Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/36837 PCT/EP99/10050
Interactive communication system comprising users connected in groups.
The invention relates to a communication system comprising a communication
medium between a main station and at least one convergence point for serving a
group of
users, said convergence point having a certain transmission capacity on the
transmission
medium.
The invention also relates to a main station and a user terminal designed for
use
in such a system.
The invention applies in particular to SMATV (Satellite Master Antenna
Television) systems.
The problem which arises in this type of system is the following: the
convergence point is provided with transmission means on the transmission
medium which
have a given capacity such that at any given moment the access to the
transnussion means is
limited for the users of one and the same group.
For example, the technical report TR 101 201 V 1.1.1 published in October
1997 by ETSI describes an interactive SMATV distribution system. In such a
system, a group
of users share the same transmitter and the same transmission antenna for
transmitting requests
to the main station of the communication system. Since the transmitter is
capable of
transmitting on one carrier only at any given moment, this means that only one
user can
transmit at any given moment.
Management means are accordingly necessary for managing the access of the
users of a same group to the transmission medium.
The solution proposed in said document is shown diagrammatically in Fig. 1. It
consists in joining together a satellite transmission network 1 and a cable
network 2: the
convergence point 3 is formed by a satellite antenna 4 connected to an
interactive satellite
terminal 5 which in its turn is connected to a central station 6 of a cable
network 2. The central
station 6 of the cable network 2 is a cable network head in the sense of
recommendation ETS
300 800 of ETSI. It serves the final users 7 and provides the interface with
the satellite
transmission network I . It is seen as one single user by the satellite
transmission network, and
the final users remain unknown to the satellite transmission network.
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO OOI36837 PC"T/EP99/10050
2
This solution involves the following problem: the central station 6 is a cable
network head in the sense of recommendation ETS 300 $00. It accordingly
involves a
comparatively expensive equipment. The cost of this equipment is shared among
the users of
the network 2. This solution is thus only viable financially if the network 2
comprises a
sufficiently great number of users.
The invention has for its object to provide an effective and less expensive
solution for small groups of users. This object is achieved with a system, a
main station, and a
user terminal as claimed in Claims 1, 5, and 7 of the present patent
application.
It is the main station which governs the path between the convergence point
and
the users in a communication system according to the invention. The main
station assigns the
reservations on the transmission medium directly, taking into account the fact
that the access
to the transmission medium is limited for one and the same group of users. In
the case of an
interactive satellite transmission system, for example, the main station
assigns to the users
speaking time intervals on a carrier, making sure not to assign the same time
interval on
different carriers to different users of one and the same user group.
This solution is advantageous financially for the following reasons:
- the management of the reservations is shifted to the main station of the
communication
system so that no management device for these reservations is necessary
anymore at the
level of the convergence point,
- no specialized, non-standard material is used (from an industrial point of
view, the
development and production of the specialized, non-standard material used in
comparatively small quantities is very expensive).
In a first embodiment of the invention, the main station is provided with
tables
which can be manually programmed by an administrator of the communication
system so as to
contain the configuration of the communication system, in particular
information on the
membership of the users of a user group.
In another advantageous embodiment, the users of a user group are each
provided with an identifier which renders it possible to identify the user and
the group to
which he belongs, and they comprise transmission means for transmitting said
identifier to the
main station when they establish connection with the communication system.
This identifier is formed, for example, by the physical address (MAC address)
of the terminal, formatted in two parts, a first part identifying the
convergence point and a
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO OOI36837 PCT/EP99/10050
3
second part identifying the terminal. This physical address is transmitted in
the address field of
the connection-establishing messages emitted by the users when they make
connection with
the system.
This solution renders possible an automatic learning process of the main
station
on the basis of the addresses of the users which make connection with the
communication
system. No manual configuration operation is accordingly necessary in this
case.
The invention also relates to a method of assigning reservations as defined in
Claim 9 and an identification method for users as defined in Claim 10.
The invention will be better understood and further details will become
apparent from the following description with reference to the annexed drawings
which are
given by way of non-limitative example and in which:
- Fig. 1 shows a system as described in the prior art,
- Figs. 2 and 3 show communication systems according to the invention,
- Fig. 4 shows the format of a physical address of a user terminal according
to the invention,
- Fig. 5 shows the format of a connection message sent by a user terminal to
the main
station, and
- Fig. 6 shows a method of assigning reservations on to the transmission
medium by a main
station according to the invention.
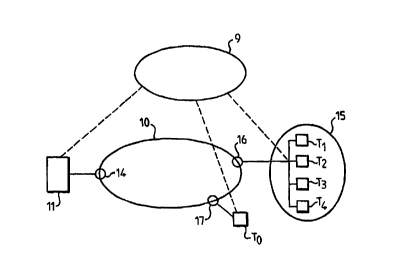
Fig. 2 shows a communication system according to the invention. This system
comprises two transmission media 9 and 10. The transmission medium 9 is a
distribution
medium which renders it possible for a main station 11 to distribute data to
users T; (i = 0, 1,
2, 3, 4). The transmission medium 10 constitutes a return path which renders
it possible for the
users T; to transmit requests to the main station 11. The main station 11 is
provided with an
access point 14 for the transmission medium 10. The users T; (i = 1, 2, 3, 4)
are part of a user
group 15 which is connected to the transmission medium 10 via a convergence
point lb. The
user To is an individual user. He is connected to the transmission medium by
means of an
individual access point 17.
The invention relates to all communication systems of the type as shown in
Fig.
2 in which a convergence point 16 has a transmission capacity over a
transmission medium 10
which is limited such that at any given moment the access to the transmission
medium 10 is
limited for the users of one and the same group. The transmission medium 10 is
formed, for
example, by radio wave links or satellite links.
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/36837 PCT/EP99/10050
4
According to the invention, the main station 11 assigns to the users T;
reservations on the transmission medium in dependence on their membership of a
user group.
To achieve this in a preferred embodiment of the invention, each user is given
an identifier
which renders it possible to identify the user and the group to which he
belongs. This identifier
is then transmitted to the main station by the user when making connection
with the
transmission system.
This identifier is formed, for example, by the physical address of the
terminal T;
which is transmitted in each connection request sent by a terminal to the main
station 11. A
particular physical address format is used for this: the physical addresses
are formatted in at
least two parts, one part identifying the convergence point and the other part
identifying the
terminal.
In a first embodiment, all addresses of the terminals are formed by stringing
together a first address part A1 stored in the convergence point or in the
access point of the
terminal and a second address part A2 stored in the terminal.
In a second embodiment, two distinct physical addresses may be applied to the
terminal depending on its mode of connection (individual or collective) to the
transmission
medium. To achieve this, a physical address part A2 and a complete physical
address A3 are
stored in the terminal. If the terminal is connected in the individual mode,
the terminal is
assigned the physical address A3, which is fully stored in the terminal. If
the terminal is
connected in the collective mode, a physical address formed by stringing
together the physical
address part stored in the terminal (A2) and the physical address part stored
in the convergence
point (A1) is assigned to the terminal. The individual or collective mode of
connection of the
terminal (and thus the address to be used, A3 or A1 and A2 joined together) is
indicated by a
status variable S which is stored in the terminal and whose value is defined
during the
installation of the terminal.
This second mode of realization renders it possible to have more addresses
available for groups of terminals.
Upon the reception of connection requests, the main station 11 registers the
physical address of the connected terminals in a table. The main station 11
traverses this table
for assigning reservations to terminals of the communication system in order
to determine the
membership of the relevant terminals of a group of terminals.
Fig. 3 shows an example of an interactive SMATV distribution system
according to the invention.
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/36837 PCT/EP99/10050
In such a system, the main station I 1 distributes data and control
information to
the user terminals T; via a satellite 20. These users T; transmit data and
requests to the main
station 11 by means of this same satellite 20.
The following description will exclusively relate to those operating
principles
5 of an interactive satellite transmission system which are necessary for
understanding the
invention. More details can be found, for example, in the technical report TR
l0I 201 V 1.1.1
of ETSI.
For communicating with the main station, the terminals of an interactive
satellite transmission system access the transmission medium by an access
mechanism, for
example a TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) mechanism combined with a
frequency
division FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access).
Each Garner is for this purpose subdivided into time intervals with which
different access modes are associated. The following are used in particular:
- time intervals which are accessible in a contention mode and to which all
the terminals
have free access, with the risk of collisions (a classical collision-resolving
algorithm is
used for resolving any collisions which may occur). These contention time
intervals are
particularly used by the terminals for making connection with the
communication system.
- time intervals which are accessible upon reservation and which are
dynamically granted by
the main station 11 upon a request from the terminals. The requests are
transmitted, for
example, in the contention time intervals, or following payload data in time
intervals
previously granted by the main station.
The following problem arises when the terminals are connected to transmission
media by means of a transmitter and a collective antenna: the transmitter is
capable of
transmitting and receiving only one carrier at any given moment. The main
station accordingly
must not grant the same time interval on different carriers to users of one
and the same group.
To solve this problem, a specific addressing format is used for the terminals
of
the communication system.
In practice, each terminal of a communication system as represented in Fig. 3
is
provided with a 48-bit address (referred to as MAC address) which is fixedly
coded in each
terminal or which is provided by an external source. For example, one might
choose to assign
to these MAC addresses the format shown in Fig. 4:
the two bits of highest order (b0 and bl) are reserved for ensuring the
compatibility with
the addresses defined in accordance with the IEEE 802.2 standard. According to
the 802.2
standard, the physical address of a terminal is coded in 48 bits. The bit of
highest order
4
According to the invention, t
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/36837 PCT/EP99/10050
6
(b0) indicates that it is an individual address or a group address (the use of
a group address
in the destination address field of a frame renders it possible far several
terminals to
receive the same frame). The next bit (bl) serves to define the nature of the
addresses,
local or global. The local addresses are administered by the responsible
manager of a given
S network and have a significance only in this network, while the global
addresses (also
called universal addresses) are unique at planet level and are administered by
the IEEE,
who assign them to various manufacturers. To ensure the compatibility with the
addresses
defined by the IEEE 802.2 standard, the choice made here is accordingly b0 =
bl =1 (local
group address in accordance with the IEEE 802.2 standard).
- the next twenty bits (b2-b21) are used for identifying the convergence
point,
- the next six bits (b22-b27) are used for identifying the manufacturer of the
terminal,
- the last twenty bits (b28-b47) are used for identifying the terminal.
In a first embodiment, one part A1 of the address of 22 bits length is stored
in
each access point and in each convergence point (i.e. in the equipment which
connects the
antenna to the terminal and which ensures in particular the functions of
frequency translation),
and one part A2 of the address of 26 bits length is stored in each terminal
which is connected
to this convergence point.
In a second embodiment, a part A1 of the address of 22 bits length is stored
in
each convergence point, and the following are stored in each terminal:
- a complete address of 48 bits which is an individual universal address (b0 =
bl = 0) and
which is used when the terminal is connected to transmission media in the
individual
mode,
- a part A2 of the address of 26 bits length which corresponds to the two last
groups-of six
and twenty bits, respectively, and which is used when the terminal is
connected in the
collective mode. In this case this address part is stringed together with the
address part of
22 bits stored in the convergence point sa as to form a 48-bit address which
constitutes the
physical address of the terminal.
In this second embodiment, it is indicated by a status variable S stored in
the
terminal which address should be used, the value of said variable being
defined during the
installation of the terminal.
These two embodiments are compatible in one and the same communication
system.
The terminals achieve connection to the transmission system through the
transmission of connection messages in time intervals which are competitively
accessible.
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/3b837 PCTIEP99110050
7
These connection messages are diagrammatically shown in Fig. 5. They comprise
more in
particular an address field F1 which contains the physical address of the
terminal and a data
field F2 which contains the characteristics of the required connection (the
data rate required,
the type of service, ...).
The main station, which receives these connection messages, thus automatically
gets to know the groups of terminals.
The main station 11 assigns to the users reservations on the transmission
media,
taking into account their membership of a user group such that one and the
same time interval
is not granted to users of a same group on different carriers. An example of
the method
according to the invention of granting reservations is shown in Fig. 6. This
method renders it
possible to grant n; reservations to each of the n terminals T; which are
connected to the
communication system. Fn the example described here, each reservation is
formed by a pair
(time interval / carrier). The main station carries out the following steps
for each terminal T;:
- step 100: it searches among the terminals T,, ..., T;.I (i.e. among the
terminals to which it
has already granted reservations) those which belong to the same group as the
terminal T;.
This group is referred to as group GK in the following description. If at
least one of the
terminals TI, ..., T;_1 belongs to the group GK (arrow Y in the Figure), the
method proceeds
to step 110. If not (arrow N in the Figure), it proceeds to step 120.
step 1 I0: the main station grants n; reservations to the terminal T;. The
time intervals Sa(T;)
(with j = 1, ..., n;) for these reservations are chosen such that they are
different from the
time intervals of the reservations already granted to the terminals of the
group GK. This
operation is diagrammatically represented in the Figure by the following
mathematical
expression:
S~(i)~SP(Tm) d p-I,...,nm
d TmEGx
- step 120: the main station assigns n; access rights to the terminal T; in
any manner.
In an advantageous embodiment, the users which are part of a user group
comprise listening-in means for listening in to the assignments made by the
main station to the
other users of their group, and control means for blocking the use of a time
interval which is
accessible in a contention mode if the main station has granted this same time
interval (on
another carrier) to another user of the same group. Said listening-in means
consist in that an
analysis is made of the signaling information transmitted by the main station
11, which
CA 02320970 2000-08-14
WO 00/36837 PCT/EP99/10050
8
information gives the structure of the upcoming frames for each carrier. The
listening-in
facility may be limited to a given number of carriers if the main station
comprises means for
assigning carriers chosen from among a sub-set of carriers to the users of a
same group, as
well as means for transmitting to the users of a group the list of the Garners
liable to be
relevant to them, i.e. the list of the carriers to be listened in to.
The embodiments described above do not render it possible to avoid that two
users of a same group access a same contention time interval if this time
interval has not been
granted to a terminal of the same group by the main station. In another
advantageous
embodiment, this collision risk is limited by the introduction of a power
measurement device
before the transmission. The determination of a power threshold value which is
considered
normal for one single transmission and a comparison of the power level with
this threshold
value renders it possible to determine whether several users are trying to
transmit data in the
same time interval and to block the transmission if this is the case.
An example has been described in which the terminals access the transmission
medium by a multiple access mechanism on the basis of time division, combined
with a
frequency allocation. This example is by no means restrictive. For example,
the invention is
also applicable if the multiple access mechanism to the transmission medium is
a CDMA
(Code Division Multiple Access) mechanism.
In the example described, the transmission media 9 and 10 are both formed by
satellite links. The broadcasting media and the return path, however, may be
of different types.