Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
NOVEL COMPOUNDS
This invention relates to novel sulphonamide compounds having
pharmacological activity, processes for their preparation, to compositions
containing
them and to their use in the treatment of CNS disorders.
US patent 5,703,072 discloses bicyclic nonane and decane compounds having
dopamine receptor affinity which are claimed to be of use in the treatment of
schizophrenia. US patent 5,457,121 discloses cis-hexahydro-5-(1,2,3,4-
Tetrahydro-2-
10 naphthalenyl)pyrrolo<3,4,c>pyrroles as inhibitors of serotonin reuptake.
European
patent application EP 0815861 discloses a series of aryl sulphonamide
compounds
that are said to possess 5-HT6 receptor activity and are useful in the
treatment of
various CNS disorders. A structurally distinct class of compounds has now been
discovered, which have been found to have 5-HT6 receptor antagonist activity.
15
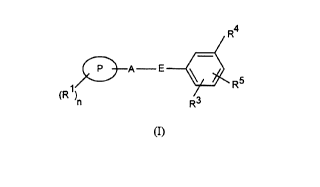
- The present invention therefore provides, in a first aspect, a compound of
formula (I) or a salt thereof
R4
P A E ~ R5
1
(R )n R3
(I)
20 in which
E is -S02NH- or NHS02-
P is a phenyl, naphthyl, a bicyclic heterocyclic ring or is a 5 to 7-membered
heterocyclic ring each containing 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from oxygen,
nitrogen
or sulphur;
25 A is a single bond, a C 1 _6alkylene or a C 1 _balkenylene group;
Rl is halogen, C1_6alkyl optionally substituted by one or more fluorine atoms,
C3_
6cycloalkyl, C 1 _6alkoxy, OCF3, C 1 _6alkoxyC 1 _6alkoxy, C 1 _6alkanoyl,
amino,
alkylamino or dialkylamino, SRl1 where Rl 1 is hydrogen or C1_6alkyl or Rl is
phenyl, benzyl, naphthyl, a bicyclic heterocyclic ring or is a 5 to 7-membered
30 heterocyclic ring each containing 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from oxygen,
nitrogen
or sulphur, and
nis0, 1,2,3,4or5;
R3 is a group RS or together with RS forms a group (CH2)20 or (CH2)30;
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
R4 is selected from a group of formula {i), (ii) or (iii):
Formula i
(R ~q
rN
/N
m
in which R6 is C 1 _6alkyl optionally substituted by one or more halogen
atoms;
5 m is 0, 1 or 2;
q is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4; or
Formula ii
(RS~q
~N
/N
'm
10 in which R6, m and q are as defined in formula (i); or
Formula (iii)
(RS~q
-N ~ ~ ~- R~
''m
in which R6, and q are as defined in formula (I) and R~ is hydrogen or C 1
alkyl;
15 RS is hydrogen, halogen, C 1 _6alkyl, C 1 _6alkoxy optionally substituted
with one or
more fluorine atoms, trifluoromethyl, or together with R3 forms a group
(CH2)20 or
(CH~30.
Alkyl groups, whether alone or as part of another group, may be straight chain
20 or branched. The term 'halogen' is used herein to describe, unless
otherwise stated, a
group selected from fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
When the group P is a bicyclic heterocyclic ring suitable examples include
benzothienyl, indolyl, quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl. When P is a 5 to 7-
membered
heterocyclic ring suitable examples include thienyl, furyl, pyrrolyl,
triazolyl, diazolyl,
2
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
imidazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, oxadiazolyl, isothiazolyl, isoxazolyl,
thiadiazolyl,
pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrrolidinyl and pyrazinyl. The heterocyclic rings can be
linked to
the remainder of the molecule via any suitable carbon atom or, when present, a
nitrogen.
5 Preferably P is phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl and most preferably benzothienyl,
Suitably A is a single bond, a methylene or ethylene group or a -CH=CH-
group. Preferably A is a single bond or methylene.
Suitably Rl is hydrogen, halogen, phenyl, C1-6alkoxy most preferably OMe,
SR11 most preferably SMe or C1-galkyl optionally substituted by one or more
10 fluorine atoms, for example methyl or trifluorornethyl. When R1 is a
heterocyclic
group suitable examples include those listed above for P. Preferably n is 1, 2
or 3.
It will be appreciated that when R3/RS groups are linked together the two
groups must be attached to adjacent carbon atoms of the phenyl ring.
Preferably R3 is a group R5, in particular hydrogen.
15 Preferably R4 is a group:
~N ~N ~N
~N~~..~ ~N
> >
~N -~N-R7
~ N ~~~ .
or
Preferably RS is C 1-6alkoxy, most preferably methoxy. Preferably RS is para
with respect to the sulphonamide linkage.
20
Particularly preferred compounds of the invention include
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid(4-methoxy-3-
(octahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-2-yl) phenyl] amide,
S-5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo(b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydro-
pyrrolo[1,2-
25 a]pyrazine-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl],
R-5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydro-
pyrrolo[1,2-
a]pyrazine-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide,
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid[3-(1,4-diazabicyclo-
[3.3 .1 ]non-4.-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide,
30 5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(1,4-diazabicyclo-
[3.2.1 ]oct-4-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide,
3
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [4-methoxy-3-(5-
methythexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2-yl)phenyl]amide,
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydropyrrolo-[3,4-
c]pyrrol-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide,
N-(5-Bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methoxy-3-(5-methyl-cis-
hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2-yl]-benzenesulfonamide,
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
The compounds of the formula (I) can form acid addition salts with acids, such
10 as conventional pharmaceutically acceptable acids, for example malefic,
hydrochloric,
hydrobromic, phosphoric, acetic, fumaric, salicylic, citric, lactic, mandelic,
tartaric
and methanesulphonic.
Compounds of formula (I) may also form solvates such as hydrates, and the
invention also extends to these forms. When referred to herein, it is
understood that
15 the term 'compound of formula (I)' also includes these forms.
Certain compounds of formula (I) are capable of existing in stereoisomeric
forms including diastereomers and enantiomers and the invention extends to
each of
these stereoisomeric forms and to mixtures thereof including racemates. The
different
stereoisomeric forms may be separated one from the other by the usual methods,
or
20 any given isomer may be obtained by stereospecific or asymmetric synthesis.
The
invention also extends to any tautomeric forms and mixtures thereof.
The present invention also provides a process for the preparation of a
compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which
process
25 comprises:
(a) when E is a group NHS02-, the coupling of a compound of formula
(II):
~A-NH2
(R1)
n
30 (II)
in which R1, P, n and A or protected derivatives thereof with a compound of
formula
(III):
4
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
R4
LO S ~ R5
R3
(III)
in which R3, R4 and RS are as defined in formula (I) and L is a leaving group;
or
5
(b) when E is a group -S02NH-, the coupling of a compound of formula
(IV):
-j-A- SO~- L
(R~ /~)
n
10 (IV)
in which Rl, P, n and A are defined in formula (I) and L is a leaving group
with a
compound of formula (V) or protected derivatives thereof
4
NH2
R5
R3
15 in which R3, R4 and RS are as defined for formula (I)
and optionally thereafter:
~ removing any protecting groups,
~ forming a pharmaceutically acceptable salt.
20 Suitable leaving groups include halogen such as chloro or bromo, in
particular chloro. The reactions of compounds of formula (II) and (III) and
that of
compounds of formula (IV) and (V) are typically carried out by mixing the two
reagents together, optionally in an inert solvent such as dichloromethane or
acetone.
Such a reaction may be carried out in the presence of base.
5
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that it may be necessary to protect
certain groups. Suitable protecting groups and methods for their attachment
and
removal are conventional in the art of organic chemistry, such as those
described in
Greene T. W. 'Protective groups in organic synthesis' New York, Wiley ( 1981
). For
example, suitable protecting groups for the piperazine group include BOC,
COCC13 ,
COCF3 and methyl the latter of which may be removed by treatment with 1-
chioroethyl chloroformate according to standard procedures.
Compounds of formulae (II) to (IV) are commercially available or may be
10 prepared according to known or analogous methods or following procedures
described
below. The procedures below are by way of illustration rather than limitation.
A compound of formula (III) (in which R4 is a group of formula (iii)), that
is,
4-methoxy-3-(5-methyl-cis-hexahydropyrrolo [3,4-c]pyrrolo-2-yl)-
benzenesulfonyl
chloride can be prepared by coupling cis-hexahydro-2-methylpyrrolo[3,4-
c]pyrrole
15 hydrochloride (US 5,457,121 ) with 2-bromoanisole using a palladium
coupling
reaction according to the general methodology disclosed by Buchwald (Tet.
Lett.
1997, 38, 6359-6362). The resulting amine can be treated with chlorosulfonic
acid in
dichloromethane to give the required compound.
Aryl octahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazines of formula (V) (in which R4 is a group
20 of formula (i)), can be obtained by a synthetic procedure as represented by
scheme 1.
Scheme 1
R
NH2 R
i ii
OiN R H
L is a leaving group eg. Br R
R ~ iii R
i) DMF or chlorobenzane;
(N) ethyl bromoacetate/ethanoUE;Nlretlux;
(fif) NaH / dioxane; iv
(iv) Hi ~ PdIC:
(v) BhI~:THF.
25 Alternatively a modified strategy based on the use of a suitably protected
proline derivatives can be used to prepare hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazines of
general formula (V) using a synthetic procedure as represented by scheme 2. It
is
6
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
noted that both enantiomers can be prepared starting from the appropriate
chiral
proline.
Scheme 2
NHz R R
R
\ R
OzN ~~
' N
~OH i ~ O
R i~ COCHzB I ~ R
PG O O N
2
PG is a protecting group
i
R O ~ iv
i) EtOCOCIlTHF/4-methylmorpholine; ~N ~N R
ii) CF3COOH/CH2CI2; N 1 J N
iii) BrCH2COBr~Pr2EtN; ~ ~ "; ~;
iv) NaH/DMF; ~ R ~----I ~p R
v) H2 / Pd/C
vi) BH3:THF. HZN ~ o N
2
5
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts may be prepared conventionally by
reaction with the appropriate acid or acid derivative.
10 Compounds of formula (I) and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts have
SHT6 receptor antagonist activity and are believed to be of potential use in
the
treatment of certain CNS disorders such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy,
obsessive
compulsive disorders, migraine, cognitive memory disorders e.g. Alzheimers
disease,
Parkinson' Disease, ADHD (Attention Deficit Disorder/Hyperactivity Syndrome),
15 sleep disorders (including disturbances of Circadian rhythym}, feeding
disorders such
as anorexia and bulimia, panic attacks, withdrawal from drug abuse such as
cocaine,
ethanol, nicotine and benzodiazepines, schizophrenia, and also disorders
associated
with spinal trauma and/or head injury such as hydrocephalus.
Thus the invention also provides a compound of formula (I) or a
20 pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use as a therapeutic
substance, in
particular in the treatment or prophylaxis of the above disorders.
The invention further provides a method of treatment or prophylaxis of the
above disorders, in mammals including humans, which comprises administering to
the
sufferer a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a
25 pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
7
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCf/EP99/01013
In another aspect, the invention provides the use of a compound of formula
(I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in the manufacture of a
medicament
for the treatment or prophylaxis of the above disorders.
The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition, which
5 comprises a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof,
and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
A pharmaceutical composition of the invention, which may be prepared by
admixture, suitably at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure, is
usually
adapted for oral, parenteral or rectal administration and, as such, may be in
the form
10 of tablets, capsules, oral liquid preparations, powders, granules,
lozenges,
reconstitutable powders, injectable or infusible solutions or suspensions or
suppositories. Orally administrable compositions are generally preferred.
Tablets and capsules for oral administration may be in unit dose form, and
may contain conventional excipients, such as binding agents, fillers,
tabletting
15 lubricants, disintegrants and acceptable wetting agents. The tablets may be
coated
according to methods well known in normal pharmaceutical practice.
Oral liquid preparations may be in the form of, for example, aqueous or oily
suspension, solutions, emulsions, syrups or elixirs, or may be in the form of
a dry
product for reconstitution with water or other suitable vehicle before use.
Such liquid
20 preparations may contain conventional additives such as suspending agents,
emulsifying agents, non-aqueous vehicles (which may include edible oils),
preservatives, and, if desired, conventional flavourings or colourants.
For parenteral administration, fluid unit dosage forms are prepared utilising
a
compound of the invention or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a
sterile
25 vehicle. The compound, depending on the vehicle and concentration used, can
be
either suspended or dissolved in the vehicle. In preparing solutions, the
compound
can be dissolved for injection and filter sterilised before filling into a
suitable vial or
ampoule and sealing. Advantageously, adjuvants such as a local anaesthetic,
preservatives and buffering agents are dissolved in the vehicle. To enhance
the
30 stability, the composition can be frozen after filling into the vial and
the water
removed under vacuum. Parenteral suspensions are prepared in substantially the
same
manner, except that the compound is suspended in the vehicle instead of being
dissolved, and sterilization cannot be accomplished by filtration. The
compound can
be sterilised by exposure to ethylene oxide before suspension in a sterile
vehicle.
35 Advantageously, a surfactant or wetting agent is included in the
composition to
facilitate uniform distribution of the compound.
8
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/424b5 PC'T/EP99/O10I3
The composition may contain from 0.1% to 99% by weight, preferably from
10 to 60% by weight, of the active material, depending on the method of
administration.
The dose of the compound used in the treatment of the aforementioned
disorders will vary in the usual way with the seriousness of the disorders,
the weight
of the sufferer, and other similar factors. However, as a general guide
suitable unit
doses may be 0.05 to 1000 mg, more suitably 0.05 to 20.0 mg, for example 0.2
to S
mg; and such unit doses may be administered more than once a day, for example
two
or three a day, so that the total daily dosage is in the range of about 0.5 to
100 mg; and
10 such therapy may extend for a number of weeks or months.
When administered in accordance with the invention, no unacceptable
toxicological effects are expected with the compounds of the invention.
The following Descriptions and Examples illustrate the preparation of
compounds of the invention.
15
Description 1
(2-Methoxy-5-nitrophenyl)piperidin-2-ylmethylamine (D1)
A mixture of 2-bromomethylpiperidine hydrobromidel (3.0 g, I 1.6 mmol) and
2-methoxy-5-nitroaniline (34.8 mmol, 5.85 g) in chlorobenzene ( 100 mL) was
heated
20 under reflux for 17 h. The solvent was removed and the residue was
dissolved in
dichloromethane (100 mL), washed with IO% aqueous sodium hydroxide (3 x 20 mL)
and dried (MgS04). The solvent was removed and the residue was purified by
column
chromatography on silica gel (eluting with dichloromethane-methanol gradient)
to
give the title compound (D 1 ) as a dark green solid ( 1.45 g, 47%). MS: m/z
(MH+) _
25 266.
1. T. A. Crabb and R. F. Newton, Tetrahedron,1968, 24, 2485.
Description 2
30 {2-[(2-Methoxy-5-nitruphenylamino)methyl]piperidin-1-yl}acetic acid ethyl
ester
(D2)
A mixture of (2-methoxy-5-nitrophenyl)piperidin-2-ylmethylamine (D1) (0.27 g,
1
mmol), ethyl bromoacetate (0.15 mL, 1.35 mmol) and triethylamine (0.19 mL,
1.35
mmol) in dry ethanol (20 mL) was heated under reflux for 4 hours. The solvent
was
3 S removed, the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane (70 mL), washed with
aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate (2 x 10 mL) and dried (MgS04). The solvent
was removed and the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica
gel
9
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
(eluting with dichloromethane-methanol gradient) to give the title compound
(D2) as
a tan gum (0.21g, 60%). MS: m/z (MH+) = 352.
Description 3
5 2-(2-Methoxy-5-nitrophenyl)hexahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one (D3)
A mixture of {2-[(2-methoxy-5-nitrophenylamino)methyl]piperidin-1-yl}acetic
acid
ethyl ester (D2) (0.3 g, 0.85 mmol) and sodium metal (20 mg, 0.87 mmol} in dry
dioxane (8 mL) was heated under reflux for 40 minutes. The mixture was
concentrated to a small volume, diluted with dichloromethane (50 mL), washed
with
I O brine (2 x 10 mL) and dried (MgS04). The soivents were removed and the
residue
was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluting with
dichloromethane-
ethyl acetate gradient) to give the required product (D3) as a tan oil (0.08
g, 31%).
MS: m/z (MH+) = 306.
I S Description 4
2-(5-Amino-2-methoxyphenyt)hexahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one (D4)
2-(2-Mettloxy-5-nitrophenyl)hexahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one (D3) (0.04 g)
and
Pd/C (0.05 g) in ethanol (IS mL) were stirred at room temperature under
atmosphere
of hydrogen for 4 hours. The catalyst was filtered off and washed with ethanol
(2 x 15
20 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated to dryness. The
residue
was co-evaporated with dry toluene (2 x 10 mL) to give the title compound (D4)
as a
colourless gum (0.035 g, 97%). MS: m/z (MH+) = 276.
Description 5
25 4-Methoxy-3-(octahydropyrido[1,Z-a]pyrazin-2-yl)phenylamine (DS)
A solution of 2-(5-amino-2-methoxyphenyl)hexahydropyrido[I,2-a]pyrazin-3-one
(D4) (0.03 S g, 0.13 mmol) and borane-THF complex ( 1 M solution, 1 mL) in
tetrahydrofuran (5 mL) was heated under reflux for 4 hours. Dry methanol (2
mL)
was added and the solvents were removed. The residue was redissoived in dry
30 methanol (5 mL) and cesium fluoride (0.035 g, 0.23 mmoi)) and dry potassium
carbonate (0.035 g, 0.25 mmol) were added. The mixture was then heated under
reflux
for 5 hours. The solvent was removed, the residue was partially dissolved in
dichloromethane (30 mL), washed with brine (3 x 10 mL), water (1 x 10 mL) and
dried (MgS04). The solvent was removed to give the required product (DS) as a
35 slightly tan glass (0.038, 90%). MS: m/z (MH+) = 262.
Description 6
[N-(tent Butoxycarbonyl)-L-prolinyl]-2-methoxy-5-nitrobenzeneamide (D6)
10
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
Ethyl chloroformate (1.3 mL, 14 mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of N-
(tert-
butoxycarbonyl)-L-proline (3.0 g, 14 mmol) and 4-methylmorpholine ( 1.54 mL,
14
mmol) in tetrahydrofuran ( 30 mL) at - 10 °C. The resulting mixture was
stirred at -
10 °C for 10 minutes and 2-methoxy-5-nitroaniline (2.35g, 14 mmol) was
added. The
5 mixture was stirred at -10°C for 30 minutes and then at room
temperature for 17
hours. The precipitate was removed by fitration and washed with
tetrahydrofuran (3 x
20 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated to dryness. The
residue was dissolved in dichloromethane (100 mL), washed with aqueous sodium
hydrogen carbonate (2 x 30 mL), dried (Na2S04). The solvent was removed and
the
10 product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluting with
dichloromethane-ethyl acetate gradient) to give the title amide (D6) as a
colourless
glass (3.81 g, 75%). MS: m/z (MHNa+) =389.
Description 7
15 S-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-5-nitrophenyl)amide (D7)
A solution of [N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-L-prolinyl]-2-methoxy-5-nitrobenzene-
amide
(D6) (1.8g, 4.93 mmol), trifluoroacetic acid (2.65 mL) and water (0.1 ml) in
dichloromethane (15 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 17 hours. The
solvents
were removed and the residue was co-evaporated with toluene (2 x 40 mL). The
20 resulting solid was dissolved in dichloromethane (200 mL) and washed with
aqueous
sodium hydrogen carbonate (2 x 50 mL). The aqueous layer was extracted with
dichloromethane (4 x 50 mL), the combined extracts were dried (Na2S04) and
finally the solvent was removed to give the title compound (D7) as a cream
solid ( 1.01
g, 77%). MS: m/z (MH+) = 266.
25
Description 8
S-1-Bromoacetylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-5-vitro-phenyl)-amide
(D8)
To a solution of S-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-5-vitro-phenyl)-
amide
30 (D7) (0.2 g, 0.75 mmol) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (0.13 mL, 0.75 mmol)
in
dichloromethane (10 mL) at -10°C was added dropwise bromoacetyl bromide
(0.75
mmol, 0.07 mL) in dichloromethane ( 1 mL). The resulting reaction mixture was
stirred at -10°C for 30 minutes and then at room temperature for 20
minutes.
Subsequently, it was diluted with dichloromethane (50 mL), washed with aqueous
35 sodium hydrogen carbonate (1 x 20 mL), water (1 x 20 mL) and dried
(Na2S04). The
solvent was removed and the residue was co-evaporated with toluene (2 x 20 mL)
to
give the product (D8) (0.29 g) which was used without purification in the next
step.
MS: m/z (MH+) = 387.
11
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
Description 9
S-2-(2-Methoxy-5-nitrophenyl)hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione (D9)
A mixture of S-1-bromoacetylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-5-nitro-
5 phenyl)amide (D8) (0.28 g, 0.7 mmol) and NaH (SO mg, 60% dispersion in
mineral
oil) in N,N-dimethylformamide (5 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 2
hours. A
further amount of NaH was then added and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for additional 17 hours. The precipitate was filtered off and
washed with
dichloromethane (60 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and
evaporated to
10 dryness. The residue was co-evaporated with toluene (2 x 10 mL). The
product was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel ( eluting with dichloromethane-
methanol gradient) to give the title compound (D9) as a colourless solid
(0.079 g,
34% after two steps). MS: m/z (MH+) = 306.
1 S Description 10
S-2-(5-Amino-2-methoxyphenyl)hexahydropyrrolo [ 1,2-a] pyrazine-1,4-dione
(D10)
A mixture of S-2-(2-methoxy-5-nitmphenyl)hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-
dione (D9) (0.07 g) and Pd/C (0.08 g) in ethanol-ethyl acetate (8:2, 40 mL)
was
20 stirred at room temperature under atmosphere of hydrogen for 7.5 hours. The
catalyst
was filtered off, washed with ethanol (3 x 15 mL) and ethyl acetate ( 1 x 15
mL). The
filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated to dryness. The product was
purified by column chromatography (eluting with dichloromethane-methanol
gradient) to give the title compound (D 10) as a colourless solid ( 0.056 g,
89%). MS:
25 m/z (MH+) = 276.
Description 11
S-3-(Hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2-y1~4-methoxyphenylamine (Dll)
A solution of $-2-(5-amino-2-methoxyphenyl)hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-
30 dione (D10) (0.055 g, 0.2 mmol) and borane-THF complex (1M solution, 1.2
mL) in
tetrahydrofuran (5 mL) was heated under reflex for 5 hours. A further amount
of
boraae-THF complex ( 1 M solution, 0.6 mL) was then added and the reaction was
heated under reflex for another 2 hours. The solution was diluted with dry
methanol
(5 mL) and the solvents were removed. The residue was co-evaporated with dry
35 benzene (2 x 5 mL) and redissolved in dry methanol (5 mL). Cesium fluoride
(0.8
mmol, 0.12g) and dry potassium carbonate (0.87 mmol, 0.12 g) were added to the
solution and the mixture was heated under reflex for 17 hours. A further
amount of
methanol (5 mL), cesium fluoride (0.8 mmol, 0.12g) and dry potassium carbonate
12
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
(0.87 mmol, 0.12 g) was then added and the reflux was continued for another 6
hours.
Cesium fluoride (0.4 mmol, 0.06 g) and dry potassium carbonate (0.43 mmol,
0.06 g)
were added again and the reflux was continued for 3 hours. The solvent was
removed, the residue was partially dissolved in dichloromethane (50 mL),
washed
5 with brine (3 x 20 mL), water {1 x 10 mL) and dried (Na2S04). The solvent
was
removed to give the title compound (D11) as a tan gum (0.042 g, 85%). MS: m/z
(MH+) = 248.
Description 12
10 2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-cis-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole (D12)
A suspension of cesium carbonate ( 15g, 46mmo1), palladium (II) acetate
(O.lSg,
0.7mmo1) and 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphine)-1,1'-binaphthyl (0.63g, lmmol) in dry
1,4-
dioxan (SOmI) was degassed, purged with argon and sonicated for 10 minutes. 2-
Bromoanisole (3.3m1, 27mmol) and cis-hexahydro-2-methylpyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole
15 hydrochloride [L7S 5,457,121 (1995)](1.9g) were added and the whole was
again
degassed, purged with argon and sonicated for 10 minutes. The stirred mixture
was
then refluxed under argon for 20 hours. The mixture was partitioned between
dichloromethane (200m1) and 1 M sodium hydroxide solution ( 1 OOmI). The
aqueous
layer was further extracted with dichloromethane (SOmI) and the combined
organic
20 extracts were dried (MgSO,) and concentrated in vacuo to an oil. The oil
was purified
by column chromatography on silica gel eluting with a gradient of
dichloromethane/methanol to afford the title compound (D12) as a solid {1.2g,
56%).
'H NMR (CDCI3, 250MHz) 2.34 (3H, s), 2.43-2.48 (2H, m), 2.62-2.69 (2H, m),
2.85-
2.92 (2H, m), 2.99-3.04 (2H, m), 3.34-3.41 (2H, m), 3.85 (3H, s), 6.80-6.94
(4H, m);
25 (MH+) 232.
Description 13
4-Methoxy-3-(5-methyl-cis-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonyl
chloride (D13)
30 A solution of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-cis-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-
c]pyrrole
(D12) (O.Sg, 2.2mmo1) in dry dichloromethane (3m1) was added over 5 minutes to
ice
cooled chorosulfonic acid (3m1) under argon. After stirring at 0°C for
0.25 hours and
subsequently at room temperature for 1 hour, the solution was slowly poured
onto a
stirred mixture of ice (SOg) and dichloromethane (SOmI). The mixture was
basified by
35 addition of excess saturated solution of sodium carbonate and the layers
were
separated. The aqueous layer was further extracted with dichloromethane (SOmI)
and
the combined extracts were dried {MgS04) and concentrated in vacuo to give the
title
compound (D13) as a foam (0.25g 34%).
13
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/o1013
Example 1
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid[4-methoxy-3-
(octahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-2-yl) phenyl] amide (E1)
N
a
\ OCH~
I N I \
s s~
A solution of 4-methoxy-3-(octahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrazin-2-yl)phenylamine (DS)
(0.03 g, 0.11 mmol), 5-chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonyl chloride
(0.042 g, 0.15 mmol) and triethylamine (0.02mL, 0.15 mmol) in dichloromethane
(2
mL) was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was diluted with
10 dichloromethane (20 mL), washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate
(( 1 x 10 mL) and dried (MgS04). The solvent was removed and the product was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluting with dichloromethane-
methanol gradient) to give the title compound (E1) as a cream solid (0.019 g,
32%).
8H {250MHz, CDCi3), 1.28 (3H, m), 1.73 (3H, m), 2.08 (3H, m), 2.19 (3H, s),
2.43
15 ( 1 H, m), 2.68 ( 1 H, m), 2.84 (2H, m), 3.00 ( 1 H, m), 3 .2 I ( 1 H, m),
3 . 82 { 3 H, s), 6.46
1 H, d, J = 2.34 Hz), 6.73 (2H, m), 7.42 ( 1 H, m), 7.65 ( 1 H, d, J = 1.91
Hz), 7.72 ( 1 H,
d, J = 8.62 Hz). MS: m/z (MH+) = 506.
Example 2
20 S-5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydro-
pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2-ylr4-methoxyphenyl]amide (E2)
N
\ CHI N
N ( \ OCHa
S SOi /
A solution of S-3-(hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2-yl)-4-methoxy-phenylamine
(D 11 ) (0.04 g, 0.16 mmol), 5-chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonyl
2~ chloride (0.045 g, 0.16 mmol) and pyridine (0.1 mL, 1.2 mmol) in
dichloromethane (4
mL) was stirred at room temperature for 2 days. The mixture was diluted with
dichloromethane (30 mL), washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen
carbonate
(2 x 10 mL) and dried (Na2S04). The solvent was removed and the product was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluting with dichloromethane-
30 methanol gradient) to give the title compound (E2) as a pink glass (0.047
mg, 59%).
14
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
SH (250MHz, CDCl3), 1.31 (1H, m), 1.82 (3H, m), 2.10 (3H, m), 2.22 (3H, s),
2.41
( 1 H, m), 2.60 ( 1 H, m), 3.02 ( I H, m), 3.17 (3 H, m), 3. 81 ( 3 H, s),
6.51 ( 1 H, d, J =
2.08 Hz), 6.70 (2H, m), 7.43 ( 1 H, m), 7.66 ( 1 H, d, J = 1.90 Hz), 7.74 ( 1
H, d, J = 8.60
Hz). MS: m/z (MH+) = 492.
5
Example 3
R-5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydro-
pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2-yl}-4-methoxyphenyl]amide (E2)
Following the same procedures as described for Example 2 the title compound
(E3)
10 was prepared from N-(tent-butoxycarbonyl)-D-proline; 28% yield;
8H (250MHz, CDCl3), 1.30 (1H, m), 1.81 (3H, m), 2.I 1 (3H, m), 2.22 (3H, s),
2.38
( 1 H, m), 2.60 ( 1 H, m), 3.01 ( 1 H, m), 3.18 (3 H, m), 3 .80 ( 3 H, s),
6.50 ( 1 H, d, J =
2.16 Hz), 6.70 (2H, m), 7.44 ( 1 H, m), 7.66 ( 1 H, d, J = 1.90 Hz), 7.74 ( 1
H, d, J = 8.60
Hz). MS: m/z (MH+) = 492.
15
The following examples may be prepared by similar procedures to those
described for
Examples l and 2.
Example 4
20 5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid[3-(1,4-diazabicyclo-
[3.3.1]non-4-yl}-4-methoxyphenyl]amide (E4)
Example 5
25 5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(1,4-diazabicyclo-
[3.2.1]oct-4-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide (E5)
c~
'The following examples may be prepared by similar procedures to those
described for
30 Example 1 employing the methodology described in US-5457121.
15
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
Example 6
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [4-methoxy-3-(5-
methylhexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2-yl)phenyl]amide (E6)
5
Me
Cl
S
Example 7
5-Chloro-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulphonic acid [3-(hexahydropyrrolo-
10 [3,4-c)pyrrol-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]amide (E'n
Example 8
15 N-(5-Bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoryphenyl)-4-methoxy-3-(5-methyl-cis-
hexahydropyrrolo[3,4..c]pyrrol-2-ylJ-benzenesulfonamide hydrochloride (E8)
20 A solution of 5-bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxy-aniline (160mg, 0.73mmo1) and
4-methoxy-3-(5-methyl-cis-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2-ylrbenzenesulfonyl
chloride (D13) (240mg, 0.73mmo1) in dichloromethane (4m1) was stirred for 18
hours
under argon. The solution was concentrated in vacuo and the residue was
purified by
16
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PGT/EP99/01013
column chromatography eluting with a dichloromethaneimethanol gradient to give
the
title compound (E8) as a foam (95mg, 24%); (MH+) 514/516.
Method for assay of 5-HT6 antagonistic activity:
The test compounds were dissolved in polyethylene glycol:dimethyl sulphoxide
(1:1)
at 1 or IOmM and diluted to O.ImM using SmM tris buffer (pH 7.7 @
25°C).
Dissolution was assisted by addition of 0.02m1 SM HCl plus heating to
40°C and
sonication for 10 minutes. Serial dilutions of test compounds in the same
buffer were
carried out using either a TECAN 5052 or Biomek 2000 Workstation. Samples of
the
diluted test compounds (O.OSmI) were mixed with O.OSmI of radio-ligand [3H]-
LSD
prepared in the incubation buffer, and 0.4mi of a suspension of a preparation
of the
washed membranes of HeLa SHT6 cells (acquired from Dr. D. Sibley. NIH,
1 ~ Bethesda, see Ref 1 Xsee Table 1 ), also in the incubation buffer. The
details of the
incubation conditions for each assay are shown in Table 2. The incubation
buffer was
SOmM Trizma (Sigma, UK) pH7.7 @ 25°C, 4mM MgCl2.
After incubation at 37°C, the mixtures were filtered using a Packard
Filtermate in
Packard TopCount fon~at. Filters were washed with 4 x 1 ml aliquots of ice-
cold
incubation buffer. Filters were dried and impregnated with 0.04m1 of
Microscint 20
(Packard). IC50 values were estimated from the counts per minute using a four
parameter logistic curve fit within EXCEL (2). Ki values were calculated using
the
method of Cheng and Pmsoff (3). pIC50 and pKi are the negative 1og10 of the
molar
IC50 and Ki respectively.
Table 1 Details of the methods used to prepare membranes for binding assays
Ist spin / resuspensionIncubationprotein conc.cells /ml
1, 2 ,3 in in stored
on before stored aliquotsaliquots
final
cellslml spin
7 x 10~ Yes 20min at 4mg/ml 1.0 x 108
37C
Table 2 Sammary of receptor binding assay conditions
-.
proteinradio-ligand Specific Non-SpecificKd (nM)
[3H]-LSD Activity
(u8/ (nM) (Ci/mmol) Definition
sample)
40 2.0 83 Methiothepin3.1
17
CA 02321278 2000-08-17
WO 99/42465 PCT/EP99/01013
References
1. MONSMA, F.J., SHEN, Y., WARD, R.P., HAMBLIN, M.W., SIBLEY, D.R..
1993. Cloning and expression of a novel serotonin receptor with high affinity
for
5 tricyclic psychotropic drugs. Mol. Pharmacol., 43, 320-327.
2. BOWEN, W.P., JERMAN, J.C.. 1995. Nonlinear regression using spreadsheets.
Trends in Pharmacol. Sci., 16, 413-4I7.
3. CHENG, Y.C., PRUSSOF, W.H.. 1973. Relationship between inhibition constant
(Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes SO% inhibition (IC50) of
an
10 enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol., 92, 881-894.
18