aggregate.
The web feeding device of the invention for
feeding a web end from a first aggregate to a second
aggregate comprises a transfer gear for guiding the
track of the web from the first aggregate to the
vicinity of the second aggregate. According to the
invention, the transfer gear comprises means for moving
it from the vicinity of the first aggregate to the
vicinity of the second aggregate while the web is
resting on the transfer gear. In other words, as the
web or a leader already cut is passing from the first
aggregate to an exit space, e.g. to a pulper, the web
is supported by means of the transfer gear and its
track is removed so that the web runs from the first
aggregate to the vicinity of second aggregate and only
from there to the pulper.
The web feeding device preferably compriaes a
guiding device by means of which the web is passed into
the second aggregate from its vicinity. Preferably the
transfer gear is so disposed that it extends relatively
close to the guiding device so that the web can be
brought into contact with the guiding device by means
of the transfer gear.
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 99127184 PGTlFI98/00865
3
The guiding device may also consist of a mere
roll nip, because e.g. in a cardboard machine
application the web feeding device of the invention can
be used e.g. for web feeding between the drying section
and the machine calender. In this case, the leader can
be conveyed to the vicinity of the calender, cut off
and passed directly to the nip without actually using
roller belts or equivalent.
In an embodiment of the invention, the web
l0 feeding device comprises a cutting device placed in the
vicinity of the second aggregate for cutting off the
leader and passing the cut end to the second aggregate.
The cutting device preferably consists of a blade and a
counter blade disposed in the vicinity of the second
aggregate, between which the web is cut off. Of course,
other types of known cutting devices and means may be
used.
Thus, in the web feeding device of the
invention, the web coming from the first aggregate is
first moved by means of a transfer gear so as to make
it run in the vicinity of the second aggregate. After
this, using the cutting device, the web end can be cut
off in the vicinity of the second aggregate and, by
means of the guiding device, the cut end is conveyed to
the second aggregate. Another alternative is to pass
the web or leader in a doubled condition into the nip
formed by the roller and the guiding device, whereupon
it either breaks or is cut off. It is also possible
that part of the leader that remains intact rises up
from the pulper and passes through the nip.
The transfer gear preferably comprises a
rotatably mounted reel or roller. Connected to the reel
or roller is a suitable power means for moving it from
the vicinity of the first aggregate to the. vicinity of
second aggregate while at the same time the web is
supported by it and thus runs over said reel or roller.
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 99IZ7184 , 4 PCT/FI9$/00865
The power means used to move the reel or
roller may consist of e.g. a togged-belt driven linear
guide, a telescopic cylinder, various lever structures,
rail systems or equivalent along which the reel or
roller can move. Similarly, the transfer gear may
comprise several reels or rollers supporting the web
between the first and second aggregates. The roller or
reel at the end of the transfer gear which is used to
push the web may also be provided with a drive, in
which case it will be able to guide the web more
accurately while its own movement towards the second
aggregate is taken into account. In this way, the web
can also be drawn if necessary while its track is being
shifted.
In an embodiment of the invention, the
transfer gear consists of an endless belt running on
rollers, together with means for tension adjustment, at
least one of the rollers being movable between the
first and second aggregates. In this case, when the
track of the web is being guided by means of the
movable roller from the first aggregate to the second
aggregate, the web is supported on the endless belt and
the track of the web is removed until the web runs near
the second aggregate.
The guiding device preferably comprises an
endless circulating belt connected to the second
aggregate, e.g. to the leading roll of the second
aggregate. The endless belt of the guiding device is
preferably disposed above the web running in the
vicinity of the second aggregate so that the web or its
cut end can be brought into contact with the lower
surface of the belt, thus allowing the web end to be
conveyed, guided by the lower surface of the belt, to a
desired point in the second aggregate.
In a preferred case, the guiding device is
provided with contact elements enabling the upper
surface of the web to be brought into contact with the
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 99f17184 PCT/FI98/00865
guiding device or maintained in contact with the
guiding device. Preferably the contact elements consist
of vacuum means, placed e.g. on one side of the endless
belt of the guiding device, by means of which a suction
5 acting through the belt is generated to keep the web or
web end brought by the transfer gear in contact with
the guiding device.
If the transfer gear does not bring the web or
its end to a sufficient contact with the guiding
device, then the contact elements may also comprise a
blowing device to guide or push the web or its cut end
into contact with the lower surface of the endless belt
of the guiding device. It is also possible to maintain
this contact by means of the blowing device until the
web or its end reaches the nip of the second aggregate,
in which case the use of vacuum means and suction
through the belt may be unnecessary.
The web feeding device preferably comprises a
cutter by means of which a leader known in itself is
cut from the web, which leader is first passed to the
second aggregate using a web feeding device according
to the invention. After the leader has been conveyed to
the second aggregate , the width of the leader can then
be increased by means of the cutter so that finally the
web in its entire width runs from the first aggregate
to the second aggregate.
In the procedure of the invention for feeding
a web from a first aggregate to a second aggregate in a
chemical pulp, cardboard or paper machine, in an
3d initial condition the web is driven down from the first
aggregate to an exit space, such as e.g. a pulper.
According to the invention, the track of the web or a
leader cut from it is removed at a speed below the
running speed of the web to make it run from the
vicinity~of the first aggregate to the vicinity of the
second aggregate and further to where it has been
running, e.g. to a pulper. In other words, during the
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
wo ~nns4 pcn~9sroos6s
6
removal of the web track, the web continues to be
passed into the exit space. Thus, in the invention, a
bearing supporting the web is moved at a speed below
the running speed of the web toward the second
aggregate while the web is running into an exit space,
such as a pulper.
In a preferred embodiment, after the running
track has been moved, the upper surface of the leader
is brought into contact with the guiding device, which
guides the web and leads it to the second aggregate.
Thus, the web is drawn in contact with the guiding
device to the second aggregate.
The web or leader is held in contact with the
guiding device preferably using either a vacuum method
or a blowing method or both.
The web is preferably passed from one
aggregate to another at a clearly lower speed than the
web speed. The speed may be e.g. 30-60 m/min or only
about 2% of the web speed.
In the procedure of the invention, the web or
leader may be cut off at a point near the second
aggregate so that the cut end is taken to the second
aggregate. However, it. is also possible that no cutting
is done but the web or leader extending past the second
aggregate is bent over and passed in a doubled
condition to the nip between the roller of the second
aggregate and the guiding device.
The web feeding device of the invention and
the corresponding procedure provide significant
advantages as compared with prior art. The invention
enables automatic web feeding without the web being
touched manually. Thus it significantly improves
industrial safety. Likewise, as machine speeds are
increasing, it eliminates an operation that has become
more difficult than before and thus promotes the
conditions for further increasing the speeds. The
device takes up only a small space beside the machine
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
wo ~nms4 rc~r~9~oos6s
as it only moves along tracks substantially parallel to
the machine. The invention allows the web feeding
operation to be performed at a speed that is
independent of the speed of the web in the machine. The
web end can be passed from a first aggregate to a
second aggregate at a speed of about 30 - 60 m/min
while the machine speed is 1000 (paper machine), 500
(cardboard machine> or 100 m/min (pulp drying machine),
with the invention taking care of directing the faster
running leader e.g. to a pulper. The speed of the web
feeding process itself can be selected so that maximum
success in the web feeding operation is achieved. The
web feeding speed may be only a . g . about 2 % of the web
speed.
In the following, the invention will be
described in detail by referring to the attached
drawings, wherein
Fig. l presents a diagram representing a web
feeding device according to the invention in side view,
Fig. 2 presents another embodiment of the
invention in top view,
Fig. 3 presents a third embodiment of the
invention in side view,
Fig. 4 presents a fourth embodiment of the
invention in side view, and
Fig. 5 presents a diagram illustrating the
basic principle of the invention.
In the web feeding devices presented in the
figures, the same parts are indicated by the same
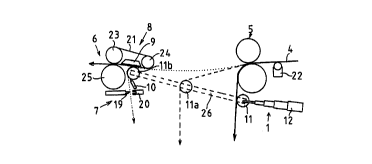
reference numbers. In the embodiment in Fig. 1, the web
feeding device comprises a transfer gear 1 disposed in
the vicinity of a first aggregate 5 and the web 4
coming out of it. The transfer gear consists of a
roller 11 rotatably mounted with bearings and connected
to a telescopic hydraulic cylinder 12 and supported by
a linear guide 26 extending from a point below the
first aggregate 5 to a point near a second aggregate 6.
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 99127184 PCTIFI98/00865
8
Disposed in the vicinity of the second aggregate 6, to
which the end of the web 4 is to be fed, is a guiding
device 8, which consists of an endless belt 21
supported by and driven around rollers 23 and 24.
Roller 23 rests on the leading roll 25 of the second
aggregate 6. Thus, a nip is formed between the rollers
23 and 25, into which the web end is to be conveyed.
Moreover, disposed above the lower portion of the belt
21 are vacuum means acting as a contact element 9,
which are used to generate a suction through the belt
21 to keep the web in contact with the lower surface of
the web.
The web feeding device also comprises a
blowing device acting as a second contact element 10,
which can be used to produce an air blast to push the
web in a desired direction. In addition, the web
feeding device comprises a cutting device 7 disposed in
the vicinity of the second aggregate 6, consisting of a
blade 19 and a counter blade 20, by means of which the
web running between them can be cut.
Disposed in the vicinity of the first
aggregate 5 is also a slitting device 22, which cuts
from the web 4 a narrow leader which can be fed to the
second aggregate 6 first.
The device illustrated by Fig. 1 works as
follows. In the initial situation, the web 4 is running
from the first aggregate 5 directly down e.g. to a
pulper. When the web 5 is to be passed from the first
aggregate 5, e.g. a drying chamber, to the second
aggregate 6, e.g. a sheet cutter, a narrow leader is
cut from the web using the slitting device 22. The rest
of the web continues to be passed down directly to the
pulper. The leader also continues to run to the pulper,
the transfer gear l pushes the leader slang the linear
guide 26 towards the second aggregate 6, intermediate
position 11a, right up to it to a position 11b below
the endless belt 21 of the guiding device 8. The web
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 9912'1184 9 PCT/FI98/00865
can be pushed into direct contact with the guiding
device or it can be left at a short distance from it.
In this position, the leader still continues
to run around the roller li and down to the pulper.
Using the cutting device 7, the leader is now cut off
and at the same time a blast is applied by the blowing
device 10 to force the cut end of the leader up towards
the lower surface of the endless belt 21 of the guiding
device 8. Due to the action of the vacuum means 9, the
end of the leader remains in contact with the lower
surface of the belt 21, and while the belt 21 is being
driven around the rollers, it takes the leader end
along with it through the nip between rollers 23 and 25
to the second aggregate 6.
After this, using the slitting device 22, the
width of the leader now running to the second aggregate
6 can be increased until finally the web 4 in its
entire width is running to the second aggregate 6. When
the web is running smoothly from the first aggregate to
the second aggregate, the guiding device 8 or at least
one 23 of its rollers is raised so that the belt 21 is
disengaged from contact with the leading roll 25 of the
second aggregate 6.
Fig. 2 presents another embodiment of the
invention, which mainly corresponds to the embodiment
in Fig. 1. The difference lies in the structure of the
transfer gear, which consists of a cog-belt driven
linear guide 26 on which a roller 11 is supported by a
carriage 27. Thus, the roller 11 can take the leader 28
from the first aggregate 5 to the guiding device 8 in
the vicinity of second aggregate 6. As can be seen from
the figure, the web feeding device takes up but a very
small space beside the machine. The web feeding roller
11 itself need not be pulled transversely out of the
machine, but it can be brought to an initial position
below the first aggregate 5. Thus, in a situation where
the web feeding operation fails for some reason, the
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
WO 99/27184 PCT/FI98/00865
web feeding roller can simply be driven back to its
initial position, and once the leader is again running
normally, the web feeding operation can be started
again.
5 Fig. 3 presents a third embodiment which
mainly corresponds to the embodiment in Fig. 1 in
respect of both structure and operation. The only
difference is the transfer gear 2, which consists of an
endless circulating belt 16 running around several
10 rollers. The belt has been arranged to run via
tensioning devices 17 known in themselves because, as
in the embodiment in Fig. 1, one 18 of the rollers can
be moved from the vicinity of the first aggregate 5 to
the vicinity of the second aggregate 6. When the roller
18 is moved towards the second aggregate 6, the web 4
will be running along the surface of the belt 16 and is
supported by it throughout the distance between the
first and second aggregates. This is to ensure that
even a heavy web or leader will run smoothly forward.
In other respects, the device works in a manner
corresponding to the device in Fig. 1.
Fig. 4 presents a fourth embodiment, in which
the transfer gear 3 consists of a pair of rollers 15
movable along a rail 13. The rollers 15 are connected
to each other via a power means 14, i.e. a telescopic
structure that allows adjustment of the distance
between the rollers. Thus, by moving the roller pair
along the rail while the distance between the rollers
is changing, the web 4 can be removed from the vicinity
of the first aggregate 5 to the vicinity of the second
aggregate 6. It is also possible to have the rollers
connected to each other via a suitable linkage
structure allowing them to be moved farther apart or
closer to each other in the direction of the rail 13.
After the web 4 or a leader cut from it has been
removed in this way to the vicinity of the second
CA 02310579 2000-OS-OS
wo 99mis4 1l ec-rm9sroos6s
aggregate 6, the web end is fed to the second aggregate
6 in the manner described in connection with Fig. 1.
Fig. 5 is diagram representing the basic idea
of the method of the invention. The first aggregate 5
may consist of e.g. a drying cylinder section where the
web 4 is circulating from one drying cylinder to the
next. In the initial situation, the web 4 is passed
from a first aggregate directly down to an exit space
30, which may be a pulper. When it is desirable to have
the web 4 running to a second aggregate 6, e.g. a size
press, a transfer gear 31 is engaged to support the web
on it in the vicinity of the first aggregate 5. Next,
the transfer gear is moved to the vicinity of the
second aggregate while the web is supported by the
transfer gear, thus removing the track of the web so as
to make it run close by the second aggregate. At the
same time, however, the web is running to the exit
space 30 all the time during the removal. In this way,
the removal can be achieved tranquilly and slowly, at a
speed substantially lower than the running speed of the
web, so the speed of removal of the track is
independent of the running speed of the web.
Once the web has been brought to run along a
track close by the second aggregate 6, the web can be
e.g. cut off and its end can be conveyed into the nip
of the second aggregate, for it is always necessary to
have some type of nip (roll nip, belt nip, roll/belt
nip, rope nip, and so on) into which the web is
directed to create a pull on it.
In the foregoing, the invention has been
described by way of example by the aid of the attached
drawings, but different embodiments of the invention
are possible within the scope of the inventive idea
defined by the claims.