Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02325698 2003-08-O1
d~:,~, s~x;.'FH~t:~~S 'x.~3~~~-~~ss-'?~
~.~o.~.~~
~s ~'~~' 4~~'~,~z~:~'~~: E~"i'"°~":~~F"s f~:~:'s'L~NU; ~C3 ~~
t:,CDen~.~~'EF~ t~x3~'~~~'r"~;;F.Fw; ~~',3~' ;'e~3r ~'k,°lf;r~,
rf'~~'~E~'~C,,"e s'''ts :'~'k.~~~E,~,? i'.3s'';~f'~ r'~ ~'~'E~5:2~~t~
3fe;F;'~,'k F;'k~' ~~.~f~3:c~'3'~,
~~~~~F~rr ~~~~~~;i~~.;~1~-~ : ~.~~ ~r~~~~~ s~~~f~; t~:~c~~ r~l~tr~~s
°..:~s ~ c~a~t~~ ~'~~sz~a:~~~:~
~x~:~:~~=v~ t~~; ~~~S~i~~~i~s~ ~~ t~~ w~~s~~g ~~~~~~~"i~to t~~
W~~~~;~ ~~~~~~~~a~~~ ~~ ~~~~i~ ~r~w~~aiF~:~, ~~~: ~~~~i~t~~~~nw~ ~ ~~~~~Y
~~~ ~~>n r~~~~~~~~ ~~a~~~s~': ~s~ ~~~~~r~~ ~~~t~~~~~.
~. ~"k'~' t~'~'r'e'#t~'F,~",~" :"Fs"'t»s~f,'r'sus; ~.~,''?a'~~>' ~:,f~~~6ff~
iF~f3'YSfs x~'F~fFs x~'t.;,. c",~~'k~~~~.'~F.'.'F' ~:~'3.r;51~';:~~'3
k.~i f'~f~...~.W;..'k'~t°vt a~~',~.'S'~ '~f"~~~~~o~~~~
~.'',°~r.Sa.f'~5:~~'w~ ~yi.~.~~"'f ~C~4~.i ;'.,~~3~~3.~'.~'3~3~ ~CY.S
~f.nCi S,'~'~~~k~~c~ :.$~S i5' t!~!~'"~
~''F~Sa~ ~~"st'~'sPE~'~~ t3~.f~~s s'3~~5~,s ~ 's'~"s~~'i~Yls'''~f~3 '~;~s"~ ~~
r.3" s~'~'~» ~~~.~a'~~'~"s~~:,~ s'~''sl"F"sw::3~s~'~~is~
E.'~si:3'yf~fE'3~'~~'wz"F~'?'E ff~.'o'a''~~3v'~ ~G ~~"fc". xi~~.'3'
~'E's~s~f~s k;;~"si~ .c..z~~1r,3'v'''s,s3t's~'',~~ ~.f1'u' .~;i~z,ci:<f~
a~c"'e'L'c<F"~~~~
..e#'3~.'~5 °>'~'F'~' s'~~F~'~.°~~'~~~ b'~~~,'.'~Z~
'~~~ ~'~~:a'~:~:~ ~Y ~~~~~c~~;~' tFi~c~~ ~~ ;.~r~~~ ~~s;~~~~'z~ ~~k~ ;;~.~~i;q
~~~~~~~~
~~~~~:~5 ~ Fr~~~~~~ fad a~ I>H~~wx~ t;~~~ ~~~~:~l~f'~~~~ ;~I~'y 'sr~~~~~;~;~
~~~ws= ;:sf
~'8~~~~~sE~~"i;r.:i~~ k:.2~~'f~:'$~ wX~s~i;~31(~ E~'3 ~
a:,f:".E~er~~f;~t:~~~Ft?~ .~t3"~~~~L~t?'3.
'H '~..r'u:vc:"";.,~.-~'~'~
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
2
Additionally, a finishing blade is disposed downstream relative to the
applicator blade such that the finishing blade is adjustably urged against the
applied coating material for applying a finished coating contour to the
coated web.
However, in recent years, there has been a tendency in the coating
industry toward more specific or tailor-made coating compositions. Such
specific coating compositions typically include an all synthetic composition
as opposed to the more traditional types of coating material which include
starch, or other materials as the binder, respectively, co-binder.
More specifically, in a typical coating composition utilizing starch as
the binder, such compositions exhibit coating characteristics approaching
that of a Newtonian liquid. More particularly, as in the case of water, such
typical coating compositions display little change in viscosity when shear
forces are applied thereto.
However, with the trend toward the use of the aforementioned
synthetic coatings, there is a tendency for the viscosity of the coating
material to decrease rapidly upon application of shear forces thereto.
Accordingly, in the prior art fountain coater when, for example, the
coating material is supplied to the coating chamber from one side thereof,
inherently, more shear is applied to the synthetic coating material at the
inlet end of the chamber rather than at the opposite end of the coating
chamber.
Consequently, the coating material flowing adjacent to the inlet end .
of the chamber acquires a lower viscosity leading towards splashing of the
coating material adjacent to the inlet end. However, at the opposite end of
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
3
the coating chamber, the coating material is subjected to lesser shear
forces and the viscosity of such coating material will remain relatively high.
Although it is possible to supply the coating material from both ends
of the chamber or indeed fram multiple inlets along the cross-machine
direction of the coating chamber, clearly such a supply arrangement
becomes extremely complicated. Such is the case, particularly in view of
the fact that the coater housing must be permitted to rotate for adjustment
of the exit slot relative to the moving web or surface.
The present invention overcomes the aforementioned problem of
variations in the viscosity in the cross machine direction by the application
of uniform viscosity to the coating material at an exit slot of the coating
chamber.
More specifically, in order to accommodate various coating
formulations, the present invention provides a shear imparting means which
can be rotatable or stationary and which can be conveniently mounted in
the coating chamber. In the case of a rotatable shear imparting means, the
arrangement is such that the rotational speed of the shear imparting means
may be varied to optimize the degree of shear imparted to the coating
composition in order to insure uniform viscosity in a cross-machine
direction flowing through the exit slot and onto the moving web or surface.
Therefore, it is the primary feature of the present invention to
provide a coating apparatus which overcomes the aforementioned
inadequacies of the prior art arrangements and which makes a significant
contribution to the art of coating a moving web or surface.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
4
Another feature of the present invention is the provision of a coating
apparatus which imparts shear forces to the coating material so that the
viscosity of the coating material in a cross-machine direction remains
substantially uniform when such coating material is applied to a moving
web or surface.
Another feature of the present invention is the provision of a
rotatable shear imparting means which is driven at a speed commensurate
with the type of coating formulation being used in order to optimize the
cross-machine directional flow of such formulation onto the moving web.
Other features and advantages of the present invention will be
readily apparent to those skilled in the art by a consideration of the
detailed
description contained hereinafter taken in conjunction with the annexed
drawings.
The present invention applies controllable or variable shear to the
coating material thus decreasing its viscosity and as a result improving the
flow of the coating material in the chamber.
Moreover, in a conventional coating applicator, such as a pre-
metering chamber, as stated hereinbefore, the flow of coating material will
be non-uniform along a cross-machine direction as there is a tendency for
the coating material to Magnate at the end of the coating chamber opposite
to the chamber inlet.
By way of example, in Rotogravure Printing there is a trend toward
the use of specific or tailor-made formulations which typically have very
shear thinning flow characteristics. Such formulations exhibit large
variations in coating material flow in the coating chamber from the inlet to
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
the other side of the chamber. These variations result in uneven viscosities
of the coating material across the width of the web or surface to be
coated.
Applicant has discovered that the provision of perforate static
elements within the coating chamber enhances the cross-machine
directional uniformity of the applied coating.
Nevertheless, although the provision of a static triangular shaped
perforate element together with a v-shaped static element between the
triangular shaped element and the exit slot improved uniformity, it was also
discovered that after cleaning the coating chamber with water, coating
formulation was still found to be lodged within the static elements when
the coating chamber was opened for inspection.
Accordingly, and as encompassed by the present invention, the
provision of a rotatable shear imparting means includes a further advantage
in that such rotary shear imparting means is self-cleaning without having to
dismantle the coating apparatus when changing from one formulation to
another.
Also, as stated hereinbefore, the provision of a rotary shear
imparting means having a variable speed of rotation makes it possible for
the speed of rotation and the applied shear to be adjusted to enhance the
amount of shear applied to the formulation in order to optimize cross-
machine directional uniformity.
Whereas, the inventive concept according to the present invention
may be applied to a coating chamber of a typical BA 1500 coater or any
other chamber type coater, it has been further discovered that it is
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98!44200 PCT/US98/04008
6
desirable to have the rotatable shear imparting means disposed as close as
possible to the inlet end of the narrow exit slot, that is, as close as
possible
to the web or surface to be coated.
Therefore, although in the BA 1500 coater, the coating chamber is
typically of a pear-shaped or tear drop shaped configuration, a more ideal
shape for the coating chamber would be cylindrical so that the rotary shear
imparting means can be disposed concentrically within the coating chamber
for rotation therein and so that the shear imparting element is disposed
close to the exit slot. However, the ideal shape may not always be
desirable taking into account the abrasion characteristics of highly pigment
charged coating materials.
The present invention in its preferred form provides a coating
apparatus having a driven shaft which is provided with readily replaceable
shear imparting rotary elements.
Also, the apparatus according to the present invention permits the
feeding of coating material from one side only into the coating chamber
thereby avoiding the feeding of coating material from both ends of the
coating chamber or at multiple points along the length thereof as in a so-
called Christmas tree type configuration. The aforementioned one sided
feed arrangement is clearly the type that is preferred by the coating
industry.
The variable shear imparting mechanism according to the present
invention also improves the distribution of the coating material in a cross-
machine direction thereby providing more uniform flow characteristics and
lower viscosity of the coating material.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
7
Additionally, as stated hereinbefore, the present invention provides a
coating apparatus which avoids the problem of increased shear adjacent to
the inlet end of the coating chamber. The increased shear results in
improved viscosity which permits a lower operating pressure at the exit slot
of the coater chamber thereby avoiding splashing at the inlet edge or inlet
edges as in the case of a coating chamber fed from both sides thereof.
Moreover, coating formulations and particularly synthetic
formulations unlike stock flowing through a papermachine headbox, exhibit
shear thinning characteristics. Shear thinning material such as tomato
ketchup and the like, tends to flow more readily when shear forces are
imparted thereto. Thus, by rapidly shaking a bottle of ketchup, shear is
imparted to the ketchup which enhances the uniform flow of the material
through the neck of the ketchup bottle.
In an analogous manner, when shear is imparted to the coating
formulation within the coating chamber as by the rotation therein of a
perforate cylindrical wall disposed within the coating chamber, such shear
has an affect on the shear thinning characteristics of the coating
formulation thereby enhancing the uniform flow thereof through the exit
slot.
More particularly, the imparting of shear forces to the coating
material provides a more homogenous coating material having a uniform
viscosity and flow behavior at the exit of the slot and at any point along
the length of the slot in a cross-machine direction.
Additionally, with the rotary shear imparting means according to the
present invention, it is possible to operate the coater with a lower pump
pressure.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
8
Although the rotary shear imparting means rotates at a selectable
rotational speed within the coating chamber, and a certain amount of
clearance between the shear imparting means and the chamber is required
for practical operation, it is envisaged that the aforementioned clearance
may be as little as 2-3 millimeters.
The coating apparatus according to the present invention provides
means for even and uniform application of coating material while providing
rapid setting of the coating formulation upon application thereof to the
web.
The present invention relates to a coating apparatus and a method
for applying coating material onto a moving web. The apparatus includes a
housing which defines a chamber for the reception therein of the coating
material. The housing also defines an exit slot for the passage
therethrough of the coating material from the chamber.
Shear means are disposed within the chamber for applying shear to
the coating material prior to application of the coating material onto the
web or surface. The shear reduces the viscosity of the coating material
and maintains a reduced viscosity of the coating material prior to
application thereof onto the web or surface so that uniform flow of the
coating material through the exit slot taken in a cross-machine direction is
facilitated.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the shear means
includes a member of preferably cylindrical configuration. More specifically,
the shear means includes a cylindrical member which has a peripheral
perforate wall rotatably disposed within the chamber about a rotational axis
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
9
disposed substantially parallel to the cross-machine direction of the moving
web. The arrangement is such that during operation of the apparatus, the
coating material flows into the member and through the perforate wall
thereof toward the exit slot so that shear is applied to the coating material
during passage through the perforate wall for facilitating the application of
a uniform flow of coating material onto the moving web or surface.
More specifically, the shear means is rotatably disposed within the
chamber. The coating apparatus also includes a variable speed drive means
drivingly connected to the shear means for varying the rotational speed of
the shear means within the chamber commensurate with the type of
coating material being applied to the moving web in order to optimize the
uniform flow of the coating material through the exit slot.
Many variations and modifications of the present invention will be
readily apparent to those skilled in the art by a consideration of the
detailed
description contained hereinafter taken in conjunction with the annexed
drawings. However, such modifications and variations fall within the spirit
and scope of the present invention as defined by the appended claims.
Fig. 1 is a sectional view of a typical prior art fountain type coater.
Fig. 1 A is a side etevational view of another prior art coater.
Fig. 1 B is a side elevational view of yet another prior art coater.
Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a coater apparatus according to
one embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a reduced bottom view partially in section of the apparatus
shown in Fig. 2.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view of a coater apparatus according to
another embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 5 is an enlarged sectional view of a preferred embodiment of the
coating apparatus according to the present invention.
Fig. 6 is a bottom view partially in section of the apparatus shown in
Fig. 5.
Fig. 7 is a sectional view of yet another embodiment of the present
invention.
Fig. 8 is a sectional view taken on the line of 8-8 of Fig. 7.
Fig. 9 is a sectional view taken on the line of 9-9 of Fig. 7.
Fig. 10 is a sectional view of yet a further embodiment of the
present invention.
Fig. 11 is a sectional view of still another embodiment of the present
invention; and
Fig. 12 is a sectional view of yet another embodiment of the present
invention.
Similar reference characters refer to similar parts throughout the
various embodiments of the present invention.
Fig. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a typical fountain coater of the
type known as the BA 1500 coater manufactured by Beloit Corporation.
The coating apparatus generally designated 10 applies coating
material 12 on to a moving web 14. The apparatus includes a housing 16
which defines a chamber 18 for the reception therein of the coating
material 12. The housing 16 also defines an exit slot 20 for the passage
therethrough of the coating material 12 from the chamber 18.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
11
The enlarged inset shown in Fig. 1 shows a metering or applicator
blade 22 which is disposed immediately downstream relative to the exit
slot 20 for metering or applying the coating 12 onto the moving web 14
supported by a rotatable backing roll 24.
A finishing blade 26 is disposed downstream relative to the
applicator blade 22 for applying a finished configuration to the coating
material 12.
Fig. 1 A is a side elevational view of a coater according to U.S.
Patent No. 5,104,697 assigned to Valmet.
Fig. 1 B is a side elevational view of a coater according to U.S. Patent
No. 4,869,933 assigned to Voith.
The concept of the present invention may be applied as a retrofit to
any of the coaters shown in Figs. 1, 1 A or 1 B.
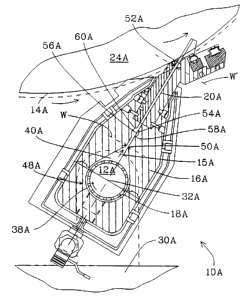
Fig. 2 is an enlarged cross-sectionalof a coating
view apparatus
generallydesignated 10A according to one present
embodiment of the
invention.More specifically, Fig. 2 shows concept of present
the the
inventionincluded as a retrofit to the coater manufactured
BA 1500 by
Beloit applies coatingmaterial
Corporation.
The
coating
apparatus
10A
12A a moving web indicated by the line 14A. coating
onto dashed The
apparatus10A includes a housing 16A defininga chamber for
18A the
receptiontherein of the coating material The housing
12A. 16A also
defines coating
an
exit
slot
20A
for
the
passage
therethrough
of
the
material2A from the chamber 18A.
1
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT1US98/04008
12
Shear means generally designated 28A are disposed within the
chamber 18A for applying shear to the coating material 12A prior to the
application of the coating material 12A on the web 14A. The shear
reduces the viscosity of the coating material 12A and maintains a reduced
viscosity of the coating material 12A prior to the application of the coating
material 12A onto the web 14A. The arrangement is such that a uniform
flow as indicated by the arrow 15A of the coating material 12A through
the exit slot 20A taken in a cross-machine direction is facilitated.
As shown in Fig. 2, the coating apparatus 10A also includes a frame
30A with the housing 16A being pivotally secR~red to the frame 30A about
a pivotal axis 32A which is disposed substantially parallel to the cross-
machine direction of the moving web 14A. The arrangement is such that
adjustment of the location of the exit slot 20A relative to the moving web
14A is permitted.
The BA 1500 coater partially shown in Fig. 2 typically includes the
chamber 18A which is of generally tear-drop shaped configuration when
taken in a section perpendicular to the cross-machine direction of the
moving web 14A.
More specifically, the tear-drop sectional configuration of the
chamber 18A includes a first portion 38A having a partially cylindrical
configuration and a second portion 40A which is disposed between the
first portion 38A and the exit slot 20A. The second portion 40A is of
triangular sectional configuration.
Fig. 3 is a reduced bottom plan view partially in section of the
arrangement shown in Fig. 2 and shows the coating apparatus as including
an inlet 42A which is disposed in fluid communication with the chamber
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
13
18A for permitting the flow as indicated by the arrow 44A of the coating
material 12A through the inlet into the chamber 18A.
As shown in Fig. 3, the chamber 18A includes a first and a second
end 46A and 48A, respectively, the inlet 42A being connected to the first
end 46A of the chamber 18A.
The exit slot 20A also includes a first and a second extremity 50A
and 52A, respectively with the first extremity 50A extending from the
chamber 18A and the second extremity 52A being disposed adjacent to the
moving web 14A during operation of the coating apparatus 10A.
As shown in Fig. 2, the exit slot 20A tapers from the first extremity
50A toward the second extremity 52A. The arrangement is such that the
second extremity 52A of the exit slot 20A is more narrow than the first
extremity 50A.
More specifically, the first extremity 50A has a width W within the
range 2 to 4 millimeters and preferably 3 millimeters while the second
extremity 52A has a width W' within the range .6 to 1.9 millimeters and
preferable 1.5 millimeters.
As shown in Figs. 2, the exit slot 20A further includes an expansion
chamber 54A which is disposed between the first and the second extremity
50A and 52A, respectively. The expansion chamber 54A is of generally
cylindrical sectional configuration having an axis of symmetry 56A disposed
substantially parallel to the cross-machine direction of the moving web
14A.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
14
The expansion chamber 54A as shown in Fig. 2 also includes an
upstream portion 58A which tapers outwardly in a direction from the first
extremity 50A toward the second extremity 52A and a downstream portion
60A which tapers inwardly in a direction from the first extremity 50A
toward the second extremity 52A.
Fig. 4 is a sectional view of a further embodiment of the subject
invention in which the shear means 28B includes a perforated plate 62B
which extends along substantially the entire width of the chamber 18B in a
direction substantially parallel to the cross-machine direction of the moving
web 14B. The arrangement is such that during operation of the apparatus
10B, when the coating material 12B flows through the perforated triangular
shaped plate 62B toward the exit slot 20B, a shearing action is applied to
the coating material 12B which reduces the viscosity of the coating
material 12B so that such reduced viscosity is maintained during passage
of coating material 12B through the exit slot 20B such that uniformity of
flow of coating material 12B onto the moving web 14B in a cross-machine
direction is enhanced.
Also, as shown in Fig. 4, coating material 12B is supplied from an
inlet to the inside of the plate 62B. The coating material has shear applied
thereto as the coating flows through the perforated plate 62B and a V-
shaped perforated plate 63B disposed between the plate 62B and the exit
slot 20B.
Fig. 5 is a sectional view of a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, in which the chamber 18C is of cylindrical configuration. The
chamber 18C has an axis of symmetry 36C which is disposed substantially
parallel to the cross-machine direction of the moving web 14C.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCTNS98/04008
In the preferred embodiment of the present invention as shown in
Fig. 5, the shear means 28C includes a member 64C of substantially
cylindrical configuration. The cylindrical member 64C has a peripheral
perforate wai! 66C which is rotatable disposed within the chamber 18C
about rotational axis 36C disposed substantially parallel to the cross-
machine direction of the moving web 14C. The arrangement is such that
during operation of the apparatus 10C, the coating material 12C flows into
a stationary perforated distribution tube 62C extending in a cross machine
direction from the inlet. Thereafter, the coaxing 12C flows through the
member 64C and through the perforate wall 66C thereof toward the exit
slot 20C so that a shear force is applied to the coating material 12C during
passage thereof through the wall 66C for facilitating the application of a
uniform flow of coating material 12C onto the moving web 14C.
In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the shear
means 28C is rotatably disposed within the chamber 18C as indicated by
arrow 19C.
Fig. 6 is a bottom view of the apparatus 10C shown in Fig. 5. As
shown in Fig. 6, the coating apparatus 10C also includes a variable speed
drive means 70C drivingly connected to the shear means 28C for varying
the rotational speed of the shear means 28C within the chamber 18C
commensurate with the type of coating material 12C being applied to the
moving web 14C in order to optimize the uniform flow of the coating
material through the exit slot 20C as shown in Fig. 5.
As shown in Figs. 2-6 coating apparatus 10A-10C applies a shear
thinning coating material 12A-C onto a moving web 14A-C. The apparatus
10A-C includes a housing 16A-C defining a chamber 18A-C for the
reception therein of the coating material 12A-C. The housing 16A-C also
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
16
defines an exit slot 20A-C for the flow therethrough of the coating material
12A-C from the chamber 18A-C.
Shear means 28A-C are disposed within the flow for imparting shear
to the coating material 12A-C prior to application of the coating material
12A-C on the web 14A-C. Such shear alters the shear thinning
characteristics of the coating material 12A-C so that uniform flow of the
coating material 12A-C through the exit slot 20A-C when taken in a cross-
machine direction is maintained.
The present invention also encompasses a method of applying a
coating 12A-C on a web 14A-C. The method comprises the steps of
feeding the coating 12A-C into a chamber 18A-C defined by the coater
housing 16A-C. The coater housing 16A-C also defines an outlet slot 20A-
C which extends from the chamber 18A-C toward the web 14A-C.
The method includes the step of applying shear to the coating so
that the viscosity of the coating flowing from the chamber 18A-C through
the slot 20A-C is reduced such that taken in a cross-machine direction, a
uniform flow rate of the coating is maintained as the coating flows through
the slot 20A-C for application onto the web.
Fig. 7 is a sectional view of a further embodiment of the present
invention. Fig. 7 shows a coating apparatus 10D having a shear means
generally designated 28D. The shear means 28D includes a plurality of
disks 72D, 73D and 74D of various diameters.
Fig. 8 is a sectional view taken on the line 8-8 of Fig. 7 and shows
that each of the disks 72-74D and as shown in Fig. 8 the disk 74D as
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCTNS98/04008
17
having a plurality of peripheral cutting edges 76D, 77D and 78D for
imparting shear to the coating material 12D.
Fig. 9 is a sectional view taken on the line 9-9 of Fig. 7 and shows
the plurality of disks of various diameters including disks 72D-74D. The
drive means 70D drives the longitudinal shaft 71 D to which all of the disks
72-74D are rigidly secured.
Fig. 10 shows yet another embodiment of the present invention
which is similar to the embodiment shown in Figs. 5 and 6. However, in
the arrangement shown in Fig. 10, the apparatus 10E includes a cylindrical
shear imparting means 28E in which the spacing of the shear imparting
holes such as 80E and 81 E is greater at the inlet 42E than at the opposite
end 48E of the chamber 18E. In the aforementioned manner, the amount
of shear imparted to the coating can be varied from the first end 46E to the
second end 48E of the chamber 18E.
Additionally, Fig. 1 1 is a diagrammatic representation of yet another
embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 1 1 shows a coating apparatus
10F having a plurality of inlets 42F and a shear imparting means 28F which
defines a plurality of holes 80F-81 F disposed between the first and second
ends 46F and 48F of the chamber 18F.
Fig. 12 is a diagrammatic representation of another embodiment of
the present invention. Fig. 12 shows a coating apparatus 10G in which the
shear imparting means 28G includes a plurality of disks 72G, 73G and 74G
disposed between the first and second ends 46G and 48G of the chamber
18G. The arrangement is such that a uniform flow and viscosity of the
coating material is attained prior to the flow of the coating material through
the exit slot for application on to the web.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
18
In both the arrangements shown in Figs. 11 and 12, the holes and
disks, respectively, are dimensioned to accommodate the inlet points 100F
and 1006 respectively, where lower shear is needed.
As will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, there are many
variations that fall within the spirit and scope of the inventive concept of
the present invention. The configuration of the shear imparting means will
in many respects depend on the type of coating material being used and
the quality of the web that is to be coated.
The shear rate is influenced by the rotational speed of the motor and
the number and diameter of the holes in the rotating cylinder.
In the case of the embodiment including rotating disks, the shear rate
will be influenced by the diameter of the disks and the dimensions of the
razor edges which may be of rectangular configuration.
Accordingly, the rate of shear will increase with the number of holes
or slits provided in the rotating cylinder and will increase when the diameter
of the holes or width of the slits is decreased.
Similarly, the shear rate will increase with the number and diameter
of the disks and the size of the razor edges.
The shear rate can be optimized by varying the design of the rotor
shear imparting means dependent on the number of inlets for the coating
color.
CA 02325698 2000-09-25
WO 98/44200 PCT/US98/04008
19
Additionally, the rate at which the shear imparting means is rotated
may be adjusted relative to the coating color pump speed in order to
optimize uniformity of flow.
in general, the shear generated by the shear imparting means should
ideally be higher than the shear generated by the structure following the
shear generator and prior to the metering or pre-metering elements such as
a blade or rod.
The concept of the present invention also includes the application
thereof in connection with a blade metering size press where the coating is
applied to the surface of a roll for subsequent transfer to a web moving
past such coated roll.
The present invention provides a unique coating apparatus which is
eminently suitable for the application of highly synthetic coating
compositions in which the application of shear to the coating material
causes reduced viscosity and uniform flow of the coating material onto the
web to be coated.
While the invention has been described in connection with certain
shear producing elements which are currently considered to be the best
practical way of imparting shear to the coating mixture, it will be
understood by those skilled in the art that other shear inducing elements
can be readily used. For example, a smooth non-perforate cylinder will
impart a certain amount of shear and can be useful for certain coating
formulations. Other shear inducing devices well known to those versed in
the art of preparing coating mixture can be readily adapted to practice the
principles of the present invention.