Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
INDOL-3-YL-CYCLOI~XYL AMINE DERIVATTVES FOR TEIE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION (5-
HTl RECEPTOR
ANTAGONISTS)
FIELD OF INVENTION
This invention relates to compounds useful for the treatment of diseases
affected
by disorders of the serotonin-affected neurological systems, such as
depression and
anxiety. More specifically, this invention relates to various indol-3-yl-
cyclohexylamine
derivatives useful for the treatment of such diseases.
BACKGROUND OF INVENTION
Phanmaceutical compounds which enhance the transmission of serotonin (5-
HT) are useful for the treatment of many psychiatric disorders, including
depression
and anxiety. The first generation of non-selective serotonin-affecting drugs
operated
through a variety of physiological functions which cause them to possess
numerous
undesired side effects, such as blurred vision, dry mouth, and sedation. The
more
recently introduced compounds, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
(SSRIs), act
predominately by inhibiting 5-HT, which is released at the synapses, from
being
actively removed from the synaptic cleft via a presynaptic serotonin transport
carrier.
Since SSRIs require several weeks before they exert their full therapeutic
effect, this 5-
HT blockade mechanism cannot fully account for their therapeutic activity. It
is
speculated that this two week induction which occurs before a full
antidepressant effect
is observed, is due to the involvement of the 5-HTlA autoreceptors which
suppress the
firing activity of the 5-HT neurons, causing a dampening of the therapeutic
effect.
Studies suggest that after several weeks.of SSRI administration, a
desensitization of the
5-HT autoreceptors occurs allowing a full antidepressant effect in most
patients.
Hence, it is believed that overriding the negative feedback with the 5-HT1A
antagonists
would increase and accelerate the clinical antidepressant response. Recent
studies by
Artigas et al., Trends Neurosci., 19:378-383 (1996) suggest a combination of 5-
HTIA
activity and inhibition of 5-HT uptake within a single molecular entity can
achieve a
more robust and fast-acting antidepressant effect.
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
-2-
U.S. Patent No. 3,058,980 discloses the preparation of compounds having the
following formula which are claimed to exhibit analgesic activity.
R3
R~~ I
0 1
NR~ R2
PCT Patent No. WO 89-07596A discloses the preparation of compounds of the
following formula which are active in a variety of central nervous system
disorders,
including depression and schizophrenia.
R5 ~ R4
N
R3 r~ I
NR~R2
Lastly, U.S. Patent No. 4,612,312 discloses compounds of the following
formula as being potentially useful as anxiolytic and antihypertensive agents.
R
r-~'
R,-~ I o
4
R3 N-~CE"~2)n
R5
O
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is directed to novel molecules which have the ability to
act
concomitantly at the 5-HT1A autoreceptors and with the 5-HT transporter. Such
compounds are, therefore, potentially useful for the treatment of depression
and other
serotonin disorders.
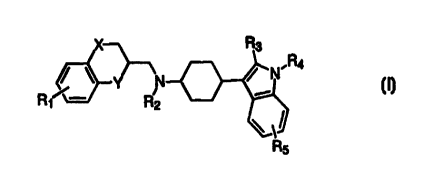
The compounds of the present invention are indol-3-yl-cyclohexyl amine
derivatives represented by Formula I:
R
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
-3-
wherein:
I
R, and RS are each, independently, hydrogen, halogen, lower alkoxy, lower
alkyl,
cyano, or trifluoromethyl;
R2 and R4 are each, independently, hydrogen, lower alkyl, phenyl, or
substituted
phenyl;
R3 is hydrogen or lower alkyl; and
X and Y are each, independently, O, NR6, or CHZ, wherein
R6 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, phenyl, or substituted phenyl; or
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Preferably, the compounds of the present invention are those represented by
Formula I, wherein:
R, and RS are each, independently, hydrogen, or halogen;
RZ and R4 are each hydrogen;
R3 is hydrogen; and
X and Y are each, independently, O or NR6, wherein R6 is hydrogen; or
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
More specifically, the compounds of the present invention are selected from
the
following:
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[ 1,4]oxazine-2-ylmethyl)-[cis-4-(5-fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)-
cyclohexyl]-amine;
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-2-ylmethyl)-[trans-4-(5-fluoro-lH-indol-3-yl)-
cyclohexyl]-amine;
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[ 1,4]oxazine-3-ylmethyl)-[cis-4-(5-fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)-
cyclohexyl]-amine; and
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[ 1,4]oxazine-3-ylmethyl)-[trans-4-(5-fluoro- 1 H-indol-3-
yl)-
cyclohexyl]-amine.
As used herein, the terms "lower alkyl" and "lower alkoxy" are meant to
include
straight and branched carbon chains containing 1-6 carbon atoms. The term
"halogen"
is meant to include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The "substituted
phenyl"
may include substitution by halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and cyano
groups.
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
-4-
The compounds of Formula I also may be used in the form of a
pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt having the utility of the free
base. Such
salts, prepared by methods well known to the art are formed with both
inorganic or
organic acids, for example: fumaric, malefic, benzoic, ascorbic, pamoic,
succinic,
bismethylenesalicylic, methanesulfonic, ethanedisulfonic, acetic, oxalic,
propionic,
tartaric, salicyclic, citric, gluconic, lactic, maIic, mandelic, cinnamic,
citraconic,
aspartic, stearic, palmitic, itaconic, glycolic, p-aminobenzoic, glutamic,
benzene-
sulfonic, hydrochloric hydrobromic, sulfuric, cyclohexylsulfamic, phosphoric
and
nitric acids.
The compounds of the present invention may be prepared by any suitable
method known to those skilled in the art. However, the present compounds may
be
prepared according to any one of Schemes 1-3 set forth below. In the Schemes,
the
intermediate compounds exemplified hereinafter are identified in parenthesis.
The
compound produced in each of the Schemes is identified by reference to the
appropriate
Example.
The compounds of Formula I are generally prepared by the overall sequence
indicated in Schemes 1-3 as follows. In the Schemes, the intermediate
compounds
exemplified hereinafter are identified in parenthesis. The compound produced
in each
of Schemes 1 to 3 is identified by reference to the appropriate Example.
Scheme 1
F
F
KOH/MeOH
HN ~
HN
F (1)
F
H2, Pd/C
--~..
i HC~ ~ \
HN ~ p-' ~~ O
HN
(2) (3)
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
-S-
Scheme 2
NH2
LiBH~ ~ ~ (BOC)20
I ~ -._I ~ o
off o ~ 0 1
OEt ~5~ OH
i30C ~OC ~OC
N N
~ T~ I ~ N~ I ~
O ~ O ~ O
OH ~OC ~) oTs ~OC ~8) N3
PPh3 _ _
TFA
Scheme 3
o
NaBH(O~ ~C F
3
NH2 ~ H
y
Ex.2 ~ NH
The present invention will now be illustrated by reference to the following
specific non-limiting examples.
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
-6-
INTERMEDIATE 1
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-en-one ethylene ketal
5-Fluoroindole (5.4 g, 0.04 mol), 1,4-cyclohexanedione monoethylene ketal
(12.5 g, 0.08 mol) were placed in 60 ml of 2N potassium hydroxide methanolic
solution. The reaction mixture were heated to reflux for 4 hours. The reaction
was
cooled and the product was isolated by filtration and washed with methanol to
give
10.1 g (93%) of product as a white solid: mp 153-155°C.
INTERMEDIATE 2
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal
A mixture of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-en-one ethylene ketal (2.7
g, 0.01 mol) and 10% palladium on carbon ( I .2 g) in ethanol (200 ml) was
hydrogenated for 4 days. The catalyst was filtered off and the filtrate was
concentrated.
The product was dried under vacuum to afford 2.8 g ( 100 %) of product as a
white
solid: mp 183-185°C.
INTERMEDIATE 3
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3~indolyl)-cyclohexanone
A solution of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal (2.8 g,
0.01
mol) in 200 ml ( 1:1 ) tetrahydrofuran-hydrochloric acid ( 1 N) was allowed to
stir at
room temperature for 16 hours. The mixture was concentrated to half volume.
The
aqueous was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic extracts were washed
with
brine, dried (anhydrous sodium sulfate), and filtered. The crude product was
purified
by flash chromatography (40% ethyl acetate in hexane) to afford 2.1 g (91 %)
of
product as yellow solid: mp 112-114°C.
INTERMEDIATE 4
2,3-Dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-2-carboxyiate ester
To a solution of 2-aminophenol ( 10.0 g, 0.089 mol) in acetone ( 100 ml) was
added anhydrous potassium carbonate (15.2 g, 0.108 mol) followed by ethyl 2,3
dibromopropionate (23.6 g, 0.092 mol) in four portions at reflux temperature.
The
reaction mixture was stirred at reflux for 21 hours and cooled. The solid was
removed
by filtration and the filtrate was concentrated. The residue was dissolved in
cold 1N
sodium hydroxide and extracted with ethyl ether. The combined organic extracts
were
washed with brine, dried (anhydrous sodium sulfate), filtered, and
concentrated.
Chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane: 1/2) afforded 6.25 g (34.4 %) of product
as a
brown oil:
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT1US99/07606
-7_
INTERMEDIATE 5
3,4-Dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazin-2-yl)-methanol
To a solution of ethyl 2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo(1,4]oxazine-2-carboxylate ester
(11.9 g, 19.0 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (60 mL) was added a 2 M
solution
of lithium borohydride ( 15 mL) at room temperature. The reaction was allowed
to stir
for 1 hour and then quenched by the slow addition of methanol. After 2 hours,
water
was slowly added ( 100 mL) and the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl
acetate (4
x 100 mL). The organic layer was separated and dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered, and the solvent removed under vacuum. Purification by
chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane/methanol: 3/6/ 1 ) afforded 1.96 g (62 %)
of
product as an oil: MS (EI) m/e 165 (M+).
INTERMEDIATE 6
2-Hydroxymethyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylic acid
tert-butyl ester
To a solution of 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazin-2-yl)-methanol (10.7 g,
65.0 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (200 mL) was slowly added di-tert-
butyl
bicarbonate (62 g) in tetrahydrofuran (40 mL). The reaction was heated to
reflux for 4
hours, allowed to cool to room temperature and then poured into water ( 100
mL) and
extracted with ethyl ether (3 x 100 mL). The organic layer was washed with
water (2 x
50 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent removed
under
vacuum. Chromatography (ethyl acetatelhexane: 1/2) afforded 12.9 g of product
as
white solid (75 %): mp 93.5-94.5 °C; MS (EI) m/e 265 (M+).
Elemental analysis for C,4H1gNO4
Calc'd: C, 63.38: H, 7.22: N, 5.28.
Found: C, 63.53: H, 7.32: N, 5.38
INTERMEDIATE 7
t-Butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-
methyltosylate
To a solution of 2-hydroxymethyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-
carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester {80 mg, 0.3 mmol) and p-toluenesulfonyl
chloride (86
mg) in anhydrous pyridine ( 15 mL) was allowed to stir overnight at room
temperature.
The reaction mixture was quenched with 1N HCl (20 mL) and extracted with
methylene
chloride (3 x 20 mL). The organic layer was washed with 1N HCl (2 x 20 mL) and
the
organic layer dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and the solvent
removed
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
-g-
under vacuum. Chromatography {ethyl acetate/hexane, 1/2) afforded 120 mg (94%)
of
product as a thick oil : MS (FAB) mle 419 (M+Na).
Elemental analysis for CZ,HZSNO6S
Calc'd: C, 60.13: H, 6.01: N, 3.34.
Found: C, 60.13: H, 6.11: N, 3.56
INTERMEDIATE 8
t-Butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-methylazide
A solution of t-butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-
methyltosylate ( 14.2 g, 33.9 mmol) and sodium azide (4.4 g, 67.7 mmol) in
anhydrous
dimethylformamide ( 150 mL) was heated to 60 °C for 20 hours. The
reaction mixture
was poured into water ( 150 mL) and extracted with methylene chloride (3x 150
mL).
The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered
and
the solvent removed under vacuum. Purification by chromatography {hexane)
afforded
8.7 g (88 %) of product as a white solid: mp 82-83 °C.
Elemental analysis for C,4H,$N4O3
Calc'd C, 57.92: H, 6.25: N, 19.30.
Found: C, 58.07: H, 6.21: N, 19.03
INTERMEDIATE 9
t-Butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2
methylamine
A solution of t-butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-
methylazide (6.25 g, 21.6 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (6.4 g) in
tetrahydrofuran
( 150 mL) containing water (4 mL) was allowed to stir at room temperature for
18
hours. The solvent was removed under vacuum. The residue was dissolved in
ethyl
ether ( 100 mL). After addition of hexane (50 mL), the precipitated
triphenylphosphine
oxide was filtered off. The filtrate was concentrated and the residue was
purified by
chromatography (5% methanol in methylene chloride) affording 7.2 g of product
(which contained a small amount of triphenylphosphine oxide).: MS (FAB) mle
265
(M+H+).
INTERMEDIATE 10
(t-Butyl-3,4-dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-methyl)-[cis-4-
(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amine
A solution of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexanone (0.74 g,3.2 mmol); t-
butyl-2,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate-2-methylamine (0.80 g,
3.02
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
-9-
mmol), sodium triacetoxyborohydride ( 1.0 g, 4.5 mmol) and acetic acid (0.18
ml, 3.2
mmol) in 1,2-dichloroethane ( 14 ml) was allowed to stir at room temperature
for 1.5
hours. The reaction was quenched with 1 N sodium hydroxide, extracted with
methylene chloride. The combined organic extracts were washed with brine,
dried
(anhydrous sodium sulfate), filtered and concentrated. Chromatography (ethyl
acetate/hexane: 3!1 to 5/5) afforded 1.40 g of the title compound product as a
cis/trans
mixture which was used without further separation.
EXAMPLE 1
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-2-ylmethyl)-[cis-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-
3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amineand (3,4-Dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-2
ylmethyl)-[traps-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amine
To a solution of cis/traps-(t-butyl-3,4-dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-4
carboxylate-2-methyl)-[4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amine in
methylene
chloride ( 15 ml) was added trifluoroacetic acid (5 ml) at room temperature.
After
stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for 2 hours, the solvent was
removed.
To the residue was added a small amount of methanol, the solution was adjusted
to
pH>9 with 2N NaOH. The aqueous was extracted with methylene chloride. The
combined organic extracts were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The product was purified by chromatography
(EtOAc/MeOH/NH40H: 99/1/0.5) to afford 0.41 g (35%) of the cis isomer as white
solid: mp 65-67 °C. The HCl salt of the cis isomer was prepared in
ethyl acetate: mp
120 °C (dec)
Elemental analysis for C~H26FN30~2HC1
Calc'd: C, 61.06; H, 6.24; N, 9.29.
Found: C, 61.06; H, 6.40; N, 8.71
The traps isomer was isolated in 19% yield (0.22 g) as a white solid: 66-68
°C.
The HCl salt of the traps isomer was prepared in ethyl acetate: mp 155
°C (dec).
Elemental analysis for C23HZ6FN30~HCl~0.75Hz0~0.33EtOH
Calc'd: C, 63.71; H, 6.85; N, 9.16.
Found: C, 63.40; H, 6.70; N, 8.97
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51591 PCT/US99/07606
- 10-
EXAMPLE 2
(3,4-Dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-3-ylmethyl)-[cis-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol
3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amine) and (3,4-Dihydro-benzo[1,4]oxazine-3
ylmethyl)-[trans-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-amine
A solution of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexanone (0.578 g, 2.5 mmol),
3-aminomethyl-1,4-benzoxazine (0.411 g, 2.5 mmol), sodium
triacetoxyborohydride
(0.78 g, 3.5 mmol) and acetic acid (0.14 ml, 2.5 mmol) in 1,2-dichloroethane
(11 ml)
was allowed to stir at room temperature for 5 hours. The reaction was quenched
with
1N sodium hydroxide, extracted with methylene chloride. The combined organic
extracts were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered
and
concentrated. The product was purified by chromatography {EtOAc/MeOH/NH40H:
99/1/0.5) to afford 0.63 g (66%) of the cis isomer as an oil. The fumarate
salt of the
cis isomer was prepared in isopropanol: mp 208-209 °C.
Elemental analysis for C23H26~30~O.SC4H4O4 0.3H20~0.24i-PrOH
Calc'd: C, 67.55; H, 6.73; N, 9.19.
Found: C, 67.75; H, 6.69; N, 8.99
The trans isomer was isolated in 33% yield (0.32 g) as an oil. The fumarate
salt
of the trans isomer was prepared in isopropanol: mp 275-277 °C (dec).
Elemental analysis for C23H26~30~O.SC4H4O4 0.3H20
Calc'd: C, 67.79; H, 6.51; N, 9.49.
Found: C, 67.58; H, 6.47; N, 9.18
The activity of the present compounds is demonstrated by the following
standard pharmacological test procedures.
The PCR cloning of the human 5-HT,A receptor subtype from a human genomic
library has been described previously Chanda et al., Mol. Pharmacol., 43:516
(1993).
A stable Chinese hamster ovary cell line expressing the human 5-HT,A receptor
subtype
(5-HT,A.CHO cells) was employed throughout this study. Cells were maintained
in
DMEM supplemented with 10% foetal calf serum, non-essential amino acids and
penicillin/ streptomycin.
Cells were grown to 95-100% confluency as a monolayer before membranes
were harvested for binding studies. Cells were gently scraped from the culture
plates,
transferred to centrifuge tubes, and washed twice by centrifugation (2000 rpm
for 10
min., 4°C) in buffer (50 mM Tris; pH 7.5). The resulting pellets were
aliquoted and
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
-11-
placed at -80°C. On the day of assay, the cells were thawed on ice, and
resuspended in
buffer. Studies were conducted using [3H]8-OH-DPAT as the radioligand. The
binding assay was performed in 96 well microtiter plates in a final total
volume of 250
pL, of buffer. Competition experiments were performed by using 7
concentrations of
unlabelled drug and a final ligand concentration of 1.5 nM . Non-specific
binding was
determined in the presence of 10 pM SHT. Saturation analysis was conducted by
using
[3H]8-OH-DPAT at concentrations ranging from 0.3-30 nM. Following a 30 minute
incubation at room temperature, the reaction was terminated by the addition of
ice cold
buffer and rapid filtration using a M-96 Brandel Cell Harvester (Gaithersburg,
MD)
through a GF/B filter presoaked for 30 minutes in 0.5% polyethyleneimine.
A protocol similar to that used by Cheetham et al., Neuropharmacol. , 32:737
( 1993) was used to determine the affinity of compounds for the serotonin
transporter.
Briefly, frontal cortical membranes prepared from male Sprague-Dawley rats
were
incubated with'H-paroxetine (0.1 nM) for 60 min at 25°C. All tubes also
contained
either vehicle, test compound (one to eight concentrations), or a saturating
concentration of fluoxetine ( 10 p,M) to define specific binding. All
reactions are
terminated by the addition of ice cold Tris buffer followed by rapid
filtration using a
Tom Tech filtration device to separate bound from free 3H-paroxetine. Bound
radioactivity was quantitated using a Wallac 1205 Beta Plate~ counter.
Nonlinear
regression analysis was used to determine ICso values which were converted to
Ki
values using the method of Cheng and Prusoff, Biochem. Pharmacol., 22:3099
(1973);
Ki = IC50/((Radioligand conc.)/(1 + KD)).
The [35S)-GTP~yS binding assay was similar to that used by Lazareno and
Birdsall, Br. J. Pharmacol. 109:1120 (1993). Briefly, 5-HT,A cloned receptor
membrane fragments (as used for 5-HT,A receptor binding assays) were stored at
-70
°C until needed. When needed, membranes were rapidly thawed,
centrifuged at 40,000
x g for 10 minutes and resuspended at 4 °C for 10 minutes in assay
buffer (25 mM
HEPES, 3 mM MgCl2, 100 mM NaCI, 1 mM EDTA, 10 uM GDP, 500 mM DTT, pH
8.0). These membranes were then incubated for 30 min at 30 °C with
[35SJGTPgS (1
nM) in the presence of vehicle, test compound (one to eight concentrations),
or excess
8-OH-DPAT to define maximum agonist response. All reactions are terminated by
the
addition of ice cold Tris buffer followed by rapid filtration using a Tom
Tech~ filtration
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCT/US99/07606
-12-
device to separate bound from free [33S]GTPgS. Agonists produce an increase in
the
amount of [33S]GTPgS bound whereas antagonists produce no increase in binding.
Bound radioactivity was counted and analyzed as above.
The following assays were performed by incubating the cells with DMaVI
containing 25 mM HEPES, 5 mM theophylline and 10 liM pargyline for a period of
20
minutes at 37°C. Functional activity was assessed by treating the cells
with forskolin ( 1
uM final concentration) followed immediately by test compound (6
concentrations) for
an additional 10 min at 37°C. In separate experiments, 6 concentrations
of antagonist
were preincubated for 20 min prior to the addition of 10 nM 8-OH-DPAT and
forskolin. The reaction was terminated by removal of the media and addition of
0.5 ml
ice cold assay buffer. Plates were stored at -20°C prior to assessment
of cAMP
formation by a cAMP SPA assay (Amersham).
The results of the tests with the compounds of Examples 1 and 2 are given in
the following table.
Example ~ ~~) ST [3H]paroxetineKi (nM) SHT1A [3H]DPAT
1 (cis) 44 ~ 2432
1 (~~) 24 44% @ 1 N.M
2 (cis) 34% @ l~M 9% @ l~t.M
2 (trans) 10 20% @ 1N,M
The compounds of this invention may be administered orally or parenteraily,
neat or in combination with conventional pharmaceutical carriers. Applicable
solid
carriers can include one or more substances which may also act as flavoring
agents,
lubricants, solubilizers, suspending agents, fillers, glidants, compression
aids, binders
or tablet-disintegrating agents or an encapsulating material. In powders, the
carrier is a
finely divided solid which is in admixture with the finely divided active
ingredient. In
tablets, the active ingredient is mixed with a carrier having the necessary
compression
properties in suitable proportions and compacted in the shape and size
desired. The
powders and tablets preferably contain up to 99% of the active ingredient. Any
of the
solid carriers known to those skilled in the art may be used with the
compounds of this
invention. Particularly suitable solid carriers include, for example, calcium
phosphate,
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
-13-
magnesium stearate, talc, sugars, lactose, dextrin, starch, gelatin,
cellulose, methyl
cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, low melting
waxes
and ion exchange resins.
Liquid carriers may be used in preparing solutions, suspensions, emulsions,
syrups and elixirs of the compounds of this invention. The compounds of this
invention can be dissolved or suspended in a pharmaceutically acceptable
liquid carrier
such as water, an organic solvent, a mixture of both or pharmaceutically
acceptable oils
or fat. The liquid carrier can contain other suitable pharmaceutical additives
such as
solubilizers, emulsifiers, buffers, preservatives, sweeteners, flavoring
agents,
suspending agents, thickening agents, colors, viscosity regulators,
stabilizers or osmo-
regulators. Suitable examples of liquid carriers for oral and parenteral
administration
include water (particularly containing additives as above, e.g., cellulose
derivatives,
preferably sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution), alcohols (including
monohydric
alcohols and polyhydric alcohols, e.g., glycols) and their derivatives and
oils (e.g.,
fractionated coconut oil and arachis oil). For parenteral administration, the
carrier can
also be an oily ester such as ethyl oleate and isopropyl myristate. Sterile
liquid carriers
are used in sterile liquid form compositions for parenteral administration.
Liquid pharmaceutical compositions which are sterile solutions or suspensions
can be utilized by, for example, intramuscular, intraperitoneal or
subcutaneous
injection. Sterile solutions can also be administered intravenously.
Compositions for
oral administration may be either liquid or solid composition form.
Preferably, the pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of this
invention are in unit dosage form, e.g., tablets or capsules. In such form,
the
compositions may be sub-divided in unit doses containing appropriate
quantities of the
present compounds. The unit dosage forms can be packaged compositions, for
example, packeted powders, vials, ampoules, prefilled syringes or sachets
containing
liquids. Alternatively, the unit dosage form can be, for example, a capsule or
tablet
itself, or it can be the appropriate number of any such compositions in
package form.
The therapeutically effective amount of the compounds of this invention that
is
administered and the dosage regimen depends on a variety of factors, including
the
weight, age, sex, and medical condition of the subject, the severity of the
disease, the
route and frequency of administration, and the specific compound employed, and
thus
CA 02327360 2000-10-04
WO 99/51592 PCTNS99/07606
- 14-
may vary widely. However, it is believed that the pharniaceutical compositions
may
contain the compounds of this invention in the range of about 0.1 to about
2000 mg,
preferably in the range of about 0.5 to about 500 mg and more preferably
between
about 1 and about 100 mg. Projected daily dosages of active compound are about
0.01
to about 100 mg/kg body weight. The daily dose can be conveniently
administered two
to four times per day.
The present invention may be embodied in other specific forms without
departing from the spirit and essential attributes thereof and accordingly,
reference
should be made to the appended claims, rather than to the foregoing
specification, as
indicating the scope of the invention.