Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02313646 2000-06-09
,
97 P 6450
Description
Monitoring system
The present invention relates to a monitoring
system for trimming electronic components or sensors in
accordance with the preamble of claim 1.
In many electronic components and sensors, it
is necessary to set the components and/or sensors in
order to achieve the required accuracy. This setting
sequence is usually referred to as the trimming of the
corresponding component or sensor.
For this purpose, it is known to use digital
trimming cells, e.g. in the form of EEPROM cells, zener
zaps or fusible links. By means of these usually
digital trimming cells, the corresponding electronic
components or the sensor and the circuit connected
thereto can then be controlled in such a way that a
desired response is achieved.
There is a problem in achieving this trimming
of the corresponding components with high reliability
precisely with regard to electronic systems relevant to
safety. This is because it is precisely in sensitive
electronic systems that the required response of
components must be ensured and, consequently, also the
reliability in the trimming of these components.
In this respect, however, it has also been
found that the trimming cells used failed in a manner
dictated by the production batch or fell out of step in
the course of their service life, but a clear
indication of faulty behavior of the entire system was
not obtained for these situations.
Such failures or malfunctions which, moreover,
are not clearly indicated are unacceptable, however,
precisely in systems relevant to safety.
CA 02313646 2000-06-09
97 P~6450 _ 2 _
The object of the invention, therefore, is to
design a monitoring system of the generic type in such
a way that the functioning of the trimming cells or a
deviation therefrom or even a failure of trimming cells
is reliably indicated.
In the case of a monitoring system of the
generic type, this object is achieved according to the
invention by means of the features of the
characterizing part of claim 1.
An essential concept at the heart of the
invention consists, therefore, in assigning a further
trimming cell to the trimming cell or cells already
present in the system. This further trimming cell is
then designed or connected in such a way that the
monitoring system generates a parity signal which
permits a statement concerning the functioning or a
failure of one or more trimming cells in the system.
In this case, the further digital trimming cell
is advantageously connected in parallel with the other
trimming cells whose functional monitoring is to be
carried out in the system. The digital method of
operation of the trimming cells that are usually used
therefore allows the output signals of the trimming
cells to be logically combined with one another,
thereby obtaining an output signal for the parity
checking.
For this purpose, the output signals of the
trimming cells are fed directly or indirectly to a
logic circuit which generates a .parity signal at its
output e.g. only when one or more trimming cells
exhibit faulty behavior.
Although, in principle, a parity signal is
present only in the event of the failure of one or an
odd number of trimming cells, this fulfills the high
safety requirements since the fault should be indicated
in the event of the failure of just a single trimming
cell.
Examples of trimming cells that can be used for
setting the desired response of sensors are
CA 02313646 2000-06-09
97 P 6450 _ 3 _
EEPROM or EPROM cells, zener zaps or fusible links.
In the case of digital processing, a fault in a
trimming cell can be indicated by a status bit at the
output of the logic circuit.
Since it is often the case that the interfaces
provided can only transmit the sensor signal, it is
necessary to indicate the fault state as a parity
signal in another way. In these cases, a simple and
expedient possibility is for the parity signal to be
placed out of the normal operating range of the
indication, that is to say to lie outside the normal
range.
For example, in the case of an integrated
pressure sensor at whose output, in normal operation,
digital data are generated in the range +/- 0.75 as
output signals, a malfunction of the trimming cells can
be indicated with a full-scale stop at e.g. +/- 1,
As a result, the monitoring system can be
designed and defined in such a way that data lying
outside the standard range signal faulty behavior, in
particular of the trimming cells or of a trimming cell.
Therefore, when a fault is present, it is possible
simply for the range full-scale value of the
corresponding sensor to be output. In this way,
attention is drawn to the irregular behavior of
trimming cells and sensor with high reliability. This
last because, in the event of faulty behavior of
trimming cells, the sensor or sensors do not lie within
the scope of their desired response.
Although good reliability can be assumed in the
case of trimming cells, by means of the design of the
monitoring =-system in the manner mentioned above, a
fault in the system is indicated in a simple and
efficient form and, consequently, the overall
reliability is considerably improved.
CA 02313646 2000-06-09
97 P 6450 _ 4 _
The invention is explained in more detail below
with reference to a schematic drawing of an exemplary
embodiment.
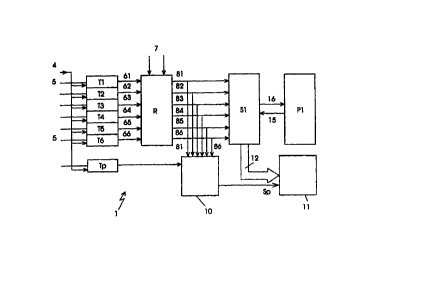
The drawing shows a schematic block diagram of
a monitoring system 1 according to the invention, with
a sensor S1. In order to set the accuracy and the
response, the sensor S1 has six bit inputs via which
the sensor S1 can be trimmed.
On the input side, the trimming cells T1 to T6
receive a common control signal 4 and separately,
furthermore, different input signals 5.
On the output side, the signals 61 to 66 of the
trimming cells are passed to a register R. The output
signals 81 to 86 of the register R then serve as input
signals for setting the response of the sensor S1.
The register R serves, in particular, for
enabling the simulation of the behavior of the sensor
S1 in the event of the failure of one or more trimming
cells T1 to T6. This allows the register R to be set in
such a way that e.g. the failure of the trimming cell
T3 can be run through as a test procedure and the
response of the sensor S1 can already be ascertained in
test terms. However, the register R also serves for
determining the exact desired function of the sensor S1
without trimming cells, e.g. fusible links, having to
be "blown".
The output signals 81 to 86 of the register R
are, as it were, bit lines for setting the sensor S1.
Therefore, the response or the accuracy of the sensor
S1 is set via six bit lines.
In the example illustrated, the sensor S1 is
bidirectionally connected to a process unit P1.
The sensor S1 may be e.g. a pressure sensor
KP 100, which detects the pressure at the corresponding
process unit P1 in a bidirectional mode of operation.
CA 02313646 2000-06-09
97 P 6450 _ 5 _
In order to achieve maximum security and
reliability of the monitoring system, a further
trimming cell Tp is provided as parity trimming cell in
parallel with the six trimming cells T1 to T6 present
in the example.
The output signal of this parity trimming cell
Tp is fed to a logic block 10, which simultaneously
receives the output signals 81 to 86 which identify the
functionality or faulty behavior or even a failure of
individual trimming cells T1 to T6 or a plurality of
trimming cells T1 to T6.
In the logic block 10, these signals including
the output signal of the further trimming cell Tp are
processed and a parity signal Sp is output at the
output e.g, in the event of a fault in one of the
trimming cells T1 to T6.
This parity signal Sp is indicated by means of
a display unit 11.
It is expedient for the parity signal Sp to be
fed to the sensor S1 as well, e.g. in the sense of a
blocking signal, since said sensor is set defectively.
The display indication 11 is connected to the
sensor S1 via a bus 12, so that the corresponding
sensor values can be indicated.
In the event of a parity signal Sp generated by
the logic block 10, the indication of the corrPSponding
sensor signal, as identification of a fault, can be
placed in the full-scale region of the indication,
whereby a fault in the monitoring system is clearly
signaled.