Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
doehrincer ingeiheim International GmbH 3/4qg ~CT
i
Container for a medical liquid
The invention concerns a container `or a medical liquid, the
container being gas- and liquid-tight.
The invention aims to make the production of such a container
which is intended for one-trip use more economical without adversely
affecting its usefulness, and to simplify handling thereof.
EP-0 182 094 A2 sets forth a bottle-shaped pack comprising an
outer container which is stiff in respect of shape and an inner
container which is disposed in the outer container and which is in the
form of an easil..y deformable bag for containing the filling material.
The preform is produced by co-extrusion of two coaxial tubular portions.
The two portions comprise two thermoplastic materials which are not
joined together. The preform is expanded in a blow moulding mould. A
welded seam is provided at the flat bottom of the inner container. The
flat bottom which is formed on the outer container has an opening in the
form of a slot. The outer container and the inner container are
connected together in positively locking relationship in the region of
the discharge opening. That pack is produced substantially in one
working operation.
The filling material is discharged from the container by means of
:: pznp which is disposed in the discharge opening, in which case the
inner container suffers deformation as its volume decreases. Air passes
into the space between the outer container and the deformed inner
container, through the open slot in the flat bottom of the outer
container, thereby preventing the occurrence of a reduced pressure in
that intermediate space. The inner container does not involve a fixed
contact with respect to the outer container, except in the region of the
discharge opening. The pack can be provided with a dip tube which
extends almost as far as the flat bottom and which holds the inner
container in the extended condition. That pack can be satisfactorily
used and completely emptied, only when it is in a given position in
space.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
2
A tubular bag of composite foil is described in EP-0 620 165 Al.
The composite foil comprises at least an outwardly disposed plastic
foil and an inwardly disposed metal foil. The tubular bag is closed at
both ends in a sack-like configuration. The bag is provided with a
desired-rupture location, by means of which it can be reliably opened
at that point. A tubular bag of that kind serves to store a hardenable
material which is expelled from the tubular bag by means of an
expelling device.
EP-0 068 653 Al describes a flexible and collapsible container
which is intended for one-trip use and which is made from a foil and
which is used in- a suction or feeding bottle which can be used a
plurality of times. The one end of the container is open while the
other end is closed by means of a welded seam and provided with a
tongue portion. The tongue portion is clamped in a gap provided at the
bottom of the suction or feeding bottle. That provides that the bag-
like container is constantly held in an extended condition in the
suction or feeding bottle.
The object of the present invention is to provide a container for
a medical liquid, which container is gas- and liquid-tight and whose
filling volume is suited to the intended purpose of use, which
p,astically and irreversibly collapses under a slightly reduced
pressure in a predetermined manner and which can be approximately
completely emptied.
In accordance with the invention that object is attained by a
container for a medical liquid, which container is gas- and liquid-
tight and which is characterised by:
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
3
- a foil bag which is closed at both ends and which, at a
differential pressure between the interior of the container and its
surroundings below 300 hPa (300 mbar), is deformable by the external
pressure and collapses, and
- a flange which is stable in respect of shape and which is
sealingly mounted to the foil bag and which is in the form of a
releasable connecting element for fitting the container on to a
discharge connection member, and
- at least one welded seam with which the foil bag is closed at at
least one end and which extends substantially transversely with respect
to the axis of the bag, and
- a sealing location in the flange which is stable in respect of
shape, and
- a discharge location for the liquid in the region of the flange
which is stable in respect of shape.
In a further embodiment the collapsible foil bag can already be
deformed by and collapsed due to the external pressure at a differential
pressure of below 150 hPa (150 mbar) or preferably below 80 hPa (80
mbar).
The foil bag can be closed by a welded seam at both ends. In that
case the flange which is stable in respect of shape is sealingly welded
to the side of the foil bag, preferably in the proximity of an end of
the foil bag. The foil bag however may also be sealingly closed at one
end by a welded seam and at the other end by the flange which is stable
in respect of shape. In this case the one end of the foil bag is welded
to the flange which is stable in respect of shape, preferably on the
periphery thereof.
The flange which is stable in respect of shape can be of different
shapes. If it is disposed at the end of the foil bag as the closure
means thereof, it can be of a rotationally symmetrical form and can be
adapted to the size of the end of the foil bag. The flange which is
stable in respect of shape can be provided with a guide passage into
which the discharge connection member can be introduced and in which the
discharge connection member is disposed when the container is f"ttted on.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01 __
4
It may be desirable to provide the guide passage with a press fit
which embraces the discharge connection member. The press fit can be a
portion of the guide passage which comprises a smooth inside wall of an
inside diameter which only slightly differs from the outside diameter of
the discharge connection member. In a further embodiment a plurality of
bulge portions can be provided in a portion of the guide passage on the
inside wall thereof. The bulge portions can be for example three bulge
portions which are of ar, elongate configuration and which are arranged
symmetrically extending in the axial direction. It is further possible
to provide a plurality of bulge portions which are arranged at an axial
spacing from each other and which extend in the azimuthal direction and
which for example form two rings or which comprise a plurality of ring
pcrtions. Furthermore the bulge portions can extend in a helical
configuration; they can comprise a plurality of helix portions
distributed on the inside wall of the guide passage or a helix portion
whose length is greater than the periphery of the guide passage. A press
fit of that kind permits the container to be fitted on to the discharge
connection member and can provide for a sufficiently firm fit of the
flange on the discharge connection member. Furthermore, after it has
20. been emptied, the container ca^ be withdrawn from the discharge
connection member without damaging the latter.
The flange which is stable in respect of shape comprises rubber,
metal or plastic material, preferably a thermoplastic material. It may
be desirable to produce the flange which is stable in respect of shape
from the same plastic material as that forming the foil bag or the
inward side of the foil bag.
The.welded seam at one or both ends of the foil bag can be of a U-,
V- or T-shaped configuration; it extends substantially transversely
with respect to the axis of the bag. It can extend partially in the
direction of the axis of the bag, whereby the defined deformation of the
foil bag is promoted when liquid is drawn therefrom.
A sealing location or sealing means can be provided within or at
one of the ends of the guide passage. The sealing location can comprise
a ring which is disposed in a groove provided on the inside wall of the
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
-- ----------
guide passage. The ring can be of an 0-shaped or substantially
rectangular cross-section. The ring is possibly provided with a sealing
lip. The ring can comprise an elastomer, a thermoplastic elastomer or
rubber. The sealing location closes the filling space or chamber cf the
container which is fitted on to the discharge connection member gas- and
liquid-tightly in relation to the ambient air. It permits the emptied
container to be withdrawn from the discharge connection member. The
sealing location is required if the sealing effect of the press fit is
not sufficient.
The discharge location is preferably in the form of a puncture or
perforation location. A pierceable membrane can be provided at the
puncture or perforation location, the membrane being pierced when the
container is fitted on to the discharge connection member. The membrane
is preferably arranged between the sealing location and the liquid
chamber or space in the foil bag. The pierceable membrane can be
disposed at one of the ends or within the guide passage. It is
preferably disposed directly at the end of the guide passage or in the
proximity of that end which is towards the liquid space. It can be a
part of the flange which is stable in respect of shape, or a part of the
foil bag. If it is a part of the flange, it can be produced at the same
time as the flange. It can comprise the same plastic material as the
flange. The pierceable membrane acts as an original closure means for
the filling space or chamber in the foil bag.
In a further embodiment the discharge location can be sealed with
a sealing foil which is pulled off before the container is fitted on to
the discharge connection member or which is pierced when the container
is fitted on to the discharge connection member.
The flange which is stable in respect of shape can be in one or
more parts. The multi-part flange can preferably be a two-part flange.
The outwardly disposed part of the flange is sealingly connected to the
foil bag. The outer part contains an opening which is sealingly closed
with the inner part. The two parts can be screwed together by means of a
screwthread or they can be connected together by means of a snap-action
connection or by ultrasound welding. The one-part flange is of a similar
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
6
configuration- to the two-part flange, but it does not include any
connecting elements.
The flange which is stable in respect of shape can be produced at
the same time with a press fit, a groove for the sealing location, and
a pierceable membrane.
The foil bag can comprise a tube which does not have a welded seam
extending in the axial direction of the foil bag. It can also be
produced from one foil and may have one or two welded seams extending
in the longitudinal direction. It can be in the form of a flat bag or
in the form of a bag with side folds. A bag with a welded seam
extending in the longitudinal direction is preferred.
The welded seams on the foil bag can be from 0.7 rrm to 3 mm wide;
the width thereof is selected in accordance with the demands made in
terms of sealing integrity and durability of the seam. Wide
longitudinal seams on the foil bag can be bent over after the welding
operation so that they approximately bear on the outside against the
foil bag and the foil bag is only a little wider than its width in the
unwelded part between the welded seams.
The foil bag can comprise a foil of metal or metal alloy -
preferably aluminium, gold or copper - or plastic material - preferably
a thermoplastic material. In another embodiment the foil bag can
comprise a composite foil of plastic material and metal. The composite
foil preferably comprises two or three foils which are joined together.
The foil bag may further comprise a plastic foil to which a layer of
metal, glass or ceramic is applied, for example by vapour deposition.
The foils of plastic material or metal are some micrometers thick. The
thickness of the vapour-deposition layers of metal, glass or ceramic is
in the sub-micrometer range.
The composite foil consisting of two foils can comprise a metal
foil and a plastic foil which are joined togehter. The metal foil forms
the inward side or the outward side of the composite foil. In another
embodiment the composite foil comprises two different plastic foils.
The composite foil comprising three foils preferably comprises two
plastic foils, between which there is a foil comprising metal. All
three foils are joined together. In place of the metal foil, the
composite foil may have a layer of glass or ceramic, for example of
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
7
silicon oxide (SiOx), which is produced by vapour deposition on a
plastic foil.
In a further embodiment the inner foil of the composite foil
comprises a copolymer, for example a polyethylene copolymer of
ethylene-acrylic acid. The outer plastic foil of the composite foil is
preferably a plastic material, for example polyethylene terephthalate,
the melting temperature of which is higher than the melting temperature
of the plastic material of the inner foil. That facilitates seam-wise
welding of the plastic material of the inner foil, in the production of
the foil bag.
In the composite foil, a bonding layer may possibly be privided
between two foils.
The foil bag can comprise a plastic foil of a thickness of between
um and 100 um. It may also comprise a composite foil with an inner
15 foil of plastic material of a thickness of between 20 um and 100 pm and
an outer foil of metal of a thickness of between 8 jim and 20 um. It may
also comprise a composite foil with an inner foil of plastic material
of a thickness of between 20 um and 100,um, a central foil of metal of
a thickness of between 8um and 20 um and an outer foil of plastic
20 material of a thickness of between 10 um and 40,um.
The welded seams on the foil bag and the weld location between the
foil bag and the flange which is stable in respect of shape are
produced using known processes such as thermal welding, ultrasonic
welding or induction welding in the case of composite foils with a
metal layer, wherein the weld locations are preferably pressed together
in the heated condition. Such processes are set forth for example in
EP-0 111 131 and EP-0 130 239.
A flange which is stable in respect of shape and which comprises
rubber or metal can be connected to the foil bag by glueing or possibly
by vulcanisation.
The container may be disposed in a casing which is stable in
respect of shape, comprising metal or plastic material, of which one
end is releasably or non-releasably connected to the flange which is
stable in respect of shape, while the other end of the casing is
possibly closed with a bottom. The casing can be substantially closed
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
8
all around. It includes however at least one opening or there is a gap
at the location of connection to the flange. The casing can also be in
the form of a basket which is stable in respect of shape and which has
many openings. Instead of the casing, the container may be disposed in
a U-shaped holder which is stable in respect of shape, wherein the end
of each limb of the U-shaped holder is secured to the flange which is
stable in respect of shape, and the limbs are longer than the foil bag.
The container disposed in a casing is connected to the casing only
at the flange which is stable in respect of shape. The end which is
closed with a welded seam or the two ends of the foil bag, which are
closed with a welded seam, are not connected to the casing.
Upon the transfer of liquid out of the container into the
discharge connection member the foil bag collapses flat due to the
action of the external pressure. Air passes through the opening in the
casing or through the gap between the casing and the flange wr,ich is
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
9
stable in respect of shape, into the space between the casinc and the
foil bag, and provides for pressure equalisation. That means that no
valve is required in the foil bag and the liquid in the foil bag does
not come into contact with air.
The foil bag is diffusion-tight in relation to the medica' liquid
and its constituents and in relation to gases. The material for the foil
bag and possibly the structure of the composite foil are suitably
selected. Diffusion-tight in accordance with the present invention
denotes a loss of liquid (measured with ethanol at ambient temperature)
of the container due to diffusion of less than 0.6 mg per day,
preferably less than 0.4 mg per day, particularly preferably less than
0.2 mg per day, in particular less than 0.1 mg per day.
The inner foil or the inward side of the foil bag is in contact
with the liquid introduced into the bag. The material adopted for that
foil is a material which is not attacked by the liquid and which does
not adversely affect the liquid. That foil is preferably in the form of
a weldable foil.
One of the foils or a layer which is applied for example by vapour
deposition is the diffusion barrier which prevents diffusion of the
liquid or the constituents thereof and the diffusion of gases from or
into the foil bag. It may be desirable to protect the diffusion barrier
from mechanical damage and from tearing thereof when the foil is bent by
means of a further plastic foil which is applied to the diffusion
barrier so that the diffusion of liquid or gases remains durably
prevented.
As the foil bag is diffusion-tight in relation to gases, the
reduced pressure which occurs in the foil bag due to the discharge of
liquid therefrom cannot be compensated by gas diffusing thereinto and
the foil bag reliably collapses even when liquid is very slowly
discharged from the container. The liquid can also be drawn from the
foil bag in a large number of partial quantities, for example 200 metered
amounts, distributed over a prolonged period of time, for example three
months.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
------------._
10
The container which is disposed in a substantially closed casing
is inaccessible from the exterior and cannot be damaged when it is
stored and when it is fitted on to the discharge connection member. The
substantially closed casing or the casing which is provided in the form
of a basket with many openings or the holder which is stable in respect
of shape facilitates storage of the container with the thin-gauge foil
bag and handling thereof when it is fitted on to the discharge
connection member and when the empty container is withdrawn from the
discharge connection member.
The discharge connection member is for example the hollow plunger
of an atomiser for medical liquids. An atomiser of that kind is
described in DE-195 36 902.5 and in W0-97/12687 (specifically in
Figures 6a and 6b) thereof. The hol l ow plunger of that atomiser is in
the form of a discharge connection member for the medical liquid
contained in the container according to the invention. The container is
fitted on to the hollow plunger which is preferably disposed on the
axis of the atomiser, in which case the end of the hollow plunger
sticks into the discharge location and thus dips into the medical
liquid. The sealing locationin the flange which is stable in respect of
shape sealingly closes off the interior of the container relative to
the outside wall of the hollow plunger. The press fit can hold the
container sufficiently mechanically fast on the hollow plunger.
It may be desirable instead of or in addition to the press fit
(force-locking connection) between the container and the discharge
connection member to provide a releasable, positively locking
connection between the flange which Is stable in respect of shape of
the container and the discharge device, for example an atomiser. A
connection bf that kind can be in the form of a push-in snap connection
comprising a plurality of snap hooks which are mounted in a connecting
portion in the discharge device. When the container is fitted into the
discharge device the snap hooks engage into an opening in the flange,
for example into a peripherally extending groove or behind an edge of
the flange which is stable in respect of shape. The snap noses are
preferably of a round shape or are bevelled in both directions of
movement of the container so that an empty container can be removed
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
CA 02319834 2006-09-26
27855-89
11
with the application of a moderate amount of force and a full container
can be fitted into the discharge device with a moderate force.
The container according to the invention is particularly suitable
as an interchangeable cartridge for inhalable medicament solutions in
propellant-free atomisers. The filling volume of the container can be
from 0.5 millilitres to 5 millilitres, preferably from 1 ml to 4 ml and
particularly preferably from 1 ml to 3 ml or from 2 ml to 4 ml. Those
solutions are discharged in a portion-wise manner with a respective
dosage of 10 microlitres to 50 microlitres, preferably from 15 ul to 20
)1l.
The casing d*ameter can be from 10 mm to 30 mm, preferably from 12
mm to 17 mm. The length of the container including the part, which
projects out of the casing, of the flange which is stable in respect of
shape can be from 20 mm to 60 mm, preferably from 30 mm to 50 mm.
The container according to the invention serves as a primary
packaging means for accommodating a medical liquid which for example
contains a medicament dissolved in a solvent. Suitable solvents are for
example water, ethanol or mixtures thereof. The medicaments used are
for example BerotecM(fenoterol-hydrobromide; 1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-
[[1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-ethyl]-amino]-ethanol-hydrobromide), AtroventM
(ipratropium bromide), BerodualTM(combination of f enoterol-hydrebromide
and ipratropium-bromide), Salbutamol (or Albuterol), Combivent;M OxiventTM
(oxitropium bromide), Ba 679 (tiotropium bromide), BEA 2108 (di-(2-
thienyl)-glycol acid tropenol ester), Flunisolid, Budesonid,
Beclomethason and others.
W0-98/27959 describes stabilised aqueous medicament preparatians
for the production of propellant-free aerosols for inhalation.
Suitable medicament preparations in ethanol solution are set forth
for example in W0-97/01329, in particular to the
active substances specified therein (see therein pages 2 and 3) and the
stabilised formulations claimed therein.
12
The container according to the invention has the following
advantages:
- It is economical to produce, it is suitable for one-trip use and
it requires only a small amount of material usage.
- It can be produced in a sterile condition and filled and sealed
in a sterile condition.
- It can be used for medicaments intended for inhalation, which
occur in the form of solutions in ethanol, ethanol/water or water.
- The liquid is discharged under sterile conditions; when that
happens no air is sucked into the container. The liquid does not come
into contact with -air, oxygen or carbon dioxide.
- The container according to the invention permits gas bubble-free
discharge of the medical liquid.
- It is sealed in relation to the diffusion of liquids and gases.
- It can be stored in the filled condition, depending on the
respective medicament involved, over several years and satisfies the
requires of all official pharmacopoeiae.
- It is already easily deformable at a slightly reduced pressure.
In the collapsed condition it remains flat and approximately stretched
out, and it retains its initial length after emptying.
- It does not require a valve for pressure equalisation after a
part of the liquid has been discharged.
- The container can be substantially emptied, even in a
fluctuating position and when it is upside down.
- The foil bag is only connected to the flange which is stable in
respect of shape. It is not fixed to the casing if such is provided.
- Its filling volume can be easily adjusted to a predetermined
value within a certain range by changing the length and/or the diameter
of the foil bag.
- It can be filled prior to closure, before the single or the
second welded seam is produced; there is no need for a separate closure
means.
- The container can be used with or without a casing.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
CA 02319834 2008-07-22
27855-89
13
- The container disposed in a casing is protected
from external damage.
- The liquid in the foil bag is protected from the
effect of light by an opaque foil bag or by an opaque casing
which is closed all around.
- It can be fitted into and removed from a
discharge device in a simple fashion and without rotary
movement.
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided use of a gas-tight and fluid-tight
container as a replaceable cartridge for a medicinal fluid
in a propellant-free atomiser, which has a discharge
connection piece in the form of a hollow piston, wherein the
container comprises a film bag which is closed at both ends,
wherein at least one end is closed by a weld seam which
extends substantially transversely to an axis of the bag,
and the film bag is deformable by external pressure when
there is a pressure differential between the internal space
of the container and its surroundings of less than 300 hPa
(300 mbar), a flange of stable shape which is arranged
sealingly on the film bag, a guide passage in the flange,
wherein a sealing location is formed in at least one of the
guide passage and a force fit embracing the discharge
connection piece, and a discharge location for the fluid in
the region of the guide passage into which the hollow piston
plunges during use, so that it is immersed in the medicinal
fluid.
CA 02319834 2006-09-26
27855-89
13a
The container according to the invention is
described in greater detail with reference to the Figures by
way of example.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
The foregoing and other features and advantages of
the invention will be apparent from the following, more
particular description of a preferred embodiment of the
invention, as illustrated in the accompanying drawings.
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a first embodiment
of a foil bag of the present invention which is closed at
both ends.
FIG. 2 is a perspective view of a second
embodiment of a foil bag of the present invention which is
closed at both ends.
FIG. 3 is a perspective view of a third embodiment
of a foil bag of the present invention which is closed at
both ends.
FIG. 4 is a sectional view of a first embodiment
of a flange of the present invention.
FIG. 5a is a sectional view of a second embodiment
of a flange of the present invention.
FIG. 5b is a sectional view of the second
embodiment of the flange taken along a line 5-5 of FIG. 5a.
FIG. 6 is a sectional view of a third embodiment
of a flange of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a sectional view of a fourth embodiment
of a flange of the present invention.
CA 02319834 2006-09-26
, 27855-89
13b
FIG. 8a is a view of a one-part flange of the
present invention, which is disposed on the side of a foil
bag.
FIG. 8b is an exploded view of a cross-section of
laminate foil used to make up the foil bag of FIG. 8a.
FIG. 9a is a side view of first embodiment of a
welded seam of the present invention.
FIG. 9b is a sectional view of the welded seam
taken along a line 9-9 of FIG. 9a.
FIG. 10a is a side view a second embodiment of a
welded seam of the present invention.
FIG. 10b is a sectional view of the welded seam
taken along a line 10-10 of FIG. 10a.
FIG. lla is a side view of a third embodiment of
the welded seam of the present invention.
FIG. llb is a plan view of the welded seam of
FIG. lla.
FIGS. 12a-12g show a series of perspective views
of manufacturing and filling of a container according to a
first embodiment of the present invention.
FIGS. 13a-13f show a series of perspective views
of manufacturing and filling of a container according to a
second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 14 is a partial sectional view of a container
according to the present invention.
CA 02319834 2006-09-26
27855-89
13c
FIG. 15a is a sectional view of a first embodiment
of a connecting portion of a container of the present
invention.
FIG. 15b is a side view of one end of the
container of FIG. 15a.
FIG. 16a is a sectional view of a second
embodiment of a connecting portion of a container of the
present invention.
FIG. 16b is a side view of one end of the
container of FIG. 16a.
Figures 1 to 3 are perspective views of various
embodiments of the foil bag which is closed at both ends.
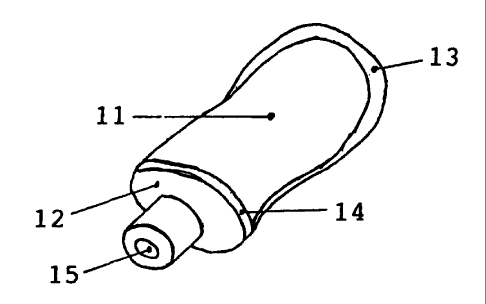
Figure 1 shows a tubular bag 11 with a cylindrical
flange 12 which is stable in respect of shape, and a
U-shaped transverse seam 13 which closes the one end of the
tubular bag and which partially extends in the longitudinal
direction thereof. The edge 14 of the flange is connected
to the other end of the tubular bag. Disposed on the axis
of the flange is a hole 15 into which a discharge connection
member can be introduced.
Figure 2 shows a sealed-edge bag (21) which
comprises two foils which are disposed one upon the other.
It has two welded seams 22 extending in the longitudinal
direction of the bag and, at its one end, a welded seam 23
extending in the transverse direction. The other end is
connected to a flange 24 which is stable in respect of shape
and which is of a fish-like form. Disposed at the centre of
the flange is a hole 25 into which a discharge connection
member can be inserted.
14
Figure 3 shows a side fold bag 31 with folds at both longitudinal
sides, which is closed at each of its two ends by a respective
transversely extending welded seam 32. The flange 33 which is stable in
respect of shape is welded on to the bag on a flat side thereof. A
discharge connection member can be inserted into the hole 34 of the
flange.
Figures 4 to 7 are sectional views of various embodiments of the
flange which is stable in respect of shape.
Figure 4 is a view in longitudinal section through a one-piece
flange 41 having a cylindrical guide passage 42, which is in the form of
a press fit, for a cylindrical discharge connection member. The outer
end of the guide passage is bevelled while the other end is closed by a
membrane 43 which is disposed inclinedly with respect to the axis of the
flange. That flange is produced in one working operation. The edge,of
the flange is connected to a foil bag 44.
Figure 5a shows a multi-part cylindrical flange in longitudinal
and Sb shows a cross-section on the line identified at A-A
in Figure 5a. The lower part 51 is connected to a foil bag 53. The upper
part 52 fits in an opening in the lower part. The upper part is provided
with a guide passage 54 in which there are three elongate ridges 55
extending in the axial direction of the flange as a press fit for a
discharge connection member and an annular ridge 56 as a seal. The lower
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
,--..
15
part 51 and the upper part 52 are welded together at their cor,tact
surface 57. The entry opening with inclined insertion surface of the
guide passage is sealed off by a sealing foil 58.
Figure 6 shows a multi-part cylindrical flange which is stable in
respect of shape. The lower part 61 is connected to a foil bag 63. The
upper part 62 projects into the annular lower part. Disposed in the
upper part as a seal is an 0-ring 64 which is held in place by a gland
65 that is pressed into position. The opening in the gland 65 serves as
a guide passage for a discharge connection member. Disposed on the
inside of the seal on the upper part is a peripherally extending ridge
66 which is in the form of a press fit. A discharge connection member 67
is inserted into the guide passage. The container is held on the
discharge connection member by means of the ridge-shaped press fit 66.
The lower part 61 and the upper part 62 are welded together at their
contact surface 68.
Figure 7 shows a further multi-part flange. The lower part 71 is
connected to a foil bag 73. The upper part 72 is disposed in the annular
lower part which is provided with a shoulder. The upper part includes a
flat ring 74 as a seal, which is held in place by a gland 75 which is
pressed into position. Disposed beneath the flat seal is the guide
passage 76 for a discharge connection member. The press fit comprises
two ridges 77 within the guide passage, extending therearound in a
screwthread-like configuration. Provided in the proximity of the lower
end of the guide passage, perpendicularly to the axis of the flange, is
a membrane 78 which is pierced when the container is fitted on to the
discharge connection member. The membrane is produced with the upper
part in one working operation. The lower part and the upper part are
connected together at their contact surface 79.
Figure 8a is a view in cross-section of a one-part flange 81 which
is stable in respect of shape and which is disposed on the side of a
foil bag 82. The flange has an opening 83 which serves as a press fit
for a discharge connection member. That flange is sealed on its outward
side by a sealing foil 84. When the container is fitted on to a
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
16
discharge connection member 85 with a bevelled end, the foil bag is
pierced at the inner end 86 of the guide passage.
Figure 8b shows a view in cross-section through a commercially
available laminate foil having three layers making up the foil bag. The
inner foil 87 comprises polyethylene (40 um in thickness), the central
foil 88 is the diffusion barrier of aluminium (12 )jm in thickness) and
the outer foil 89 comprises polyethylene terephthalate (12 iim in
thickness).
Figures 9 to 11 show various embodiments of the welded seam with
which the foil bag is closed at at least one end, as a side view and in
cross-section (Figures 9b and lOb) or as a plan view on to the end of
the bag (Figure llb).
Figure 9a shows a U-shaped welded seam 91 which extends partially
in the longitudinal direction of the foil bag 92 and on one side goes
into a welded seam 93 of the foil bag, with the welded seam 93 extending
in the longitudinal direction. Figure 9b is a view in cross-section
through the foil bag at the line identified by 6-6 in Figure 9a. The
inner layer of the folded multi-layer foil 94 is welded in the welded
seams.
Figure l0a shows a V-shaped welded seam 101 which extends
partially in the longitudinal direction of the foil bag. In this case
the foil bag comprises a tubul ~r-= fci ?v: i t"out a 1 oig i tuu i ~~a i
seartt:
Figure lOb shows a view in cross-section through the foil bag at the
line identified by C-C in Figure 10a. The folded single-layer foil 103
is welded in the welded seam. ,
Figure 1la shows a T-shaped welded seam 111 as a side view while
Figure lib is a plan view on to the welded end of the foil bag 112. The
three limbs of the T-shaped seam are overall as long as the foil bag, in
the condition of being collapsed flat, outside the T-shaped seam, is
wide.
The foil bag which is welded with a U-, V- and T-shaped seam is no
greater in the region of the transverse seam than the diameter of the
casing into which the foil bag is possibly inserted.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
17
Manufacture and filling of the Container according to the
invention is diagrammatically illustrated in perspective views in
Figures 12 and 13.
A folded foil strip is provided at the cut sides with a welded
seam in the longitudinal direction, divided into portions and shaped to
form a tube (Figure 12a). The lower part, which is produced by an
injection moulding process, of a two-part cylindrical flange is welded
to the one end of a tubular portion of that kind. The other end of the
portion is welded with a U-shaped transverse seam (Figures l2b and 12c).
The finished container (Figure 12c) is pushed into a cylindrical casing
of aluminium (Figure 12d), the edge of which is pressed into a groove or
channel in the edge of the cylindrical flange. The container is fixedly
joined to the casing in that way. The empty container which is disposed
in the casing is filled with a fluid through the lower part of the
flange, which is provided with an opening (Figure 12e). After the
filling operation the upper part of the flange is pressed into the lower
part (Figure l2f) and the two parts are sealingly joined together. The
finished part (Figure 12g) is ready for being fitted on to a discharge
connection member.
A further production process is illustrated in Figure 13. A
portion of a foil tube provided with a longitudinal seam (Figure 13a) is
connected at its one end to a one-piece flange which is closed by a
sealing foil (Figure 13b). The container is filled with a fluid through
the other open end of the foil tube ( Fi gure 13c). The open end of the
foil tube is closed by a U-shaped transverse seam (Figure 13d). The
filled container is fitted into a casing of plastic material (Figure
13e). The edge of the pl ast i c cas i ng is snap-f i tted on to the edge of
the flange which is stable in respect of shape. The finished part
(Figure 13f) is ready for being fitted on to a discharge connection
member.
Figure 14 is a partly cross-sectional view of a typical container
141according to the invention which is filled with a fluid and which is
disposed in a metal casing 142. At its one end the foil bag is welded by
a U-shaped seam 143 while at its other end it is welded to the edge 144
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
18
of the lower part 145 of a two-part cylindrical flange which is stable
in respect of shape. The metal casing has a bottom 146 in which there is
a hole through which air can pass into the space between the metal
casing and the foil bag. The open end of the casing is pressed into a
groove or channel 147 in the edge of the lower part 145. The casing is
fixedly connected to the flange. The upper part 148 of the flange is
fitted into an opening in the lower part. The lower part and the upper
part are connected by a snap-action closure 149 and provided with a flat
seal 150. The guide passage 151 is closed at its inner end by a membrane
152 and sealed at its outer end by a sealing foil 153.
The metal casing shown in Figure 14 comprises aluminium. It is 43
rrm in length and is of an outside diameter of 17 mm and has a wall which
is 0.5 mm in thickness. The two-piece flange comprises polyethylene and
is produced by an injection moulding process. The upper part of the
flange including the membrane is produced in one step in the process.
The guide passage in the c:pper part of the flange is of an inside
diameter of 2.5 mm at the location of the press fit and fits firmly on
to a discharge connection member.
Figures 15a and 15b show a releasable, positively locking, push-in
snap connection between the flange which is stable in respect of shape of
the container and the connecting portion in a discharge device.
Figure 15a is a view in cross-section through the connecting
portion 154 which is disposed in the discharge device and which on its
axis includes the discharge connection member 67. The discharge
connection member is surrounded by a plurality of snap hooks 155 with
snap noses 156 of round cross-section. The snap hooks are separated 1`rom
each other by intermediate spaces and may involve an azimuthal width of
10 degrees to 60 degrees. A portion 157 which does not include any snap
nose can be provided between two snap hooks 155. That portion bears in
positively locking relationship against the outside wall of the inserted
container.
Figure 15b is a side view of the end of a container which is
disposed in a casing 142 and whose flange 148, which is stable in respect
CA 02319834 2000-08-01
19
of shape, projects out of the casing. As shown in Figure 14, the casing
has a peripherally extending groove 158, preferably in the region of the
flange part projecting into the casing. The snap noses 156 of the
container when fitted into the connecting portion 154 engage into the
groove 158, whereby the container is releasably and positively lockingly
connected to the connecting portion.
Figures 16a and 16b show a further embodiment of a releasable,
positively locking, push-in snap connection.
Figure 16a is a view in cross-section through the connecting
portion 161 which is disposed in the discharge device and which on its
axis includes t,he discharge connection member 67. The discharge
connection member is surrounded by a plurality of tongue-shaped snap
hooks 162 with snap noses 163 whose flanks are bevelled in both
directions of movement of the container. The snap hooks are disposed at
an azimuthal spacing from each other.
Figure 16b is a side view of the end of a container which is
disposed in a casing 142 and whose flange 148, which is stable in respect
of shape, projects out of the casing. When the container is fitted into
the connecting portion 154, the snap noses 163 engage into the
peripherally extending groove 147 of the part, which projects out of the
casing, of the flange 148 which is stable in respect of shape, whereby
the container is releasably connected to the connecting portion in
positively locking relationship.
CA 02319834 2000-08-01