Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
AUDIENCE R.ATTIJ,~,Y$TEM FOR DIGITAL TELEVISION AND RADIO
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus
for audience rating systems for digital television and
radio.
2. DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
The television and radio industries and commercial
advertisers have an obvious interest in knowing how many
people are watching or listening to particular stations and
programs. Various systems of audience rating have been
developed for analog television and radio, of which the
most accurate use a meter that is connected to the
television set or radio, that records when the receiver is
turned on and off, and what channels or frequencies it is
tuned to. Digital television and radio are now being
introduced, and are expected to eventually completely
replace analog television and radio. The existing rating
1
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99162260 PCTIUS99/10453
devices for analog televison and radio either will not work
at all with digital television and radio, or will work only
poorly. The present invention is a method of audience
rating for digital television and radio, that uses an
apparatus that can be connected to a digital televison set
or radio. It makes use of identification codes in the
control stream of multiplexed digital transmissions to
record the channel being received.
U.S. Patent No. 4,547,804, issued on October 15, 1985,
to Burton L. Greenberg, discloses a method and apparatus
for the automatic identification and verification of
commercial broadcast programs. A digital encoded
identifying number is embedded in the programs, by which
they can be automatically monitored, to verify that they
have been broadcast as and when intended. However, the
digital number is embedded in what is otherwise an analog
program. This method is usable only during the transition
period from analog to digital broadcasting technology, when
some digital equipment or connection is in use together
with older analog equipment or connections. It will not
work when the broadcasting stations have fully digital
operations, e.g., recording a program in digital form,
storing it digitally on tape or disk, performing nonlinear
2
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
digital edits and digital commercial insertions, and
transmitting digitally in the air, or delivering a digital
stream to a cable or satellite operator to multiplex with
other digital streams. The instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it is fully digital and will work
with broadcasting that is fully digital, and it is designed
fox audience ratings, rather than broadcast verification.
U.S. Patent No. 4,647,974, issued on March 3, 1987, to
Robert J. Butler and Ronald G. Schlameuss, discloses a
system for the automatic insertion of auxiliary video
information into an analog television signal. The system
may be used by a local station to insert its call letters
or logo into network programming. The instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it uses digital signals in digital
15_ broadcasts, and is designed to monitor receivers.
U.S. Patent No. 4,697,209, issued on September 29,
1987, to David Kiewit and Daozheng Lu, discloses a method
and apparatus for identifying television programs, by
detecting the occurrence of events such as scene changes in
a video signal, and extracting a signature from the signal.
Signatures and their times of occurrence are stored and
compared with reference signatures to identify the program.
As the system is independent of the format used to transmit
3
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
the signal, it will work with both analog and digital
television. It has the disadvantage of requiring that a
large volume of reference data be collected for every
possible station and program being transmitted, and for
every site monitored, which will require a large computing
capacity and a long computing time to correlate the two
sets of data to determine which station or program is being
received at each monitored site at each instant that each
receiver is turned on. The instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it is designed to monitor the
reception of digital transmissions only, and will work
efficiently with such transmissions, by using
identification codes in their control streams.
U.S. Patent No. 4,972,503, issued on November 20,
1990, to Everett v. Zurlinden, discloses a method and
apparatus for determining the channel to which a remotely
controlled television receiver is tuned. While it is
independent of the format (analog or digital) used to
transmit the signal, its implementation on a mass scale for
audience ratings will not be practical, as it requires an
individual hardware or software adaptation to each remote
control used in the monitored sites to determine what
function is activated when a key pressing is detected. The
4
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/6226b PCT/US99/1b453
instant invention is distinguishable, in that requires no
such adaptation to remote controls, and may be implemented
even if a remote control is not used.
U.S. Patent No. 5,019,899, issued on May 28, 1991, to
Glenn M. Boles et al., discloses an electronic data
encoding and recognition system for creating digital
signatures from frames of selected video segments such as
television commercials by a digitalizing, compression and
selection process which produces a multi-digit signature
from each frame. The instant invention is distinguishable,
in that it uses digital signals in digital broadcasts, and
may be used to monitor receivers.
U.S. Patent No. 5,278,988, issued on January 11, 1994,
to Jean P. Dejean, Enrico Massetti, Ken Straub and Everett
Zurlinden, discloses a method and apparatus for determining
the transmitting station from which analog program signals
are received and translated by a monitored receiver within
a test area. The instant invention is distinguishable, in
that it is designed to detect and record the reception of
digital transmissions by digital receivers.
U.S. Patent No. 5,425,100, issued on June 13, 1995, to
William L. Thomas, Paul C. Kempter and David H. Harkness,
discloses a multi-level encoded signal monitoring system
5
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
and a universal broadcast code for identifying programs,
commercial, networks, stations, etc. The instant invention
is distinguishable, in that it is designed for and will
work with fully digital programming, and does not require
multiple levels of encoding.
U.S. Patent No. 5,450,122, issued on September 12,
1995, to Leonard D. Keene, discloses an in-station method
and apparatus for encoding analog television programs,
including commercials, with a digital identification code
recorded on a selected video scan line which is not
normally visible to the television viewer, and for
verifying the proper airing of such programs by television
broadcast stations. The instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it is designed for determining
audience ratings for digital television and radio.
U.S. Patent No. 5,450,490, issued on September 12,
1995, to James M. Jensen et al., discloses apparatus and
methods for including an inaudible code in an analog audio
signal, and for decoding it. The instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it uses identification codes in
the control streams of multiplexed digital transmissions.
U.S. Patent No. 5,512,933, issued on April 30, 1996,
to Mark A. Wheatley and Peter Wilcox, discloses a system
6
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
for identifying a program stream being displayed at a
receiver location, by measuring the relative luminance of
a plurality of predetermined areas in each frame of a
television transmission, at both the transmitting station
S and the receiver. As the system is independent of the
format used to transmit the signal, it will work with both
analog and digital television. But, as with Kiewit et al.,
supra, it has the disadvantage of requiring that a large
volume of reference data be collected for every possible
station and program being transmitted, and for every site
monitored, as well as requiring a large computing capacity
and a long computing time to correlate the two sets of data
to determine which station or program has been received at
each monitored site at each instant that the receiver was
turned on. As before, the instant invention is
distinguishable, in that it is designed to monitor the
reception of digital transmissions only, and will work
efficiently with such transmissions, by using
identification codes in their control streams.
U.S. Patent No. 5,574,962, issued on November 12,
1996, to Michel Fardeau et al., discloses a method and
apparatus for automatically identifying a program, by
adding an inaudible encoded message to the audio signal.
7
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99162260 PCT/US99110453
The instant invention is distinguishable, in that it is
designed for multiplexed digital transmissions, and uses
identification codes already present in their control
streams.
U.S. Patent No. 5,646,675, issued on July 8, 1997, to
Robert C. Copriviza et al., discloses a system and method
for monitoring the reception of video program material,
using codes inserted on scan lines. Again, the instant
invention is distinguishable, in that it is designed for
multiplexed digital transmissions, and uses identification
codes already present in their control streams.
None of the above inventions and patents, taken either
singly or in combination, is seen to describe the instant
invention as claimed.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is an audience rating system for
digital television and radio, using identification codes in
control streams of time-multiplexed digital transmissions.
When a television set or radio, that is being monitored
pursuant to the system, is turned on and tuned into a
channel, and each time that the channel is changed, an
8
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
identification code for each audio, video or auxiliary
digital stream of the channel is extracted from the control
stream, and recorded along with the time. The time is also
recorded when the television set or radio is turned off.
This data makes it possible to determine what stations,
channels, and programs members of the audience being
monitored are watching or listening to at any particular
time. In the first preferred embodiment, the multiplexed
digital transmission is received separately by the
television set or radio (or an attached integrated receiver
and decoder? and a meter connected to it. The meter
compares the elementary digital streams of the channel
being received by the television set or radio with digital
streams of each of the channels in the multiplexed digital
transmission, until it finds a match. In the second
preferred embodiment, the meter does not receive the
multiplexed digital transmission separately, but has access
to an elementary stream extracted from the multiplexed
digital transmission by an integrated receiver and decoder.
Tn both embodiments, the meter extracts identification
codes for the channels being received from the elementary
stream. The elementary stream may be accessed through an
auxiliary connector in a digital decoder, through an access
9
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
control card connector, or through soldering electrical
connections to internal points in the integrated receiver
and decoder. In either embodiment, the digital
transmission may be either a terrestrial or satellite
broadcast, or by cable. The data recorded may be stored
on-site in the meter's memory, and/or transmitted to a
central computer for immediate processing. While designed
as an audience rating system, the invention may also be
used in recording reception of, and billing customers for,
pay-per-view digital television programs (or even "pay-per-
listen" digital radio programs, should any be developed).
Accordingly, it is a principal object of the invention
to provide an efficient means of creating reliable audience
rating reports for digital television.
It is another object of the invention to provide an
efficient means of creating reliable audience rating
reports for digital radio.
It is a further object of the invention to provide a
means for recording reception of digital programs for which
a fee is charged to the consumer.
It is an object of the invention to provide improved
elements and arrangements thereof in an apparatus for the
purposes described which is inexpensive, dependable and
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PC'T/US99/10453
fully effective in accomplishing its intended purposes.
These and other objects of the present invention will
become readily apparent upon further review of the
following specification and drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a flowchart showing the method of the first
preferred embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram showing the apparatus
used in the first preferred embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart showing the method of the second
preferred embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram showing the apparatus
used in the second preferred embodiment of the invention.
Similar reference characters denote corresponding
features consistently throughout the attached drawings.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODTMENTS
The present invention is an audience rating system for
digital television and radio, using identification codes in
control streams of time-multiplexed digital transmissions.
11
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
The multiplexed digital transmission may be broadcast
through the atmosphere by electromagnetic radiation, and/or
reflected off satellites orbiting the earth in outer space.
Or it may be transmitted by electricity through metal
cables, and/or by light through fiber optic cables. Figure
1 is a flowchart illustrating the method in the first
preferred embodiment of the invention. Multiplexed digital
transmissions are received simultaneously by both an
integrated receiver and decoder (hereinafter referred to as
the "IRD") connected to the television set or radio
(hereinafter referred to as the "receiver"), and by a meter
which is also connected to the receiver. (IRDs are now
generally separate units attached outside the receiver.
But it is expected that eventually they will be placed
inside digital receivers during manufacture. The
transmission may be received by the meter through an access
control card connector, or the meter may have its own
tuner, which can be an IRD.) Both the IRD and the receiver
must then identify the control stream (sometimes also
called the system stream) in the multiplexed digital
transmission.
The next step is demultiplexing the multiplexed
digital transmission into separate digital streams. The
12
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
control stream is used to allocate digital frames to the
separate digital streams. In digital television the
separate digital streams include at least one video stream
for each channel, at least one audio stream for each
channel, the control stream itself, and may also include
auxiliary streams for each channel. (In digital radio
there is, of course, no video stream.) (As used in this
application, a "channel" means one or more digital streams
that transmit only one program or commercial advertisement
at a time, and applies to digital radio as well as
television.) Identification codes in the control stream
are used to cause only the digital streams of the channel
to which the receiver is tuned to be passed to the
receiver, so that the channel's audio digital streams are
converted to sound, and the channel's video digital streams
are converted to pictures.
When the meter receives a signal indicating that the
receiver has been turned on, or that the channel that the
receiver is tuned to has been changed, the meter selects
one or more audio, video and/or auxiliary digital streams
belonging to a first channel in the multiplexed digital
transmission for comparison with the digital streams of the
channel to which the receiver is tuned. If the comparison
13
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
shows that the digital streams are identical, the meter
then extracts the identification codes of the streams that
match from the control stream. If the digital streams are
not identical, the meter selects digital streams belonging
to the next channel for comparison, and continues selecting
and comparing digital streams belonging to each channel in
the multiplexed digital transmission, until a match is
found, and the identification codes of the matching digital
streams received by the meter are extracted from the
control stream received by the meter. The identification
codes extracted are recorded by the meter, along with the
time and date. (If no match in found, a message that the
digital stream cannot be identified may be recorded.)
(Alternatively, the meter may continuously compare the
digital streams in each of the channels in the multiplexed
digital transmission to the digital streams in the channel
to which the receiver is tuned, and extract and record the
identification codes and the time and date whenever the
continuous comparison shows that the channel has been
changed. ) The meter also records the time and date when
the receiver is turned off or reception is otherwise ended.
Assuming that the times each program and each commercial
are transmitted on each channel belonging to each station
14
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
are known, the data recorded by the meter makes it possible
to determine what stations, channels, programs and
commercials members of the audience being monitored are
watching or listening to at any particular time.
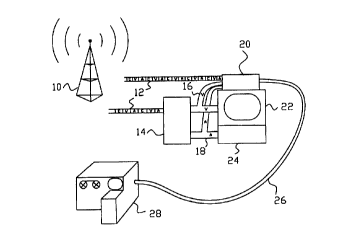
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram showing the apparatus
used in the first preferred embodiment of the invention.
The digital television station 10 broadcasts (or transmits
by cable) a time-multiplexed digital stream 12 containing
segments of a control stream C, a video stream V, and an
audio stream A. (In practice many video and audio streams
would normally be broadcast together in a single time-
multiplexed stream, but for the sake of clarity, only a
single channel with one of each is shown.) The multiplexed
stream is then received and demultiplexed by an integrated
receiver and decoder 14 into the control stream (not
shown), the video stream 16, and the audio stream 18. The
meter 20 independently receives the same multiplexed
stream, and likewise demultiplexes it into the control
stream and video and audio streams. The video stream of
the channel selected is passed to both the cathode ray tube
22 (or liquid crystal display or other visual display
device) and the meter, which compares it to each video
stream in the multiplexed digital stream. The audio stream
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99162260 PCTIUS99/10453
of the channel selected is passed to both the speaker 24
and the meter, which compares it to each audio stream in
the multiplexed digital stream. (Of course, in the case of
radio, there are no video streams to be compared). The
video stream received causes pictures to be displayed by
the visual display device, and the audio stream received
causes sounds to be emitted by the speaker. Information
recorded by the meter may be stored in an internal memory
unit for later retrieval. Optionally, in order to
instantly generate audience ratings in real time,
information recorded in the meter may be transmitted by a
cable 26 or other means to a computer 28 where data from
many different receivers being simultaneously monitored may
be compiled.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart showing the method of the second
preferred embodiment of the invention. In the second
embodiment, only the IRD receives a multiplexed digital
transmission, identifies its control stream, and
demultiplexes the separate digital streams. As in the
first embodiment, the IRD uses identification codes in the
control stream to select the audio and video streams in the
channel to which the receiver is tuned, and passes the
streams to the receiver, where they are converted into
16
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99162260 PCTNS99110453
sound and/or pictures. The IRD extracts the elementary
stream for the channel (i.e., the audio, video and
auxiliary streams for the channel, and the identification
codes for these streams) and makes it available on an
auxiliary connector (usually for the purpose of
descrambling a controlled access channel) and passes it to
the meter, which extracts the identification codes, and
records them along with the time and date when the receiver
is turned on or the channel that the receiver is tuned to
is changed. (Alternatively, the meter may have its own
tuner, which can be an IRD with a conditional access module
for a specific broadcaster.) As before, the meter also
records the time when the receiver is turned off or
reception is otherwise ended.
Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram showing the apparatus
used in the second preferred embodiment of the invention,
showing that the multiplexed digital transmission 12 is
received only by the IRC 14, which passes the elementary
stream 30 (including an audio stream, a video stream, and
identification codes) for the channel to which the receiver
is tuned to the meter 20. In the second embodiment, the
elementary stream may be accessed by the meter through an
auxiliary connector in a digital decoder, or through an
17
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
access control card connector, or by soldering an
electrical connection to an internal point in the IRD.
In either embodiment, it is possible that a plurality
of multiplexed digital transmissions can be received at
different frequencies. In this case, when the receiver is
turned on, the meter records a first frequency received,
and the time reception of the first frequency begins, and
when the frequency received is changed, the meter records
any subsequent frequency received, and the time reception
of the subsequent frequency begins.
Auxiliary streams for a channel may carry binary
strings or text characters, by means of which information
concerning the station or program being transmitted may be
displayed by the receiver. Information concerning programs
and/or stations may be displayed in a menu to enable
viewers to select transmissions, or to enable viewer to see
which transmissions have been selected.
The invention is primarily designed and intended for
use in compiling audience rating reports, but may also be
used in recording reception of, and billing customers for,
pay-per-view digital television programs (or even "pay-per-
listen" digital radio programs, should any be developed).
18
CA 02323937 2000-09-14
WO 99/62260 PCT/US99/10453
It is to be understood that the present invention is
not limited to the preferred embodiments described above,
but encompasses any and all embodiments within the scope of
the following claims.
19